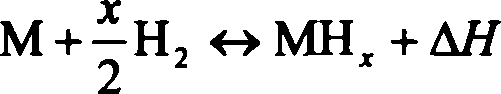Patents
Literature
279results about How to "Solve heating problems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
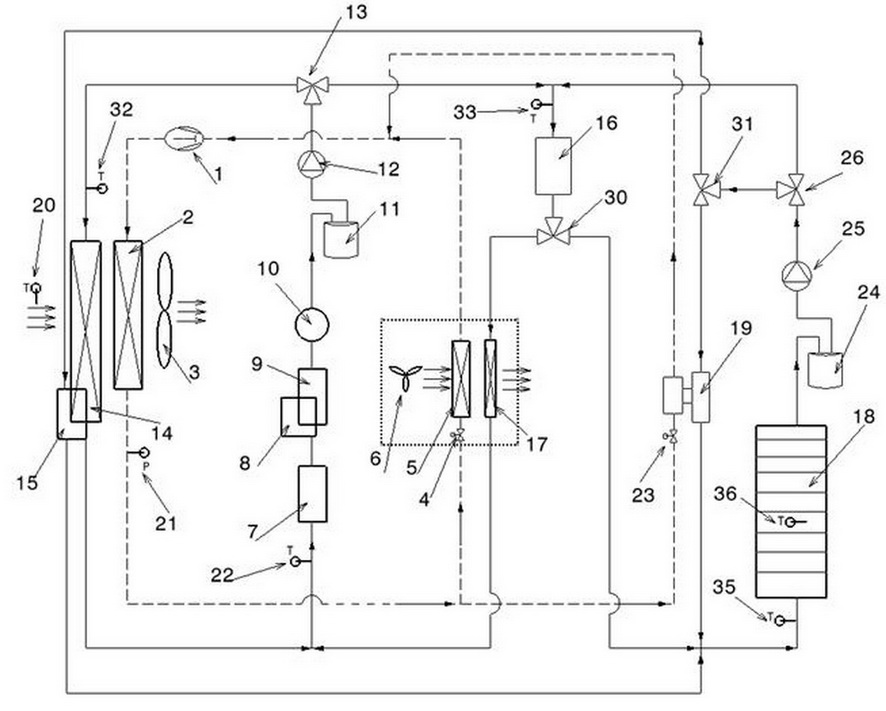
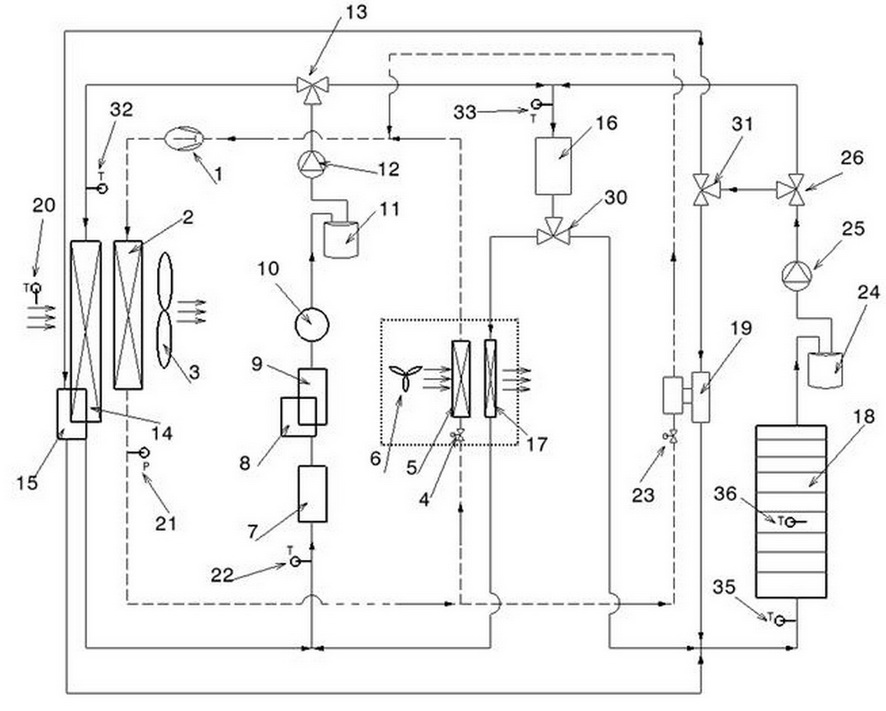
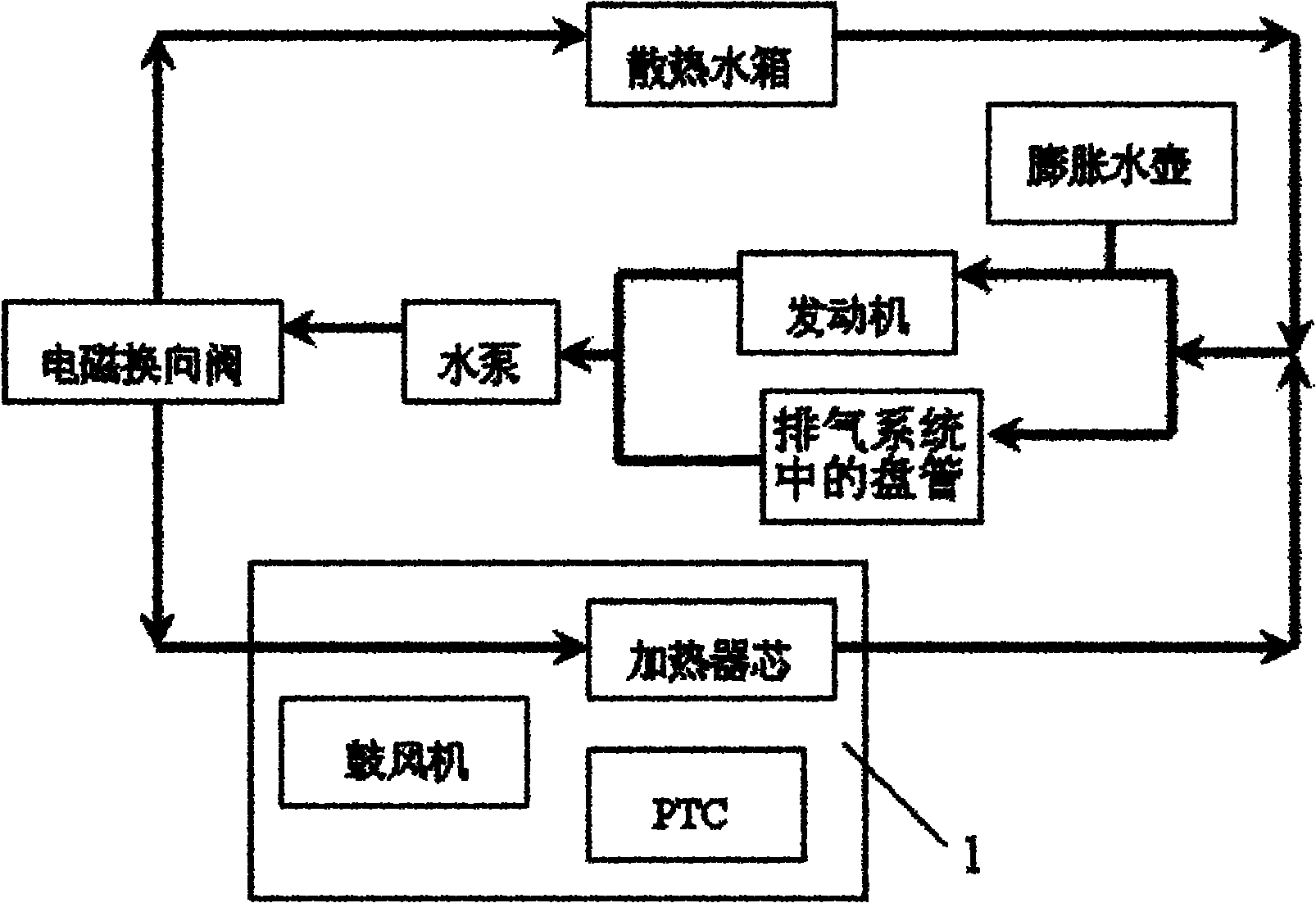
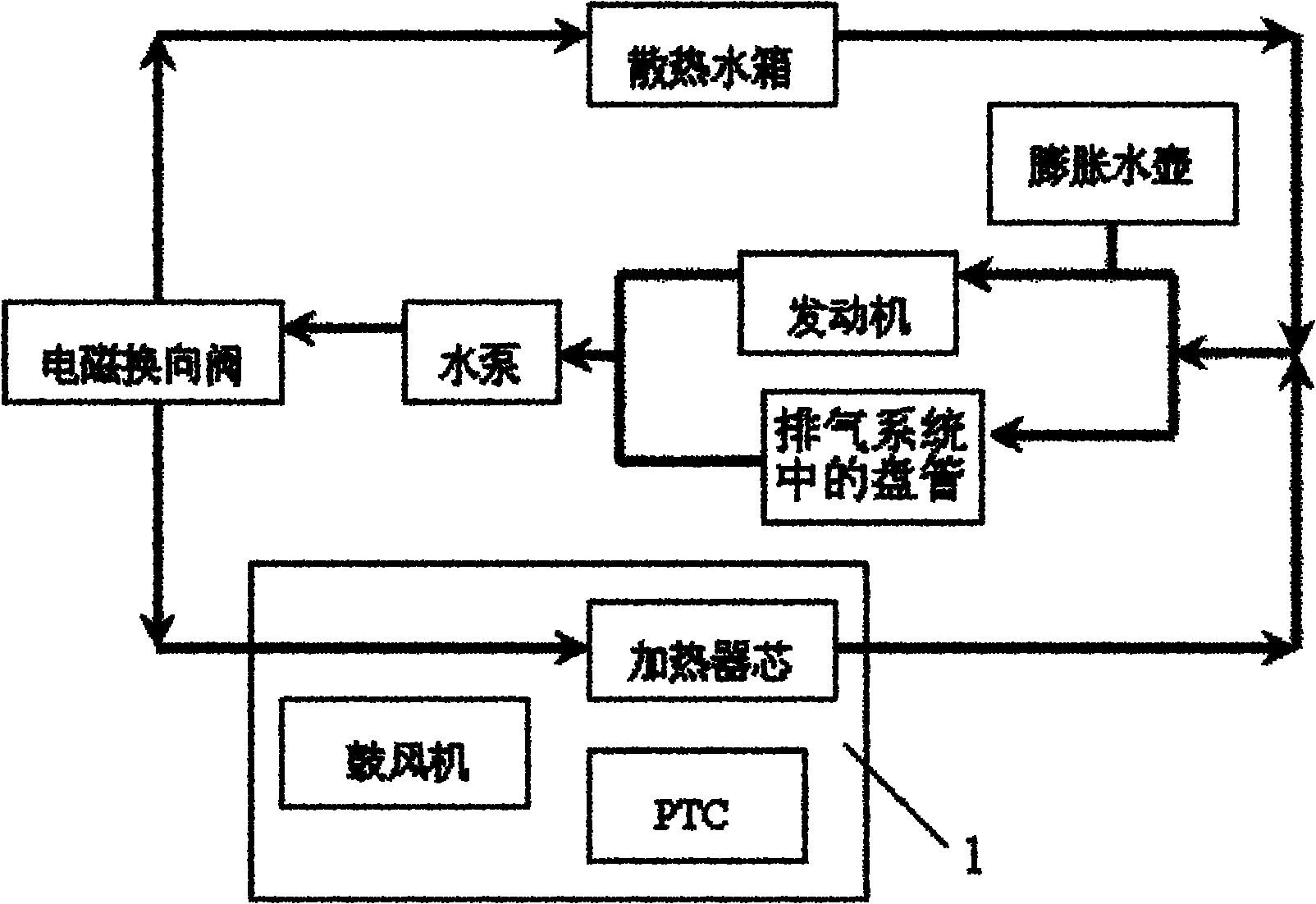
Control system for heat management of electric vehicle
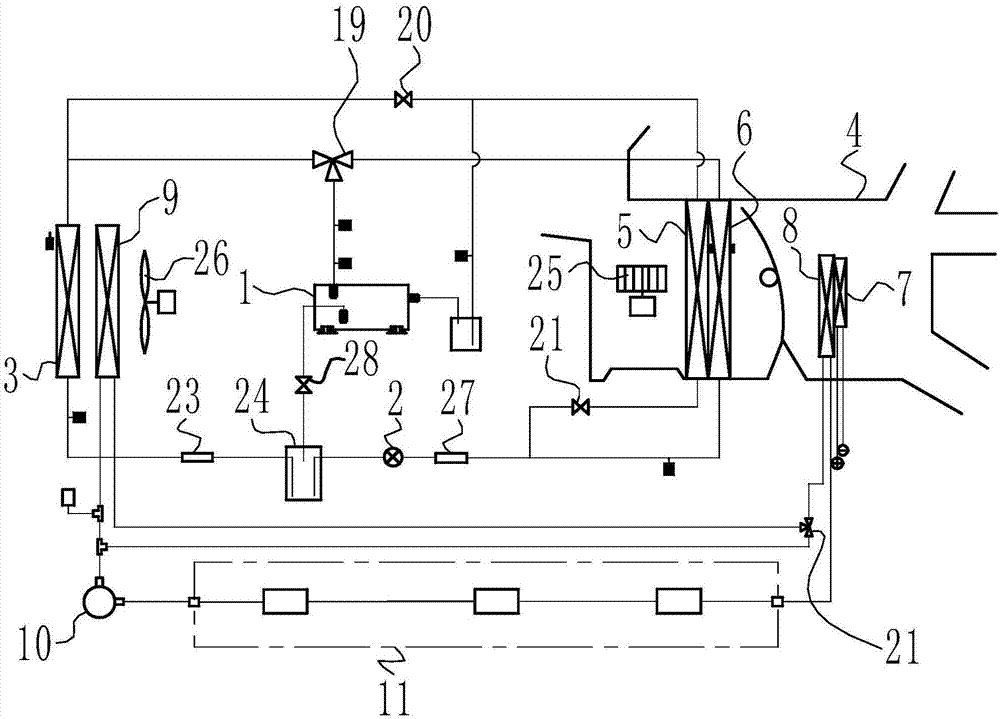
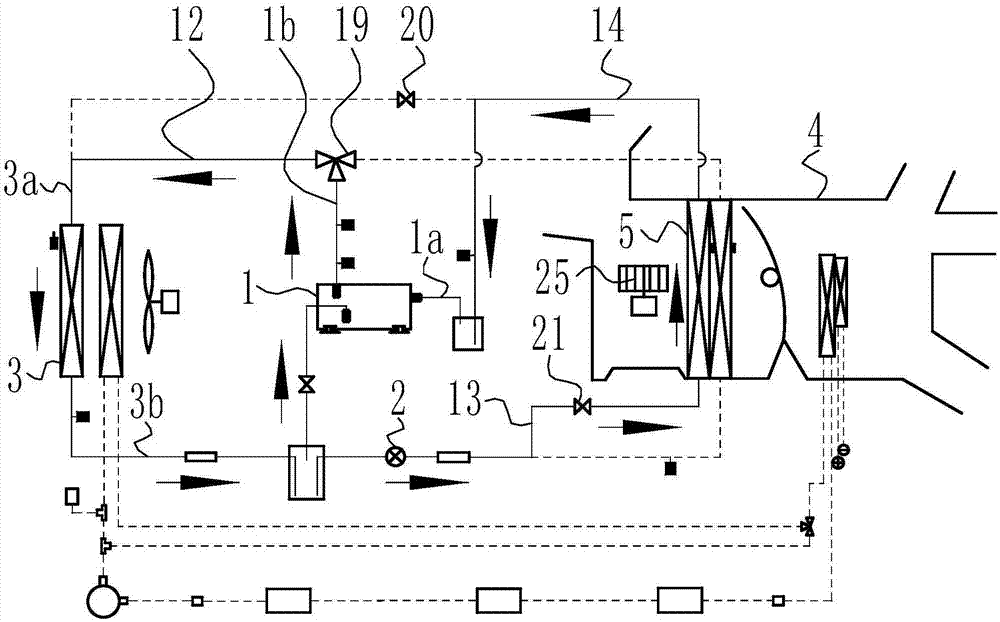
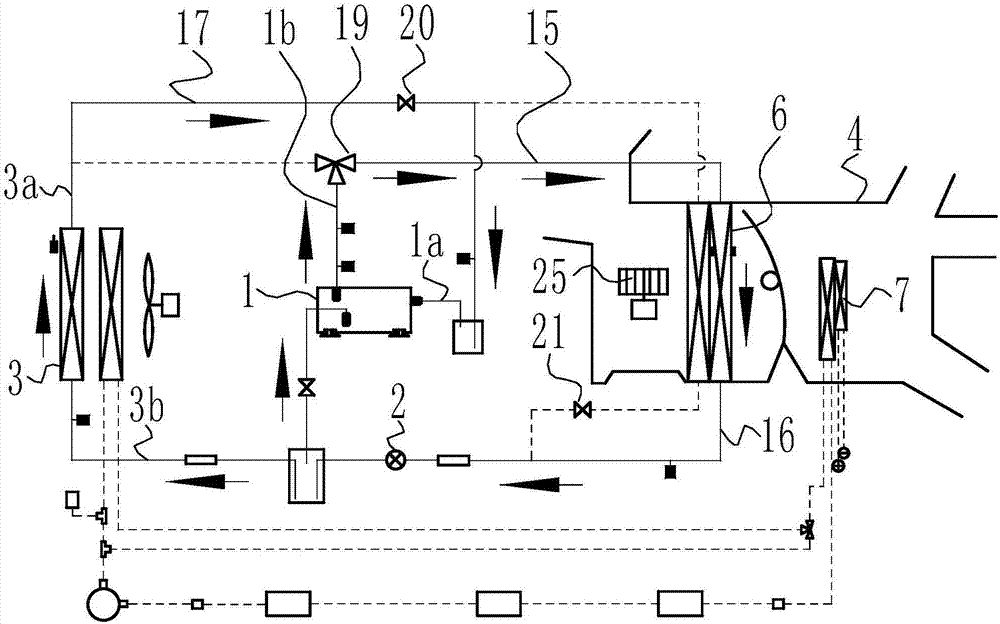
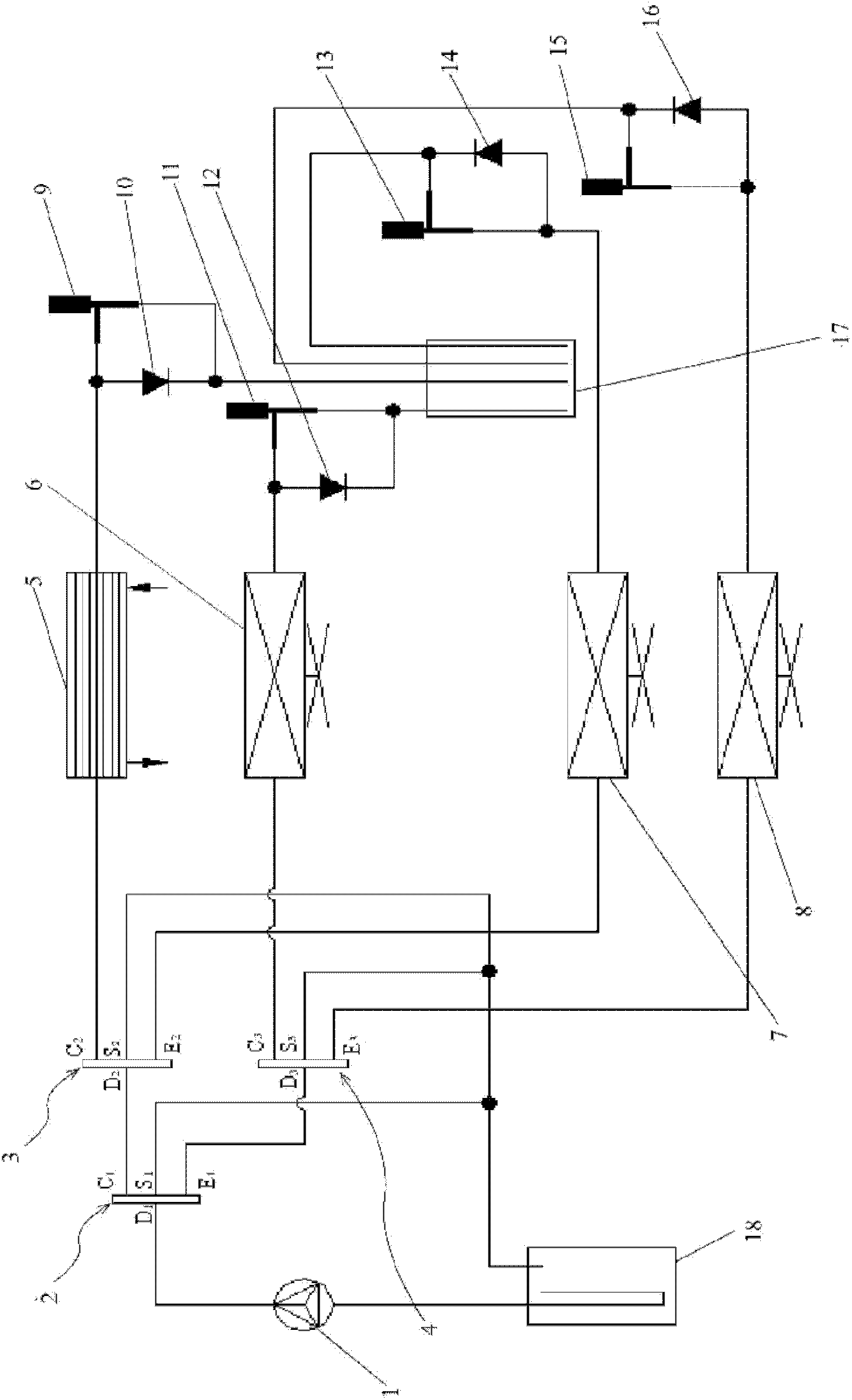
InactiveCN102050007ASolve heating problemsEfficient thermal managementCompression machines with several evaporatorsComponent optimizationAutomotive batteryElectrical battery
The invention provides a control system for heat management of an electric vehicle. The control system is characterized in that the system comprises a refrigerant circulating system, a coolant circulating system and a battery pack temperature control system, wherein the refrigerant circulating system is communicated with the battery pack temperature control system via a water cooler, and the coolant circulating system is communicated with the battery pack temperature control system via a three-way water valve, so the three systems form an intercommunicating and circulating control system to control the temperature in the carriage and the working temperature of the electrical devices of the battery pack. The control system has the following positive effects: effective heat management can be carried out on each part of the electric vehicle; the problem of heating difficulty of the electric vehicle is solved by adopting the residual heat of the electrical devices in an economical and energy-saving manner; preheating and cooling of the power battery of the electric vehicle are well controlled; and the working temperature of the battery and electrical devices of the electric vehicle can be controlled, thus realizing complete heat system management of the electric vehicle.
