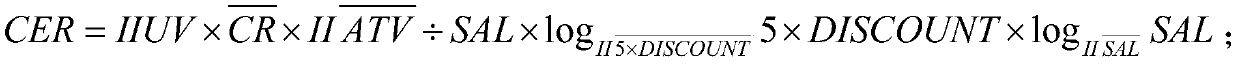Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Quick and accurate selection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
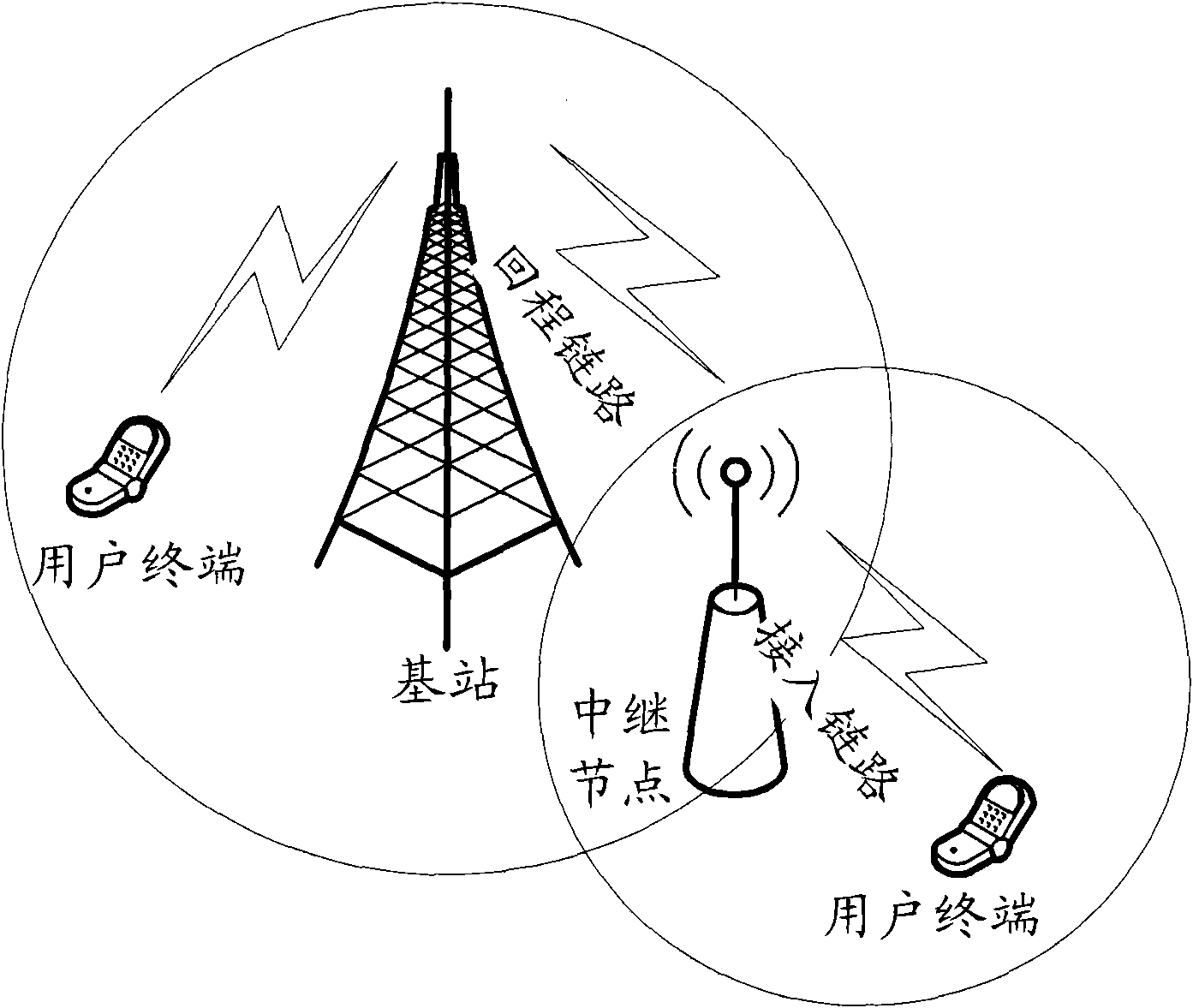
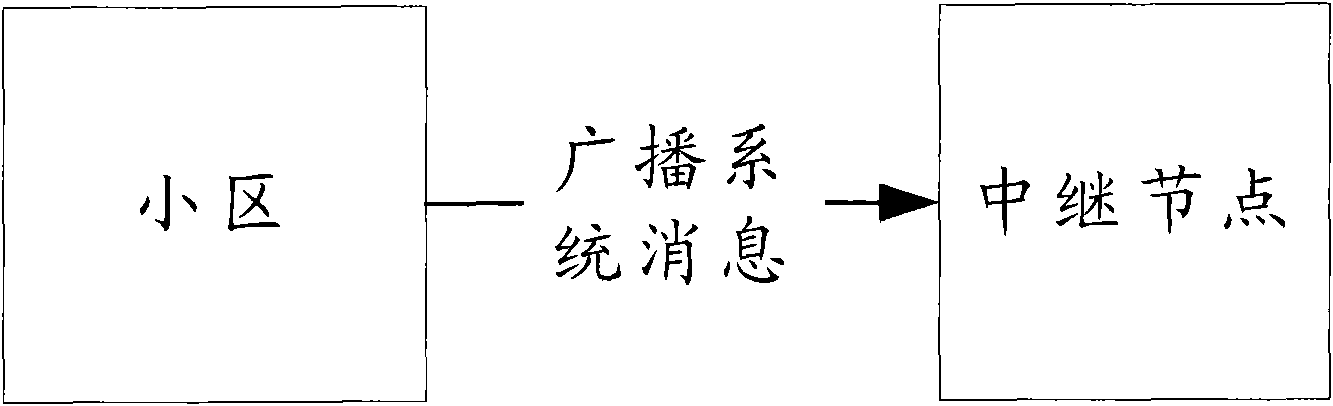
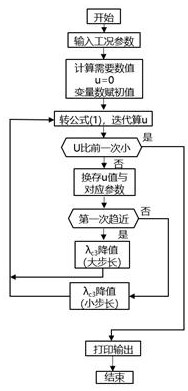
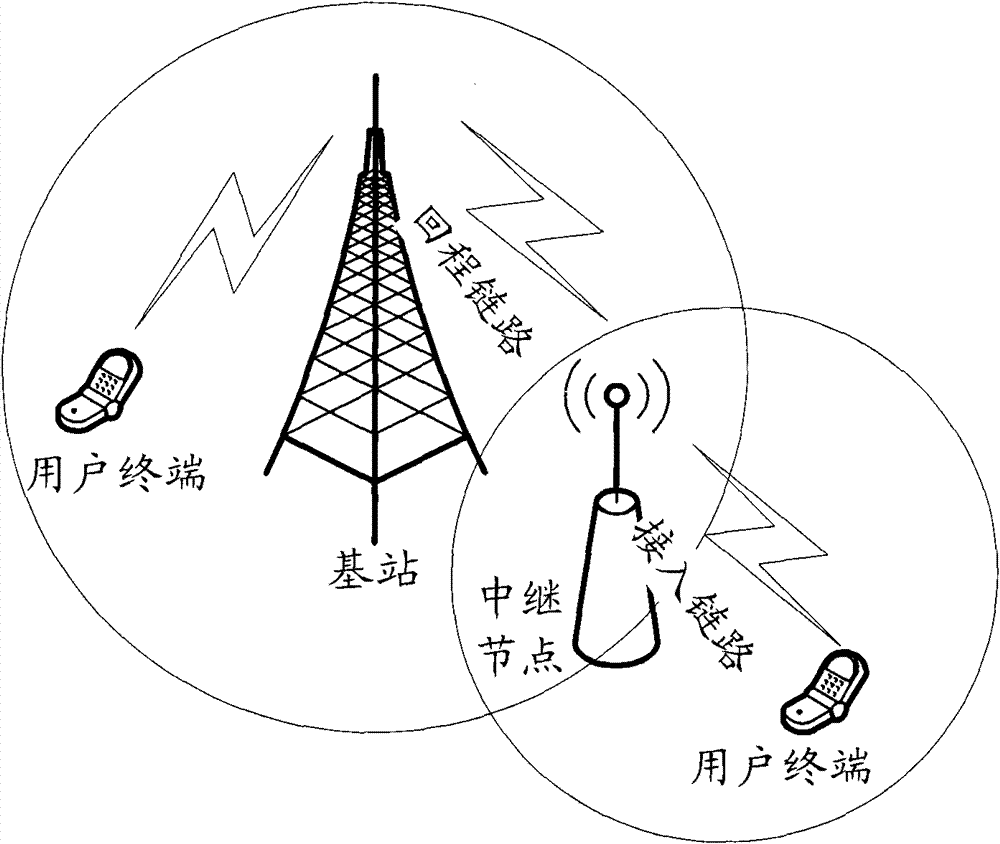
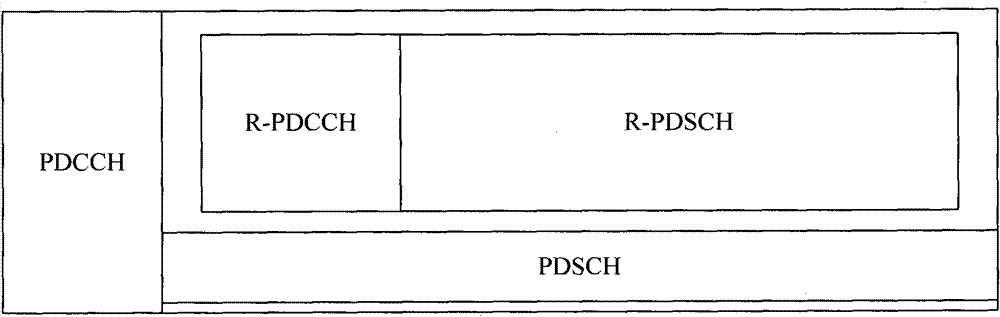
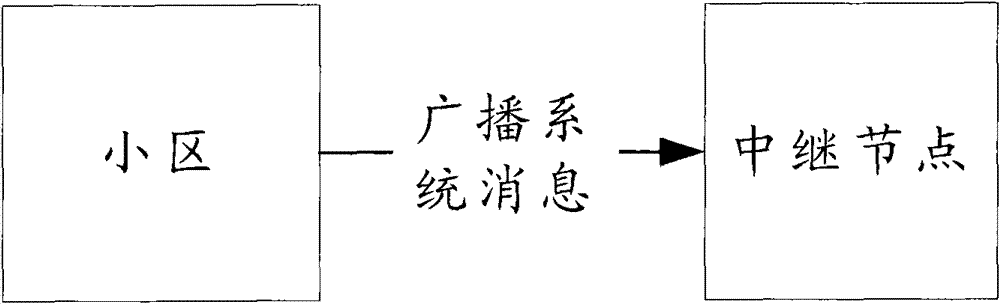
Notification and transmission method of access capability of relay node
ActiveCN102123480AAvoid wastingAvoid the problem of access delayAssess restrictionComputer networkCell Broadcast
The invention discloses a notification and transmission method of the access capability of a relay node. The notification method of the access capability of a relay node comprises the following steps: a cell broadcasts the access capability information of a relay node of the cell by system messages; and whether the relay node can access the cell is judged by the relay node according to the capability information. In the notification and transmission method disclosed by the invention, the relay node can acquire the access capability information of the relay node of the cell so as to provide a reference for the relay node in selecting the access cell, so that the problems that the access resource is wasted and the access is delayed as a relay node accesses a cell which does not support the access of the relay node are avoided.
Owner:ZTE CORP
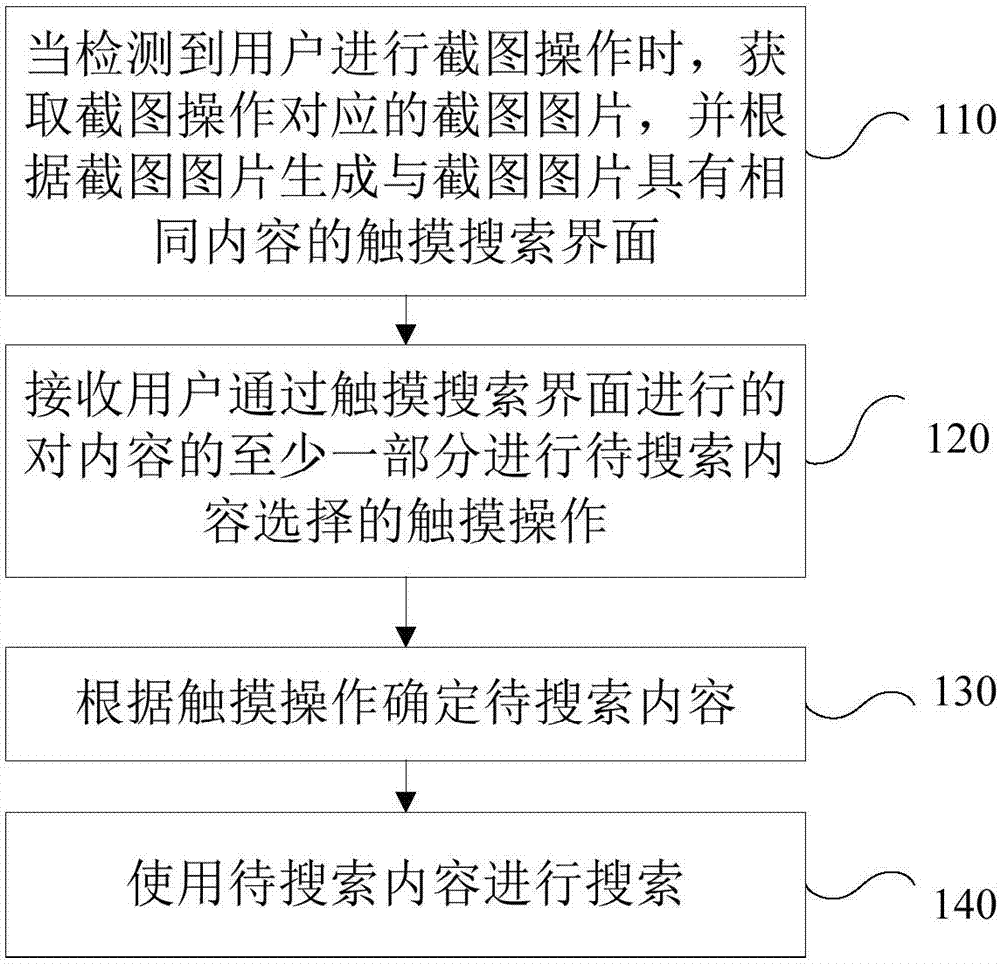
Search method and device based on touch operation
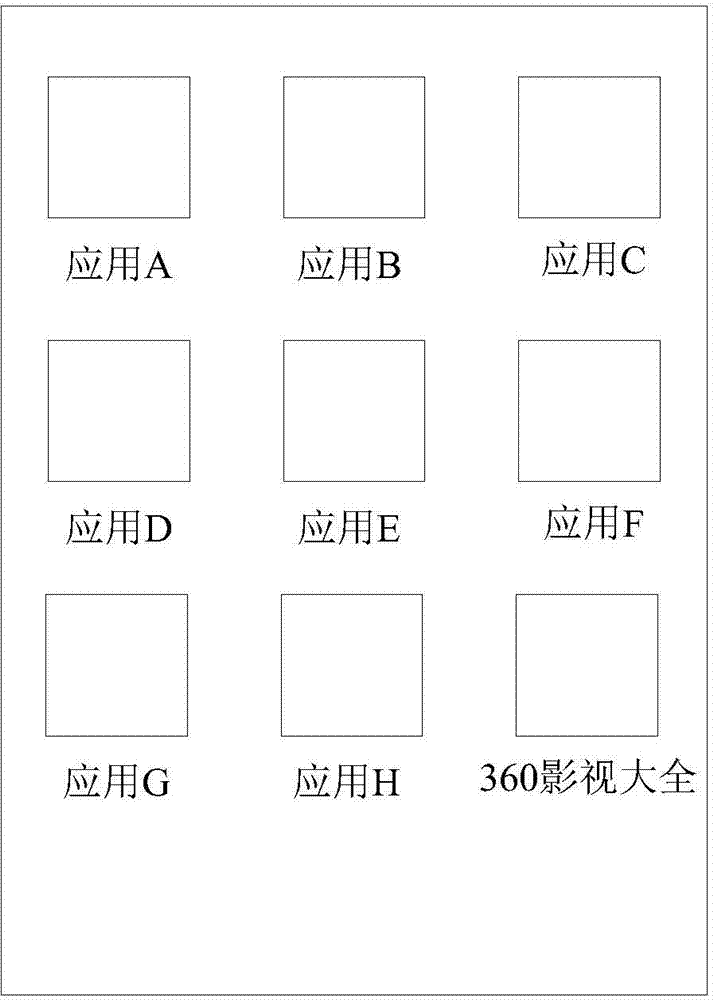
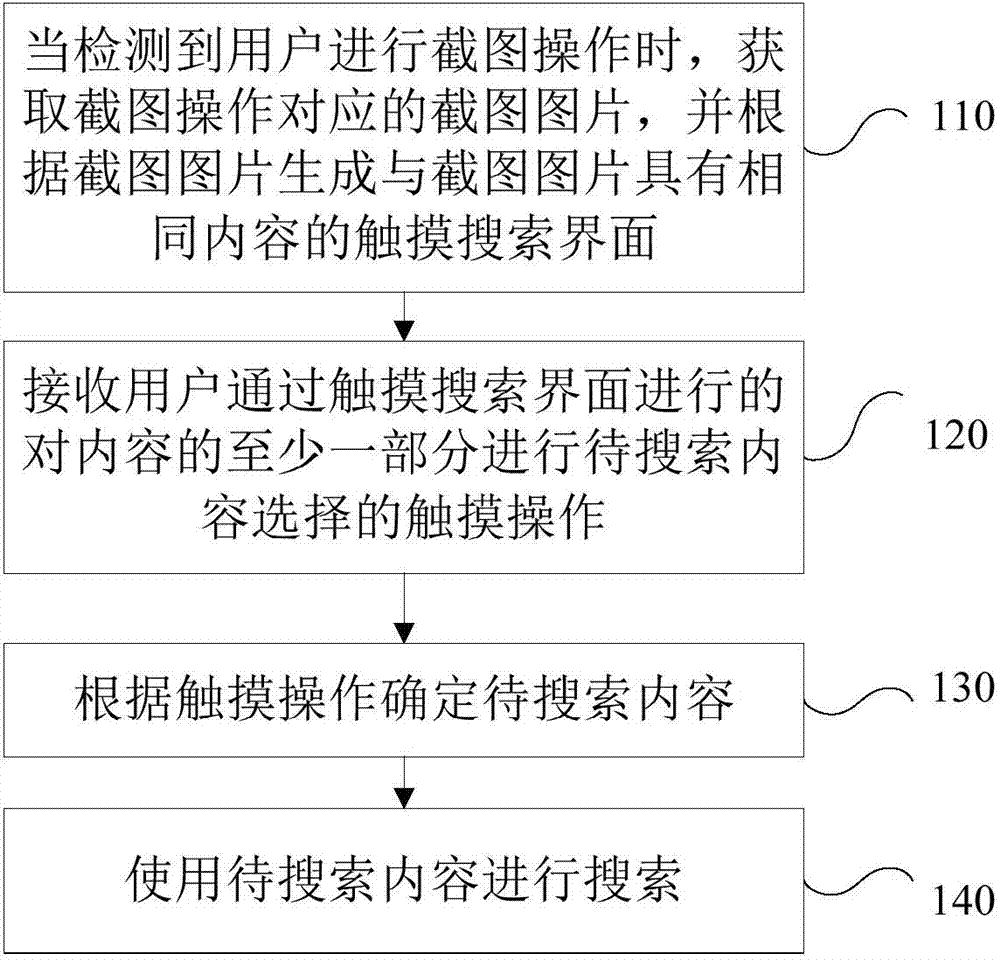
