Nutrition reinforcement method of improving artemia growth and increasing EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) content
A technology of nutritional enhancement and artemia, which is applied in the field of aquaculture and biological research, can solve the problems of unbalanced content changes, etc., and achieve the effect of improving utilization rate and growth quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Artemia sp. used in the present invention is hatched from Artemia sp. eggs in the salt field of Bohai Bay. The Dicrateria zhanjiangensis, Platymonas subcordiformis and Chlorella pyenoidosa used in the experiment were obtained from Jiangsu Marine Fisheries Research Institute.
[0021] The culture medium of Chrysoflagellate Zhanjiang, Phytophthora subcordiformis and Chlorella refer to the literature "Biological Feed Cultivation" (Chen Mingyao. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 1995: 27-37), using natural light, water temperature 24 ℃ - 26°C. After 4 days of culture, the density reached 300×10 4 cells / mL, 15×10 4 cells / mL and 500×10 4 cells / mL, as microalgae bait.
[0022] Artemia hatching
[0023] Add seawater with a salinity of 30‰ to the 100L hatch tank. Accurately weigh 10 g of Artemia eggs and put them into the hatching bucket to inflate for hatching. The hatching temperature is 28°C.
[0024] Artemia inoculation
[0025] After the Artemia hatched, isolate an...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2 Body growth of artemia larvae in different development stages