Owner:VALEO AUTOMOTIVE AIR CONDITIONING HUBEI CO LTD
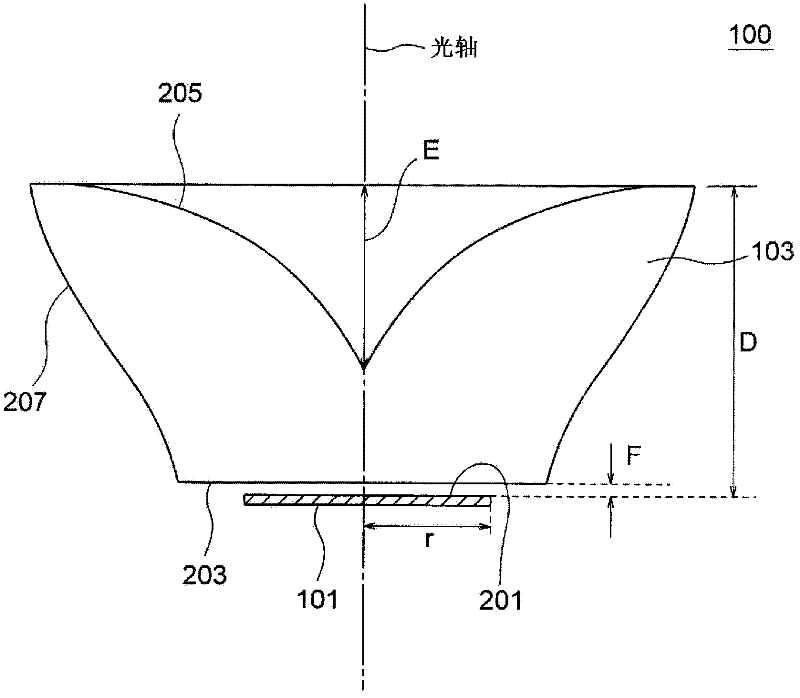
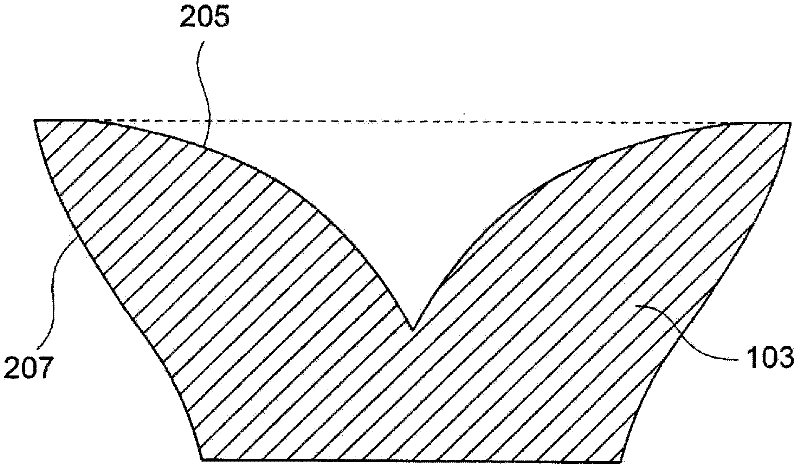
lighting device
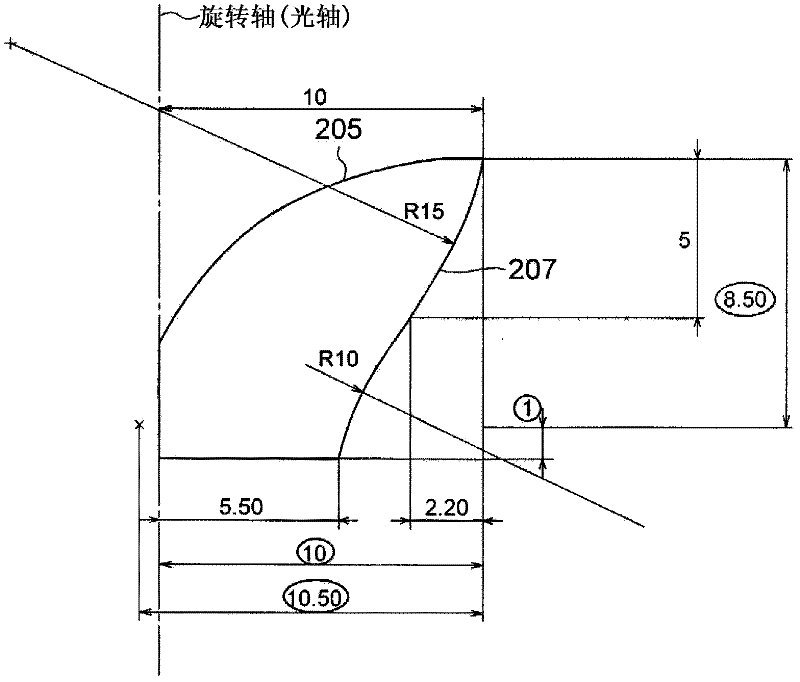
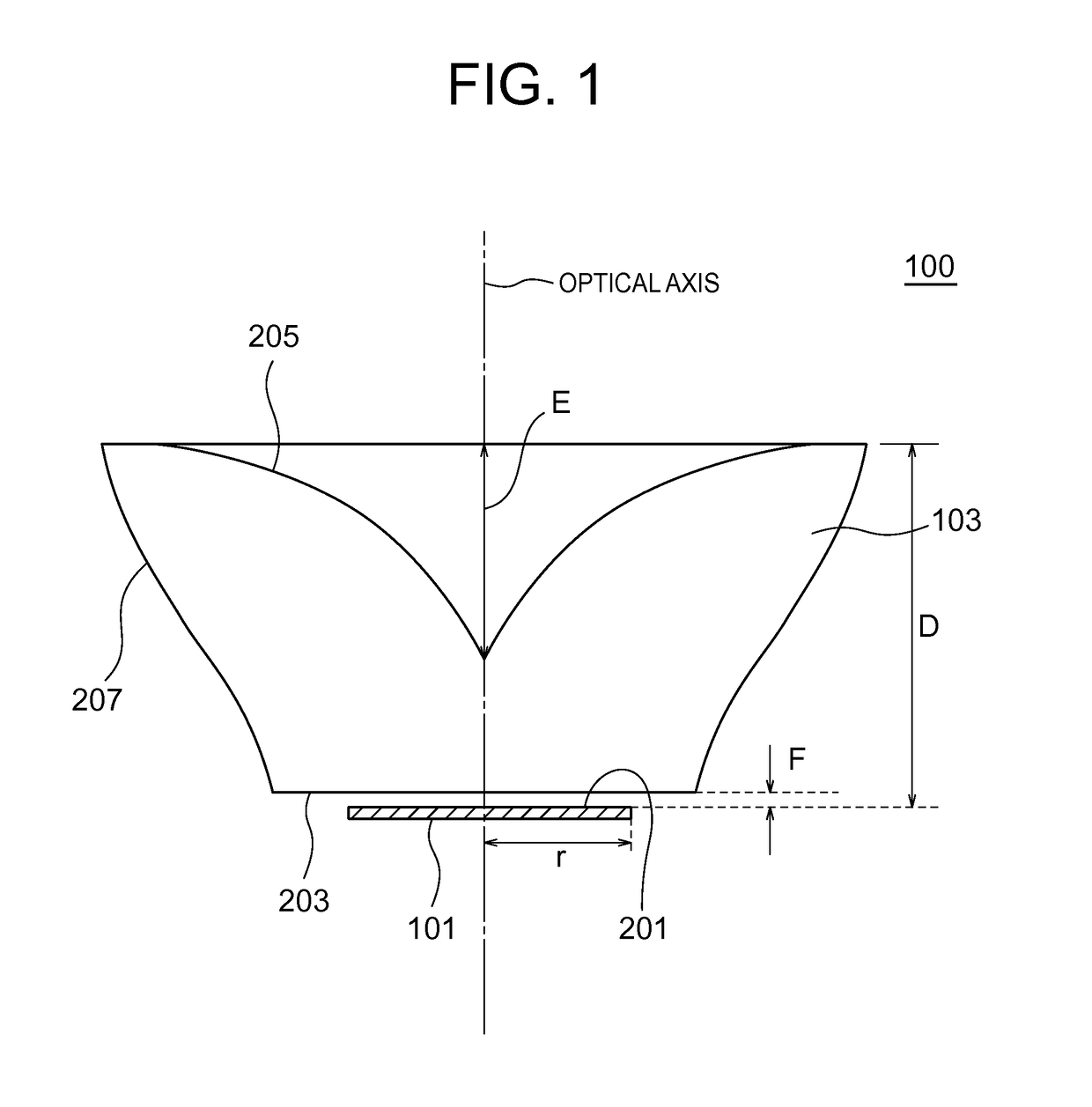
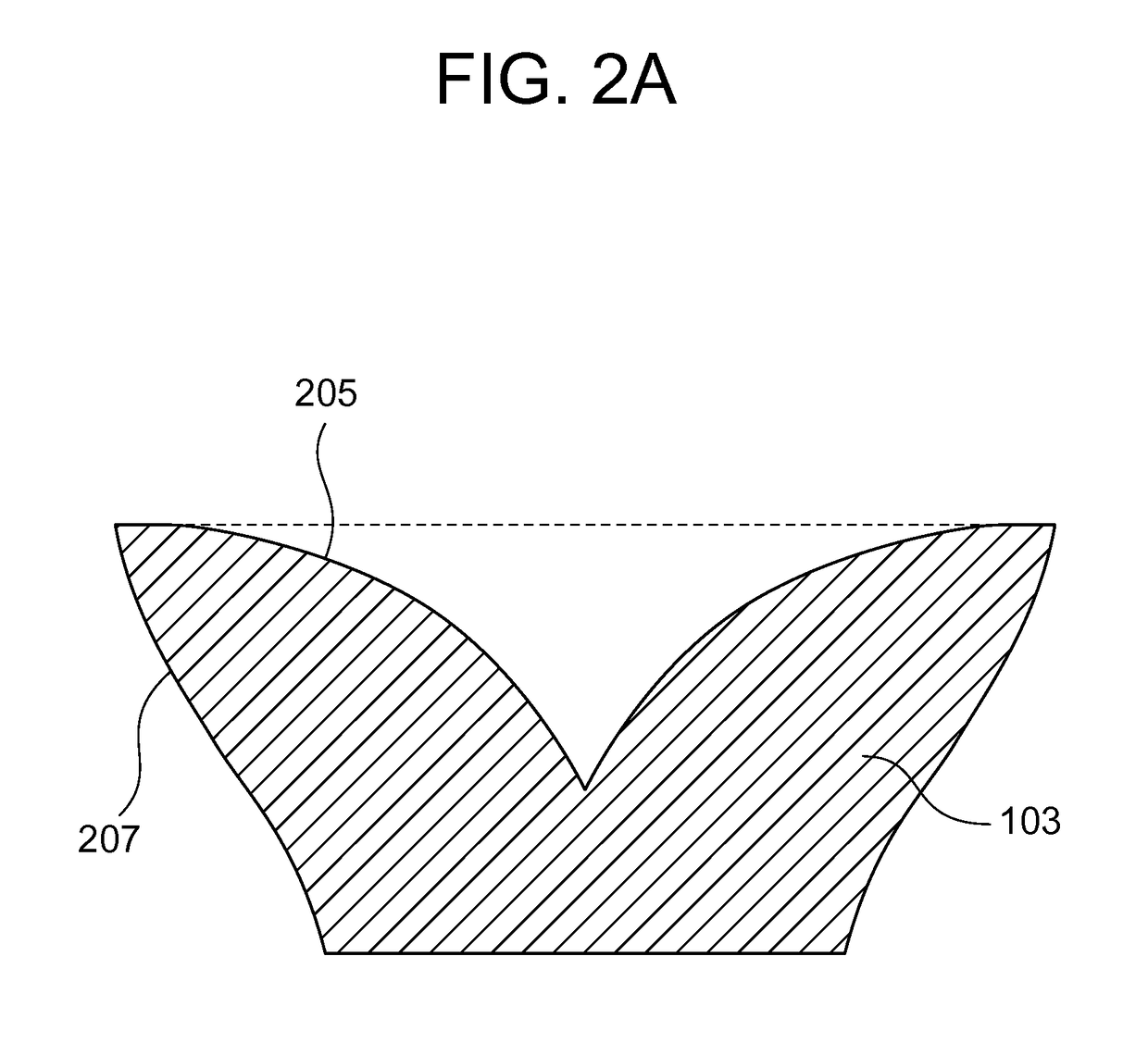
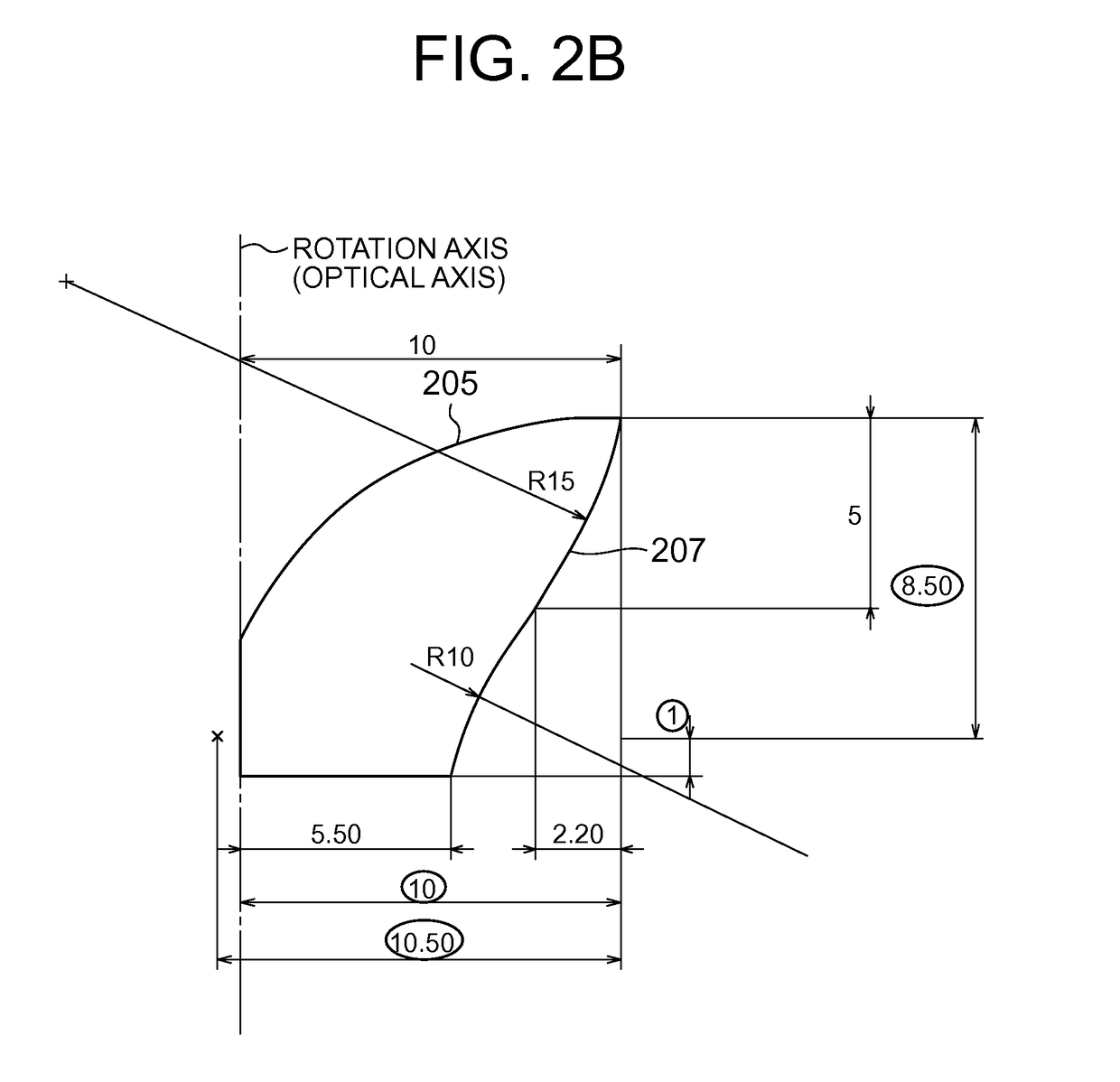
ActiveCN102282416ASolve heating problemsPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceOptical axisLight beam
A lighting device includes a surface light source (101) and an optical element (103) which is provided with an incident surface (203) and first and second exit surfaces (205, 207). When the center of a light emitting surface (201) is set as P1, an edge point thereof is set as P2, and an axis which passes through P1 and is vertical to the light emitting surface is set as an optical axis, the optical element has such a shape that the optical axis and the vicinity thereof are recessed as compared to the edge. In the cross section of the optical element, when a point on the first exit surface which is disposed at a prospective angle of 15 degrees from the optical axis about P1 is set as P3, a point at which a light beam that exits P2 and travels in parallel to the optical axis intersects the first exit surface is set as P4, and an axis that connects P1 with P2 is set as an X axis, the X coordinate of a point farthest from the optical axis on the first exit surface is equal to or larger than 1.5-times value of P2, and the first exit surface is formed so that an incident angle of light that exits P1 is equal to or larger than a critical angle in 80% or more of an area where the X coordinate is equal to or larger than the value of P3 and an incident angle of light that exits P2 is smaller than the critical angle in 80% or more of an area where the X coordinate is equal to or smaller than the value of P4.
Owner:NALUX CO LTD
Battery pack heat management device
ActiveCN103094640APerfect thermal management functionPrecise managementSecondary cellsHeat managementLiquid medium
The invention discloses a battery pack heat management device by employing a liquid medium. The device has a perfect battery pack heat management function, and according to the device, the heating and radiating of a battery pack can be finished, so that the battery pack always works in an optimal temperature range, the temperature of each battery unit can be accurately managed, and the time required for heating the battery pack is obviously shortened; and therefore, the consistency and good performance of the battery pack can be well guaranteed. The battery pack heat management device employing the liquid medium mainly comprises a liquid cooling box, an electronic fan, a liquid medium, a thermostat, a secondary liquid tank, a semiconductor and temperature sensor unit, a battery box temperature sensor, a battery unit, an outer battery box shell, a battery box insulation layer, an inner battery box shell, an electric pump, a battery management unit, a heating module and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Illuminating device
ActiveUS8118457B2Reduce unevennessSolve heating problemsPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceAngle of incidenceOptical axis
An illuminating device includes a light source and a light receiving surface, first and second light exit surfaces. When a point at the edge of the light emitting surface is P2 and an axis which passes through a center P1 of a light emitting surface and is perpendicular to the light emitting surface is an optical axis, the optical element has a hollow around the optical axis. The first light exit surface is such that x coordinate of a point most distant from the optical axis on the first light exit surface is at least 1.5 times x coordinate of P2, that in 80% or more of an area in which x coordinate of a point is at least the x coordinate of another point P3, an angle of incidence of light emitted at P1 is at least the critical angle and that in 80% or more of an area in which x coordinate of a point is equal to or smaller than x coordinate of another point P4, an angle of incidence of light emitted at P2 is smaller than the critical angle.
