Soft switching flyback converter
A converter and transformer technology, applied in the field of soft switching and synchronous rectification flyback converters, can solve the problems of increasing the size of the switch, inability to cross, and increasing common mode electromagnetic interference.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0009] In the drawings, features are not necessarily drawn to scale. If a first device is coupled to or with a second device, that connection may be through a direct electrical connection or through an indirect electrical connection via one or more intervening devices and connections.
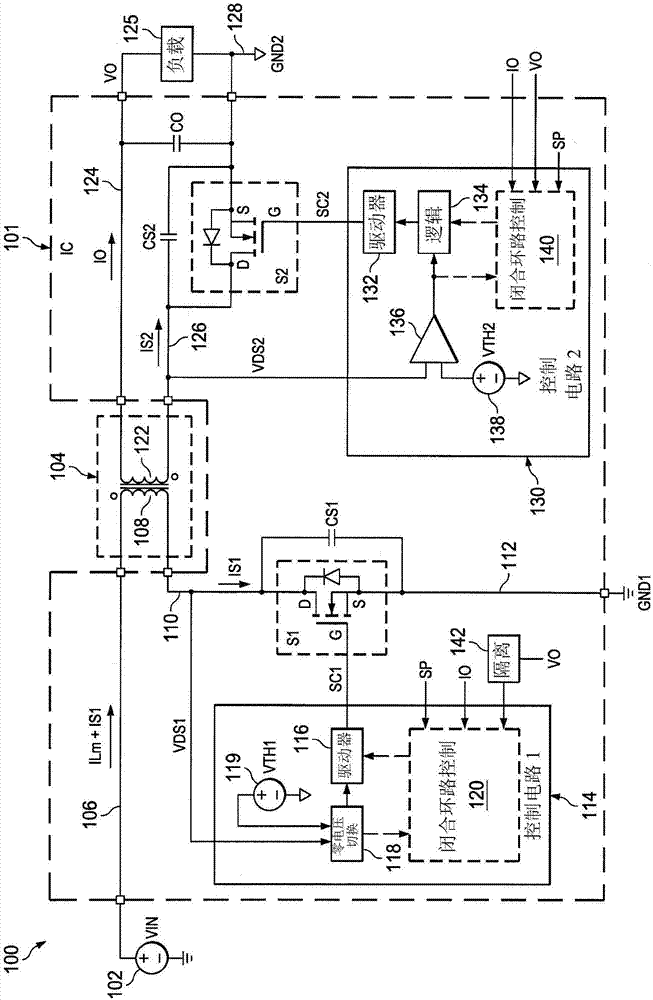
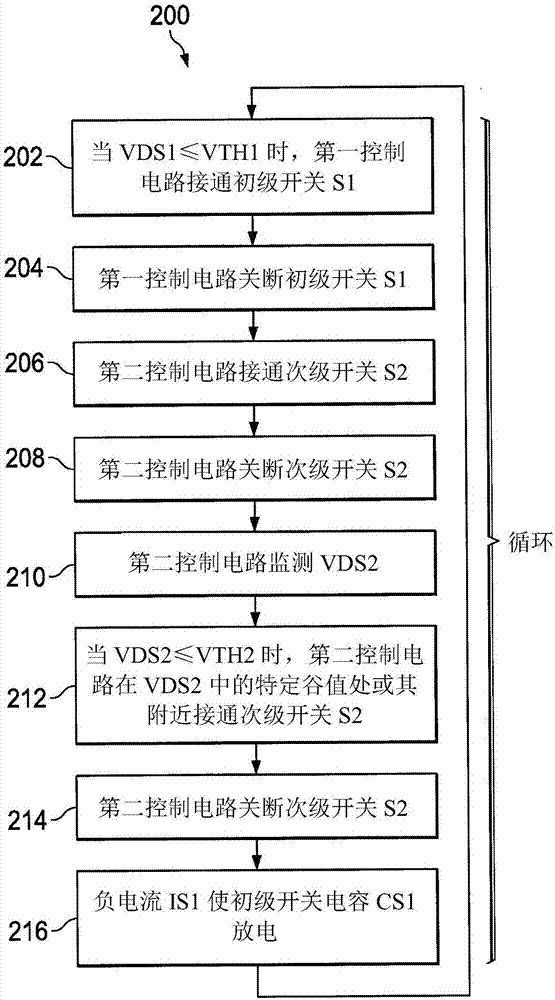
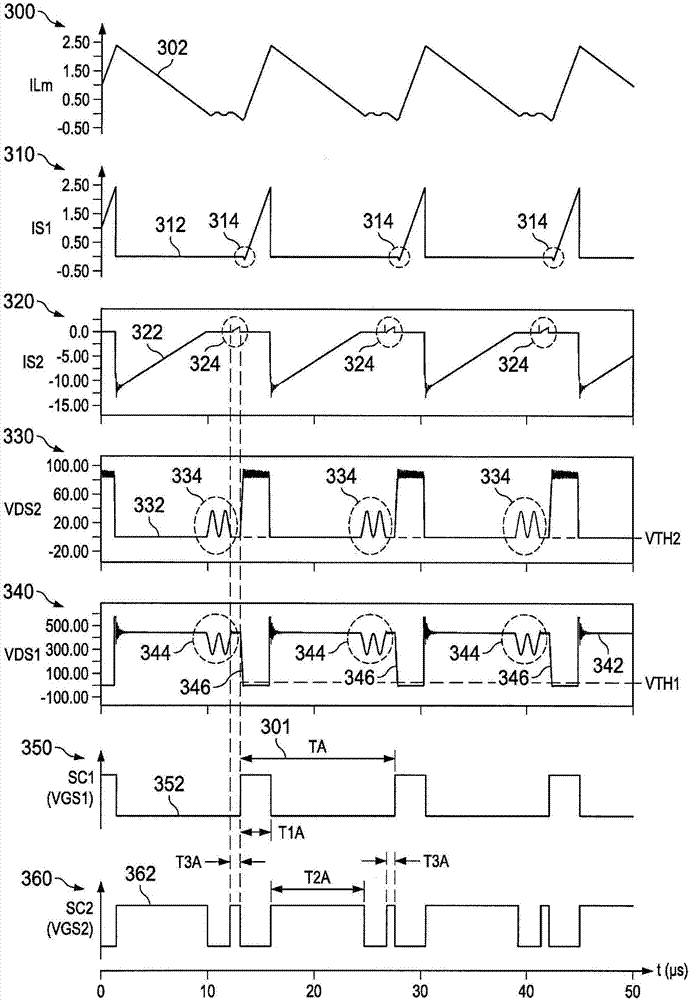
[0010] figure 1 A synchronous rectification flyback converter system 100 is shown comprising a transformer 104 to convert input power from a DC voltage source 102 to drive a load 125 , a primary side or first switch S1 and a secondary side or second switch S2 . The first switch S1 is operated by the first switching control signal SC1 provided by the first control circuit 114 , and the second switch S2 is operated according to the second switching control signal SC2 from the second control circuit 130 . In one example, switches S1 and S2 and control circuits 114 and 130 are provided in an integrated circuit (IC) 101 having terminals or pins or other suitable connections for receiving an input v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com