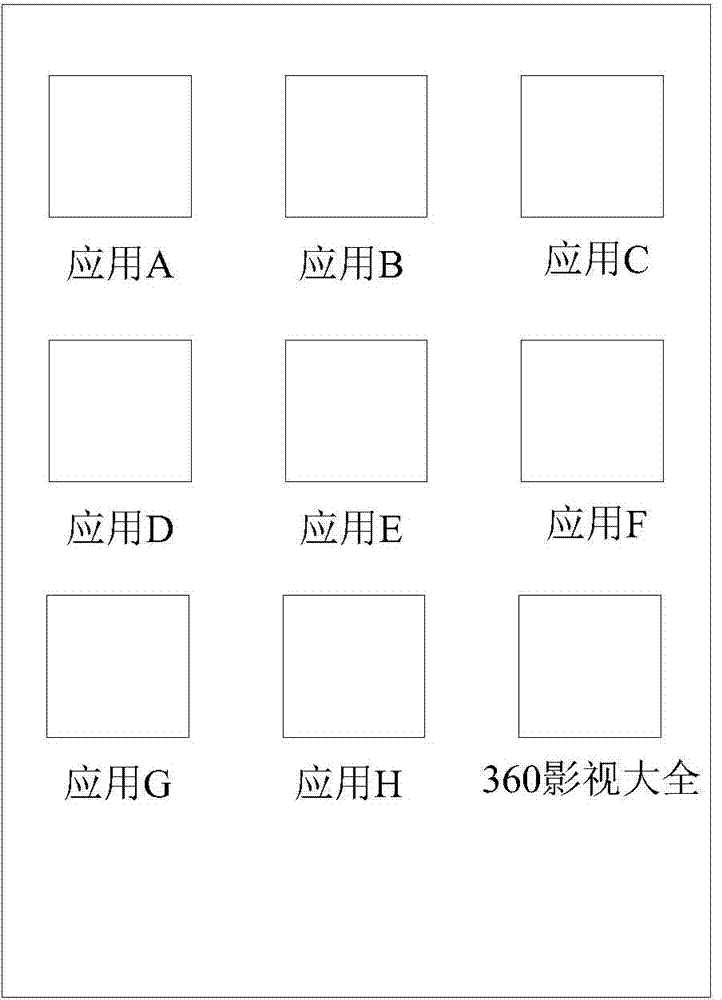
InactiveCN104778194AQuick and accurate selectionSpecial data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingSearch wordsComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a search method and a search device based on touch operation, which mainly relates to the field of information search techniques and mainly aims to provide a technical scheme of quickly inputting and searching to-be-searched words. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a screen shooting picture corresponding to screen shooting operation and generating a touch search interface with same contents as the screen shooting picture according to the screen shooting picture when the screen shooting operation of a user is detected; receiving touch operation of the user for selecting to-be-searched contents from at least one part of the contents through the touch search interface; determining the to-be-searched contents according to the touch operation; searching by using the to-be-searched contents. According to the search method, the user does not need to perform complex operation of starting a search app and pasting shorn or copied contents in a search column of the search app, so as to be quick and convenient; the contents of the screen shooting picture are kept on the touch search interface, so that the user can conveniently select the to-be-searched contents on the touch search interface, so as to be quick and accurate.
Owner:BEIJING QIHOO TECH CO LTD +1
Terminal and touch operation-based searching method
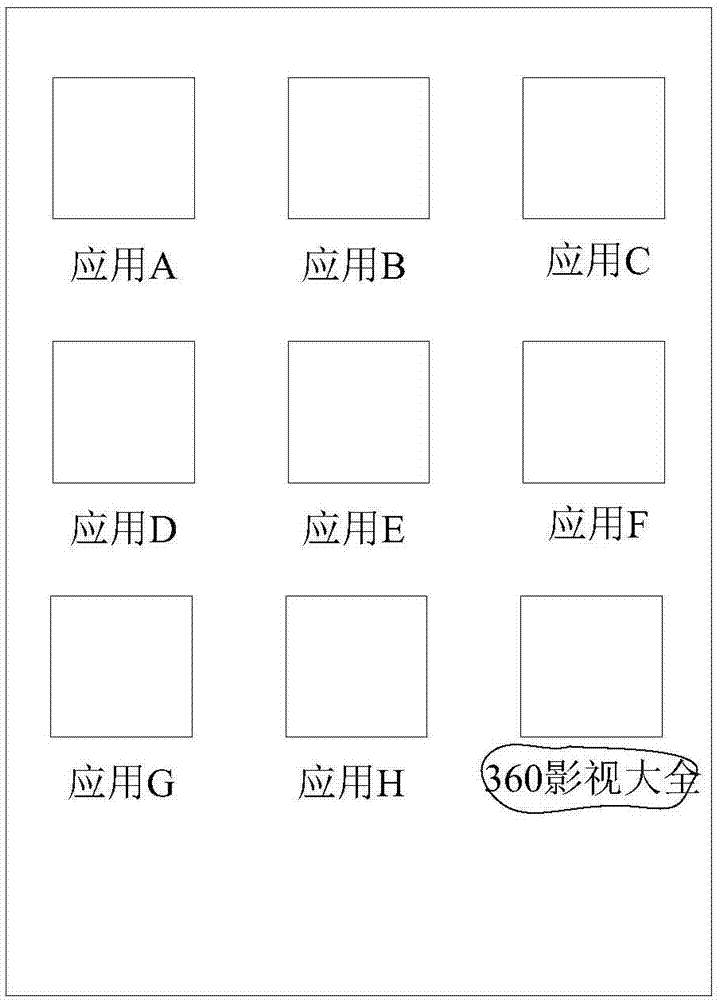
InactiveCN104778195AQuick and accurate selectionSpecial data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingContent determinationTouchscreen
The invention provides a terminal and a touch operation-based searching method, mainly relates to the technical field of information search, and mainly aims to provide a technical scheme for quickly inputting characters to be searched and performing searching. The terminal comprises a touch screen, a touch search interface generator, a to-be-searched content determiner and a searcher, wherein the touch screen is suitable for receiving user touch operation and provides a display function; the touch search interface generator is suitable for acquiring a screen capture picture corresponding to a screen capture operation when the touch search interface generator detects that a user performs the screen capture operation, and generates a touch search interface with the same contents as those of the screen capture picture according to the screen capture picture; the touch screen is suitable for further receiving the touch operation for selecting the contents to be searched from at least part of the contents by the user through the touch search interface; the to-be-searched content determiner is suitable for determining the contents to be searched according to the touch operation; the searcher is suitable for searching the contents to be searched. According to the terminal and the touch operation-based searching method, the interactive mode for searching the characters without inputting by using a keyboard is provided innovatively, and the operation of accurately selecting the characters is greatly optimized.
