Building template, manufacturing method of building template and building laminated timber
A technology of building formwork and wood cubes, which is applied in building construction, on-site preparation of building components, construction, etc. It can solve the problems of easy cracking and damage of glass fiber reinforced plastics, uneven surface of building formwork, uneven concrete surface, and achieve the appearance Beautiful appearance, saving production time, and increasing the area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
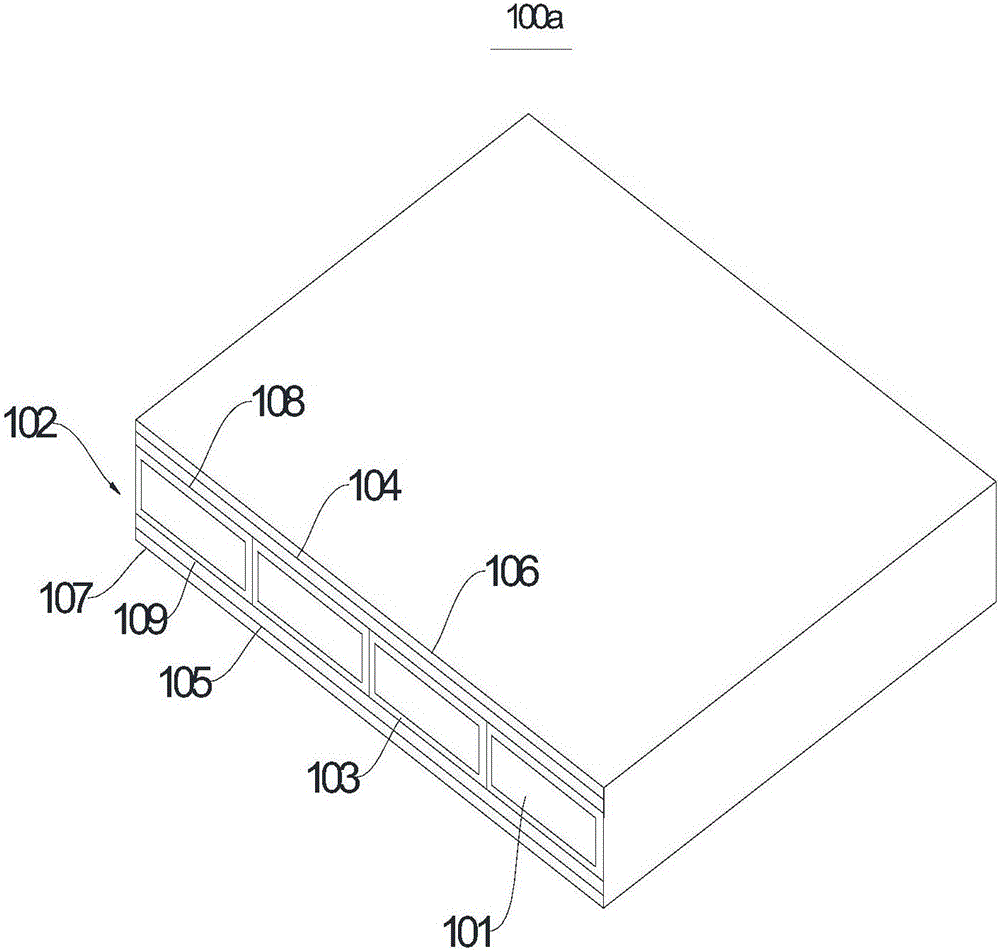
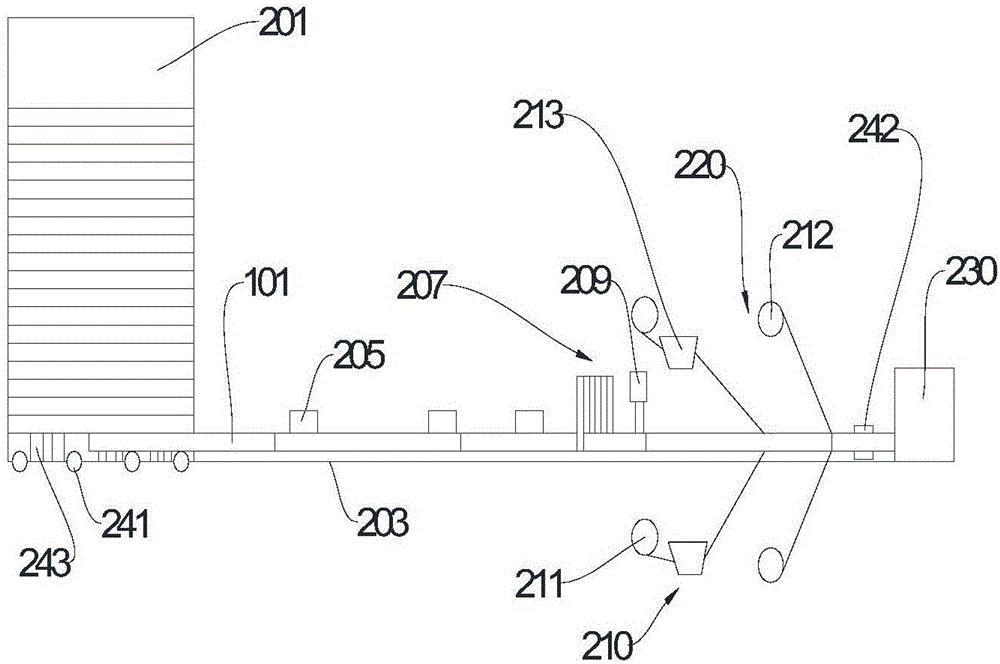
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a building formwork 100a, which includes a building formwork body 102. The building formwork body 102 includes four wooden strips 101 arranged side by side in a horizontal direction, and a layer of reinforcement is coated on the outer periphery of each wooden strip 101. The cloth layers 103 are glued together.