Owner:NALUX CO LTD
Process for preparing caprolactam by cyclohexanone-oxime gas phase rearrangement
ActiveCN1621405AHigh yieldReduce consumptionLactams preparationBeckmann rearrangementMolecular sieve
The process of preparing caprolactam with cyclohexanone oxime includes the vapor Beckmann rearrangement reaction of cyclohexanone oxime inside one first fixed bed reactor in the presence of MFI structure molecular sieve catalyst; the decomposition and conversion of the reaction side product O-alkyl-epsilon-caprolactim into caprolactam inside one second fixed bed reactor in the presence of MFI structure molecular sieve catalyst and water; and the separation and purification of the reaction effluent. Compared with single vapor Beckmann rearrangement reaction process of cyclohexanone oxime, the present invention has 1-3 % raised caprolactam yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Energy-saving cast-in-place hollow floor
InactiveCN102003010AMaintain integrityMaintain aestheticsFloorsForms/shuttering/falseworksCrack resistanceEngineering
The invention relates to an energy-saving cast-in-place hollow floor, which comprises thin-wall box bodies, a rib beam between the box bodies and an upper flange plate, wherein the upper flange plate contains an electric heating tube, and an electric heater and heat retention liquid are arranged in the electric heating tube; the top surface of the thin-wall box body is provided with at least one groove, the lateral surface of the thin-wall box body is provided with a closed hole, the closed holes of the adjacent box bodies are connected through a junction pipe, the lower end of the hole wall is connected with the bottom surface and closed, and the upper end of the hole wall is communicated with the top surface to form a hole; and the inclined plane and the bottom surface of the box bodies form an included angle of 100 to 165 degrees, and the side length of the inclined plane is more than 20 millimeters. Sunken closed holes are reserved on the lateral surfaces of the box bodies, the closed holes are opened before casting and the junction pipe can pass through the open closed holes to form an interconnected through heat energy blowing passage, and grooves for laying heating pipes are reserved on the top surfaces of the thin-wall box bodies to form a floor energy supply system. The floor adopting the thin-wall box bodies has the advantages of light weight, high hardness, reasonable structure, energy conservation, environment friendliness, cracking resistance and seismic resistance, and also can solve the heating problem by using the box bodies to transfer the heat energy.
Owner:王本淼
Strong-hybrid electric vehicle heating system
ActiveCN102019838ADoes not affect cruising rangeSolve heating problemsAir-treating devicesVehicle heating/cooling devicesWater circulationElectric vehicle
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
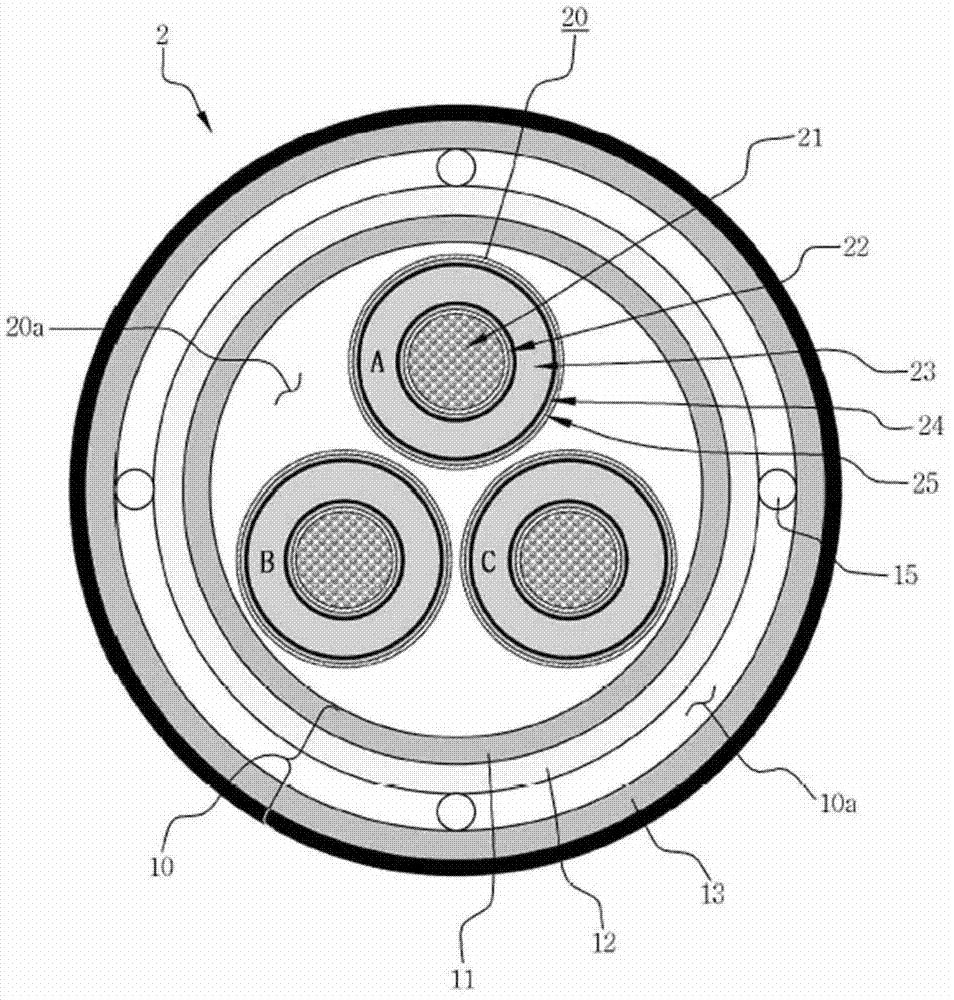
Superconducting cable
ActiveCN103177815ALess quantityImprove economySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:LG CABLE LTD (KR)
Method for producing ethylene from ethanol by combination hydrocarbons catalytic conversion
ActiveCN101104571ASolve heating problemsIncrease contentCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsLiquid productGasoline
Disclosed is a combined hydrocarbons catforming method to produce ethane from ethanol. Ethanol raw materials contact with Y zeolite catalysts and the reaction products flow to a segregator, getting coked catalysts and target ethane; hydrocarbon raw materials contact with Y zeolite catalysts and the reaction products flow to a segregator, getting spent catalysts and reaction effluent and the reaction effluent is further separated to get gas and liquid products such as gasoline; all or part of the coked catalysts or spent catalysts get into a reactivator for coke-burning regeneration; the regenerated catalysts are divided into two parts, one part returns to contact with the hydrocarbon raw materials and the other part, after cooling, returns to contact with the ethanol raw materials. The method properly uses the surplus heat energy in the course of hydrocarbons catalytic conversion, solving the problem of heat energy supply in ethanol conversion, ensuring that the ethanol can be converted to ethane continuously. The content of ethene in the gas products of the ethanol catforming exceeds 95 percent and the conversation rate of ethanol can reach 99 percent.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Windshield wiper arm elevator apparatus and control method
InactiveCN101456406AMeet the protection requirementsFlexible lifting controlVehicle cleaningElectric driveEngineering
The invention discloses a lifting device of a screenwiper arm. The lifting device comprises a signal acquisition device, a controller and an electric drive mechanism and an actuating mechanism arranged on the screenwiper arm, wherein the signal acquisition device is used for acquiring a state signal of a screenwiper and outputting the state signal into the controller; and the controller is used for judging the state of the screenwiper and controlling the electric drive mechanism to drive the actuating mechanism to lift or descend the screenwiper arm. A controlling method comprises: through acquisition of the state signal of the screenwiper, the lifting and descending of the screenwiper arm by the actuating mechanism are controlled. The lifting device has the advantages that the lifting device can use the structure of the prior screenwiper, directly mount the drive mechanism and the actuating mechanism on the screenwiper arm, is easy to modify and is flexible to control the lifting and descending of the screenwiper arm; and through the detection of the state of the screenwiper, the lifting device controls the lifting and descending of the screenwiper arm according to the state of the screenwiper, meets the protective requirements of different screenwipers, can lift the screenwiper arm when the screenwiper is stopped and solve the problem of aging due to the fact that a wiping rubber strip is contacted with windshield glass for a long time and is heated or frozen.
Owner:DONGFENG MOTOR CO LTD
Single alloy compressing-diffusing metal hydride heat pump/refrigerating method and system
InactiveCN1888725AImprove utilization efficiencySolve heating problemsEnergy efficient heating/coolingClimate change adaptationHydrogen atomAlloy
This invention is a kind of single alloy compression-diffusion type metal hydride heat pump / refrigeration method and its system. Pressure difference between metal hydride under solid solution phase and hydride phase is generated. Metal hydride absorbs hydrogen and releases heat at high- pressure side. It releases hydrogen and absorbs heat at low -pressure side. Through heat exchanger carrying away the generated heat / cold energy, heating / refrigerating is fulfilled. The hydrogen atoms, which are absorbed from metal hydride high- pressure side, are transferred to low pressure side through the inside of metal hydride continually by diffusion effect. This system includes compressor, one-way valve, hydrogen pipeline and diffusing bed. The diffusing bed includes pore filter sheet, low temperature heat exchanger, bed body insulating outer wall, metal hydride powder and high temperature heat exchanger.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for circularly and rapidly pre-vulcanizing sulfur tolerant shift catalyst and carrying out segmental pre-vulcanizing by utilizing sulfur tolerant shift catalyst
ActiveCN103657741AThe vulcanization method is simpleHeating up fastCatalyst activation/preparationSocial benefitsVulcanization
