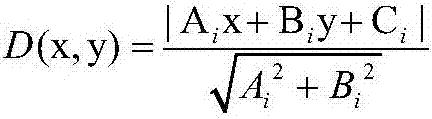Vision-based AGV patrolling navigation and positioning method
A positioning method and visual technology, applied in surveying and navigation, two-dimensional position/channel control, photo interpretation, etc., can solve problems such as high maintenance costs, accumulation of odometer deviations, and navigation failures, and reduce renovation and maintenance Effects of cost, stable positioning and navigation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A vision-based AGV line tracking navigation and positioning method, comprising steps:
[0036] Step 101: Obtain an image ahead of the current course;
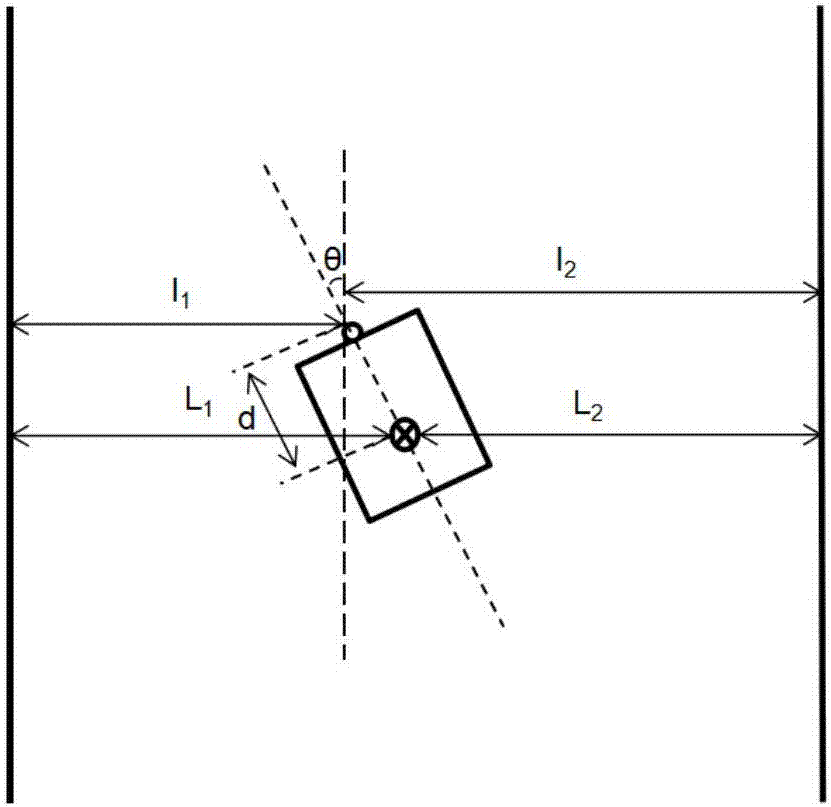
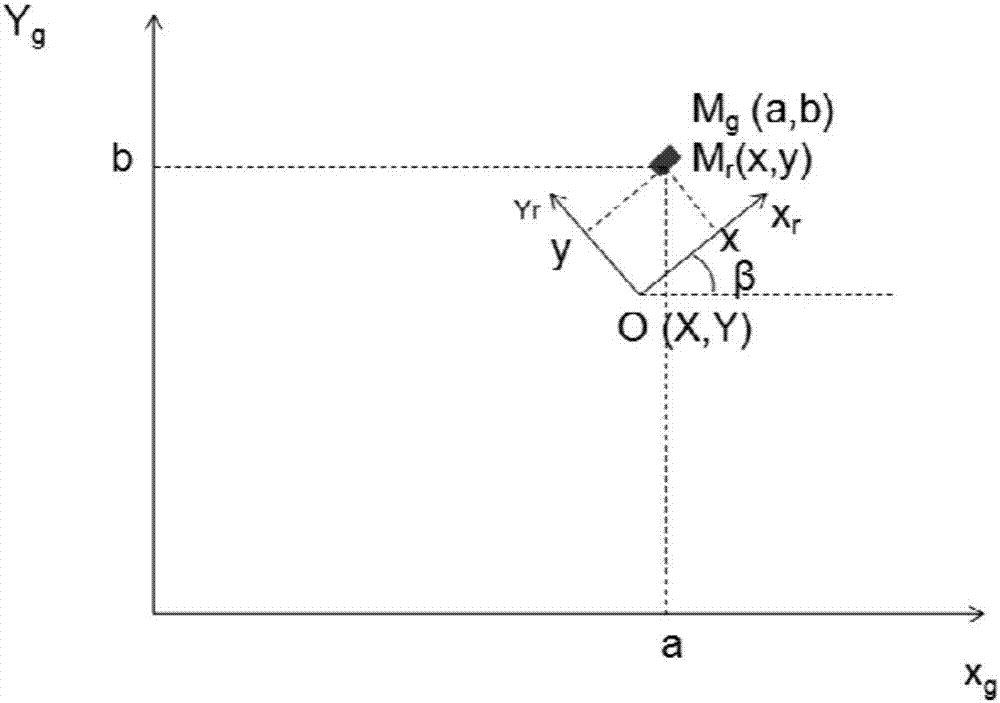
[0037] In this embodiment, the image is acquired by a camera fixed on the AGV, the optical axis of the camera is parallel to the longitudinal axis of the AGV, the direction of the longitudinal axis of the AGV is consistent with the direction of the AGV heading, and the camera is calibrated through internal and external parameters, which include the camera Focal length, distortion coefficient, camera height, pitch angle, relative positional relationship between the camera and the center of the AGV body, etc., to obtain the conversion relationship between the image and the global coordinate system, the conversion relationship between the camera coordinates and the AGV body coordinates, etc. Wherein, the center of the AGV car body is used as a feature point for describing the trajectory movement of the AGV.
[0038] Among ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] In this embodiment, the specific process of step 102 includes:
[0055] Step 201: using a line extraction algorithm to extract line segments in the preprocessed image;
[0056] Wherein, the line segment includes the following attributes: including the start point, the end point and the length of the line segment. Wherein, the line segment includes a starting point and an ending point, and both the starting point and the ending point are in the image area, or the intersection point between the image area and the line segment is used as the ending point.
[0057] Step 202: Select two line segments as a parent straight line and a sub-straight line respectively, and determine whether the parent straight line and the sub-straight line can be fused by using a set threshold; if it is less than the set threshold, it is determined that the line segment is on a straight line and can be fused;
[0058] Specifically, a line segment is selected as the parent straight line, and the ...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Embodiment 3, in the straight line extraction algorithm described in step 102, step 201, preferably select the LSD line segment extraction algorithm,
[0064] The LSD line extraction algorithm includes the following sub-steps:
[0065] Step S301: Calculate the gradient of each pixel, and define the direction of the horizontal line as the direction perpendicular to the gradient;
[0066] Step S302: Use the region growing algorithm to divide the image into several connected domains, and the maximum difference in the direction of the horizontal line between two pixels in each connected domain is τ;
[0067] Step S303: For each connected domain, select a smallest rectangle to enclose the area, then the direction of the major axis of the rectangle is the direction of the line segment, and return the two endpoints of the line segment; use the straight line equation Ax+By+C=0 to represent step S201 and this Each line segment obtained in the invention, wherein A, B, and C are ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com