Placing and recycling method for self-drilling cableless type seabed deformation long-time observation device
An observation device and cable-type technology, which is applied in surveying devices, surveying and navigation, open-air water source surveying, etc., can solve problems such as complex processes, lack of in-situ deployment devices and methods, and long time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
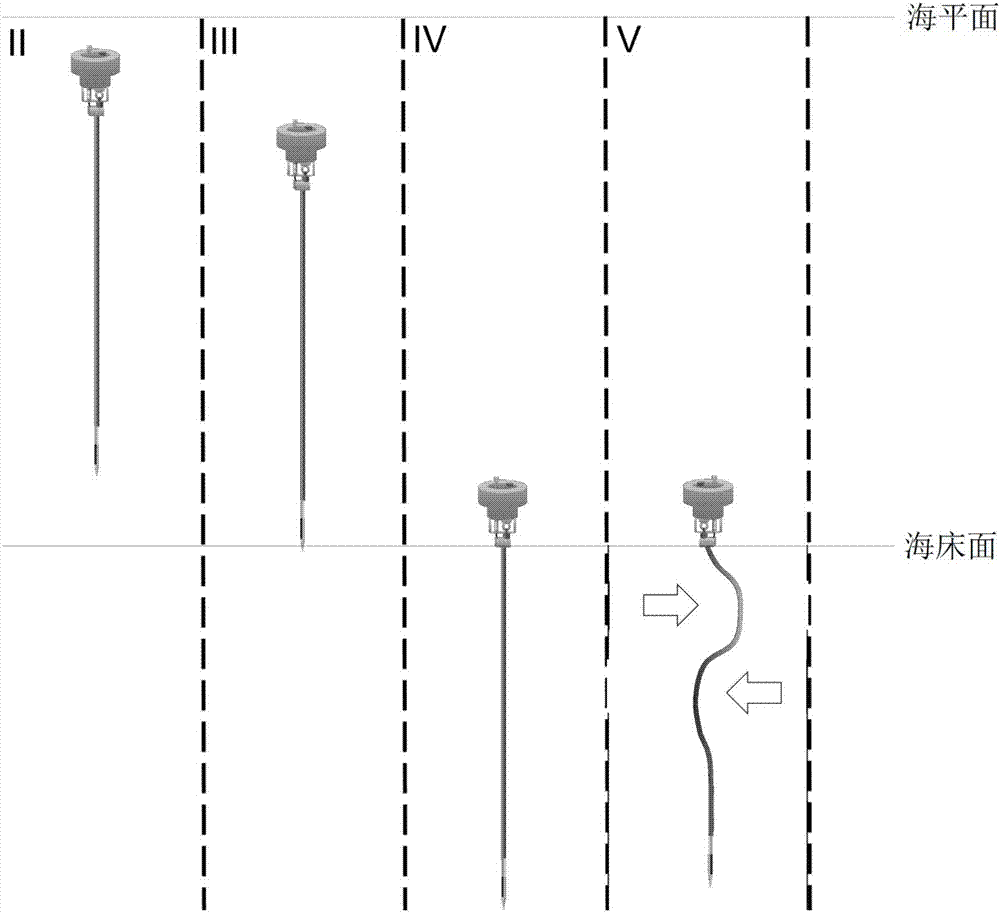
[0075] Such as figure 1 The deployment method of the shown self-drilling cable-free submarine deformation long-term observation device includes the following steps:
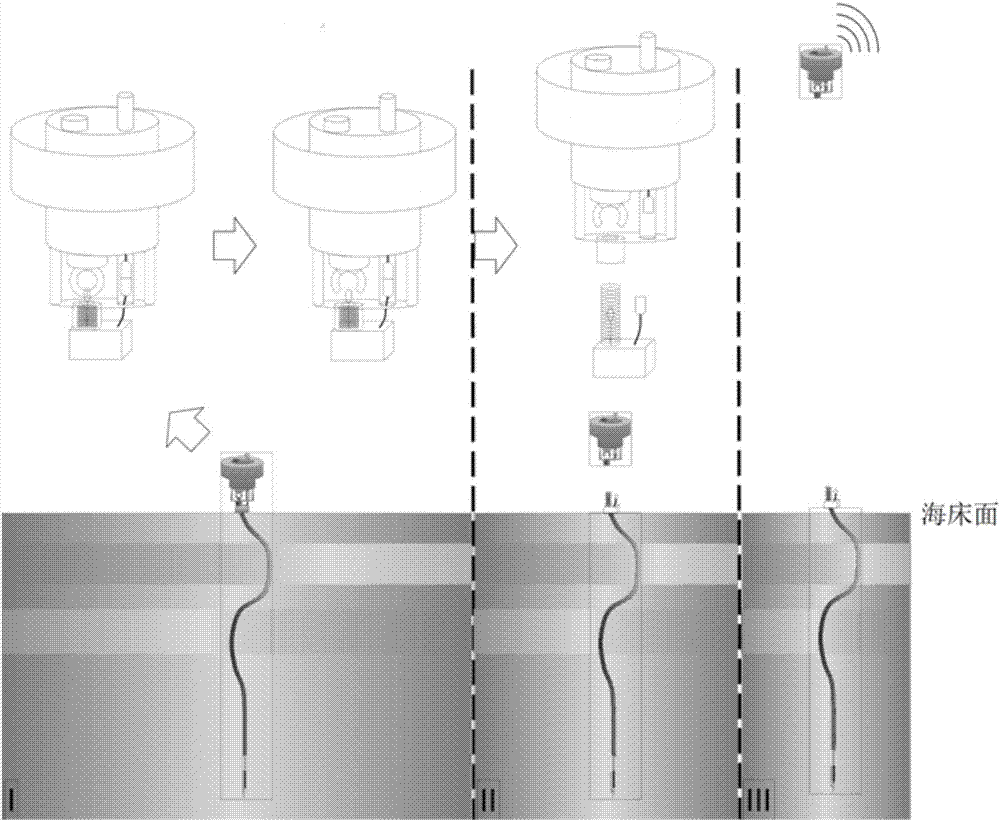
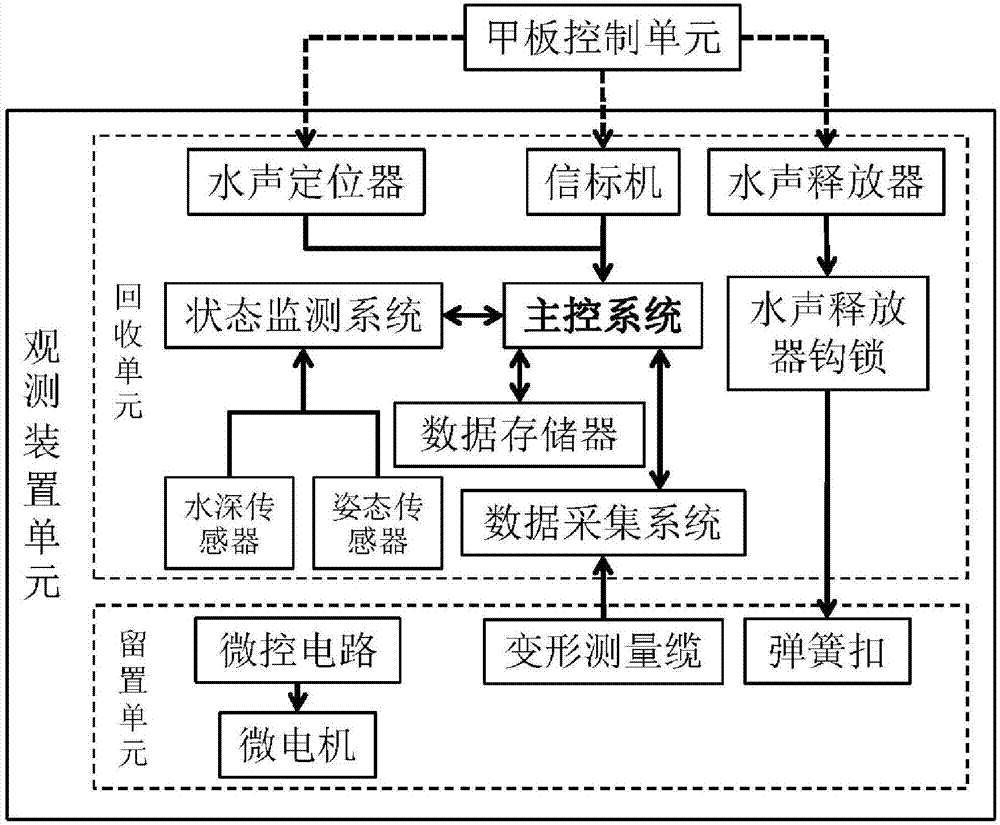
[0076] Step 1: The assembly is completed as Figure 4 The shown self-drilling and cable-free long-term observation device for seabed deformation includes a drill bit part, a deformation measurement cable 9 and a deployment and recovery part connected sequentially from bottom to top. The deployment and recovery part includes a retention part and a recovery part.
[0077] Such as Figure 5The drill bit part shown includes micro-drill bit 20, support tube 23 and micro-control cabin 19 from bottom to top, and support tube 23 and micro-control cabin 19 are connected through, and micro-control cabin 19 is provided with micro-motor, micro-control circuit and battery, The micro-motor is connected to the micro-control circuit, and the battery supplies power to the micro-motor and the micro-control circuit. The rotating ...
Embodiment 2
[0115] The difference with embodiment 1 is:
[0116] A spring protection cover 7 is arranged below the spring buckle through hole 21 , and one end of the spring protection cover 7 is fixed on the support plate 17 . Two ends are respectively fixed on the watertight connector protective cover 14 on the main control cabin 12 and the support plate 17 in the support frame, and the watertight connector protective cover 14 is facing the watertight connector through hole 22 on the support plate 17 .
[0117] The indwelling part is connected with the recovery part in the following way: the watertight connector II 13 is connected to the watertight connector I 16 through the watertight connector through hole 22 from below, and the watertight connector II 13 and the watertight connector I 16 are all located in the watertight connector protection. In the cover 14 , the spring buckle 6 passes through the spring buckle through hole 21 from below to connect with the hook lock 5 of the underwa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com