The invention relates to a segmental pre-vulcanizing method of a sulfur tolerant shift catalyst in a multi-segment conversion process, particularly relates to a method for rapidly pre-vulcanizing cobalt-molybdenum-series sulfur tolerant shift catalysts and belongs to the technical field of pretreatment of the sulfur tolerant shift catalyst. According to the method, aiming at the situations of the temperature raising and the slow vulcanizing speed caused due to insufficient vulcanizing conditions, a segmental vulcanizing method is utilized, namely the rapid pre-vulcanizing of a first-segment furnace is reinforced to raise the temperature of a subsequent second-segment furnace; first-segment vulcanizing conditions are reinforced to guarantee the vulcanization of the catalyst so as to realize the rapid, efficient and complete vulcanization, meanwhile, the temperature of a subsequent second-segment bed is raised by high-temperature vulcanized gas in a rapid vulcanizing process, and the subsequent working segments are similarly processed, so that the vulcanizing and temperature raising time is greatly shortened, and the vulcanizing cost is lowered; by utilizing a circular vulcanizing manner, the emptying quantity is few, the overtemperature is avoided, the vulcanizing process is convenient and safe, the pollution is light, and the method has remarkable economic and social benefits.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Winter and summer temperature adjusting device based on radiation cooling and solar energy utilization and construction method of winter and summer temperature adjusting device
PendingCN110567188AReduce radiant heatSolve Cooling ProblemsSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationInfraredOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a winter and summer temperature adjusting device based on radiation cooling and solar energy utilization and a construction method of the winter and summer temperature adjusting device. The winter and summer temperature adjusting device is constituted by a radiation cooling structure and a heat absorbing layer; the radiation cooling structure is composed of a reflecting layer, an emission layer and a wind screen, the emission layer is arranged between the reflecting layer and the wind screen, the wind screen is composed of an air layer and a covering material layer, andthe air layer is located between the emission layer and the covering material layer; the reflecting layer reflects sunlight out, and the emission layer emits heat in a temperature-adjusted medium outin an infrared ray mode; and the heat absorbing layer is composed of a solar heat-absorbing material layer and a metal plate, and the metal plate is located between the solar heat-absorbing materiallayer and the reflecting layer of the radiation cooling structure and is closely combined with the radiation cooling structure. The winter and summer temperature adjusting device can provide passive temperature decreasing and increasing for certain occasions and equipment, and achieves the energy saving effect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method and device of combined process for producing ethylene by ethanol dehydration and catalytic cracking
ActiveCN101659588ASolve the heat problemEliminates flow control valvesCatalytic crackingHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsFluidized bedEthanol
The invention relates to a method and a device of a combined process for producing ethylene by ethanol dehydration and catalytic cracking. The method comprises: placing an ethanol raw material and a catalyst in an ethanol conversion reactor to allow the ethanol raw material to contact the catalyst to react; separating the reaction product from the catalyst in a settler; delivering the reaction product to a post-separation system; stripping the catalyst by using steam in a stripping still; delivering the catalyst to a catalyst mixing tank to mix the catalyst with a catalyst from a catalytic cracking regenerator; and delivering one part of the mixed catalyst to the ethanol conversion reactor and delivering the other part the mixed catalyst to the catalytic cracking regenerator. The method adopts a gas-solid-solid circulating fluidized bed ethylene production process and combines the process with a catalytic cracking process, thereby solving the heat requirement problem of an ethanol dehydration reaction system, simplifying the fluidized bed ethylene production process, reducing equipment investment and contributing the easy realization of a large-scale process of ethylene production by ethanol.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
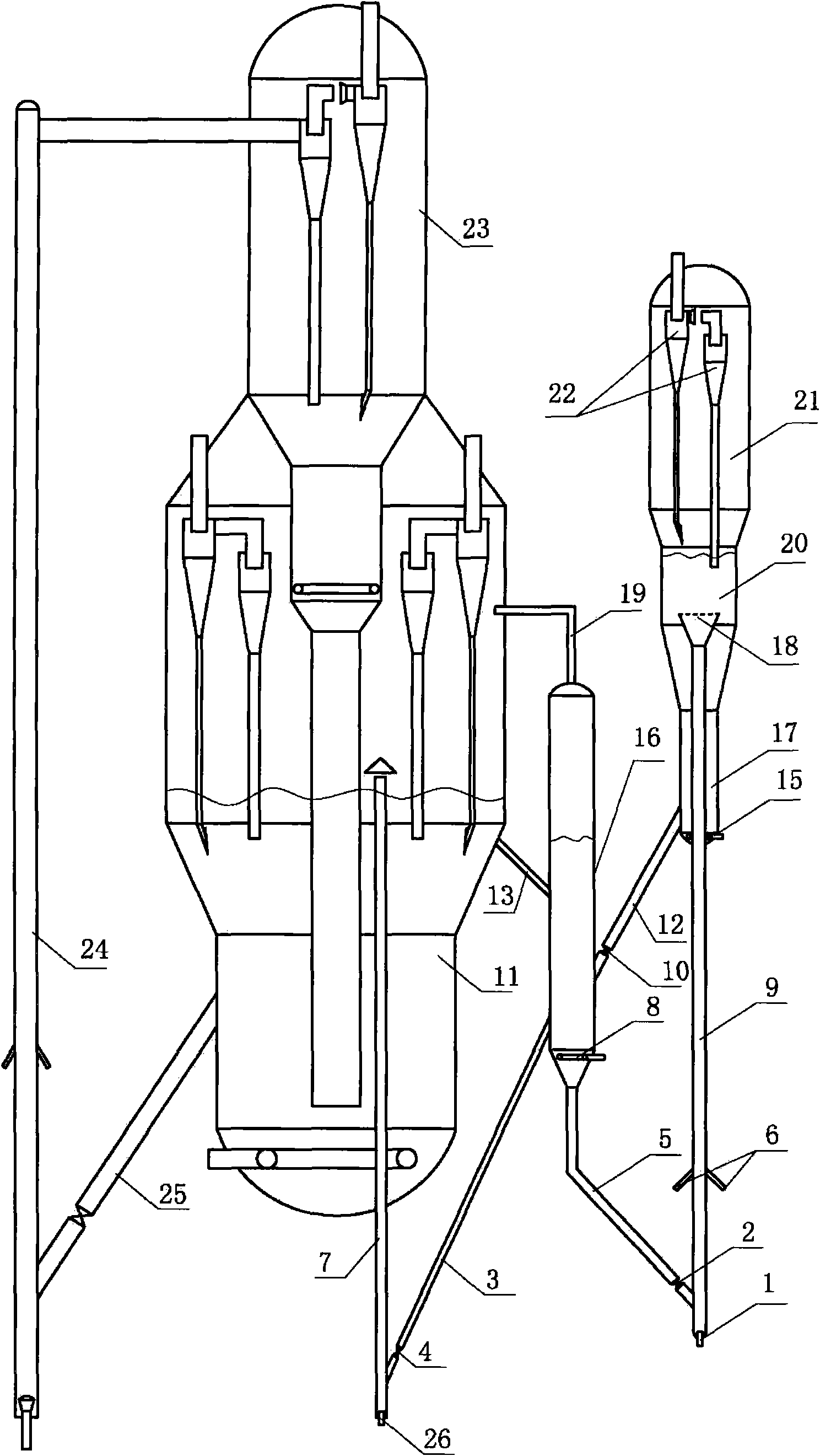
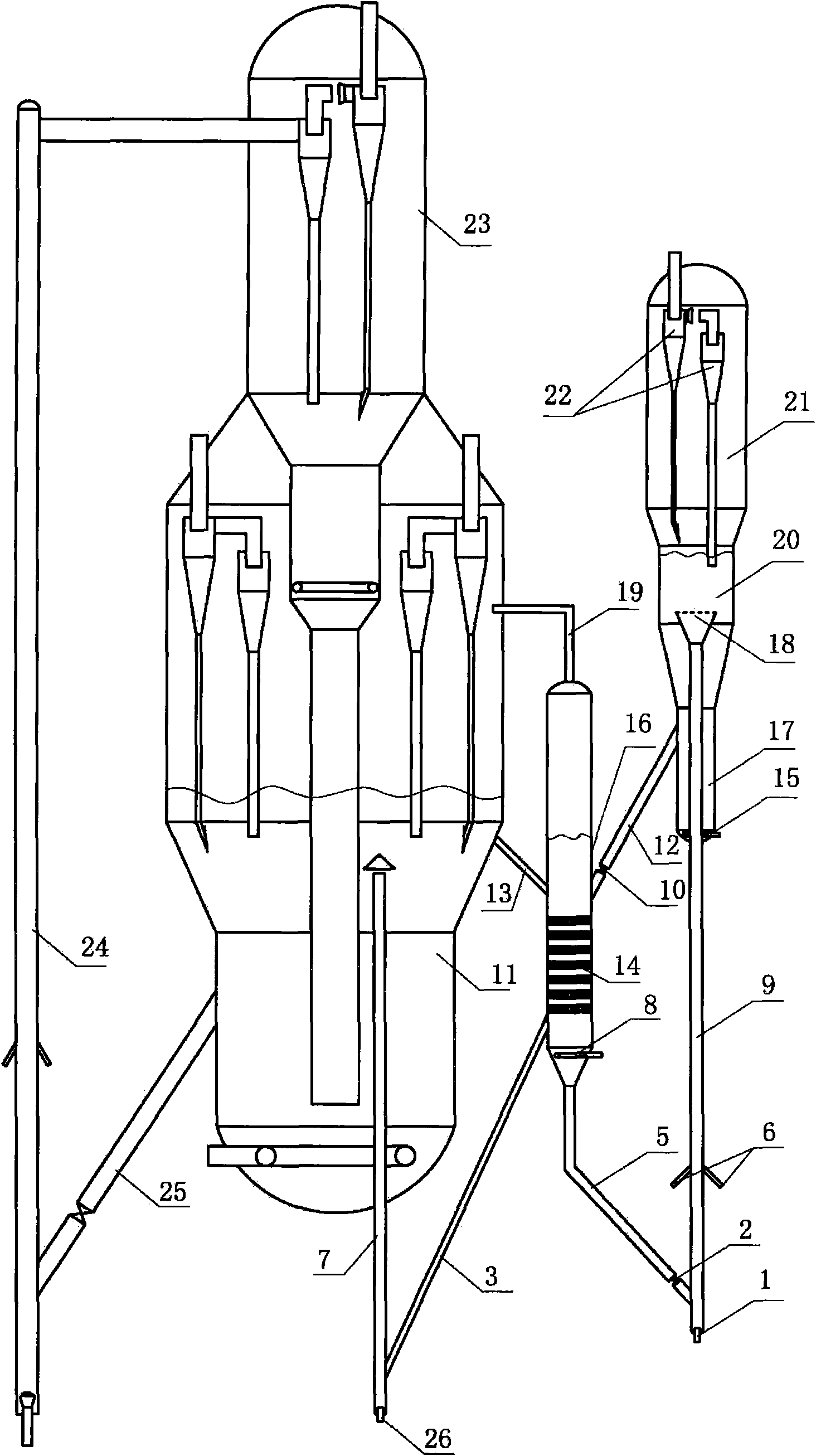
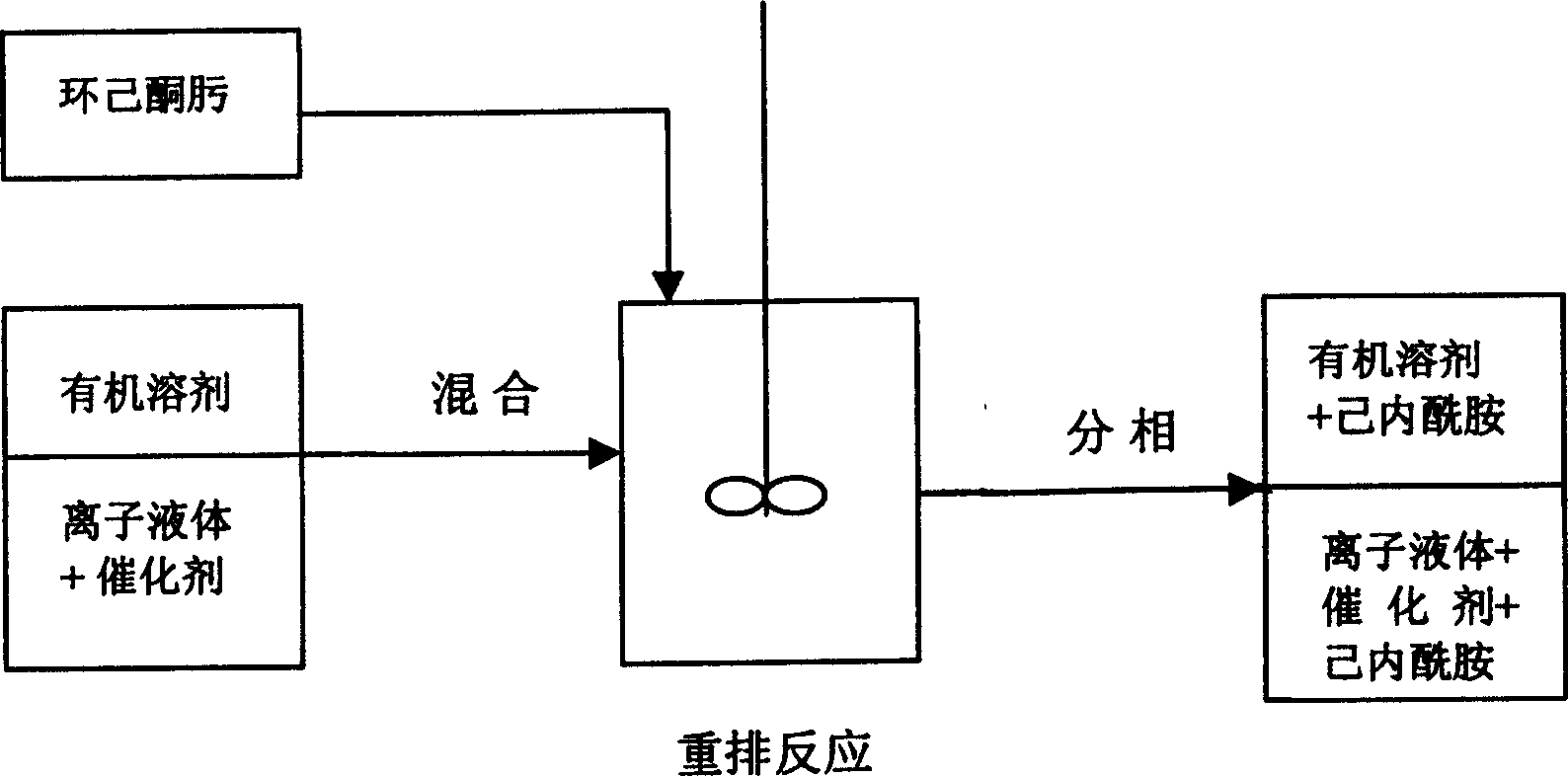
Process for preparation of caprolactam
The invention discloses a process for preparation of caprolactam from cyclic ketones through liquid phase rearrangement reaction in ionic liquid and at the presence of phosphorus-containing compounds as the catalyst, wherein the ionic liquid, organic solvent non-dissolving to the ionic liquids and acidic phosphorus-containing compound catalyst are mixed under stirring condition, dissolving the catalyst into the ionic liquid phase, heating the obtained two phase catalytic system to a rearrangement reaction temperature, charging the cyclic ketones or solution into the catalytic system for reaction, then subjecting to stewing and phase-splitting.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Active cool type radiating substrate using air convection
InactiveCN102185093AGood cooling effectReduce heat dissipation device life and efficiency issuesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAir convectionCross ventilation
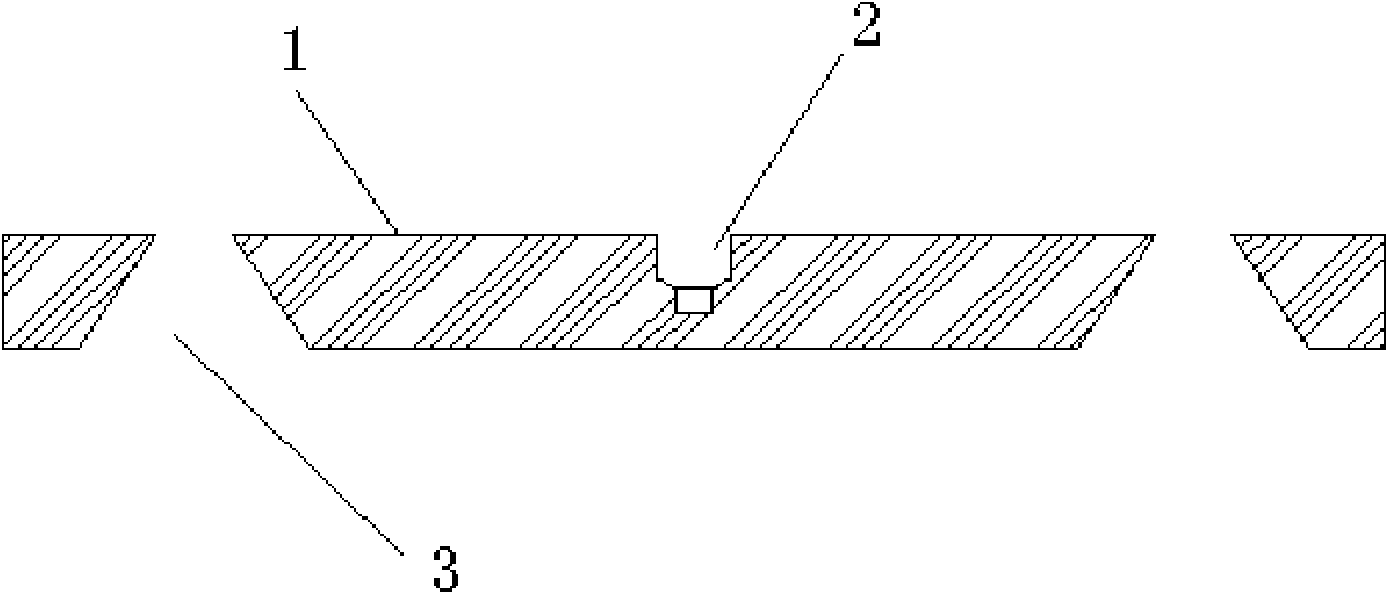
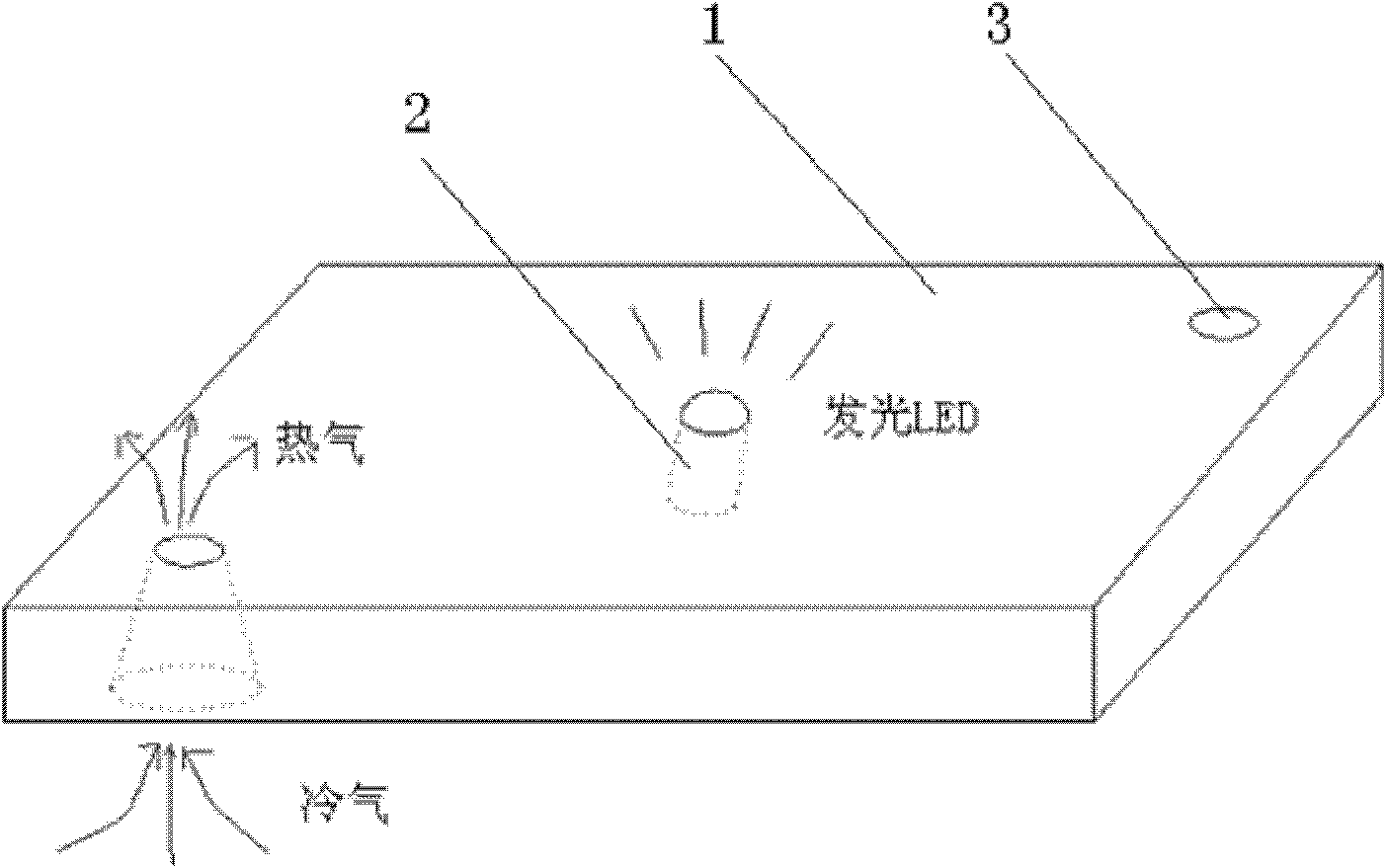
The invention provides an active cool type radiating substrate using air convection. The active cool type radiating substrate comprises a radiating substrate connected with a radiating device, and a radiating hole arranged in the radiating substrate. The active cool type radiating substrate enables the cold air and hot air to be circulated dynamically through the effective cross-ventilation of the radiating hole so as to enable the heat conduction and heat dissipation of the radiating substrate to be balanced dynamically for realizing stability. The active cool type radiating substrate solves the heat-carrying problem caused by high heat conduction and low heat dissipation of the existing radiating substrate, avoids continuous temperature rising of the radiating device, such as an LED (light-emitting diode), generates good radiating effect, reduces the radiating device service life and efficiency problems caused by thermal failure, and effectively ensures the normal work of the radiating device. The active cool type radiating substrate using air convection is simple in structure, low in cost and easy to realize volume production, and is an environment-friendly and resource-saving device.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
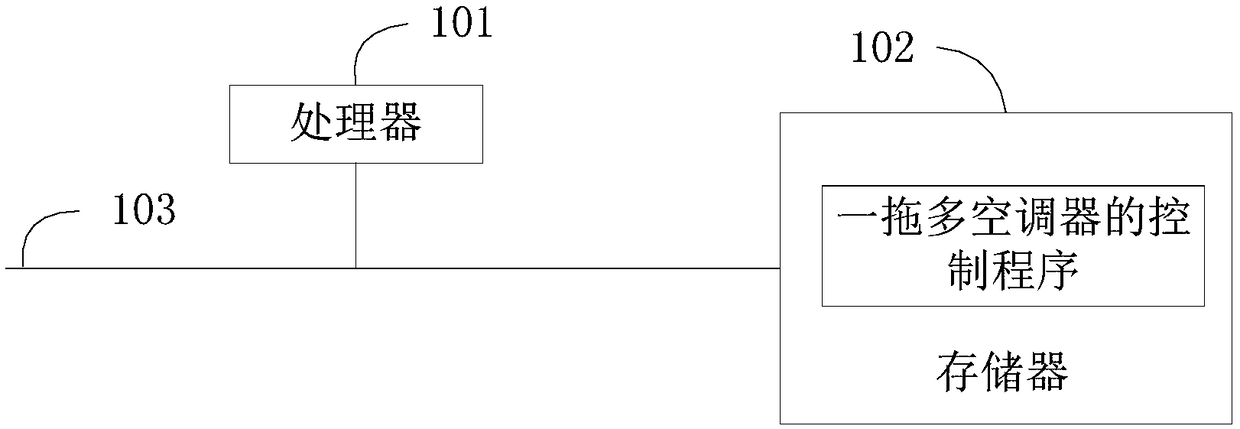
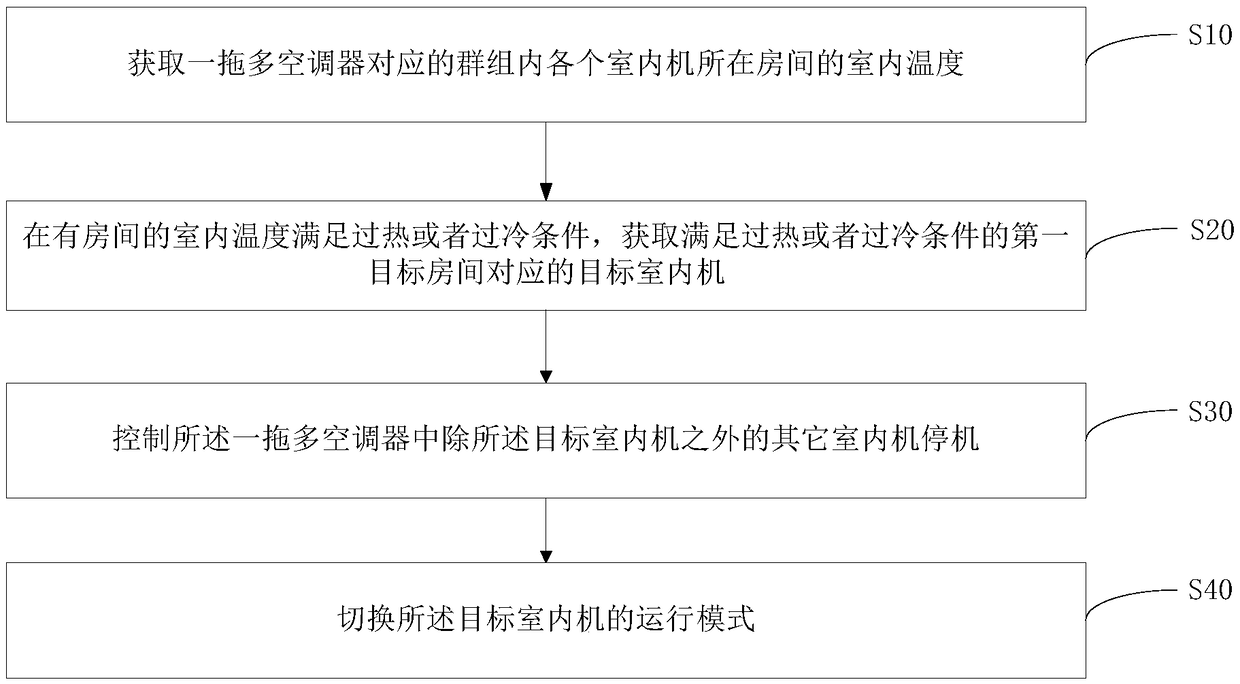
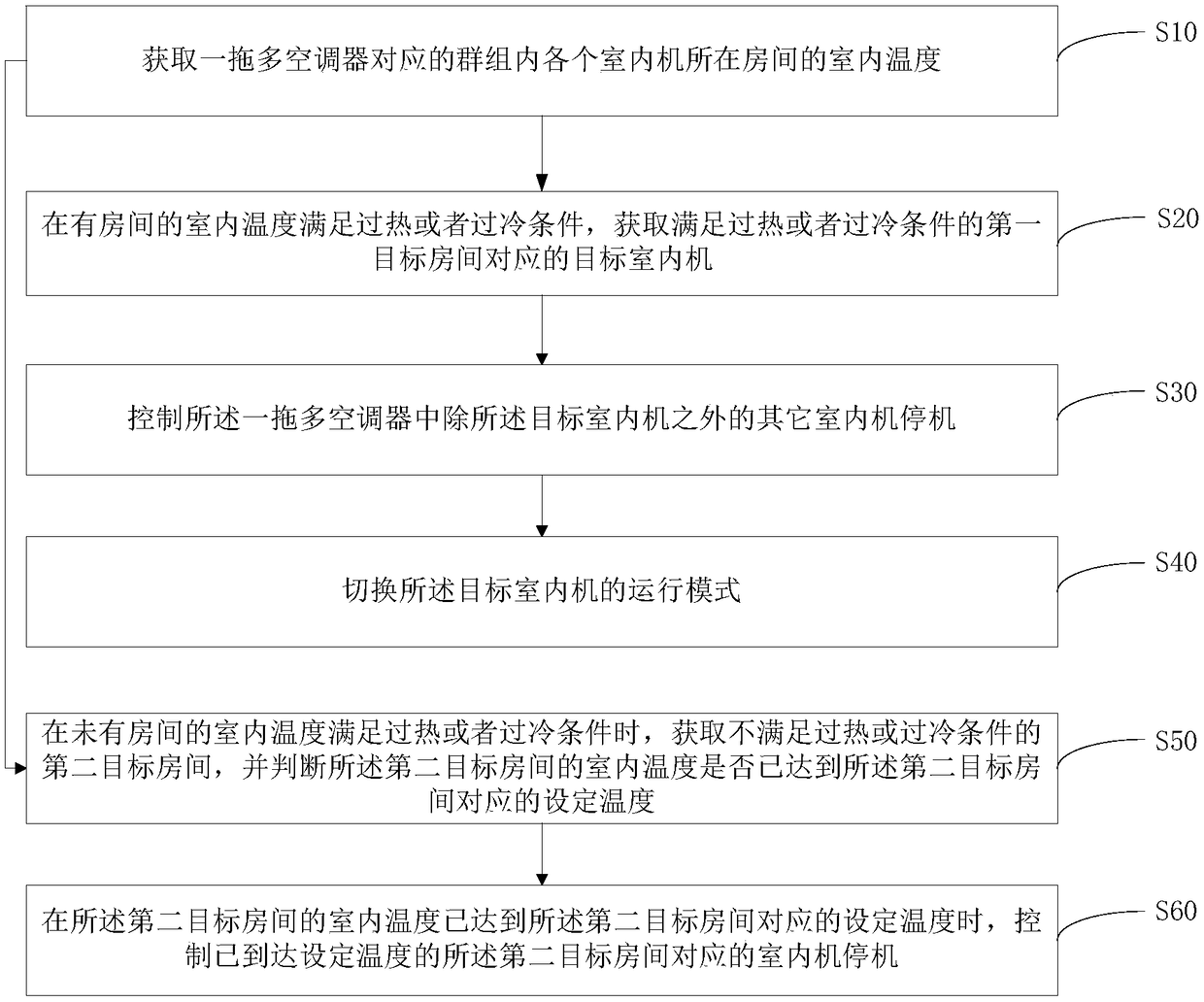
Control terminal, control method and device of multi-split air conditioner and storage medium
ActiveCN109114759AReduce indoor temperatureSolve heating problemsMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsOperation modeEngineering
The invention discloses a control method of a multi-split air conditioner. The control method of the multi-split air conditioner is characterized by comprising the following steps that the indoor temperature of rooms in which indoor units in groups corresponding to the multi-split air conditioner are located is obtained; when the indoor temperature of some rooms meets the overheating or undercooling conditions, a target indoor unit corresponding to a first target room which satisfies the overheating or undercooling conditions is obtained; and other indoor units expect the target indoor unit inthe multi-split air conditioner are controlled to be stopped; and an operation mode of the target indoor unit is switched. The invention further discloses a control device of the multi-split air conditioner, a cloud server, a control terminal and a storage medium. The control method of the multi-split air conditioner avoids the situation that a user is uncomfortable due to the fact that the useris in an undercooling or overheating environment for a long time.
