Medium and method for separating EPCs (endothelial progenitor cells) of bone marrow
A technology of endothelial progenitor cells and separation method, which is applied in the field of separation medium and separation of bone marrow endothelial progenitor cells, can solve the problems of unfavorable economic benefits, high cost, inconsistent phenotype expression rate, etc., and achieve large cell volume and high activity rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
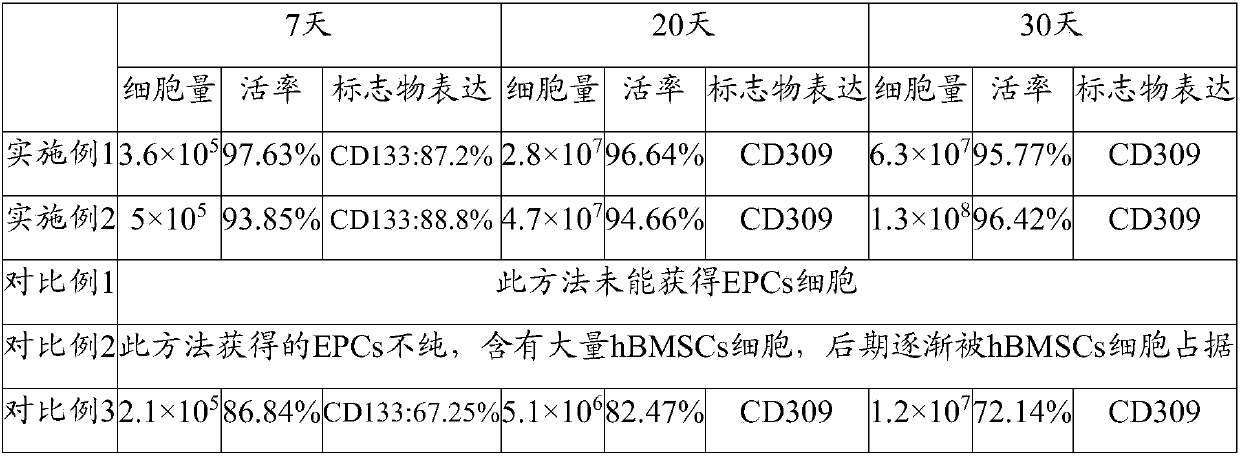
Embodiment 1
[0052] 1. Extract 5mL of human bone marrow;
[0053] 2. Add an equal volume of high-sugar DMEM basal medium and mix well;
[0054] 3. Slowly add to the centrifuge tube filled with Ficoll solution, centrifuge at 700g for 30min;
[0055] 4. Add 10ng / ml FN to T25, put it in a carbon dioxide incubator at 37°C for 60min;
[0056] 5. Absorb the middle mononuclear cell layer;
[0057] 6. Add 10ml of normal saline containing 0.2% human serum, centrifuge at 500g for 10min, repeat once;
[0058] 7. Discard the supernatant, resuspend in medium 1, take 50 μL of the cell suspension, stain with trypan blue, and count the cells;
[0059] 8. According to the counting result, press 1×10 5 / cm 2 Cells were inoculated in T25 culture flasks coated with human fibronectin at a density of ;
[0060] 9. After 24 hours, take the supernatant, centrifuge at 500g for 10 minutes, and re-inoculate the cell pellet into a new T25 culture flask that has been coated with human fibronectin;
[0061] 10. ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] 1. Extract 10mL of human bone marrow;
[0065] 2. Add an equal volume of high-sugar DMEM basal medium and mix well;
[0066] 3. Slowly add to the centrifuge tube filled with Ficoll solution, centrifuge at 700g for 30min;
[0067] 4. Add 10ng / ml FN to T25, put it in a carbon dioxide incubator and cover it for 30-60min;
[0068] 5. Absorb the middle mononuclear cell layer;
[0069] 6. Add 10ml of normal saline containing 0.2% human serum, centrifuge at 500g for 10min, repeat once;
[0070] 7. Discard the supernatant, resuspend in medium 1, take 50 μL of the cell suspension, stain with trypan blue, and count the cells;
[0071] 8. According to the counting result, press 2×10 6 cell / cm 2 Cells were inoculated in T25 culture flasks coated with human fibronectin at a density of ;
[0072] 9. After 24 hours, take the supernatant, centrifuge at 500g for 10 minutes, and re-inoculate the cell pellet into a new T25 culture flask that has been coated with human fibronectin; ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com