Fiber nonlinear equalization method for 64-qam coherent optical communication system
A 64-QAM, coherent optical communication technology, applied in the field of coherent optical data communication, can solve the problems of time consumption, long learning time, consumption of computing resources and time, etc., and achieve the effect of improving quality, reducing computational complexity, and reducing impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
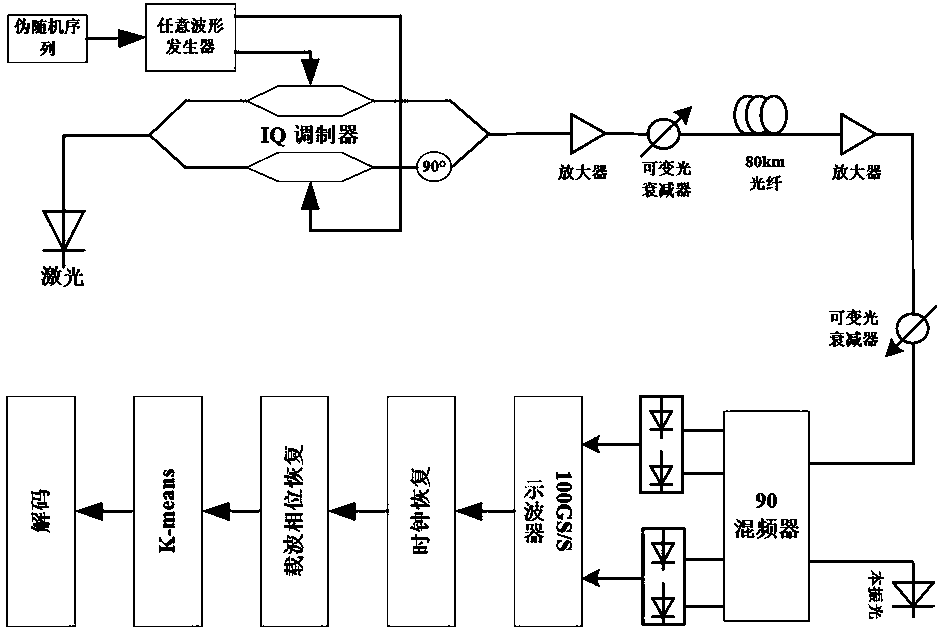
[0033] Embodiment one: see figure 1 As shown, it is a device configuration diagram of the embodiment of the present invention. The obtained 64-QAM data is processed using the blind K-means algorithm to obtain the best centroid and realize data decoding.
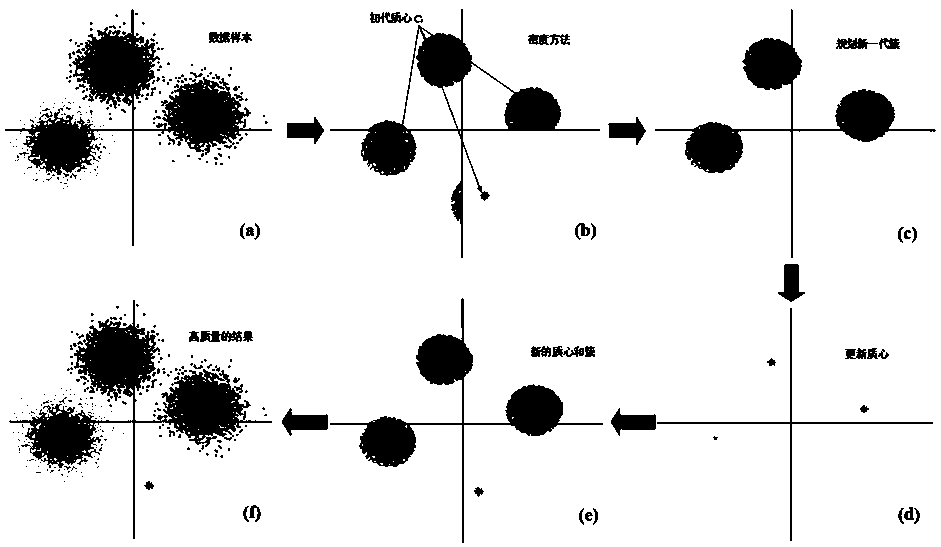
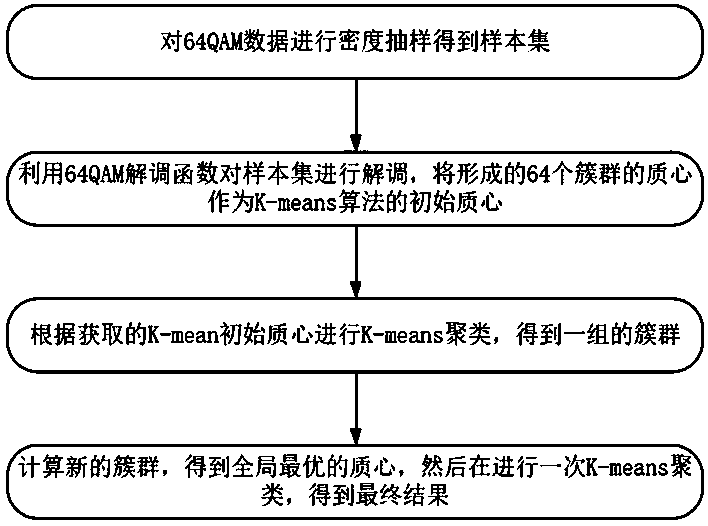
[0034] See attached image 3 , a fiber optic nonlinear equalization method for 64-QAM coherent optical communication systems, first use the density function to sample the 64-QAM data set to obtain the sample set, and use the 64-QAM demodulation function to demodulate the sample set to form 64 clusters, take their centroids as the initial centroids, perform K-means clustering according to the initial qualitative properties, obtain a group of clusters, calculate the centroids of the new clusters, obtain the best centroids, and then perform K-means clustering to obtain the final result.
[0035] The classic K-means algorithm belongs to the class of unsupervised algorithms, mainly depends on the initial cluster center, and it ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com