Owner:GD MIDEA AIR-CONDITIONING EQUIP CO LTD +1
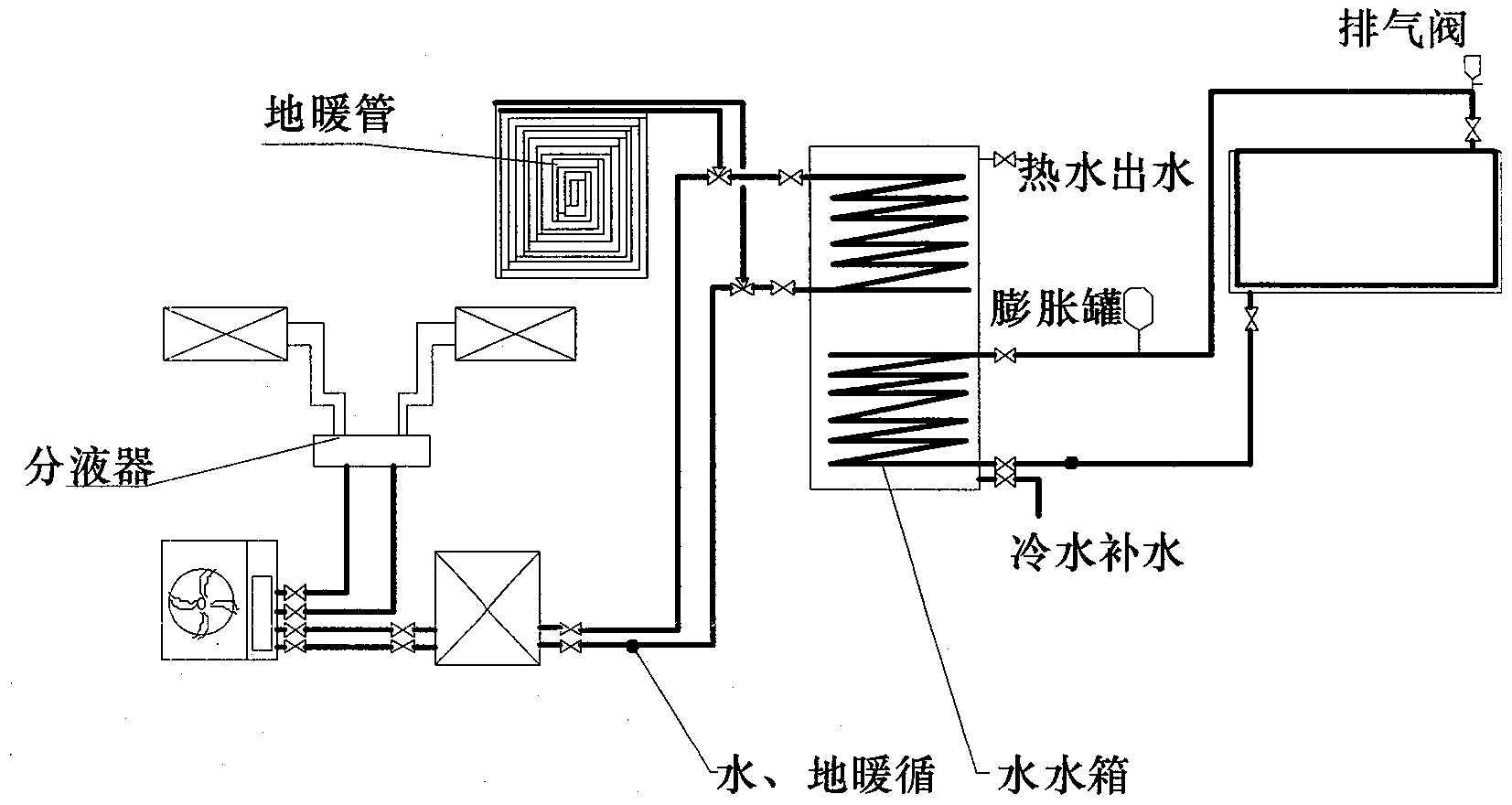
Multi-energy-complementary heating and heat supply system of nearly zero energy consumption building in alpine region
InactiveCN106439993AImprove insulation effectSolve intermittentSolar heating energyLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringHeating season
The invention relates to a multi-energy-complementary heating and heat supply system of a nearly zero energy consumption building in an alpine region. The solar energy is combined with building foundation storage energy storage to achieve heating in winter, and the solar energy is combined with an air source heat pump to achieve domestic hot water supply. The multi-energy-complementary heating and heat supply system comprises a solar thermal collector, a heat storage coil, a heat-preservation foundation heat storage layer, a plate heat exchanger, warm air blowers, the air source heat pump, a hot water tank and the like. In non-heating seasons, the solar thermal collector is used for heating domestic water which is then stored in the water tank, and the air source heat pump is used for auxiliary heating if heat energy is insufficient. In heating seasons, part of hot water flows into the heat storage coil to be stored for standby use or to be used for supplying heat to the interior of a room through the warm air blowers, and the other part of the hot water flows into the plate heat exchanger to heat domestic water. When solar radiation is weak, the hot water flows from the building foundation heat storage layer into the warm air blowers to supply heat to the interior of the room, and the air source heat pump operates in daytime with the high temperature to heat domestic water which is then stored for standby use. According to the multi-energy-complementary heating and heat supply system of the nearly zero energy consumption building in the alpine region, renewable energy sources are utilized for multi-energy complementation to achieve heating and domestic heat supply of the alpine region in winter, and nearly zero energy consumption operation of the building can be achieved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
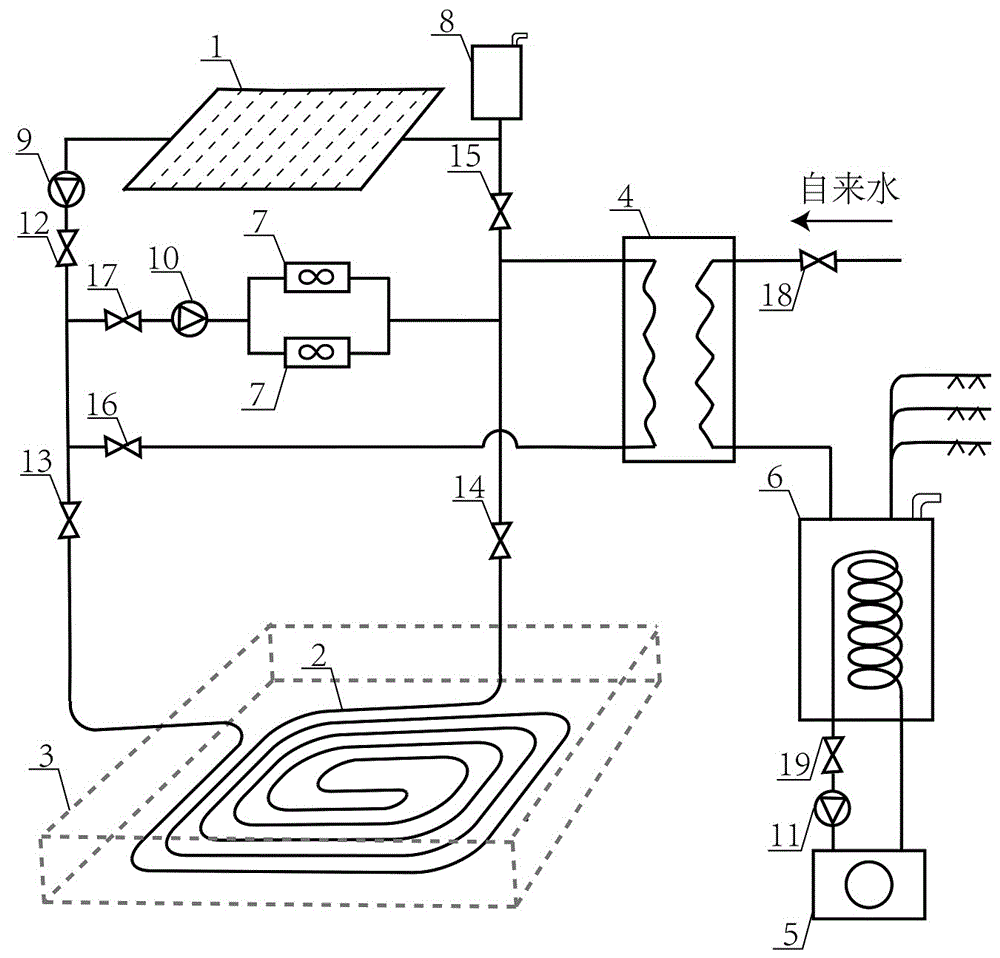
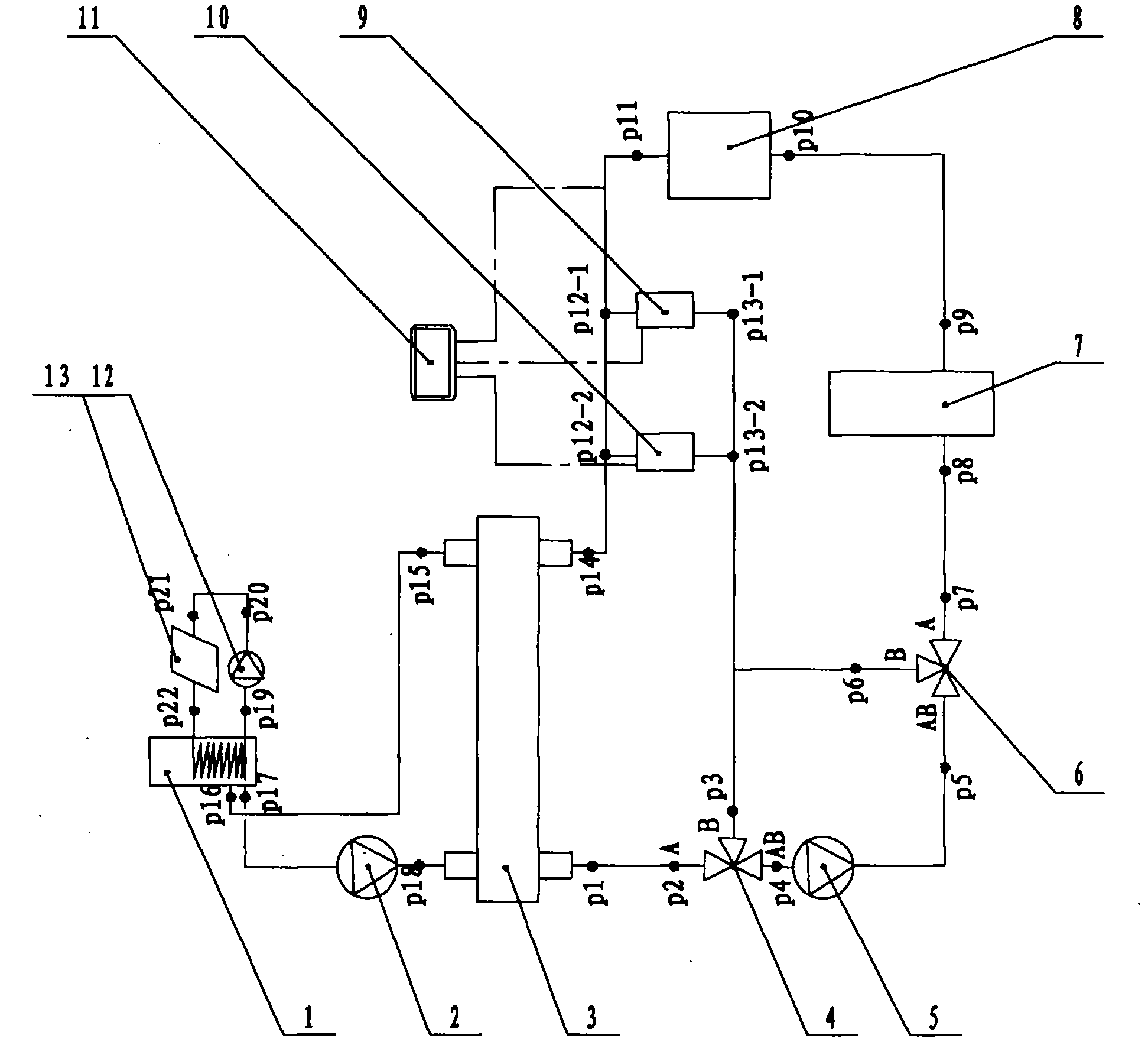
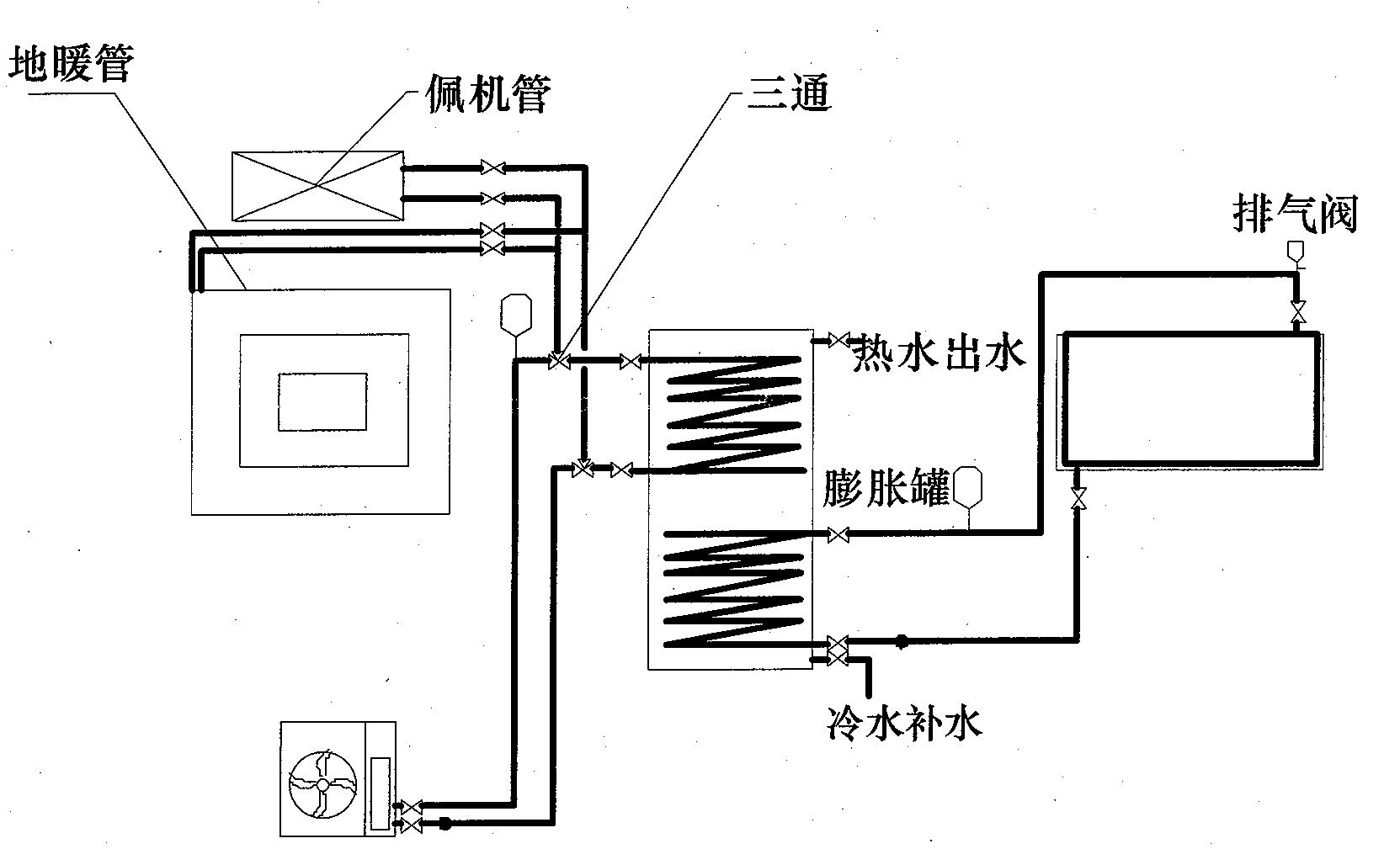
Compound type floor heating air conditioner hot water integration application system
InactiveCN103353186AExcellent heat transfer performanceSmall sizeFluid circulation arrangementRefrigeration safety arrangementEngineeringSolar power
The invention discloses a compound type floor heating air conditioner hot water integration application system, which comprises a hot water tank, a first hot water pump, a plate type heat exchanger, a first power-driven three-way valve, a second hot water pump, a second power-driven three-way valve, an air conditioner water tank, an air energy main engine, a floor heating tail-end, an air-conditioner tail-end, a controller, a solar power circulating pump, and a solar collector, wherein a second interface p15 is connected with an interface p16; an interface p17 is connected with an inlet of the second hot water pump; an outlet of the second hot water pump is connected with a third interface p18; the interface p16 is a circulating inlet of air energy; the interface p17 is a circulating outlet of the air energy; an interface p19 is connected with an interface p20; an interface p21 of the solar collector is connected with an interface p22 of the hot water tank. According to the system, each part is connected through pipelines; free switching of working modes of air energy water heating, air energy heating, air energy refrigeration, solar power water heating, and the like is realized through a special control system; meanwhile, solar heating is realized.
