Application and preparation of beta-sitosterol
A technology of sitosterol and pharmaceutical preparations, which is applied in the field of application of β-sitosterol and its preparations, and can solve problems such as unresearched
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
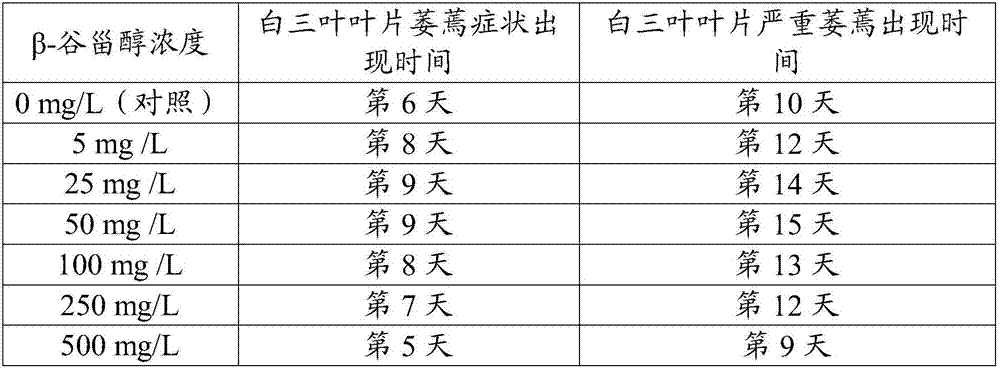
[0017] The screening of embodiment 1β-sitosterol root application concentration
[0018] Test material: widely used 'Latinuo' white clover as the test material
[0019] Material cultivation: Soak the white clover seeds with 0.1% potassium permanganate solution for 10 minutes to disinfect, wash with deionized water for 3 times, press 1g / m 2 Seeds were sown in plastic pots with a length of 20 cm, a width of 15 cm, and a height of 5 cm filled with quartz sand, and placed in a light incubator for germination (temperature day / night was 23 / 19°C; duration was 12 hours; relative Humidity is 70%; light intensity is 700 μmol m -2 the s -1 ). After the seeds germinated for 7 days, the seedlings were continued to be cultivated with Hoagland nutrient solution until 30 days, and the materials with consistent growth were selected for subsequent experiments.
[0020] Experimental design: A total of 7 β-sitosterol concentration gradients were set up, which were: 0mg / L (control, direct drou...
Embodiment 2
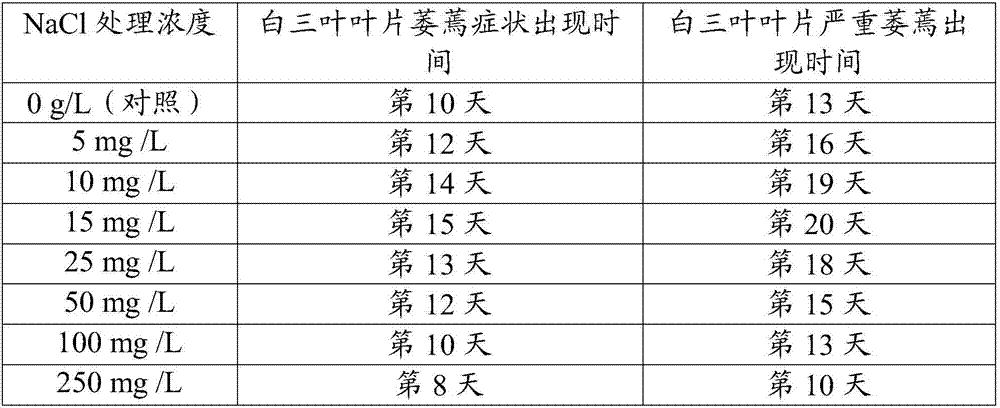
[0025] Example 2 The screening of foliar spraying β-sitosterol concentration
[0026] Test material: Drought-sensitive 'Latinuo' white clover was used as the test material.
