Lake-ecosystem catastrophe early-warning method
An ecosystem and early warning technology, applied in instruments, data processing applications, calculations, etc., can solve the problems that disturbance simulation experiments are difficult to apply to lake environments, and achieve the effect of a practical disaster early warning method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] An early warning method for lake ecosystem mutations, comprising the following steps:
[0036] (1) Step 1. Calculate the energy quality and structural energy of the ecosystem: use the dry weight content and information content of various organisms or organic matter in the ecosystem to calculate the energy quality of the ecosystem and the structural energy of the ecosystem. Includes: phytoplankton, zooplankton, benthos and macrophytes;
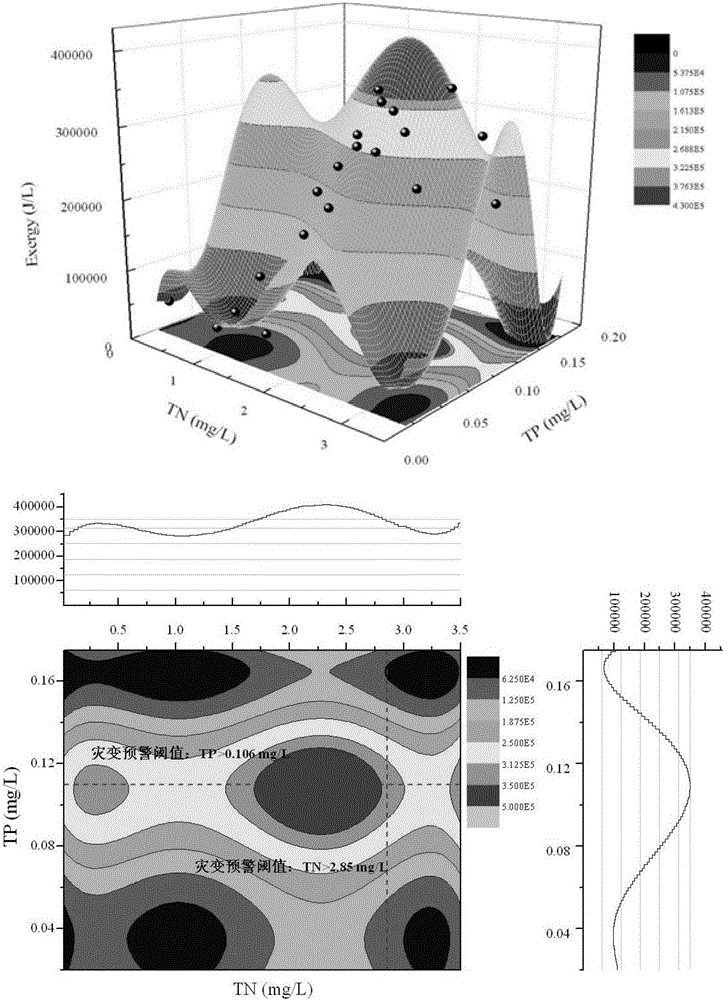
[0037] (2) Step 2, using total phosphorus and total nitrogen as the early warning indicators of lake ecosystem catastrophe, and the energy quality mutation point of the lake ecosystem obtained by continuous Student's t test is the catastrophe critical value;
[0038](3) Step 3: Use the long-term data of total phosphorus, total nitrogen and energy quality of the lake ecosystem to perform multivariate nonlinear surface fitting, construct a lake ecosystem catastrophe early warning model, and obtain the concentration of total phosphorus and ...
Embodiment 2
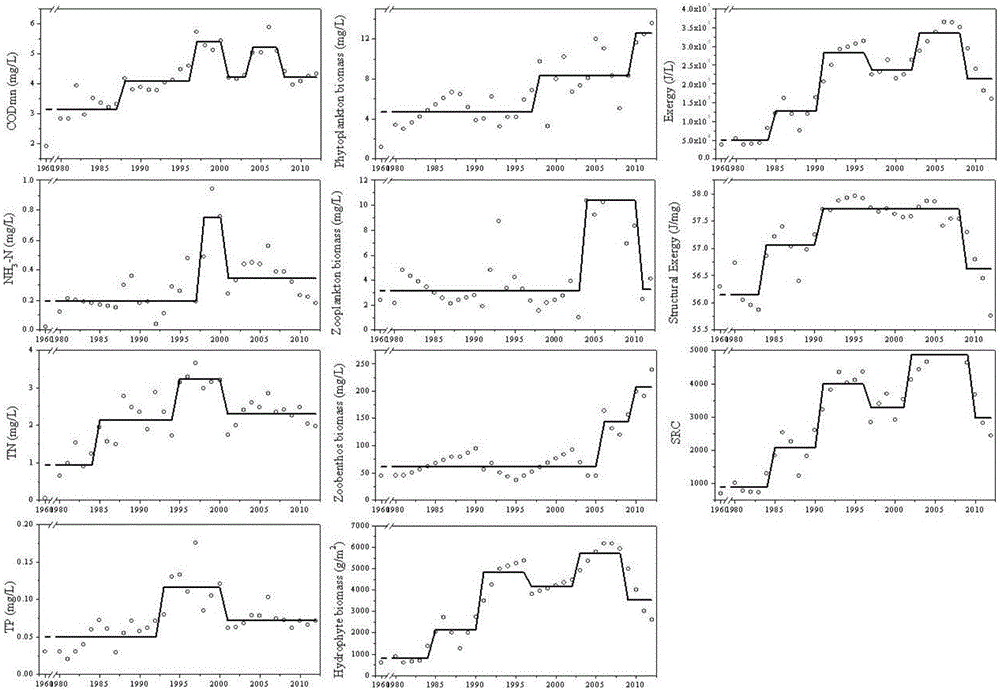
[0054] Taking the water environment of the Taihu Lake ecosystem as an example, the early warning method for the evolution law of the Taihu Lake ecosystem and the key time points for sudden changes includes the following steps:
[0055] (1) Step 1. Calculating the energy quality and structural energy quality of the Taihu lake ecosystem: use the dry weight content and information content of various organisms or organic matter in the ecosystem to calculate the energy quality and structural energy quality of the ecosystem;
[0056] In the Taihu Lake ecosystem Ex calculation, the Lake Taihu ecosystem is divided into phytoplankton, zooplankton, benthic animals and macrophytes, and the weights are assigned to 3.4, 36.6, 32.5 and 58.2, respectively.
[0057] Calculate the energy quality of the ecosystem by formula a:
[0058]
[0059] Among them, W i is the i-th organism or the information content of organic matter in the ecosystem, that is, the weight conversion factor, J / mg;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com