Owner:黄永伟
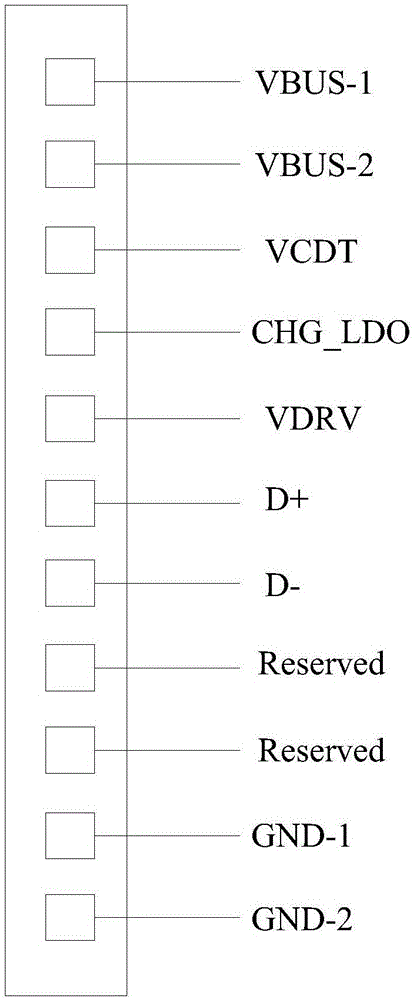
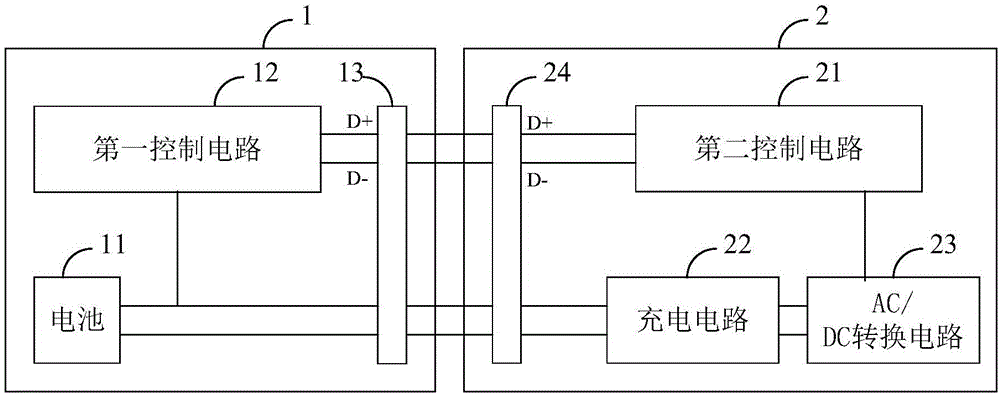
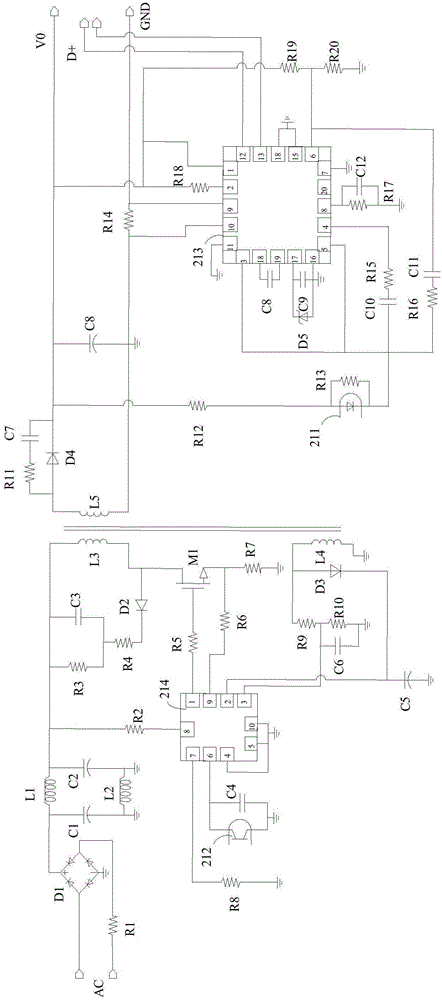
Charging system
InactiveCN105098883ASolve heatingSolve heating problemsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerEngineeringControl circuit
The invention discloses a charging system, which comprises a mobile terminal and a charger, wherein the charger is used for charging a battery of the mobile terminal; the mobile terminal comprises a first control circuit; the charger comprises a second control circuit and a charging circuit; the first control circuit is coupled to the second control circuit; the charging circuit is coupled to the battery; and when the first control circuit and the second control circuit establish handshake communication, the charging circuit charges the battery. In the manner, the charging circuit is arranged on the charger, so that the problem of temperature rise of the mobile terminal can be solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN TINNO WIRELESS TECH
Hybrid energy heating and refrigerating system
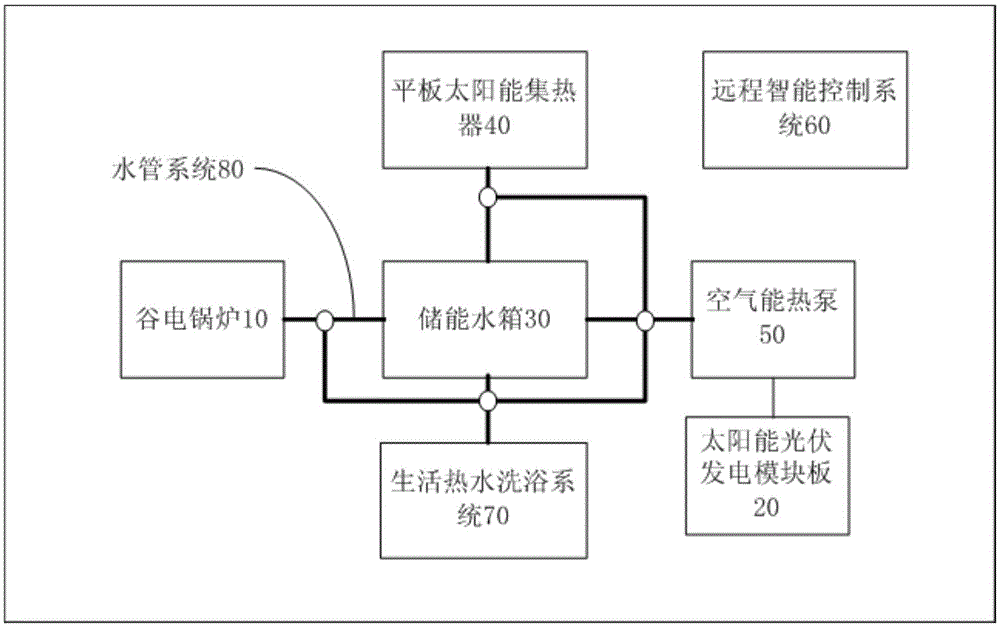
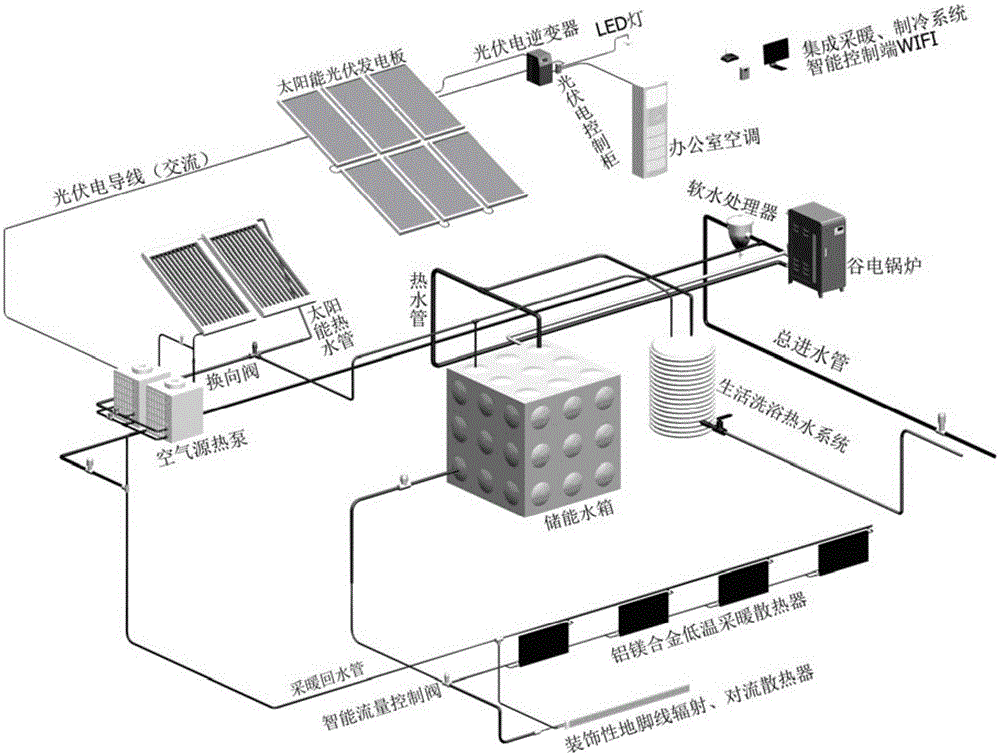
InactiveCN106352387ASolve heating problemsSolve the cooling effectSolar heating energyHeat pumpsThermal energyWater baths
The invention provides a hybrid energy heating and refrigerating system. The hybrid energy heating and refrigerating system comprises a valley electricity boiler, a solar photovoltaic power generation module board, an energy storage water tank, a flat-plate solar collector, an air energy heat pump with a heating function and a refrigerating function, a remote intelligent control system, a domestic hot water bath system and a water pipe system. The remote intelligent control system controls the valley electricity boiler, the solar photovoltaic power generation module board, the energy storage water tank, the flat-plate solar collector, the air energy heat pump, the domestic hot water bath system and the water pipe system. The valley electricity boiler heats water connected to the water pipe system through solar energy at a second time period. The air energy heat pump heats the water connected to the water pipe system through air energy at a third time period. The air energy heat pump adopts heat energy generated by the flat-plate solar collector as a low-temperature heat source at an overlapped time period between the second time period and the third time period.
Owner:SHANGHAI GANGWANG IND
Electronic ballast with PCB edge mounted output transformer/inductor
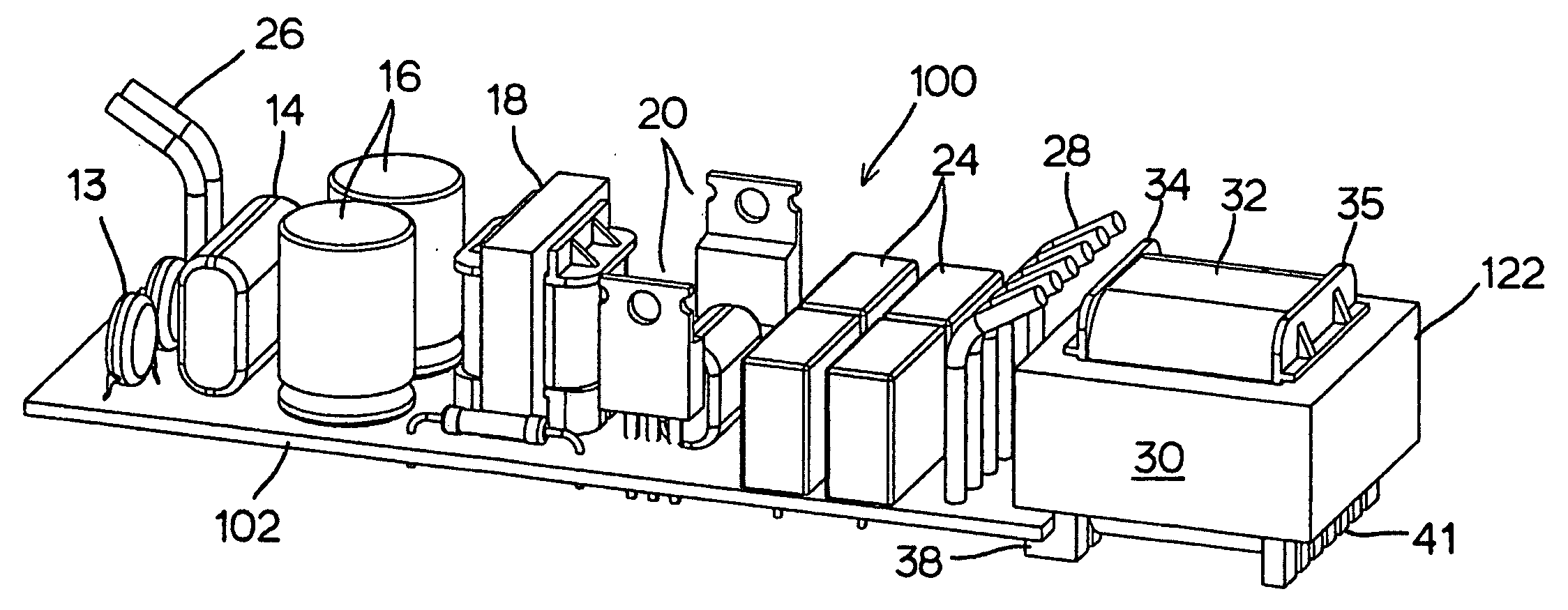
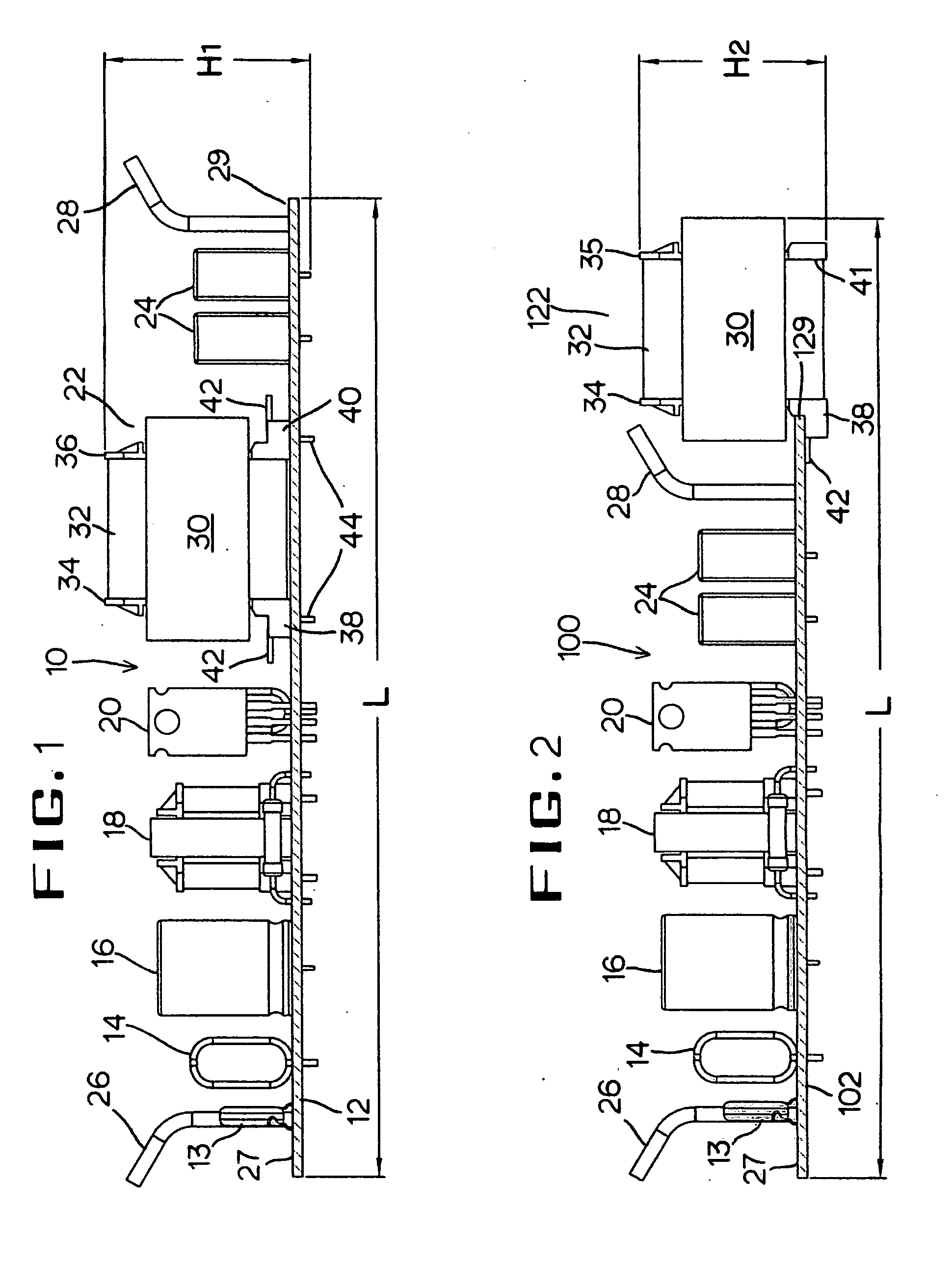
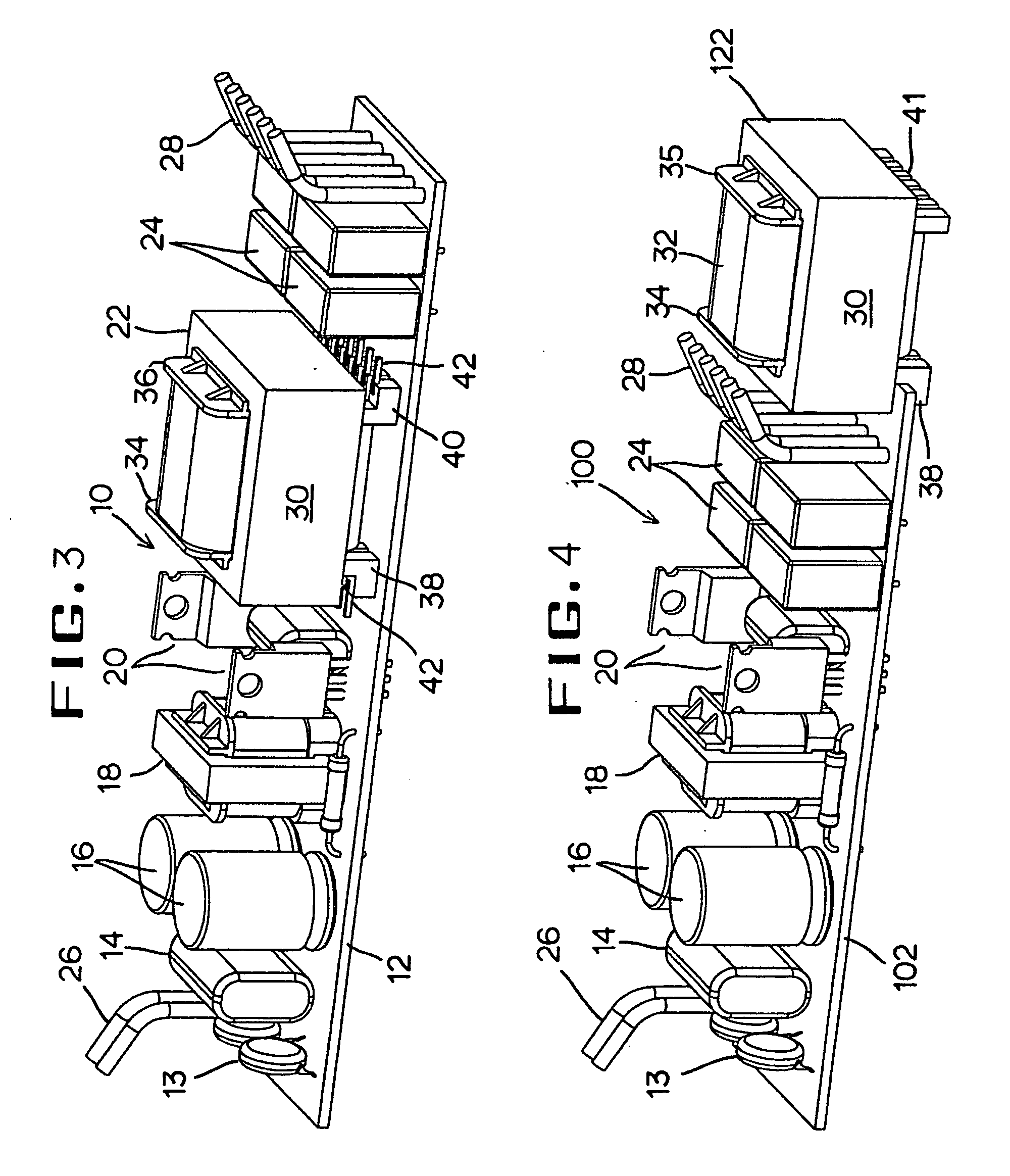
InactiveUS20080169768A1Minimal clearanceSolve heating problemsTransformersPrinted circuit aspectsInductorPrinted circuit board
An output transformer or inductor for electronic ballast which having a number of electronic components including diodes, transistors, resistors, various type of capacitors and different transformers / inductors mounted on a top surface of a PCB (printed circuit board) within a compact housing which envelops the whole ballast assembly. The PCB (printed circuit board) configured to relocate the output-transformer or inductor to an edge of the PCB (printed circuit board) away from the rest of the electronic components. The output-transformer terminal (the transformer's bobbin) has at least two of L-shaped brackets locked to the PCB's (printed circuit board) edge at its top surface. The output-transformer is designed in a cantilevered mounting so that it is able to quickly dissipate its operational heat to the ballast compact case with less interfered by other components. It also saves the PCB (printed circuit board) material cost because it uses shorter PCB.
Owner:YANG KEVIN
Test device for service life of aircraft alternating current generator fuel oil and slide oil radiator
ActiveCN109580209AHeating fastStable temperatureMachine part testingAutomatic controlAutomotive engineering
The invention discloses a test device for the service life of an aircraft alternating current generator fuel oil and slide oil radiator. The test device for the service life of the aircraft alternating current generator fuel oil and slide oil radiator comprises a slide oil side normal temperature system, a slide oil side high temperature system, a fuel oil side normal temperature system, a fuel oil side high temperature system, a refrigeration system, an automatic control system and an environment cabin. According to the technical scheme, a plurality of fuel oil and slide oil radiator bodies can be subjected to cyclic fatigue tests of flow rate, pressure, temperature and ambient temperature; under the test system, high-temperature, high-pressure and large-flow slide oil is introduced intoa product; after test conditions are stable, the automatic control system is used for automatically switching, and low-temperature, low-pressure and small-flow slide oil is introduced into the product, therefore, the impact of oil flow rate, pressure and temperature can be verified to simulate the influence of oil flow rate, pressure, temperature and environment temperature of an aircraft on the service life of the product. The test flow rate, pressure and temperature are automatically detected, adjusted, collected and recorded by the automatic control system for each detection point on a pipeline, and feedback control and data recording are carried out through the collection parameters of each detection point.
Owner:GUIZHOU YONGHONG AVIATION MACHINERY
Combined steam smoke MGGH system and flue gas treatment technology
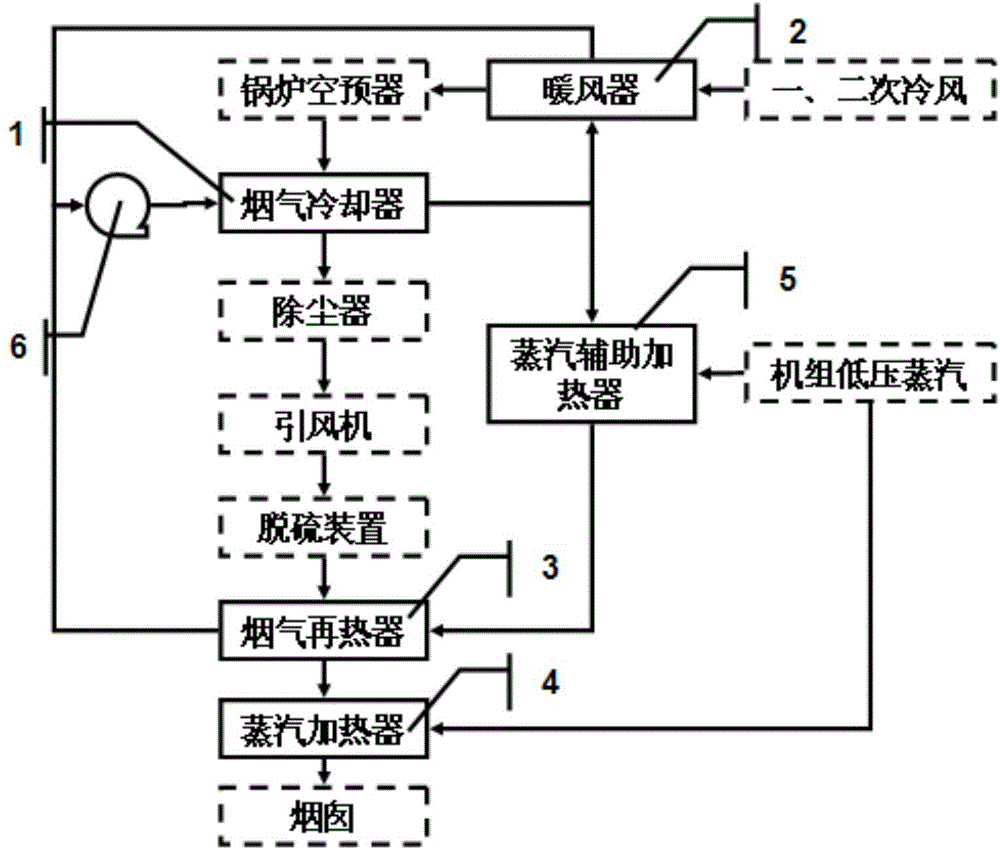
InactiveCN104566424AReduce corrosionReduce foulingLighting and heating apparatusFlue gasProcess engineering
The invention provides a combined steam smoke MGGH system. The combined steam smoke MGGH system comprises a boiler air pre-heating device, wherein the boiler air pre-heating device is connected with a flue gas cooler, the flue gas cooler is connected with a dust remover, the dust remover is connected with an induced draft fan, the induced draft fan is connected with a desulfurization device, the desulfurization device is connected with a flue gas re-heating device, the flue gas re-heating device is connected with a steam heater, and the steam heater is connected with a chimney. The combined steam smoke MGGH system is characterized in that the steam heater is arranged between the flue gas re-heating device and the chimney, a steam auxiliary heater is arranged between the flue gas cooler and the flue gas re-heating device, and the flue gas re-heating device is connected with the flue gas cooler through a variable frequency circulating pump. The combined steam smoke MGGH system and a flue gas treatment technology thereof mainly solve the problem that due to the fact that flue gas temperature is not high enough, an existing MGGH system uses steam to assist in heating, and can significantly reduce steam consumption and engineering cost investment.