[0034] The developmental stages of Artemia are mostly represented by instar. Every moult before sexual maturity is the first instar, and the digestive tract of hatched Artemia does not have physiological functions until the third instar and begins to eat. At 6 time points of artemia development, including early first instar (24h of culture), late first instar (34h of culture), early third instar (54h of culture), late third instar (72h of culture), 96h of culture, and 120h of culture, the average Body length. The results showed that the body length of the larvae increased rapidly in the first 3 days of culture, from 0.432mm to 0.808mm, with an average daily growth rate of 0.125mm; after 4 days, the growth rate decreased and reached the plateau of body length. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0035] Table 1 Body length of Artemia larvae at different stages
[0036]
Embodiment 3
[0037] Embodiment 3 microalgae nutrient enrichment is on the influence of artemia body length
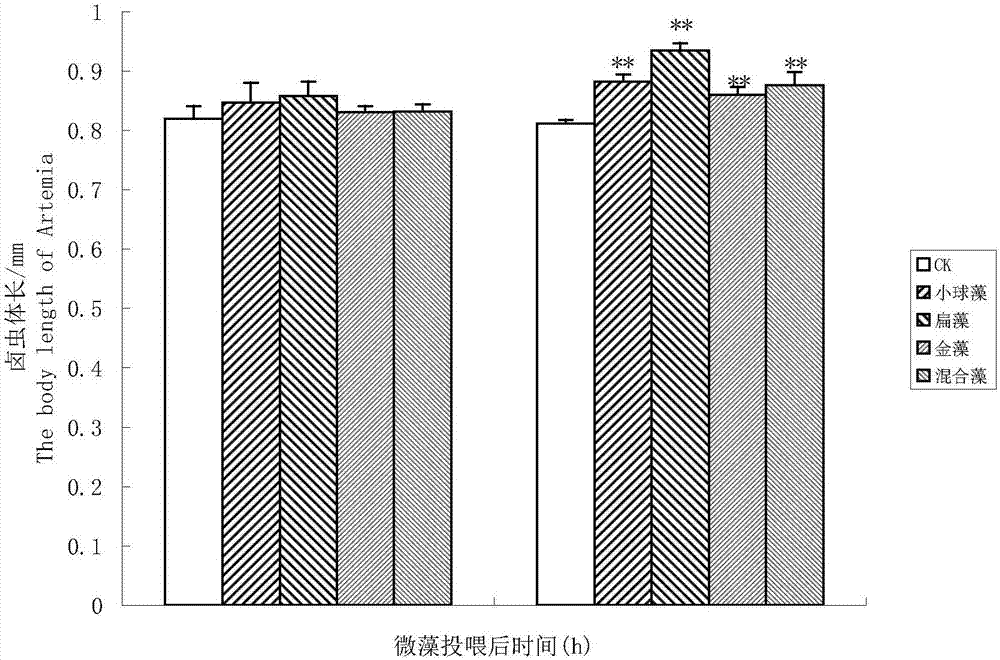
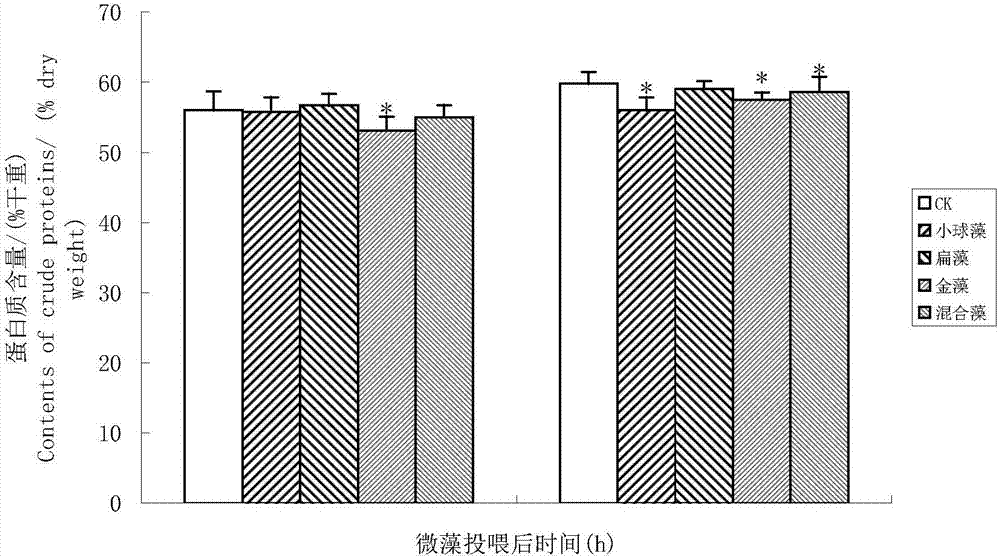
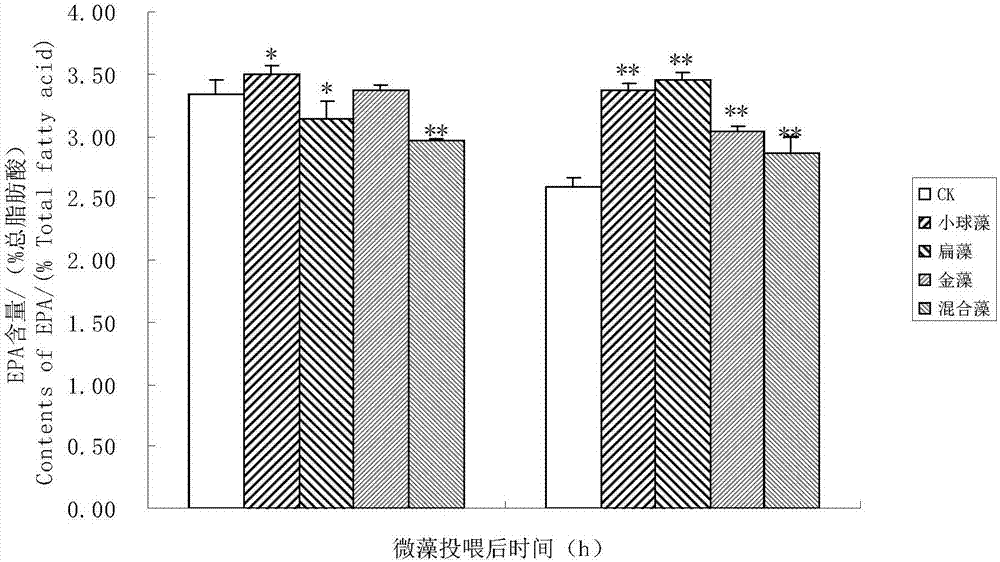
[0038] Artemia hatched and developed to the 3rd instar, and Artemia was fed intensively with Chrysoflagellate zhanjiang, Flatweed and Chlorella for 24h and 48h. Keep the bait density at 3-4×10 4 , 0.5×10 4 and 8-10×10 4 cells / mL. After intensive feeding for 24 hours, the body length of Artemia larvae was slightly increased compared with the control group (no feeding group), but there was no significant difference (p>0.05); after 48 hours of feeding, the growth rate of Artemia larvae was significantly accelerated, and the body The body length of each feeding group was significantly greater than that of the control group (pfigure 1 shown. The results suggested that the intensive feeding of flat algae had the best effect on promoting the growth of Artemia larvae.
[0039]Table 2 Effect of microalgae nutrient enrichment on Artemia body length
[0040]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com