Owner:BEIJING QIHOO TECH CO LTD +1
Display style setting method of vector electronic map information
ActiveCN102789361AQuick and accurate selectionImprove visual effectsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsInformative content
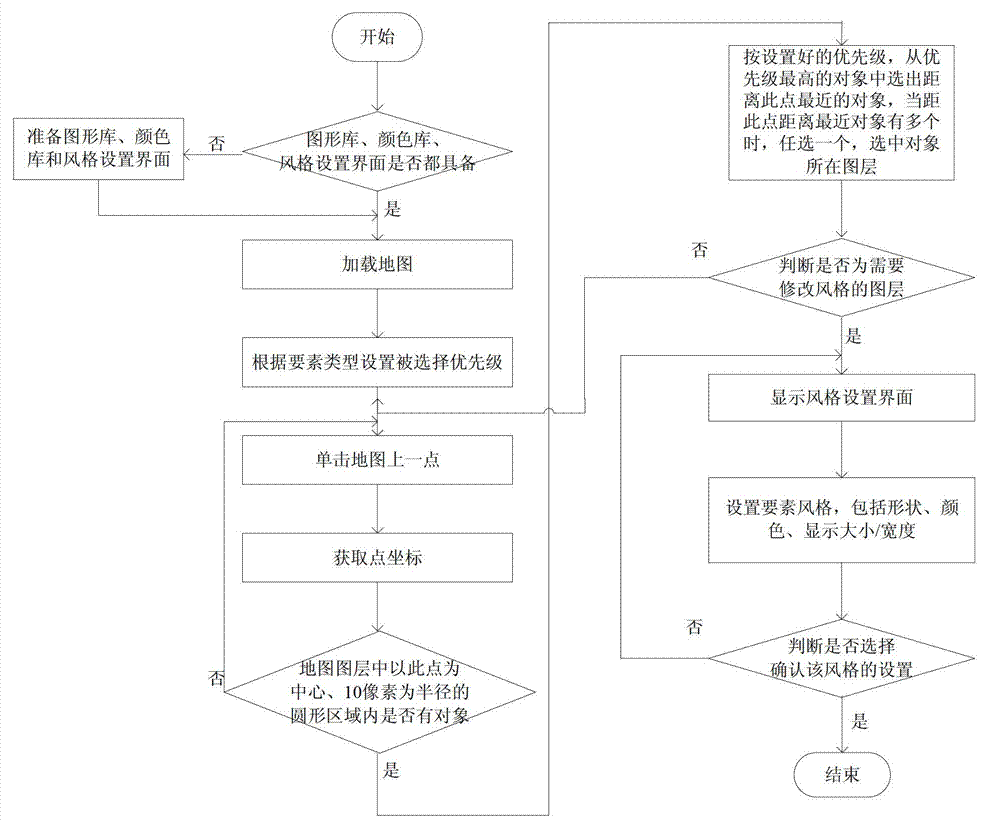
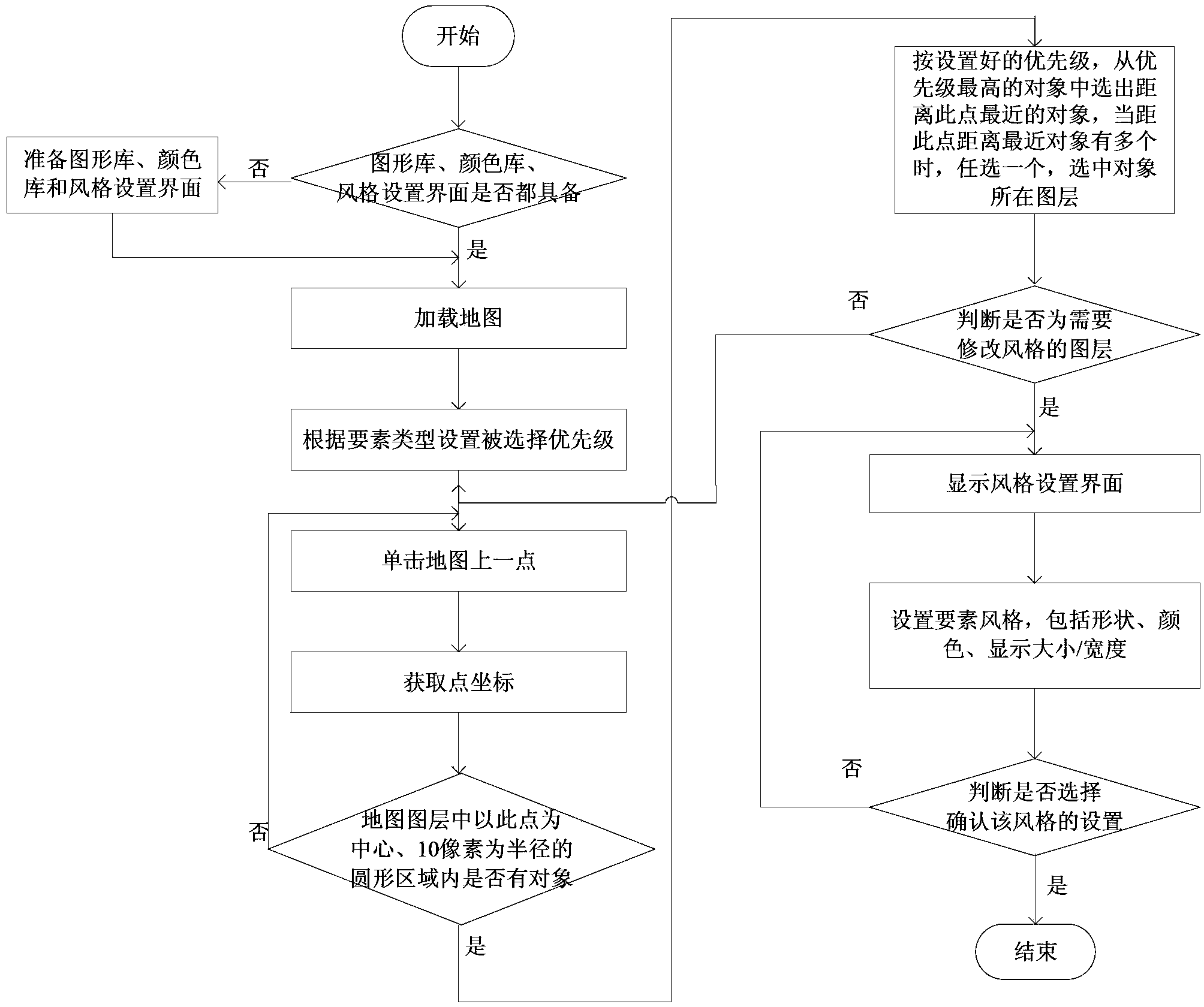
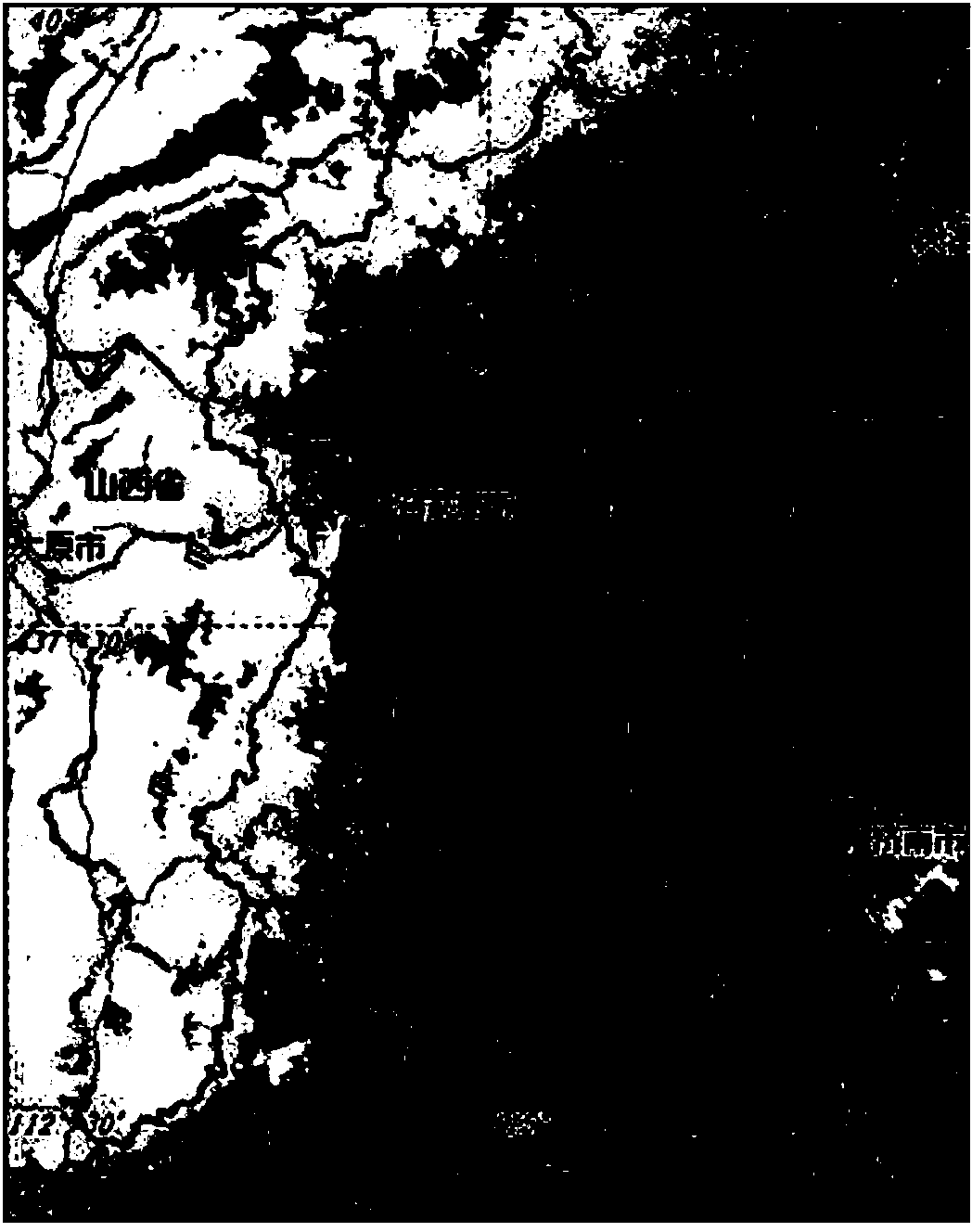
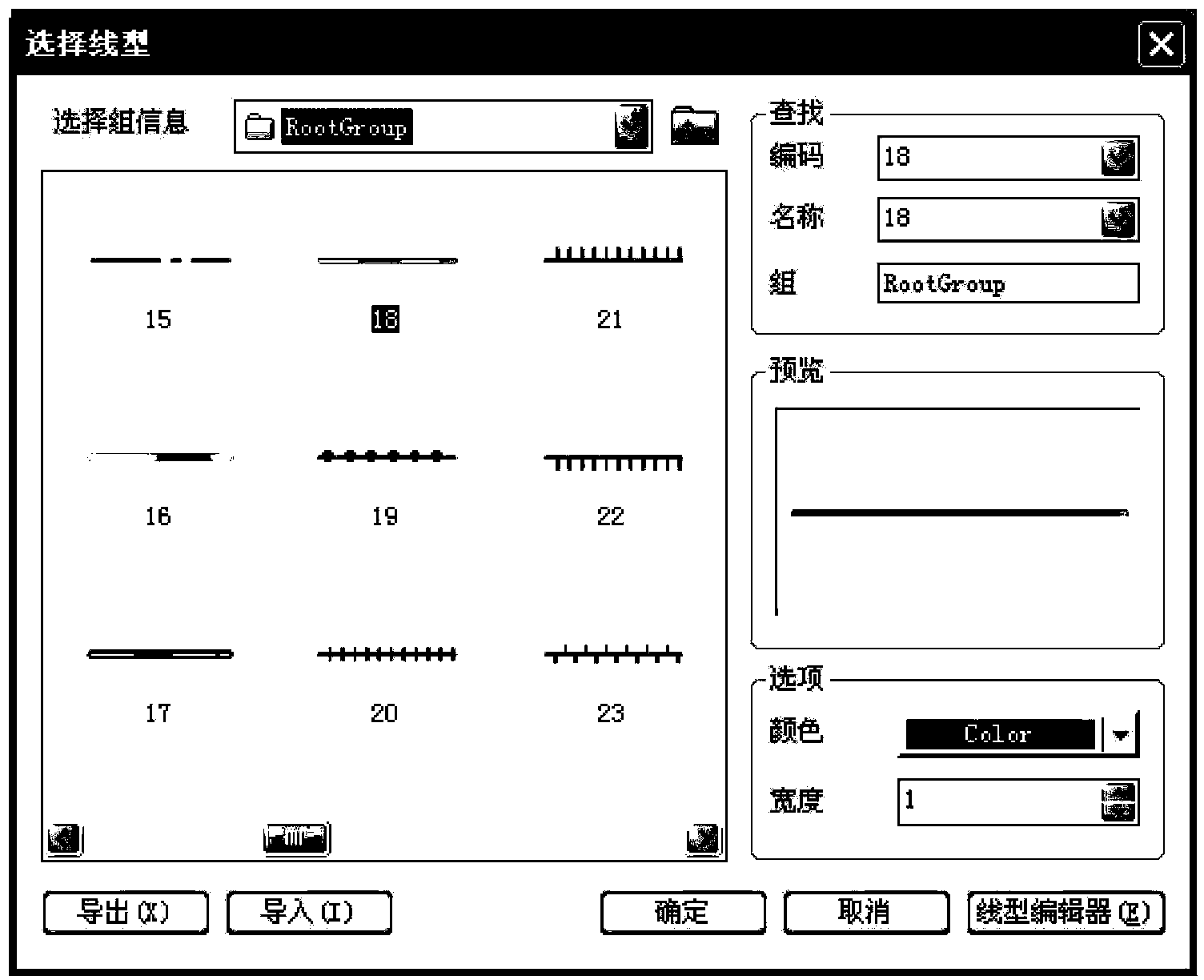
The invention discloses a display style setting method of vector electronic map information and belongs to the technical field of geographical information system map arrangement. The display style setting method includes: checking whether prerequisite conditions are already; loading a map, wherein selected priority level is set according to map element types; clicking any point on a map, obtaining the coordinate of the point, and judging whether map element objects exist in a circular area formed with a point selected from all layers displayed in the map as the center and the radius as 10 pixels; judging whether a selected layer is a layer with the style to be modified by a user; and the like. According to the display style setting method, the user can use a picture base built by the user and representing the map element types as required, set the selected priority level according to objects needed to be selected, fast and accurately select the layers where the elements are located, modify the element style and enrich contents, select appropriate style display elements autonomously and modify the style of the selected layers for many times. The display style setting method improves visual effect of an electronic map.