[0033] Wherein, the material of each wooden strip 101 is plywood, the height of each wooden strip 101 is 20 mm in thickness, and the width is 70 mm. The reinforced cloth layer 103 mainly includes the reinforced cloth layer 103 made by curing the non-woven fabric and the resin composition.
[0034] Non-woven fabric is a kind of fabric formed without spinning and weaving. It is just oriented or random arrangement of short textile fibers or filaments to form a web structure, which is then reinforced by mechanical, thermal bonding or chemical methods. Non-woven fabrics have the advantages of easy shaping and good...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Such as Figure 5 As shown, this embodiment provides another building formwork 100b, which roughly matches the structure of the building formwork 100a provided in Embodiment 1. However, the positional relationship between the reinforcing cloth layer 103 and the bonding adjacent wooden strips 101 changes, and the arrangement of the composite layer and the protective layer is also different.
[0077] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the reinforcing cloth layer 103 between two adjacent wood strips 101 is formed by curing three cloth pieces 113 and a resin composition. Cloth 113 is polyester. The three cloth pieces 113 are respectively distributed at the two ends and the middle of the wooden strip 101, and the uniform distribution can make the bonding more stable.
[0078] It should be noted that the number of cloth pieces 113 is not limited to 3, but may be 1 or 2 or 5 or even more, and the positions of the cloth pieces 113 are not necessarily uniform. At the same time, the...
Embodiment 3
[0083] The building formwork provided in this embodiment is substantially the same in structure as the building formwork 100a provided in Example 1, the difference lies in the structure of the reinforcing cloth layer 103 between two adjacent wooden strips 101, and the first surface 108 covered on the first surface. The structures of the composite layer 104 and the first protective layer 106 are different from the structures of the second composite layer 105 and the second protective layer 107 covering the second surface 109 .
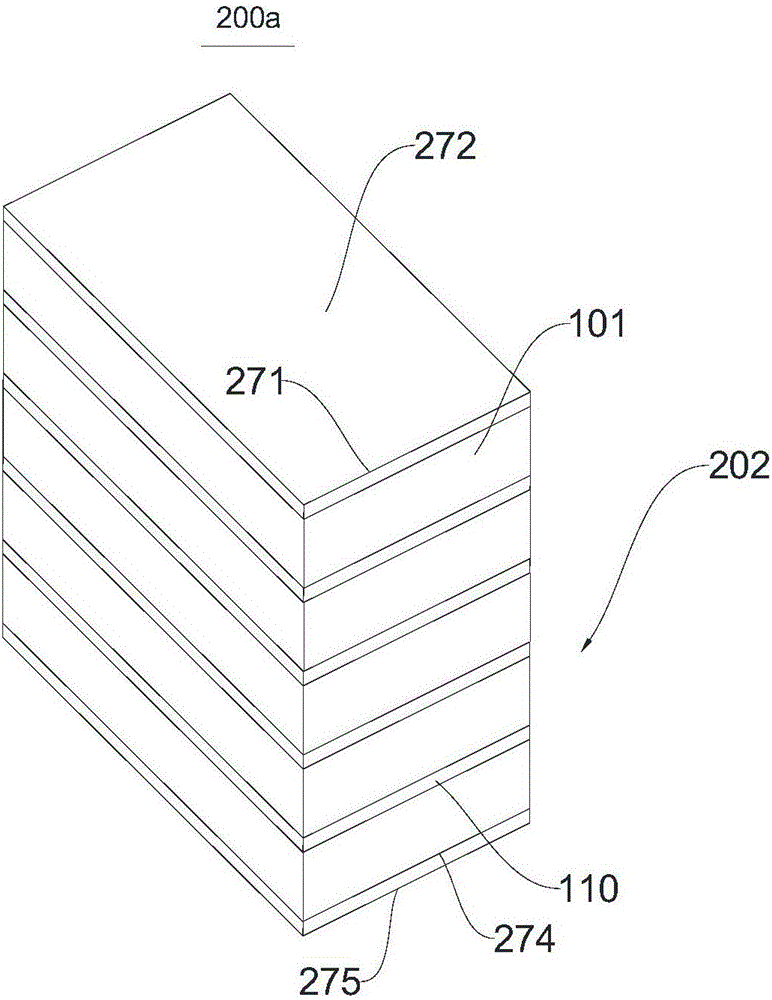
[0084] Two layers of reinforced cloth layers 103 are arranged between two adjacent wooden strips 101, and the first reinforced cloth layer 103 is formed by curing the cloth strips 110 and the resin composition. Cloth strip 110 is polypropylene fiber. The width of the cloth strip 110 is smaller than that of the wooden strip 101 . The use of cloth strips 110 saves the use of raw materials, thereby saving costs. At this time, the bonding degree and mecha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com