Owner:CHONGQING CLP ENERGY SAVING TECH SERVICE
Current control device for mutiple strings of led, and method thereof
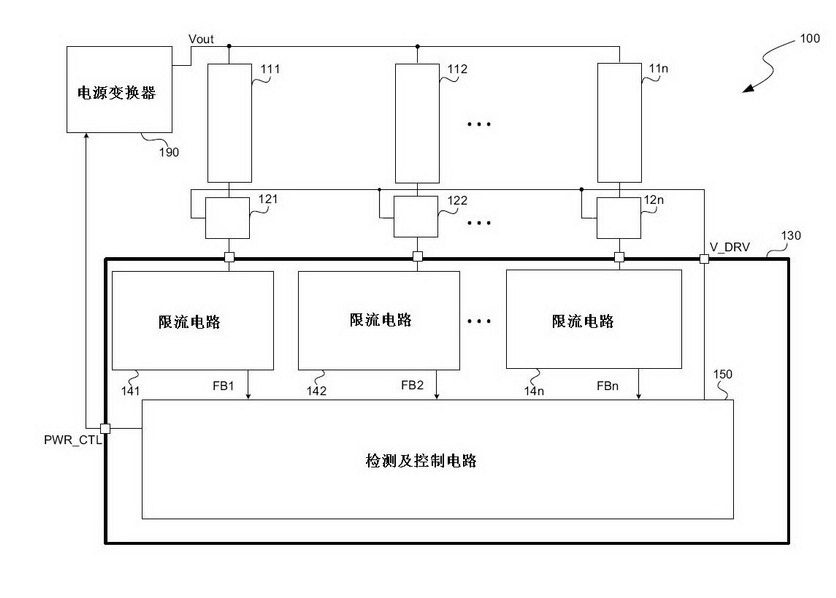
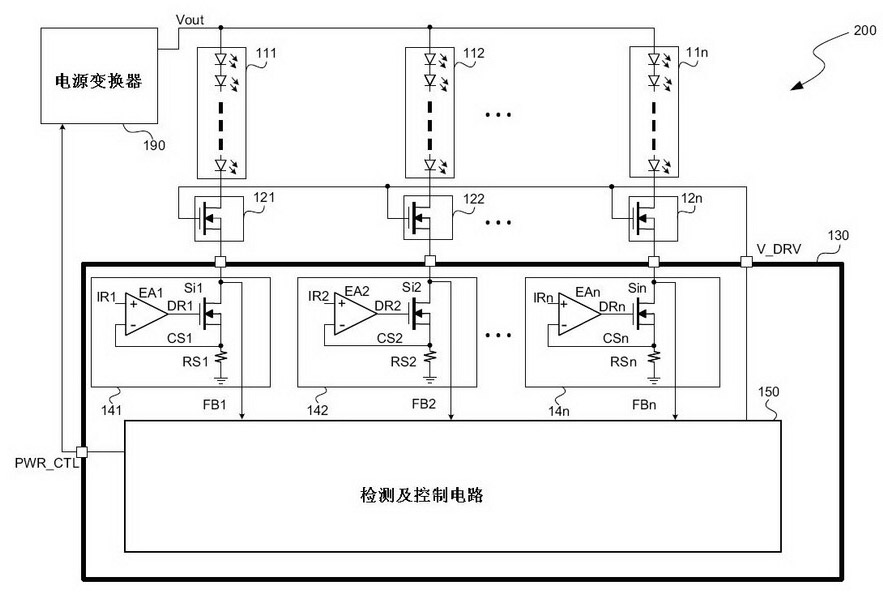
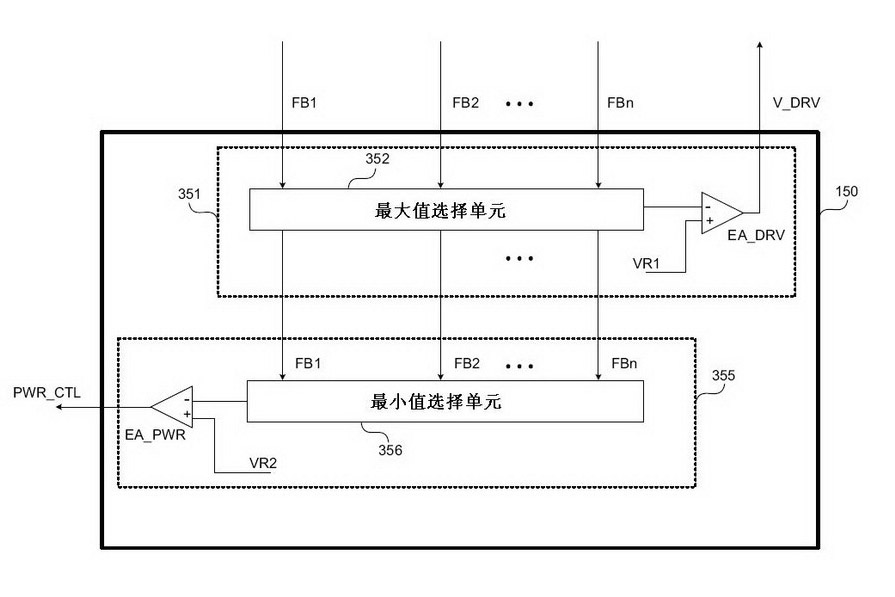
ActiveCN102014542AReduced pin countSolve heating problemsElectrical apparatusPoint-like light sourceCurrent limitingEngineering
The present invention discloses a current control device used for multiple strings of LED, and a method thereof. The device comprises one to a plurality of first current limiting circuits. Each first current limiting circuit is connected with a load in series and is used for controlling the current of the load. The device furthermore comprises a detection and control circuit which outputs at least one driving signal for controlling one to a plurality of second current limiting circuits, wherein each second current limiting circuit is connected with one first current limiting circuit and a corresponding load in series.
Owner:CHENGDU MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
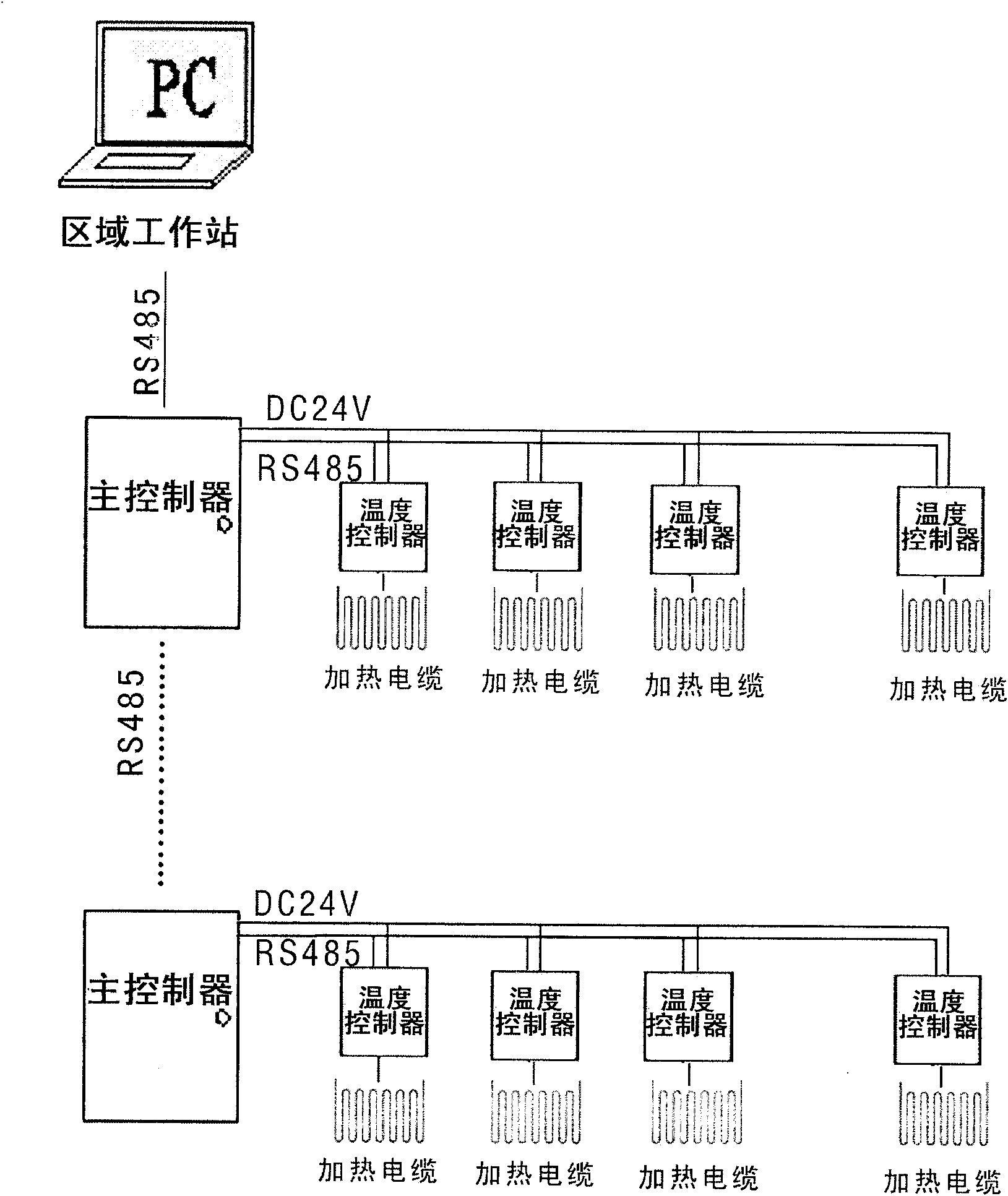
Computer control system for urban electric power central heating and control method thereof
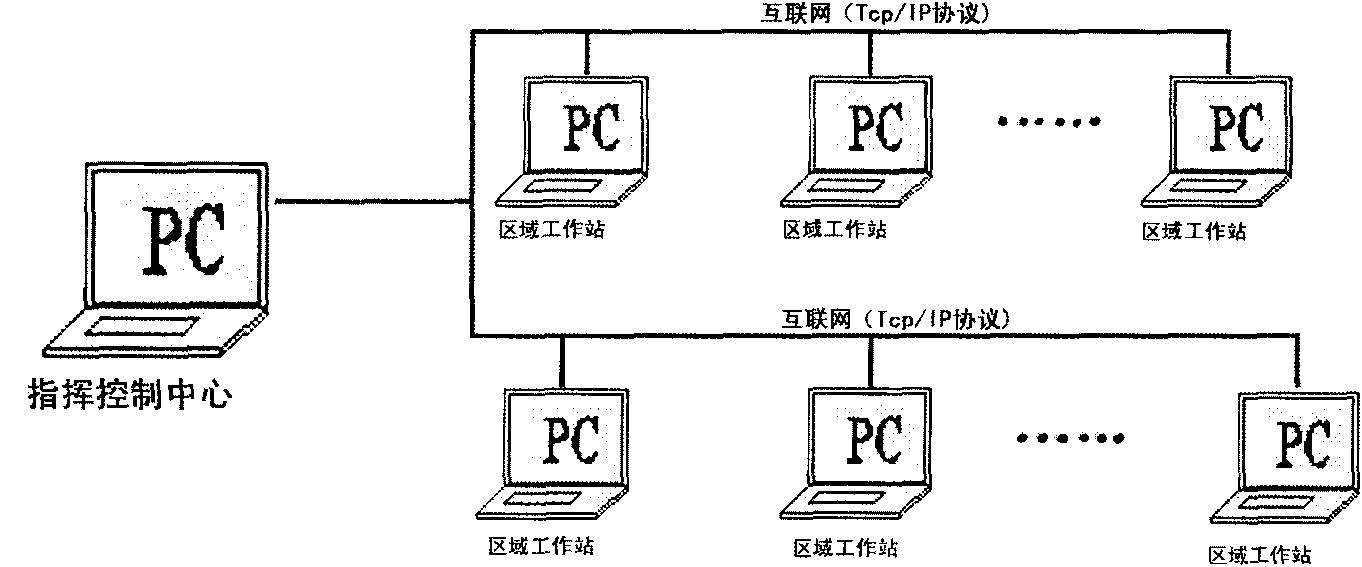
ActiveCN101876824AIncrease profitSimple network structureTransmissionTotal factory controlPower gridThermal energy
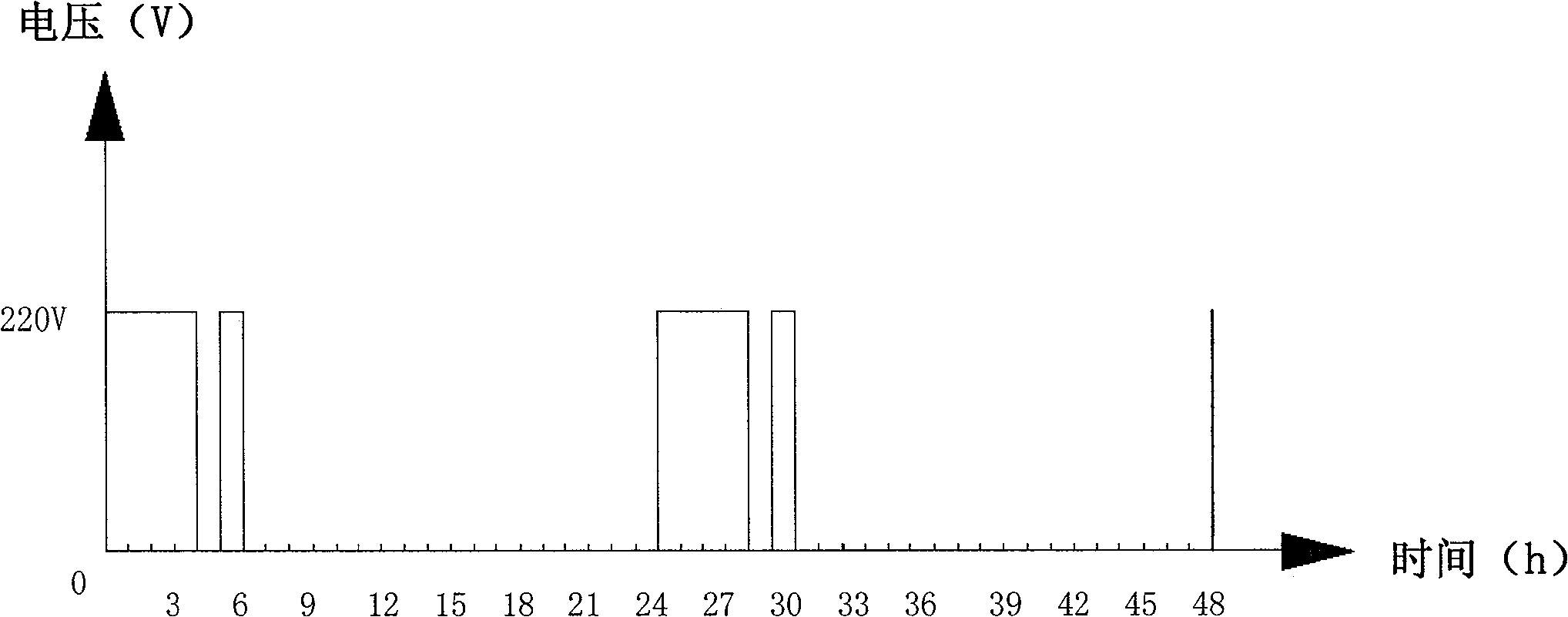
The invention relates to the technical field of urban electric power heating, in particular to a computer control system for urban electric power central heating and a control method thereof. The control system comprises a command control center, a region work station and a main control system; the command control center is connected with the region work station through internet, and the region work station is connected with the main control system of a user terminal. The control method comprises the following steps of: (1) starting a program and verifying; (2) reading data from a service center, and meanwhile starting a data server; and (3) waiting for a control command of a user, if the command of the user exists, executing the command of the user, and uploading an execution result to the data server, if no command of the user exists, executing a routing inspection command and uploading a routing inspection result to the data server. The invention can realize the interaction between electric energy and heat energy and central control of the system, is beneficial to peak load shifting of a power grid, has low electricity consumption cost, realizes the utilization of electricity at the valley period while solving the problem of urban heat supply, and achieves the aim of peak shaving and valley filling.
Owner:辽宁省鑫源温控技术有限公司
Multifunctional high-power polarization preserving fiber isolator
ActiveCN102360131ASmall device sizeStable performanceCoupling light guidesCoatingsPolarizerOptoelectronics
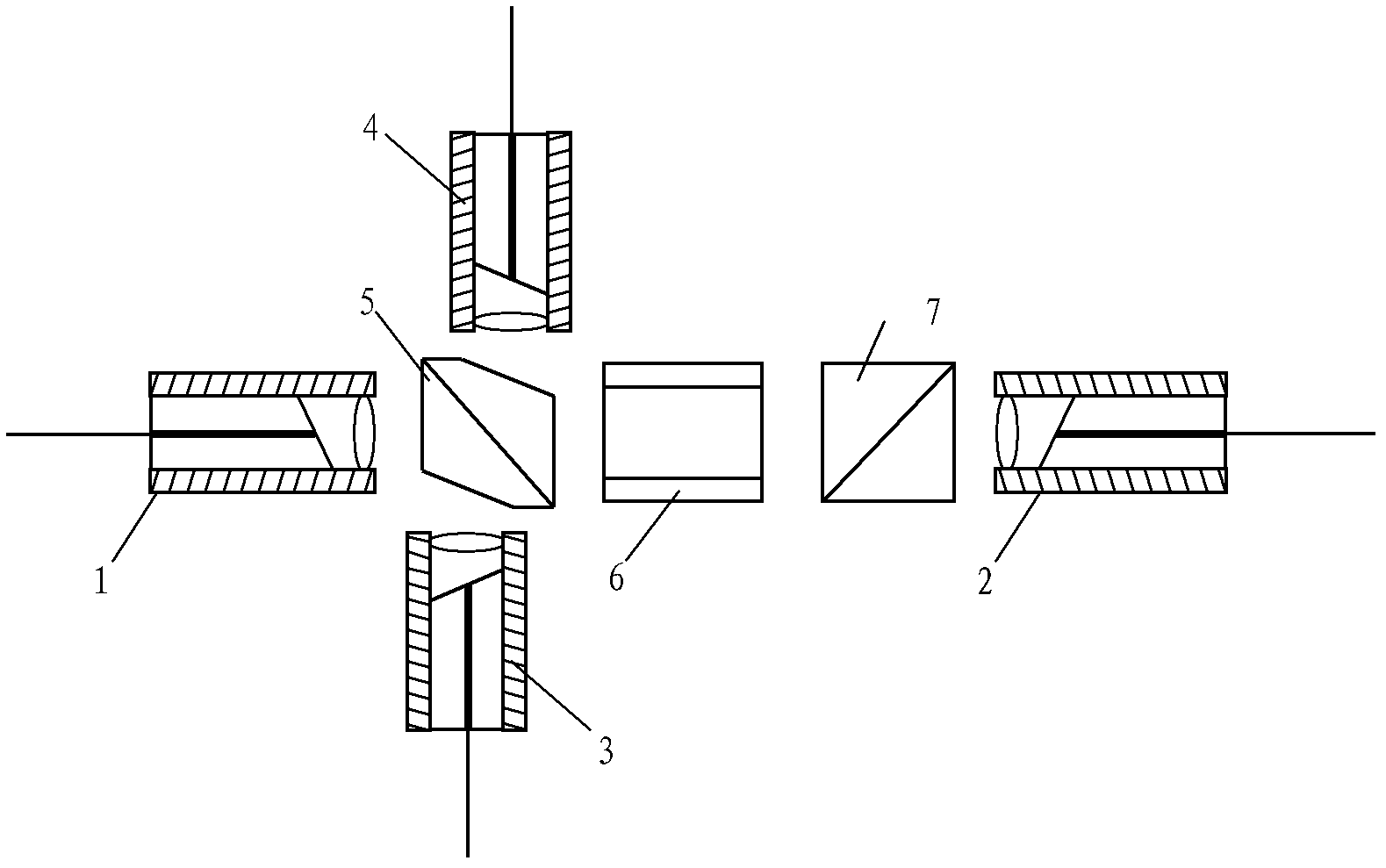
The invention discloses a multifunctional high-power polarization preserving fiber isolator. The multifunctional high-power polarization preserving fiber isolator is structurally characterized in that a first fiber collimation system, a double-window 90-degree beam splitting polarizer, a Faraday optical rotator, a birefringent crystal and a second fiber collimation system are arranged in sequence along the input direction of light, wherein the second fiber collimation system is arranged reversely; the included angle between the optical axis of the double-window 90-degree beam splitting polarizer and the optical axis of the birefringent crystal is 45 degrees; a third fiber collimation system and a fourth fiber collimation system are respectively arranged at double-window emergent parts at the two sides of the double-window 90-degree beam splitting polarizer. The multifunctional high-power polarization preserving fiber isolator not only can handle high-power input and output, but also has the characteristics of good heat stability and multiple functions; and the increase of monitoring ports is beneficial to stability and safety of the system, thereby achieving good practical applicability.