Owner:哈尔滨哈船导航技术有限公司
System and method for XML based data driven generation of a composite source user interface
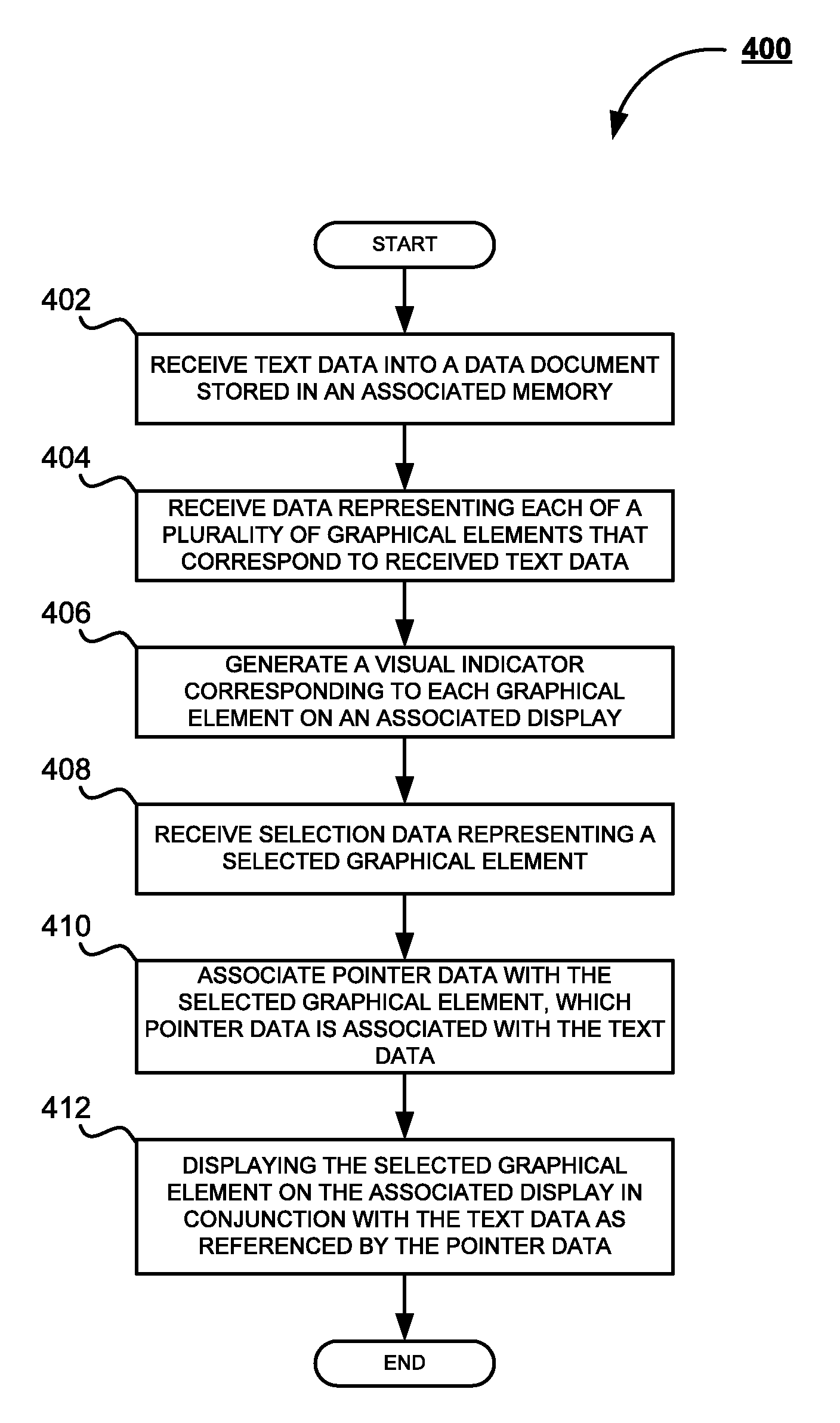
InactiveUS7624350B2Efficient and easy generationQuick and accurate selectionExecution for user interfacesInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsDisplay device
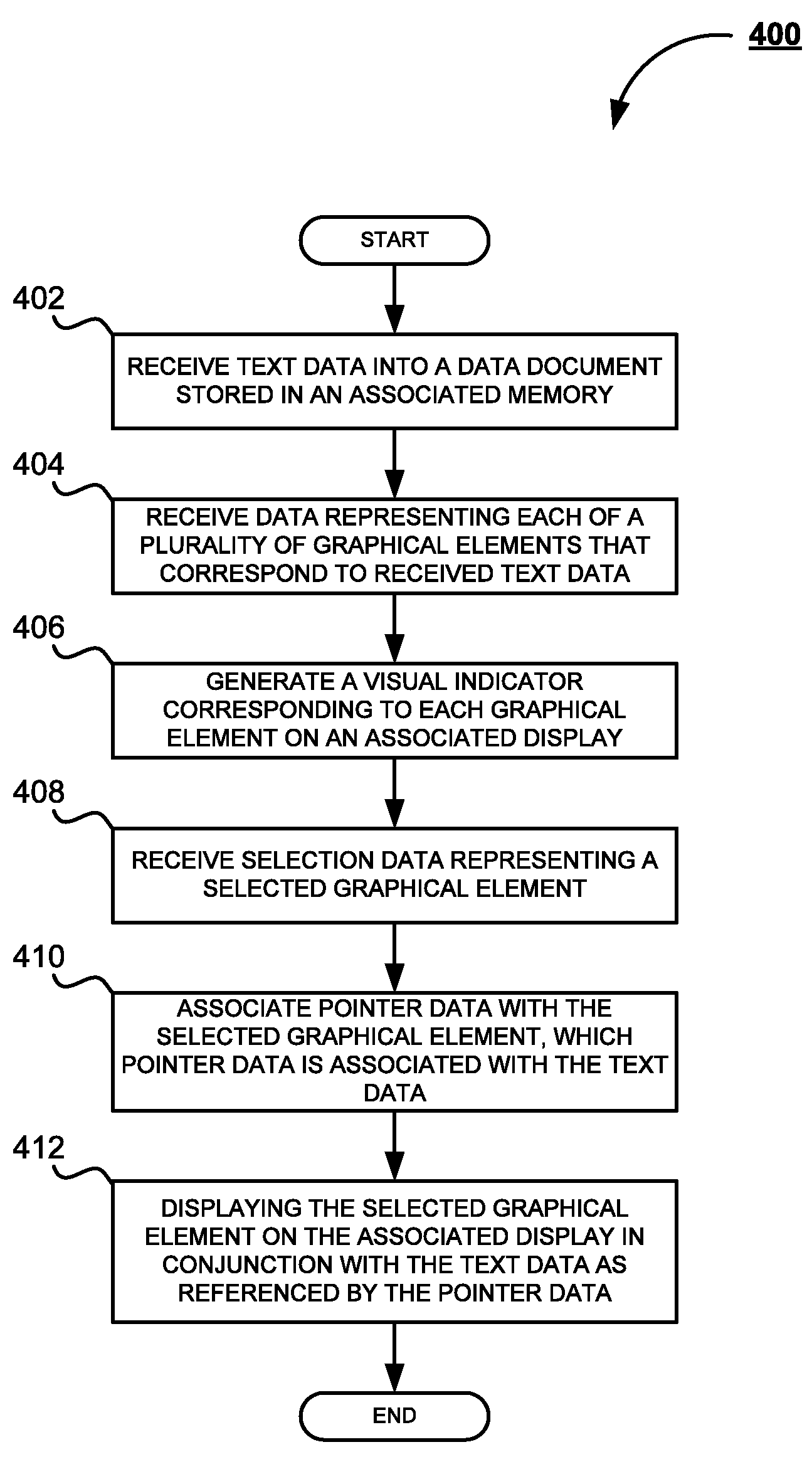
The subject application is directed to a system and method for generating a dynamic composite source user interface. Text data is received into a data document stored in associated memory. Data representing each of a plurality of graphical elements that correspond to the received text data is then received. A visual indicator, corresponding to each of the graphical elements, is generated on an associated display. Selection data representing a selection of one of the graphical elements on the associated display is then received. Pointer data is then associated with the selected graphical element. The pointer data is further associated with the text data. Next, the selected graphical element is then displayed on the associated display in conjunction with the text data, as referenced by the pointer data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Artificial intelligence K12 knowledge graph making management system and implementation method
ActiveCN110110096AFast and accurate dynamic generation of functionsImprove learning effectSpecial data processing applicationsSemantic tool creationKnowledge graphManagement system
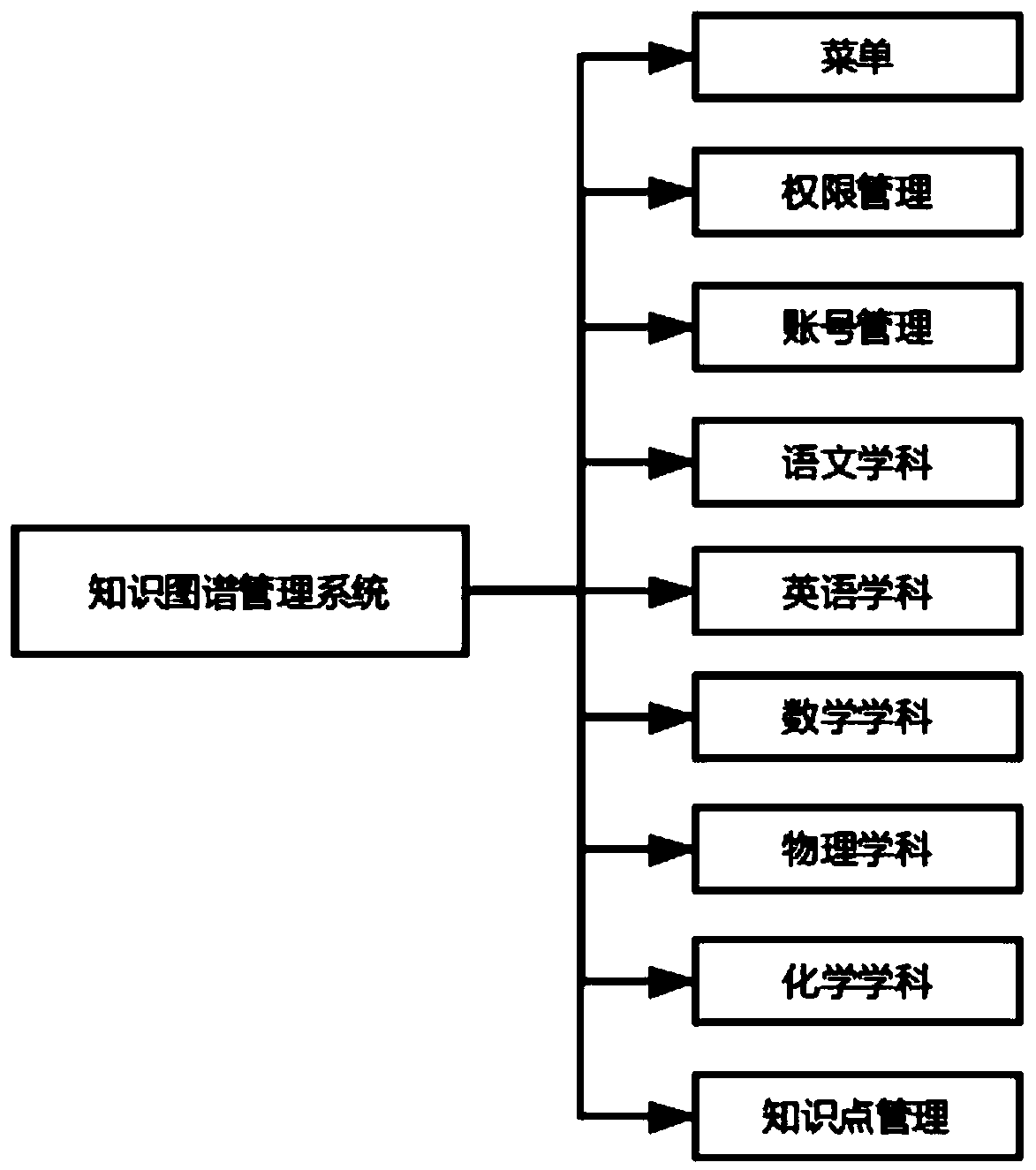
The invention discloses an artificial intelligence K12 knowledge graph making management system. Massive knowledge points can be subjected to friendly management, hierarchical splitting and relation storage. More importantly, accurate generation and verification of the graph can be intelligently realized, so that a teacher can quickly and accurately select and use the map during course development; the students can obtain the most effective learning path according to the relationship between the knowledge points in the map to obtain the best learning effect; even dynamic knowledge graph generation in the learning process of the student is realized, and the learning graph and path most suitable for each person in front of thousands of persons are really realized; based on the map information, big data can accurately analyze and trace weak points of students, and learning targets and learning plans are dynamically adjusted for the students in an artificial intelligence mode.