[0027] Material cultivation: Mix the pastoral soil and nutrient soil at a ratio of 1:1, add insecticides and fungicides and mix evenly, and place it outdoors for 3 days before use. Plant white clover in a pot with a diameter of 20cm and a depth of 25cm, and fill the pot with the same amount of mixed soil at 1g / m 2 Scatter the white clover seeds at a certain seeding rate, cover with shallow soil and water. The materials were placed in the greenhouse and cultivated for 3 months, and 250mL of Hoagland's complete nutrient solution was poured into each pot every week, and the routine management of fertilization, weeding, watering, and pests and diseases was uniformly carried out. The average temperature of the greenhouse is 23 °C, the relative humidity is 65%, the light time is 12 hours, and the light intens...
Embodiment 3
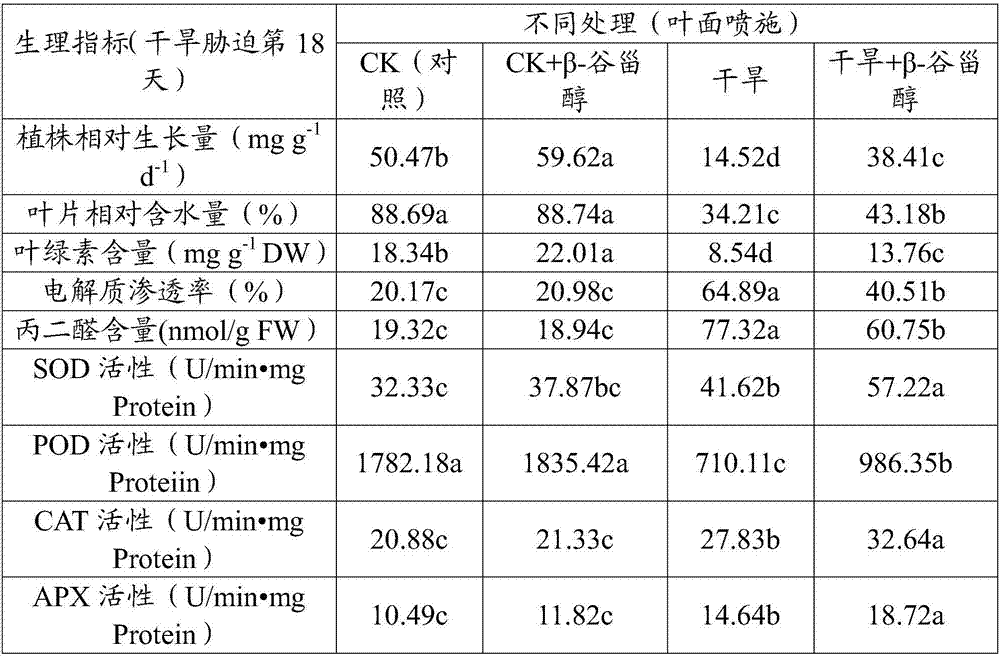
[0033] Example 3 Effect of foliar spraying of β-sitosterol on physiological indexes of drought resistance of white clover
[0034] Test material: Drought-sensitive 'Latinuo' white clover was used as the test material
[0035] Material cultivation: with embodiment 2
[0036] Design of the test: The optimal leaf spraying concentration 15mg / L screened out according to Experimental Example 2 is the spraying concentration of this experiment. There are 4 treatments in the test, and 4 independent repetitions are set for each treatment. They are respectively: 1. normal condition control (CK ): 18 days of normal culture in the greenhouse after spraying foliage without β-sitosterol as a control; ② CK+β-sitosterol: normal culture in the greenhouse after foliar spraying of 15 mg / L β-sitosterol 18 days; ③Direct drought stress: 18 days of natural drought in the greenhouse after spraying a solvent without β-sitosterol on the leaves; ④Drought + β-sitosterol: After spraying 15mg / L β-sitostero...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com