Owner:NANJING ZHONGKE SHENGUANG TECH
Electric automobile heat management system
PendingCN107399221AImprove comfortImprove securityAir-treating devicesVehicle heating/cooling devicesBusiness efficiencyHeat management
The invention discloses an electric automobile heat management system. The electric automobile heat management system comprises a compressor, an expansion valve, an automobile exterior heat exchanger and an HVAC assembly and further comprises an automobile interior evaporator and an automobile interior condenser which are arranged in the HVAC assembly. An automobile interior refrigeration loop, an automobile interior heating loop, an automobile interior defrosting / demisting loop and an automobile exterior heat exchanger defrosting loop are jointly composed of the compressor, the expansion valve, the automobile exterior heat exchanger, the automobile interior evaporator and the automobile interior condenser. By adoption of the provided electric automobile heat management system, the structure is novel and compact, the electric automobile heat management system is easy to achieve, the problem about heating under the low temperature work condition is solved, and the electric automobile air conditioner energy efficiency ratio and the electric automobile endurance mileage are increased; the automobile interior heating loop can be rapidly switched to the automobile exterior heat exchanger defrosting loop, the automobile exterior heat exchanger generates heat, automobile exterior heat exchanger defrosting is rapidly achieved, heat dissipated by large-power electric appliances can be utilized for heating for the automobile interior, the heating capability is improved, and energy is saved as well.
Owner:重庆世纪精信汽车热能科技有限公司
Heat pump system and control method thereof
ActiveCN102840716ASolve heating problemsSolve the cooling effectHeat pumpsEfficient regulation technologiesFour-way valveEngineering
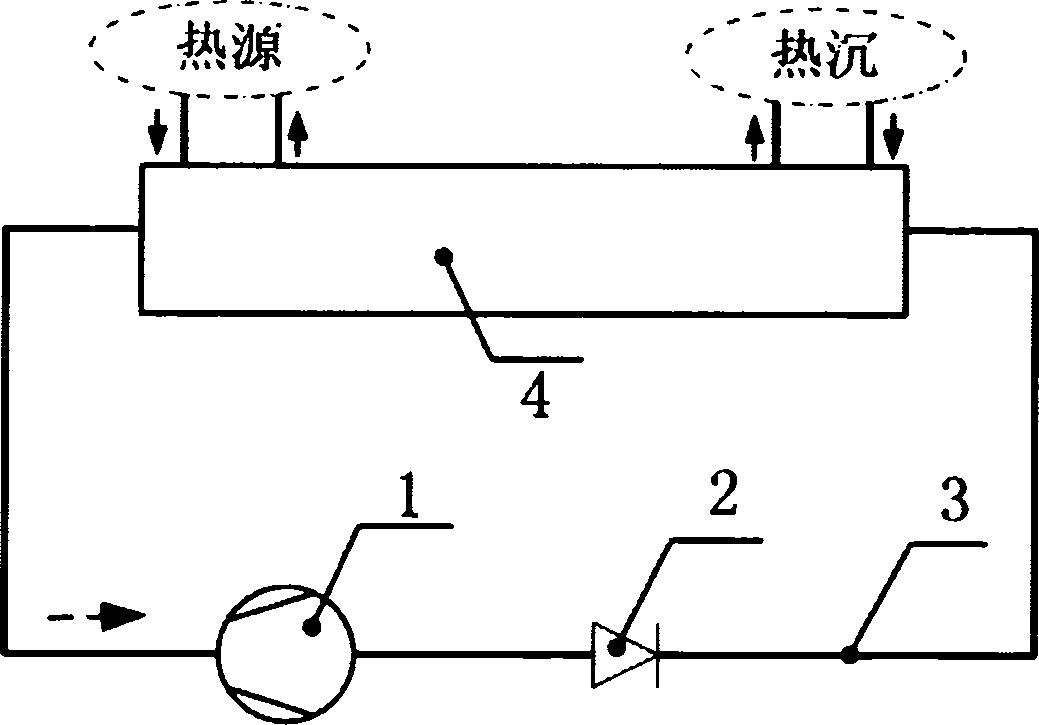
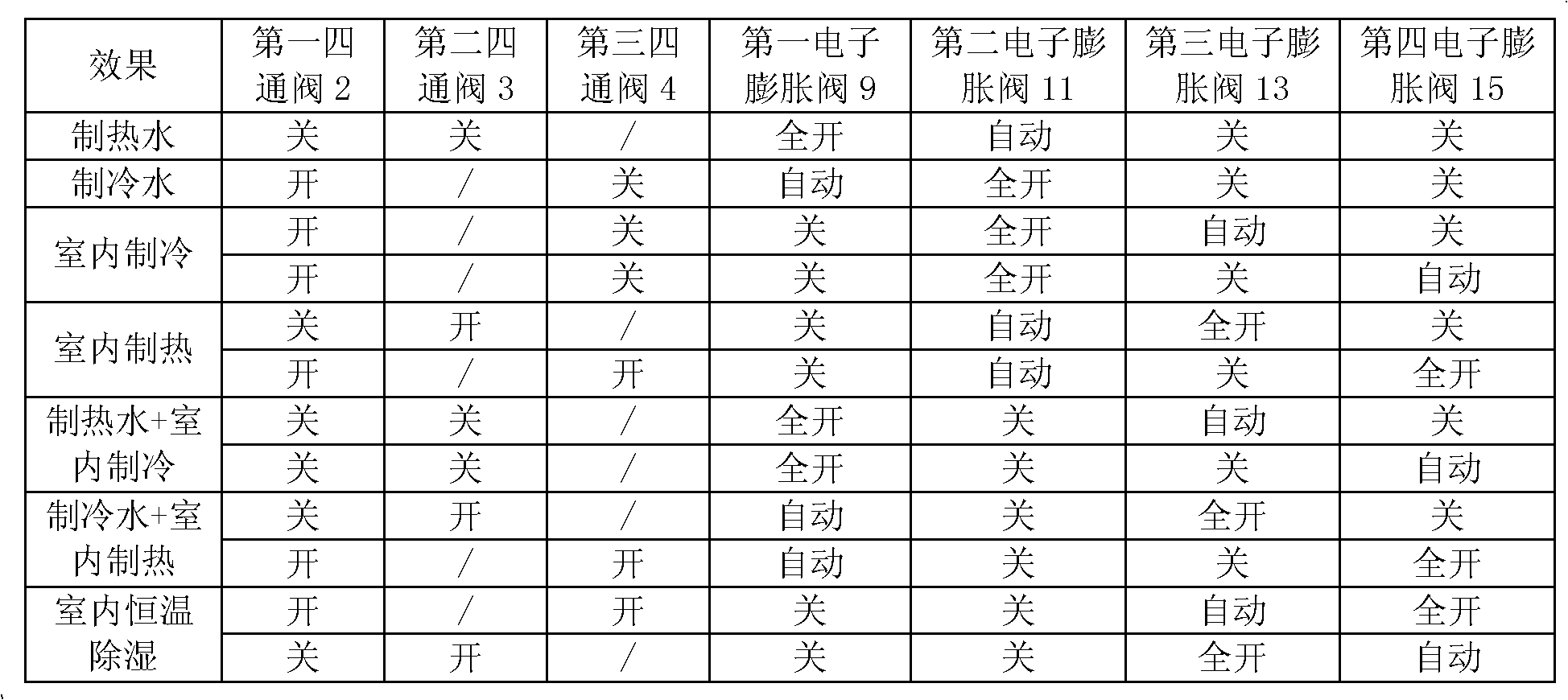
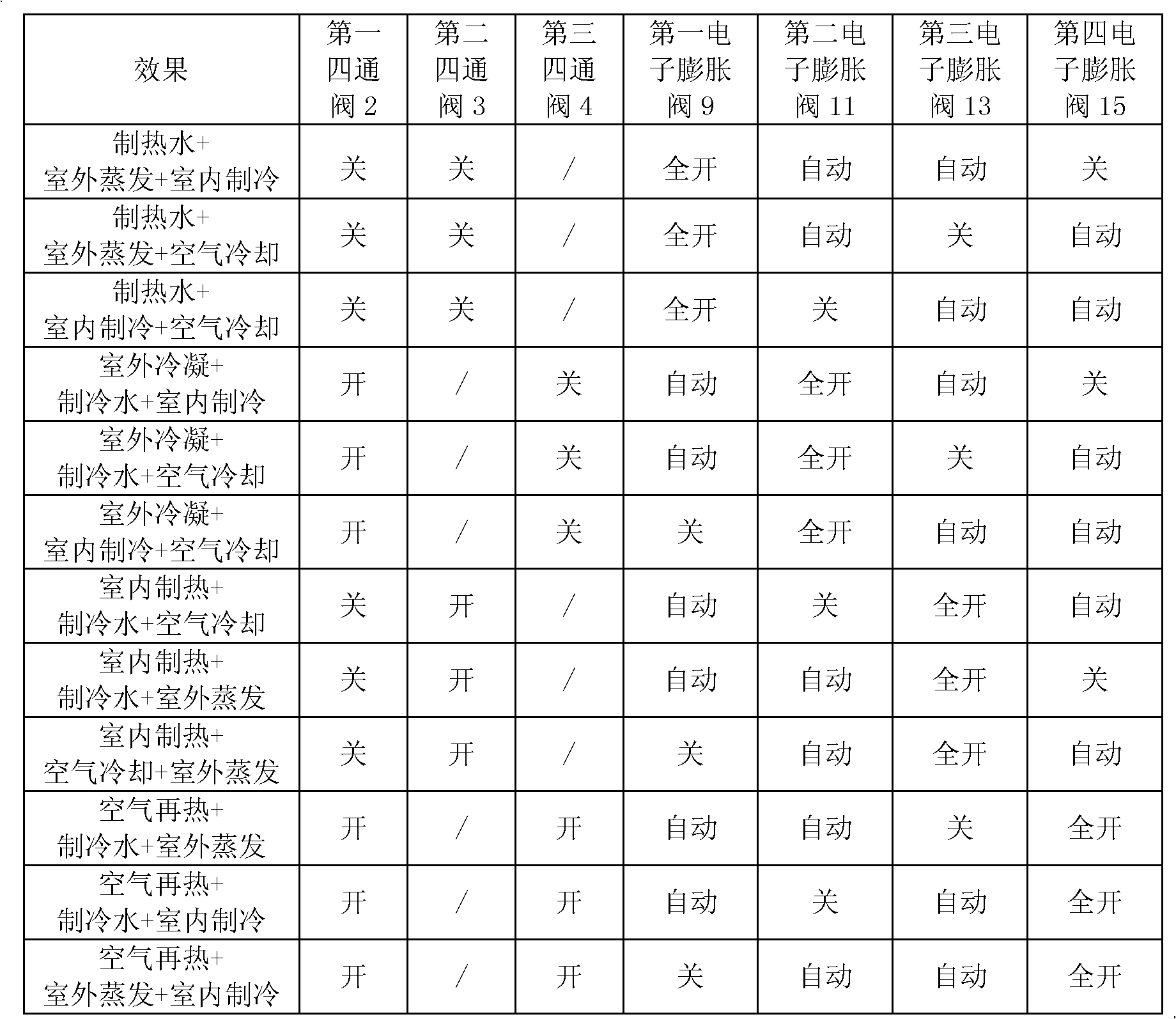
The invention discloses a heat pump system and a control method thereof. The heat pump system comprises a compressor (1), a first four-way valve (2), a second four-way valve (3), a third four-way valve (4), a first heat exchanger (5), a second heat exchanger (6), a third heat exchanger (7), a fourth heat exchanger (8), a first throttling assembly, a second throttling assembly, a third throttling assembly and a fourth throttling assembly. According to the heat pump system and the control method of the heat pump system provided by the invention, the heating and refrigerating effects of the heat pump system are better.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Method for heating by using waste heat of gas stove and gas stove with heating function
InactiveCN103836709ASolve heating problemsEffective absorptionDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusProcess engineeringCooking process
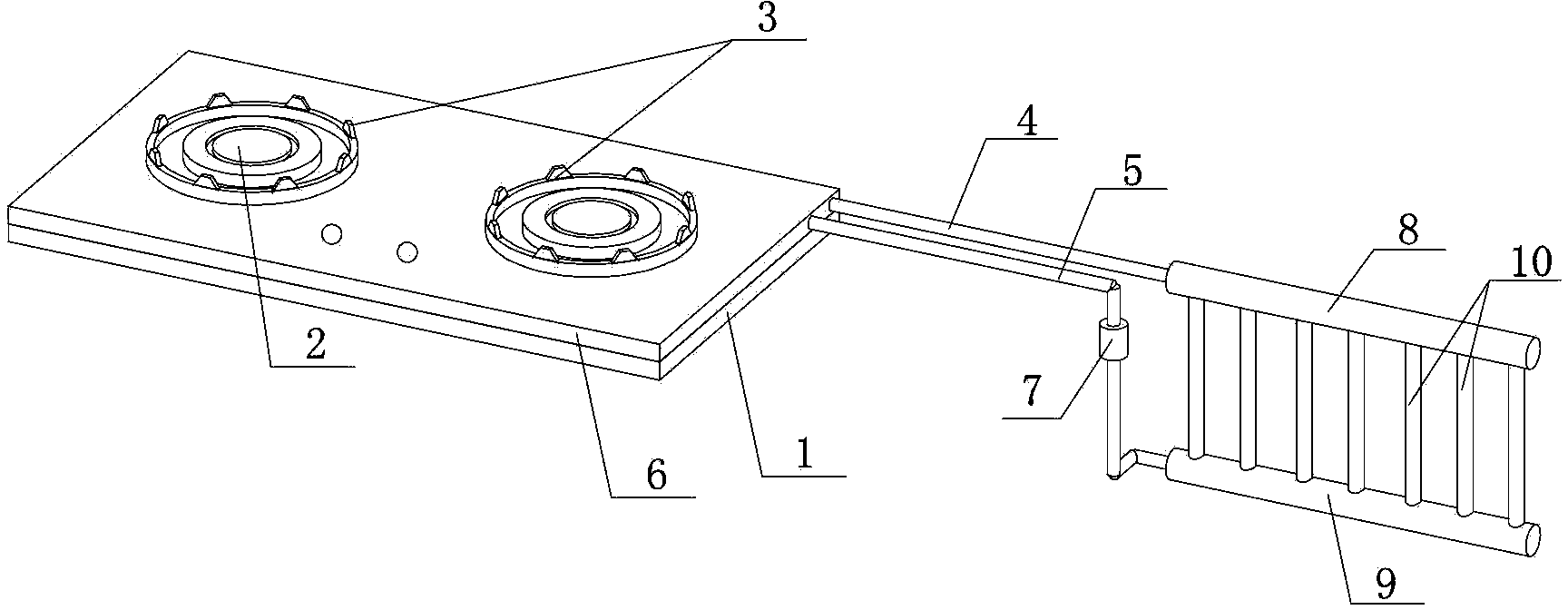
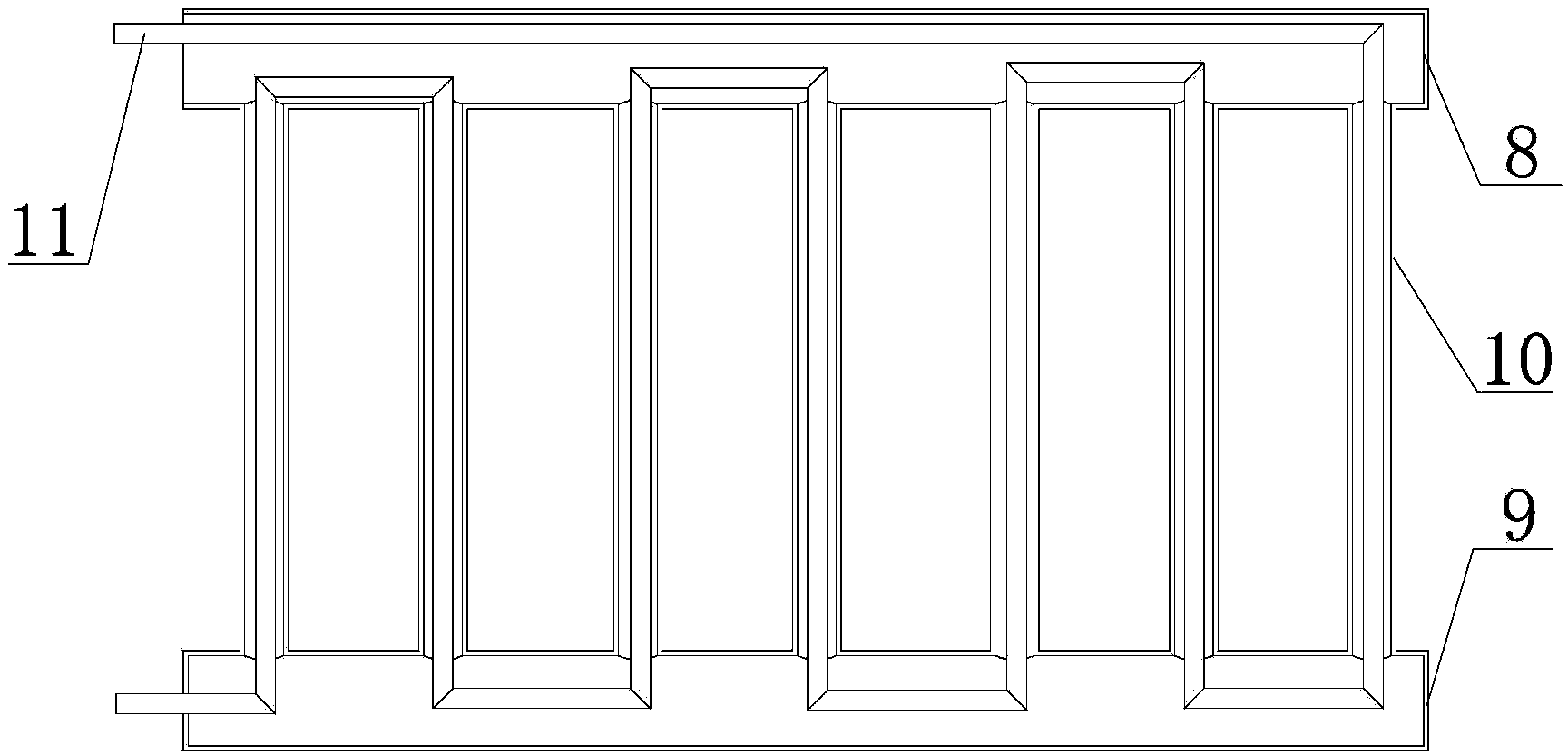
The invention discloses a method for heating by using waste heat of a gas stove and the gas stove with a heating function. When the gas stove is used for cooking, flames emit heat to the periphery when heating a pot body, a heat absorption device is arranged on a cooking bench of the gas stove, can absorb the heat emitted by the flames, and can transmit the heat to a cooler through heat conduction media so as to heat heat storage media in the cooler, the heat storage media slowly release out the heat, heat exchange is carried out on the heat and indoor air, and the indoor temperature is improved. According to the method for heating by using the waste heat of the gas stove and the gas stove with the heating function, the waste heat released by the flames of the gas stove in the cooking process can be effectively collected, and is stored and released out through the energy storage media, the heating function is achieved, and the method and the gas stove have the advantages of being environmentally friendly and simple in structure.
Owner:董金奎
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com