Owner:SHANGHAI SQUIRREL CLASSROOM ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE TECH CO LTD
Convenient and quick car wash method and system based on mobile terminal
InactiveCN108171899AQuick fixSave time queuing up at the car washReservationsApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingPaymentEngineering
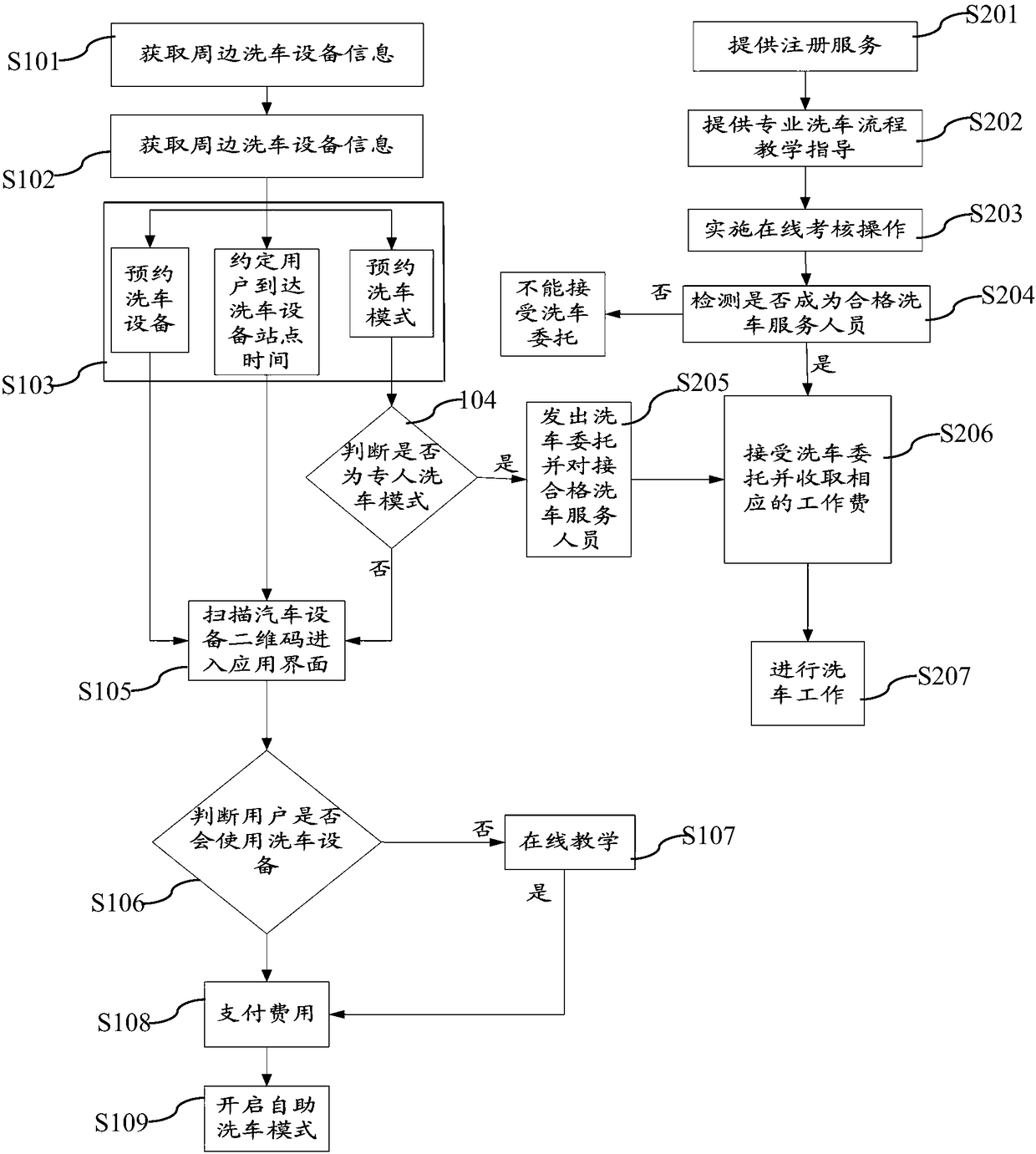
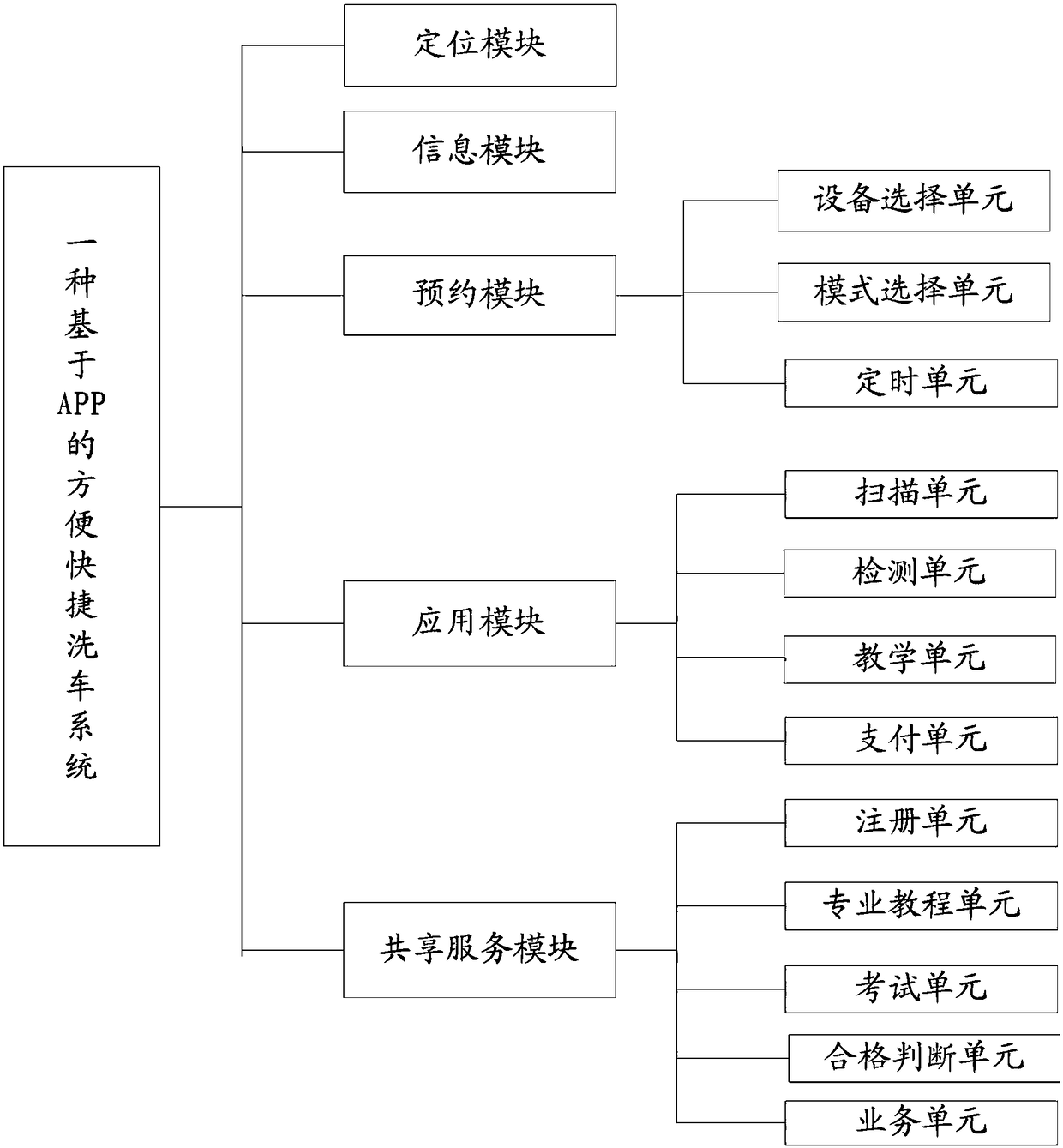
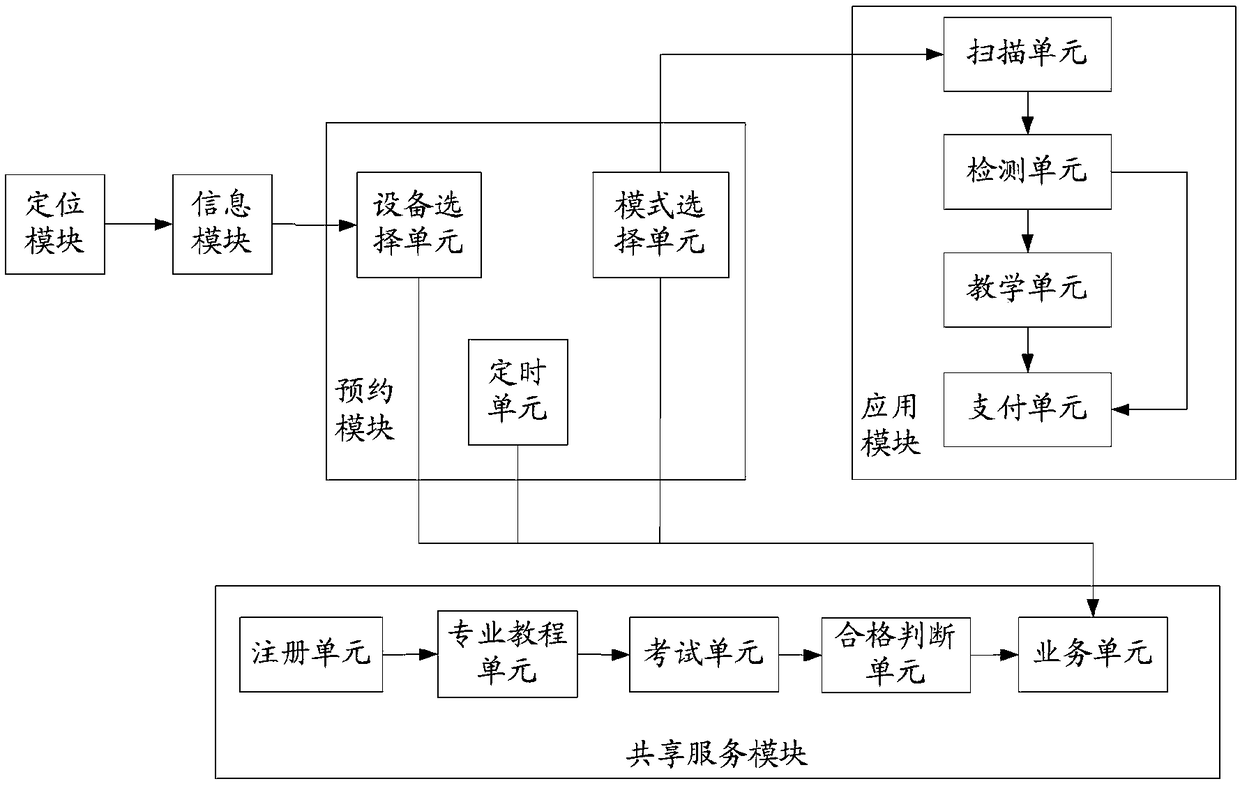
The invention discloses a convenient and quick car wash method and system based on a mobile terminal. The convenient and quick car wash method comprises the following step: acquiring positioning information of the mobile terminal; acquiring information of surrounding car wash devices; reserving a car wash device; and using the car wash device. The convenient and quick car wash system includes a positioning module, an information module, a reservation module, an application module, and a shared service module; a device selection unit, a timing unit, and a mode selection unit are arranged in thereservation module; a scanning unit, a detection unit, a teaching unit, and a payment unit are arranged in the application module; and a registration unit, a professional tutorial unit, an examination unit, a qualified detection unit, and a service unit are arranged in the shared service module. The convenient and quick car wash method and system can save the time of car wash queuing time of a user, realize the user's ready-to-use technical effect, facilitate the user to choose the car wash mode, and provide great convenience for the owner.
Owner:深圳市前海车博科技有限公司
