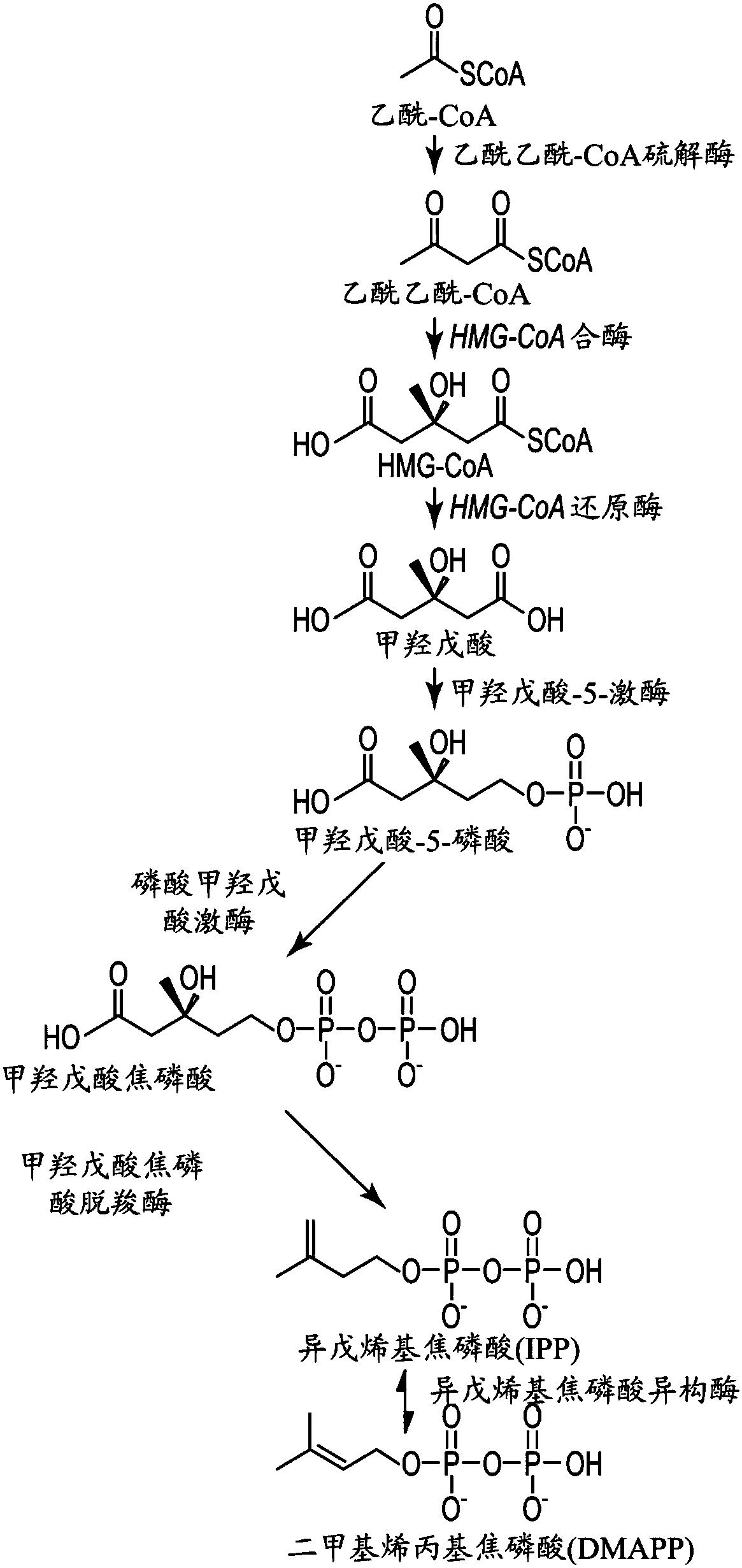
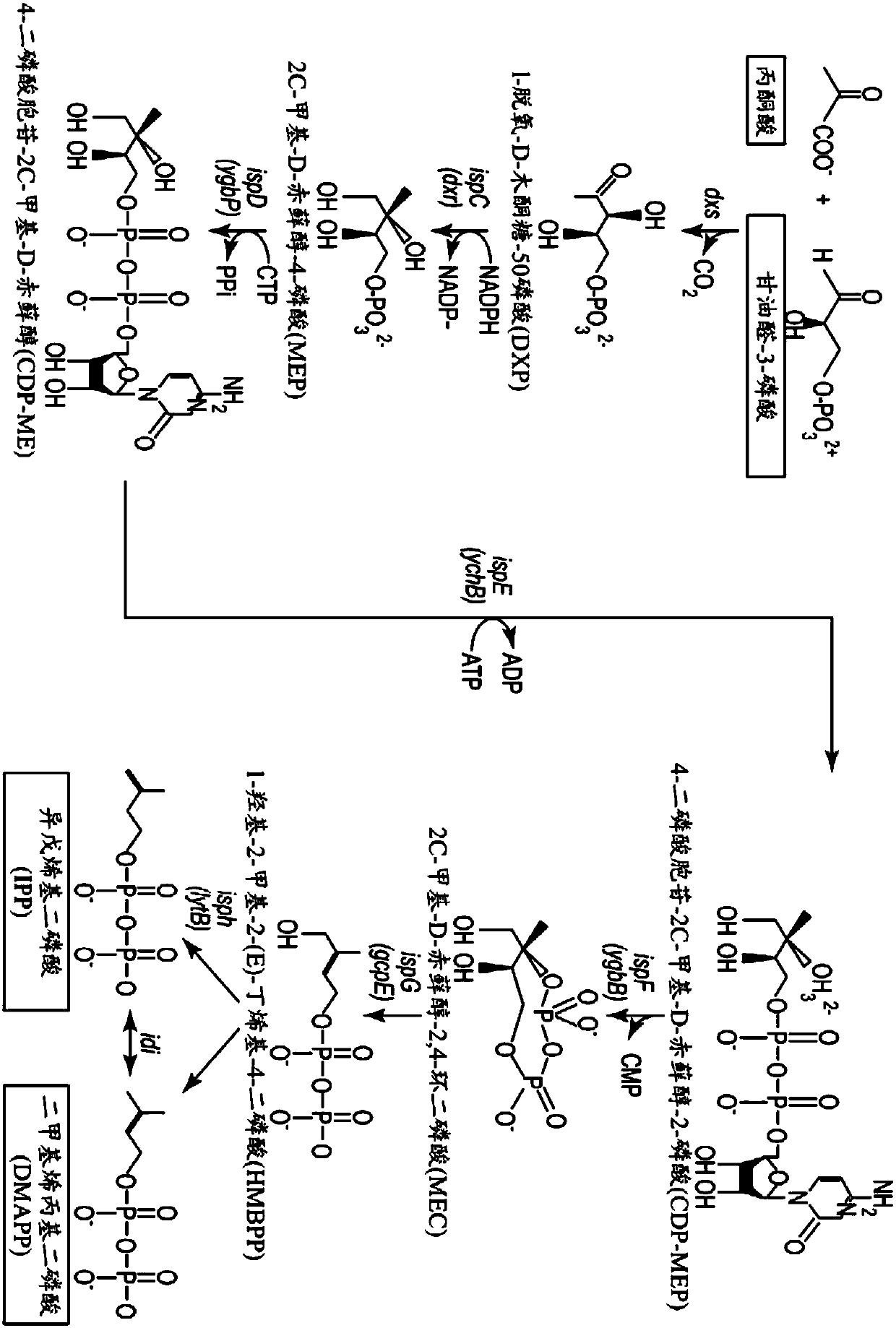
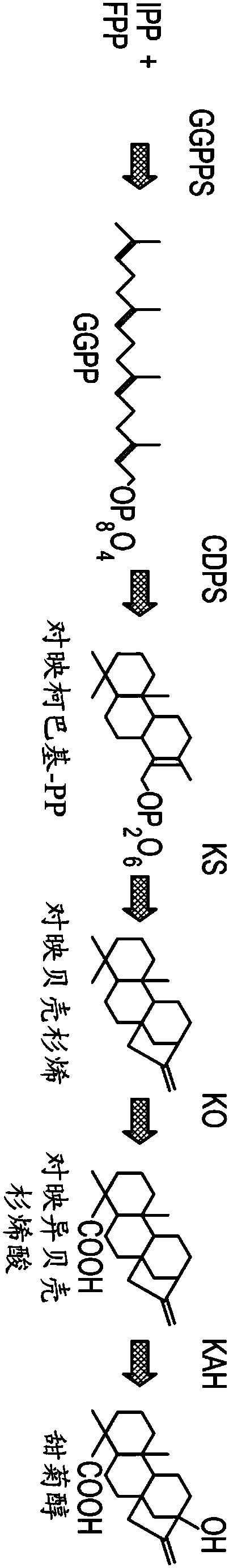
Fermentation methods for producing steviol glycosides with multi-phase feeding
A technology of steviol glycosides and steviol glycosides is applied in the field of steviol glycoside compositions, and can solve the problems such as the inability to fully provide the production rate of steviol glycosides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0112] Production of Reb D and Reb M in a two-stage feed process
[0113] For inoculum preparation, yeast strain B was grown in 150 mL inoculum flask medium in 1 liter shake flasks at 250 rpm and 30°C for 20-24 hours.
[0114] Table 1 Inoculation flask culture medium
[0115] components
Mode
concentration
unit
Biospringer 0251 Yeast Extract
7.5
g / L
C 6 h 12 o 6 *H 2 o
22.0
g / L
[0116]For fermentation, 75 mL of the inoculum culture was transferred to the initial fermentation medium as indicated in Table 2, where the initial volume was 0.75 liters (38.5% tank level). Batch-feed fermentations were performed in 2L New Brunswick BioFlo 310 fermenters. with 12% NH 4 OH controlled the fermentation at pH 5.0 and kept the temperature below 30°C throughout the process. The air flow rate was 1.75 SLPM and the stirring rate was 1200 rpm throughout the fermentation.
[0117] Glucose concentratio...
Embodiment 2
[0138] For inoculum preparation, yeast strain B was grown as described in Example 1 using the inoculation flask medium of Table 1 of Example 1. Fermentation, initial fermentation medium and fermentation feed medium were as described in Example 1.
[0139] table 5
[0140]
[0141] The stage I feed rate was kept constant and the stage II feed rate was variable but lower than that used in Example 1 . The above data show that at lower stage II feed rates, the yield increases.
Embodiment 3
[0143] For inoculum preparation, yeast strain C was grown as described in Example 1 using the inoculated flask medium of Table 1 of Example 1. Unlike Example 1, the initial fermentation medium did not contain cobalt, molybdate and borate, and only vitamins and trace minerals were added to the initial fermentation medium, but not to the fermentation feed medium.
[0144] Table 6
[0145]
[0146] An increase in yield was observed at lower feed rates compared to higher rates with faster feed (control).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com