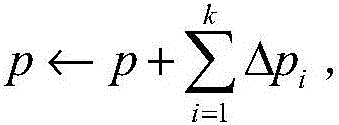Active learning-based image detection method for liver injury type
A liver injury and image detection technology, which is applied in the field of image detection of liver injury categories, can solve problems such as detection errors or omissions, accuracy reduction, manual detection limited by personal experience, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0086] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the technical content of invention is described in detail:
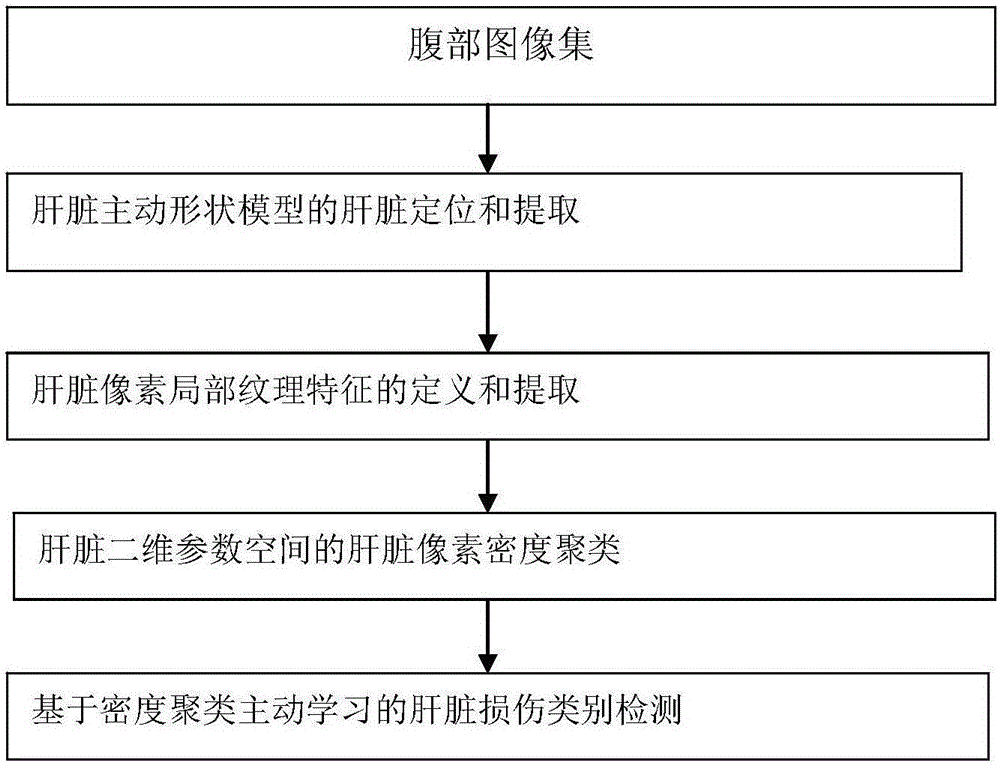
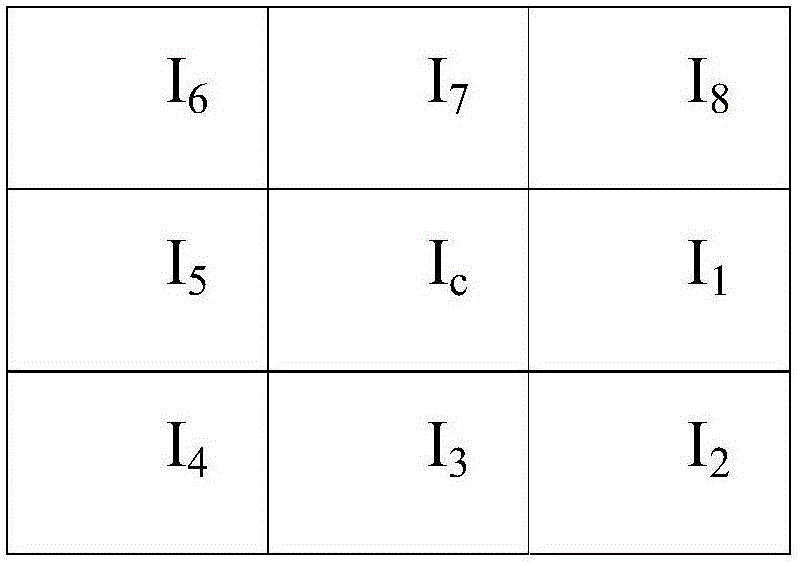
[0087] This method is divided into four parts: liver target area extraction, feature definition and extraction, liver pixel density clustering, and active learning detection. The specific workflow is as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0088] (a) Liver target regions are localized and extracted from an abdominal medical image set using a liver active shape model.
[0089] Assuming the geometric shape parameters of the liver active shape model: translation t, rotation r and scaling s, and texture scaling parameters: global scaling u and deviation w, these model parameters are denoted as p={t,r,s,u ,w}, the increment of model parameters Δp={Δt, Δr, Δs, Δu, Δw}, updated after k times of linear model iterations:
[0090]
[0091] When the area mean square difference between the adjusted liver template and the abdominal medical image is the smallest, the corresponding ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com