Composite implant material and method of making the same
A technology for implanting materials and substrates, applied in the field of surgery, can solve the problems of inability to perform high-frequency electrotherapy, heating of surrounding tissues, thermal damage of surrounding tissues, etc., achieve excellent thermal performance, promote repair, and solve heat production problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] In this example a composite implant material comprising a porous oxide intermediate layer was prepared.
[0074] (i) Preparation of silica sol: In this embodiment, silica sol is used to prepare porous SiO 2 Intermediate layer, the preparation step of described silica sol is as follows: with 1.0 grams of P123 [triblock copolymer polyoxyethylene ether-epoxy propylene ether-epoxy ethylene ether (PEO-PPO-PEO) as tensio-active agent )], 5 grams of absolute ethanol, and 0.5 grams of 2mol / L hydrochloric acid are mixed together, and the mixture is stirred at room temperature until the surfactant is completely dissolved to form a homogeneous system, and then 2.08 grams of it is added dropwise while stirring Tetraethyl silicate (TEOS), continue to stir for 10 minutes after the dropwise addition, to form a uniform and clear silica sol.
[0075] (ii) Titanium sol preparation: In this embodiment, the outer coating is TiO prepared using titanium sol 2 layer, and the preparation ste...
Embodiment 2
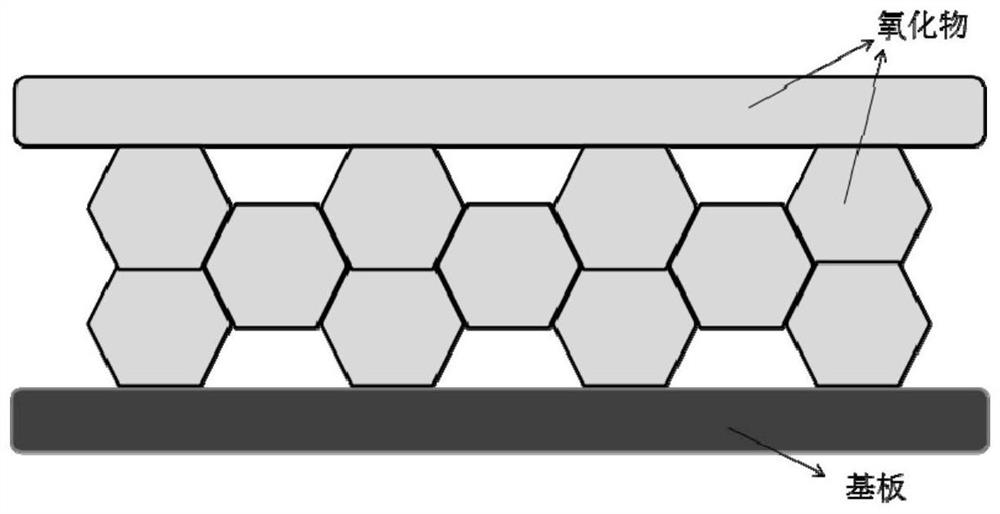
[0081] In this embodiment, the porous intermediate structure is prepared as figure 2 Composite implant material with voids shown.
[0082] (i) Formation of photoresist layer
[0083] Prepare a piece of titanium alloy (Ti 6 al 4 V) The board is used as the bottom substrate, and it is cleaned according to the following steps: the first step is ultrasonic cleaning with acetone solution for 1.5 h, the second step is ultrasonic cleaning with absolute ethanol solution for 1.5 h, and finally deionized water is used for ultrasonic cleaning for 1.5 h. h, The substrate was cleaned and stored in isopropanol solution. Just before the coating operation, the substrate was taken out and dried, and 40 mg of polymethyl methacrylate PMMA was dissolved in 1 ml of chlorobenzene to obtain a PMMA photoresist solution with a concentration of 40 mg / ml. Spin-coat a PMMA film with a thickness of about 1 micron uniformly on the titanium alloy substrate at a spin-coating rate of 2000 rpm / 60s using a...
Embodiment 3
[0091] This embodiment is carried out according to the same steps as embodiment 2, the only difference is that the photoresist pattern formed is such as image 3 shown. The thickness of the voids formed in this embodiment is 1 micron, including a plurality of parallel elongated rectangular voids, the length of each void is about 3 / 4 of the length of the substrate, and the width is about 1 micron, and the voids cover about 60% of the substrate On the surface, the thickness of the outer coating is 100 nanometers, which is a uniform and dense titanium oxide layer without voids.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com