Method for building hepatitis B e-antigen negative mouse model
A hepatitis B, mouse model technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment one, construct the mouse model of hepatitis B e antigen negative
[0039] Follow the steps below:
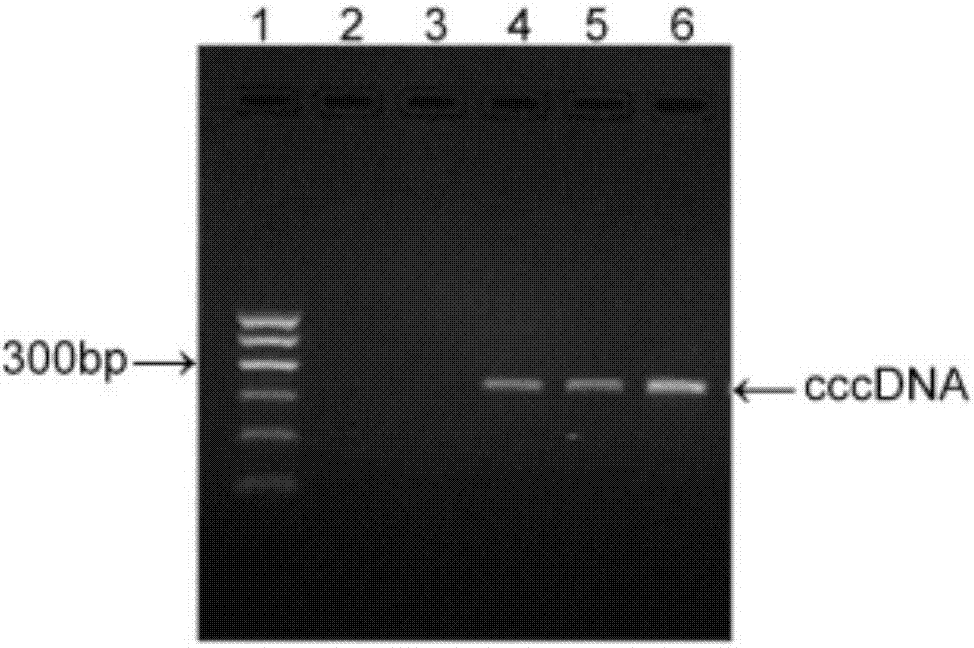
[0040] 1. Cloning of full-length DNA of HBV e-negative virus strain
[0041] 1. Amplify the full length of HBV DNA: extract the DNA from the serum of patient No. 11061008 (provided by the Department of Infectious Diseases, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University) diagnosed as HBeAg-negative infection, and use primers to perform PCR amplification of HBV-F / HBV-R , the primer sequence is:
[0042] Upstream primer HBV-F:
[0043] 5'-CCGGAAAGCTTATGCTCTTCTTTTTCACCTCTGCCTARTCATC-3',
[0044] Downstream primer HBV-R:
[0045] 5'-CCGGAGAGCTCATGCTCTTCAAAAAGTTGCATGGTGCTGGTG-3'.
[0046] 2. Sequence the PCR product obtained in step 1 to obtain its sequence, redesign the primers according to the sequencing results, delete 7 bases in the newly designed upstream and downstream primers, and change the degenerate bases of the upstream primers accordi...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment two, the detection of mouse model
Embodiment 1
[0057] Detect the experimental group, control group, and blank group mouse models constructed in Example 1:
[0058] 1. Detection of HBV-specific markers in mouse serum
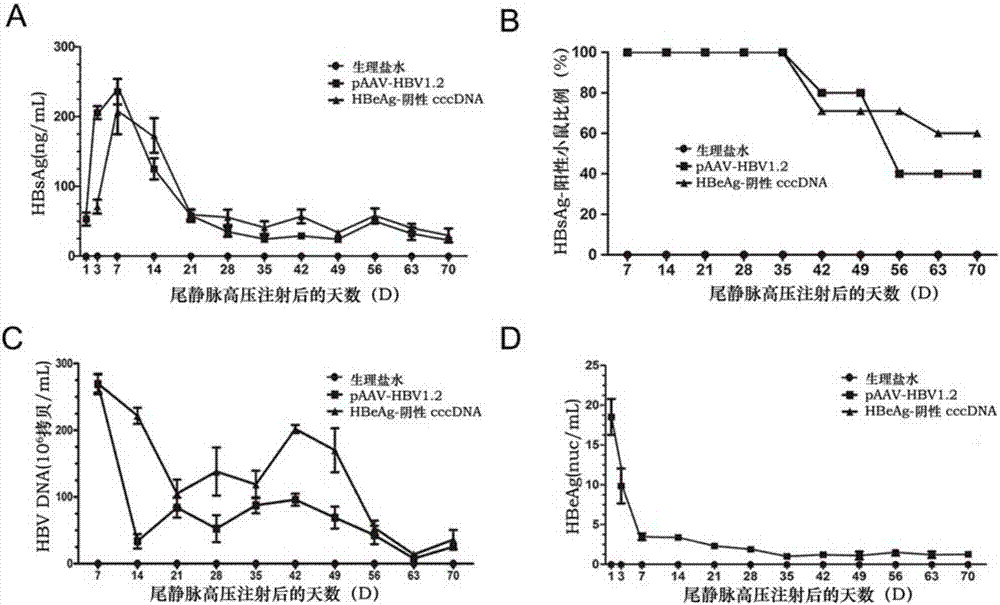
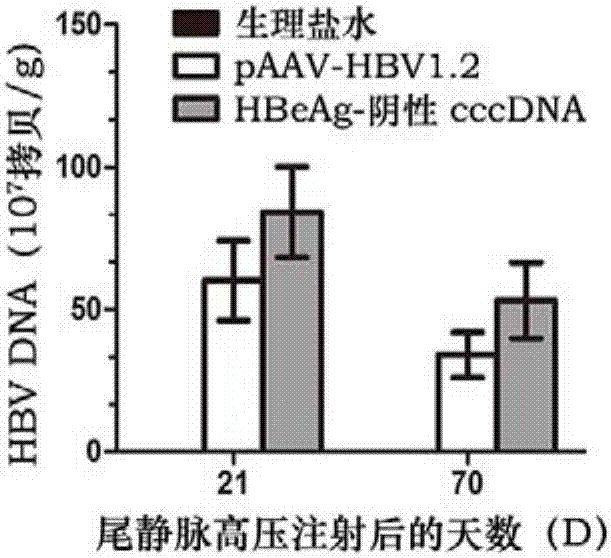
[0059] Specific markers of HBV such as HBsAg, HBeAg, viral DNA, and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) were detected in the serum of experimental mice at different time points. The detection of HBsAg and HBeAg was performed using a radioimmunoassay kit; the detection of ALT was performed using a small Mouse ELISA Kit.
[0060] The real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR method was used for the detection of HBV DNA. 50 μL serum was taken for extraction of viral DNA and RNA, 2 μL total DNA was used for qPCR, and the HBV copy number was analyzed. Primers were designed and amplified in the conserved region of the HBV gene, forward primer: HBV-Q-F: 5′-CCTCTTCATCCTGCTGCT-3′; reverse primer HBV-Q-R: 5′-AACTGAAAGCCAAACAGTG-3′, the standard curve uses pEASY-HBV / HBeAg-negative HBVDNA by 5×10 3 ,5×10 4 ,5×10 5 ,5×10 6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com