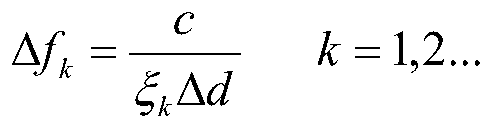A new wide temperature range temperature measurement method for saw RFID tags
A wide temperature and tag technology, applied in the field of measurement, can solve the problems of phase 2π ambiguity, reduce the coding capacity of SAW tags, limit the temperature measurement range of SAW tags, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing the temperature measurement range and improving the coding capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments. The following examples will help those skilled in the art to further understand the present invention, but do not limit the present invention in any form. It should be noted that those skilled in the art can make several changes and improvements without departing from the concept of the present invention. These all belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
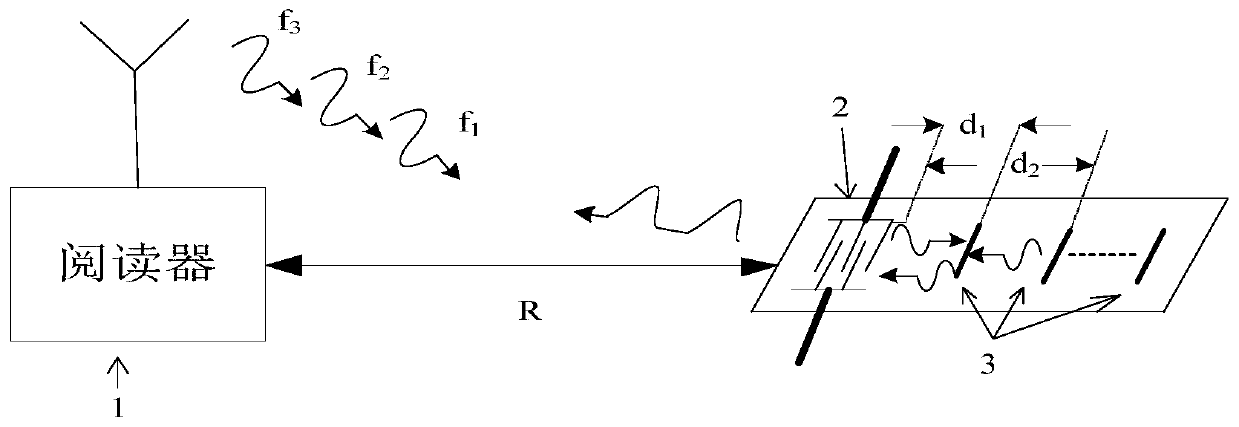
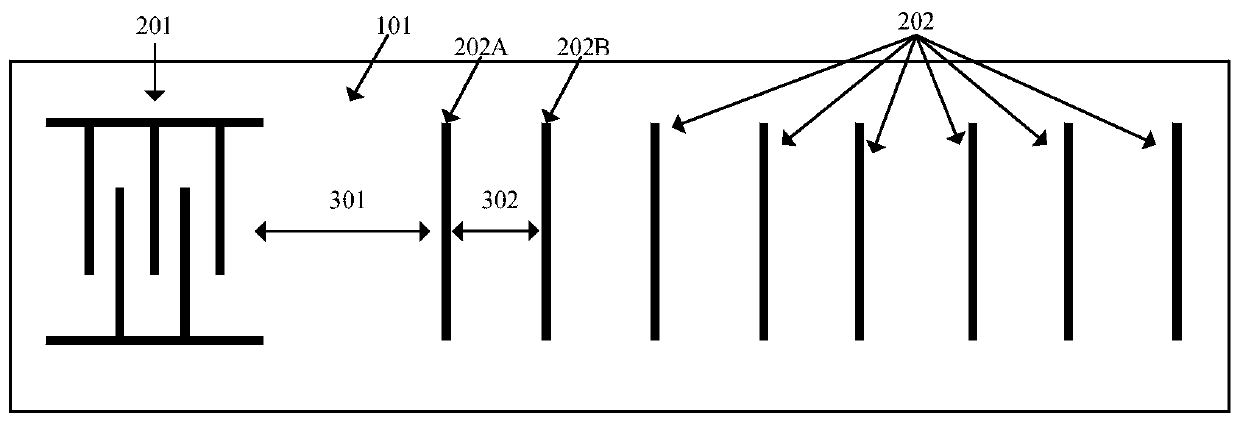
[0024] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, a novel wide temperature range temperature measurement method of a SAW RFID tag provided by the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0025] Step 1. Allocate the frequency difference within the maximum frequency interval of the query signal transmitted by the reader, and select the frequency differences of multiple query signals satisfying the construction of the congruence equation for phase difference anti-ambiguity.
[0026] When the read...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com