Method for accelerating formation of biofilm in waste water under low temperature condition
A low-temperature condition and biofilm technology, which is applied in sustainable biological treatment, chemical instruments and methods, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of long period of biofilm formation in wastewater, accelerated biofilm formation in wastewater, and poor firmness. High-level problems, to achieve the effect of shortening the film-hanging time, strong impact load resistance, and short film-hanging time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] A method for accelerating wastewater biofilm formation under low temperature conditions, comprising the steps of:
[0041] Vacuum freeze-dried Sphingomonas rubrum recovery culture: Use 75% alcohol absorbent cotton to sterilize the outer surface of the ampoule containing the freeze-dried bacteria and heat it with a flame, then knock off the top of the ampoule with a file or tweezers; then aseptic Take 0.5mL of liquid culture medium with a straw, drop it into the ampoule bottle whose top has been broken and shake it gently, so that the freeze-dried bacteria dissolve and form a suspension, then absorb all the bacterial suspension, and transplant it into a test tube containing 5mL of medium to keep the temperature For cultivation, the conditions for constant temperature cultivation are: tryptone soybean broth medium with a pH of 7.4, cultured on a shaker at a rotation speed of 120 r / min and at 30° C. for 36 hours.
[0042] (1) Sphingomonas rubrum is transferred to an Erlenm...
Embodiment 2
[0049] A method for accelerating wastewater biofilm formation under low temperature conditions, comprising the steps of:
[0050] Vacuum freeze-dried Sphingomonas rubrum recovery culture: Use 75% alcohol absorbent cotton to sterilize the outer surface of the ampoule containing the freeze-dried bacteria and heat it with a flame, then knock off the top of the ampoule with a file or tweezers; then aseptic Pick up 0.3mL of liquid culture medium with a straw, drop it into the ampoule bottle whose top has been broken and shake it gently, so that the freeze-dried bacteria dissolve and form a suspension. For cultivation, the conditions for constant temperature cultivation are: tryptone soybean broth medium with a pH of 7.4, cultured on a shaker at 150 r / min and 28° C. for 30 h.
[0051] (1) Sphingomonas rubrum is transferred to an Erlenmeyer flask containing sterilized liquid medium for expanded culture. The conditions for expanded culture are: tryptone soybean broth medium with a pH ...
Embodiment 3
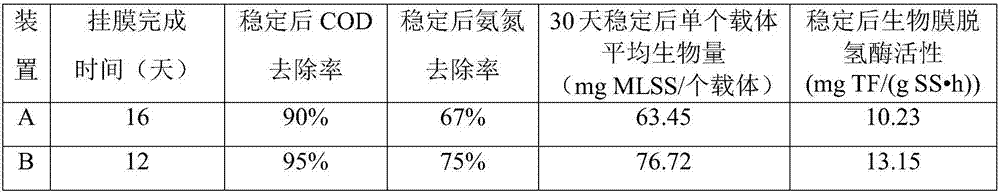
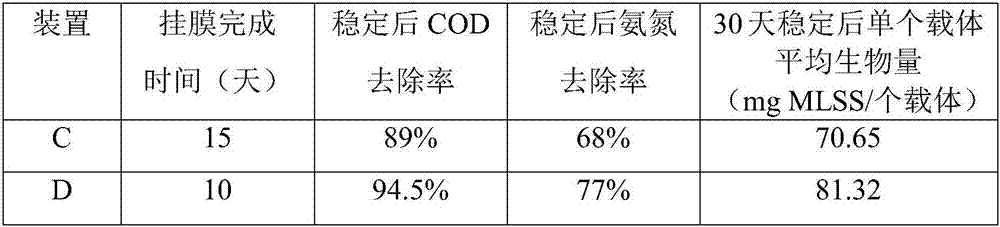
[0059] In this case, by adding low-temperature-resistant immobilized Sphingomonas rubrum pellets to the MBBR reactor at a low temperature of 5°C, we compared the addition and non-dosing of low-temperature-resistant immobilized Sphingomonas rubrum Differences in MBBR reactor film hanging time, COD, ammonia nitrogen removal rate, and biofilm extracellular polymeric material (EPS) of pellets. Wherein the recovery culture of Sphingomonas rubrum, the expanded culture and the preparation of low temperature-resistant immobilized Sphingomonas rubrum pellets are basically the same as those in Example 2.
[0060] Table 1 shows the comparison of the film formation time, COD, ammonia nitrogen removal rate, carrier biomass, and biofilm dehydrogenase in the two sets of devices. The two sets of devices were co-cultured for 35 days from the addition of the suspension filler. Among them, device A did not add low-temperature-resistant immobilized Sphingomonas rubrum pellets at the initial stag...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap