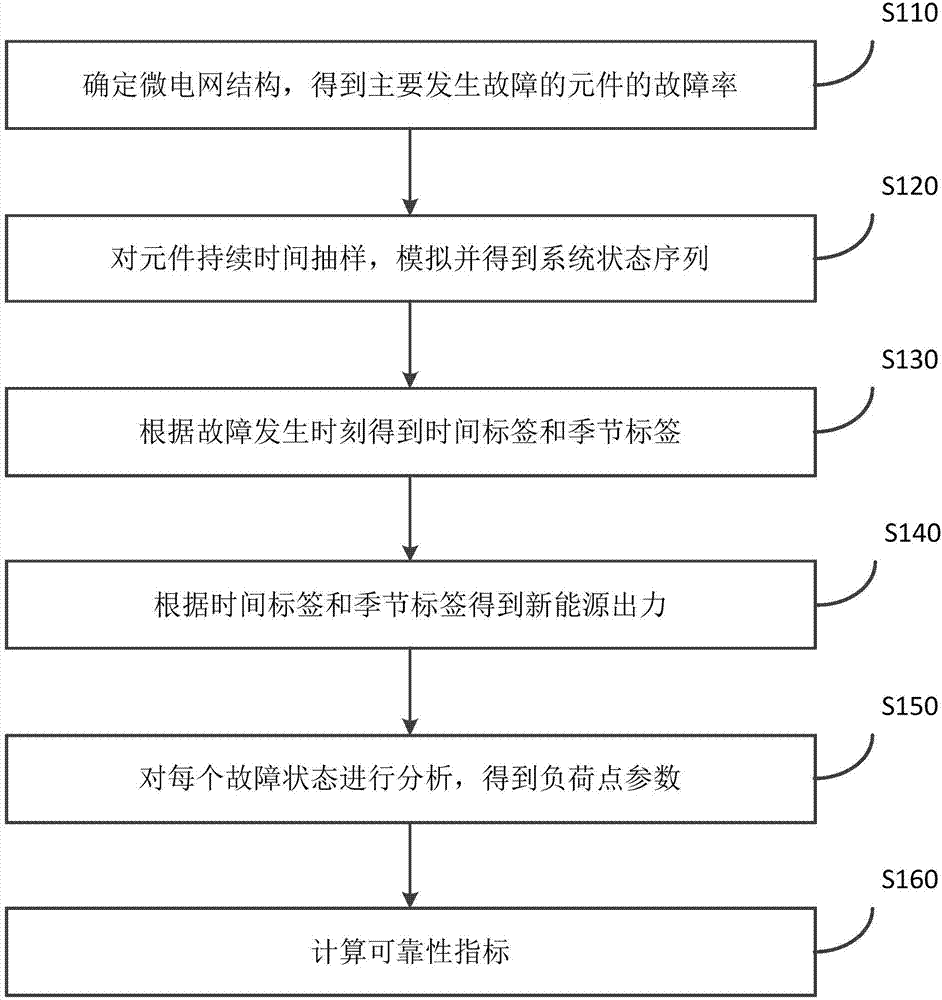
Time correlation and component runtime-based microgrid reliability calculation method
A technology of time correlation and calculation method, applied in calculation, complex mathematical operation, instrument, etc., can solve the problems of failure rate error, poor reliability index, not considering the running time of existing components, etc., and achieve comprehensive and accurate sampling. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0140]Taking a microgrid in a southern city (119°33′19″E, 23°34′02″N) as an example, the present invention will be further described.
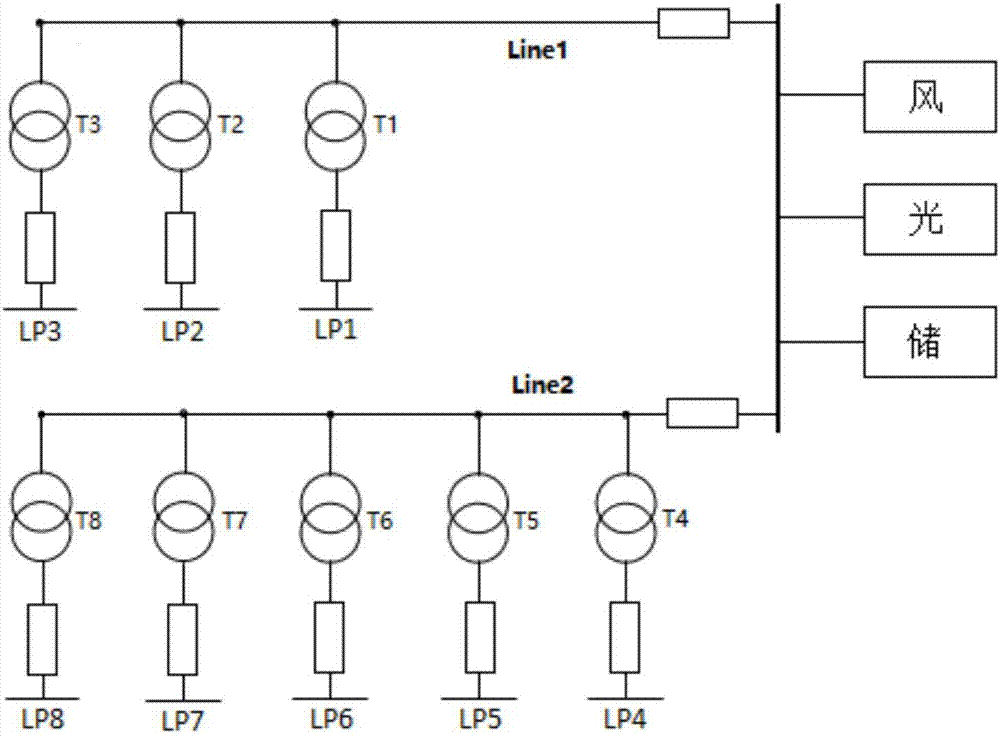
[0141] a. The microgrid is composed of wind turbines, photovoltaic panels, energy storage equipment, etc., including two feeders, ten circuit breakers, eight distribution transformers, and eight load points. The load types include residential electricity and commercial electricity. Electricity and industrial electricity, the proportion of various types of loads is stable, and the proportion of each load point to the total load is stable;
[0142] b. The microgrid includes 300 fans, 5,000 photovoltaic units, 10 diesel engines, 1.5×105 lithium batteries, and 60 supercapacitors;
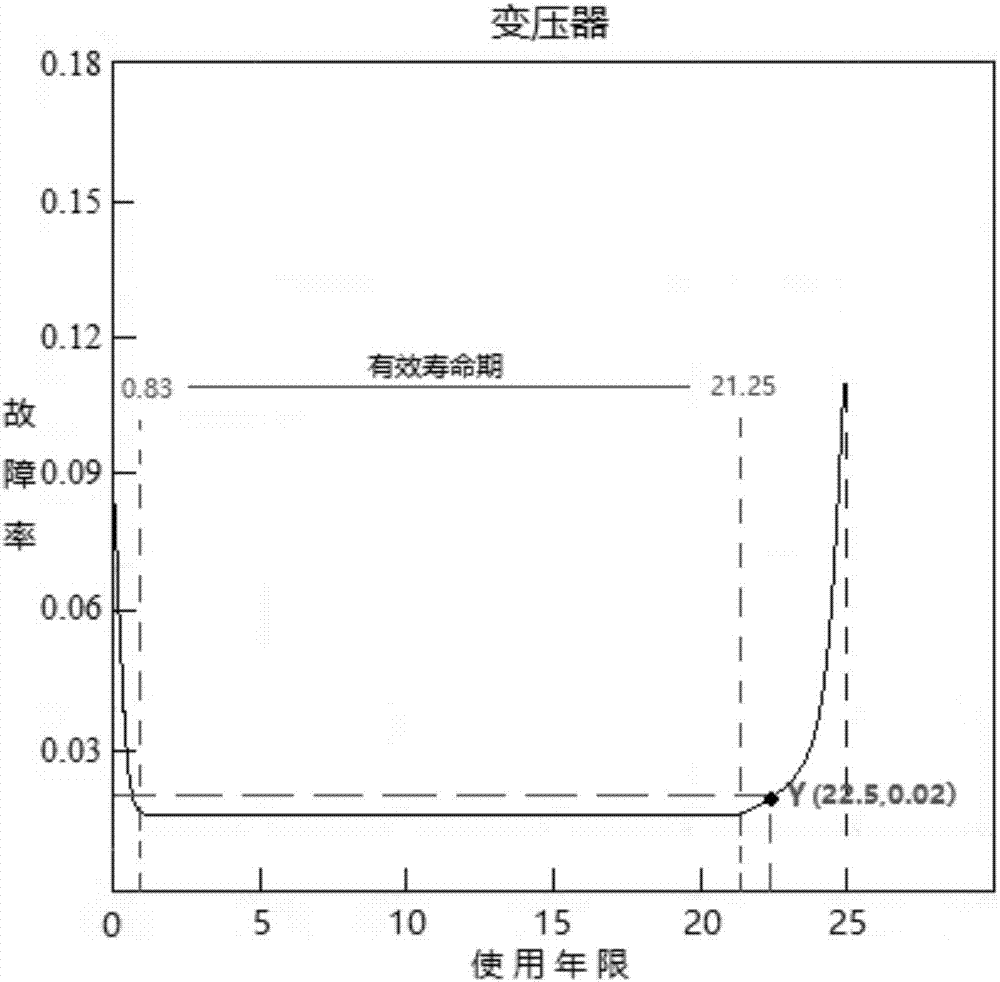
[0143] c. Fan rated power 30kW, rated wind speed 12m / s, cut-in wind speed 3m / s, cut-out wind speed 24m / s, photovoltaic unit rated power 0.2kW, standard light intensity 1kW / m2, standard working temperature 25°C, power temperature coefficient - 0.0045, diesel engine rate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com