Soft package lithium ion battery and online detection method for cathode short circuit of soft package lithium ion battery
PendingCN114035112AQuick and accurate selectionLower your own voltageShort-circuit testingCell component detailsMetal stripsElectrical battery
The invention discloses a soft package lithium ion battery. The lithium ion battery comprises a battery cell, an electrolyte, an aluminum-plastic film, a positive electrode metal strip and a negative electrode metal strip; the aluminum-plastic film comprises a protective layer, a middle layer and a heat sealing layer, wherein the middle layer of the aluminum-plastic film is an aluminum layer; the positive electrode metal strip is communicated with the aluminum layer of the aluminum-plastic film through a conductive piece; and when the whole lithium ion battery is electrified, the aluminum layer of the aluminum-plastic film is positively charged. According to the lithium ion battery, the positive electrode metal strip is communicated with the aluminum layer of the outer packaging material aluminum-plastic film through the conductive piece; and when the lithium ion battery is detected, if a negative electrode is short-circuited, the whole battery shows a self-discharge phenomenon, so that the voltage attenuation of the battery is obvious; and a batter with abnormal voltage attenuation is determined as an unqualified battery. The detection method can quickly identify the lithium ion batteries with short-circuited cathodes, and improves the precision measurement efficiency and precision.
Owner:新纶新能源材料(常州)有限公司
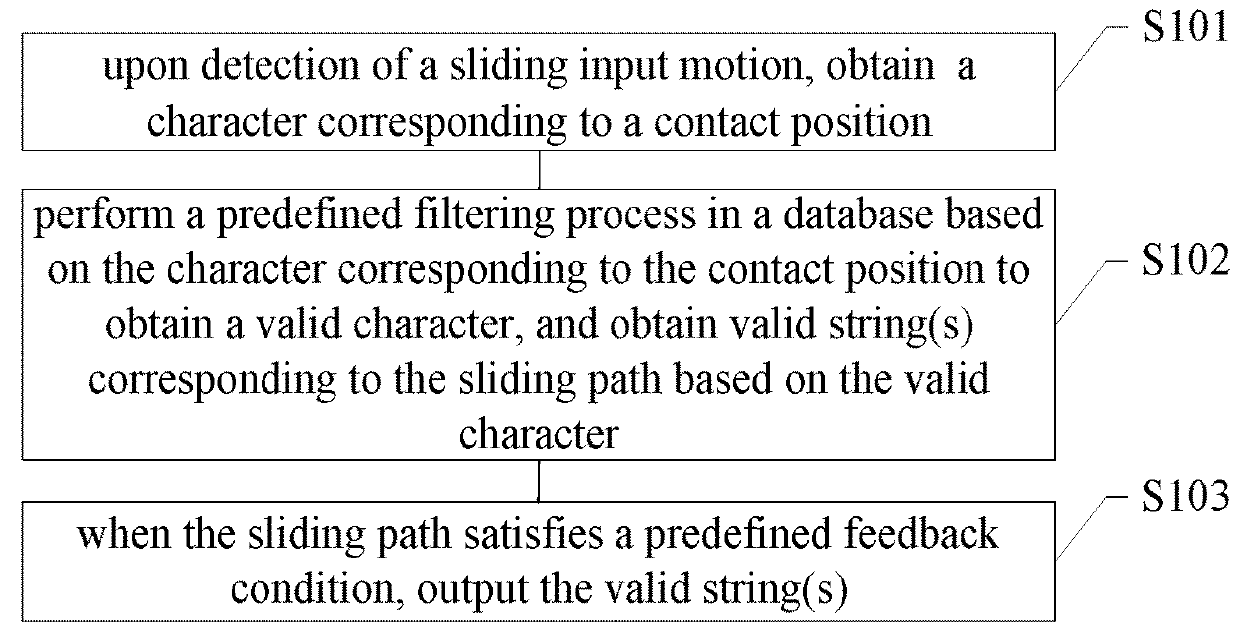
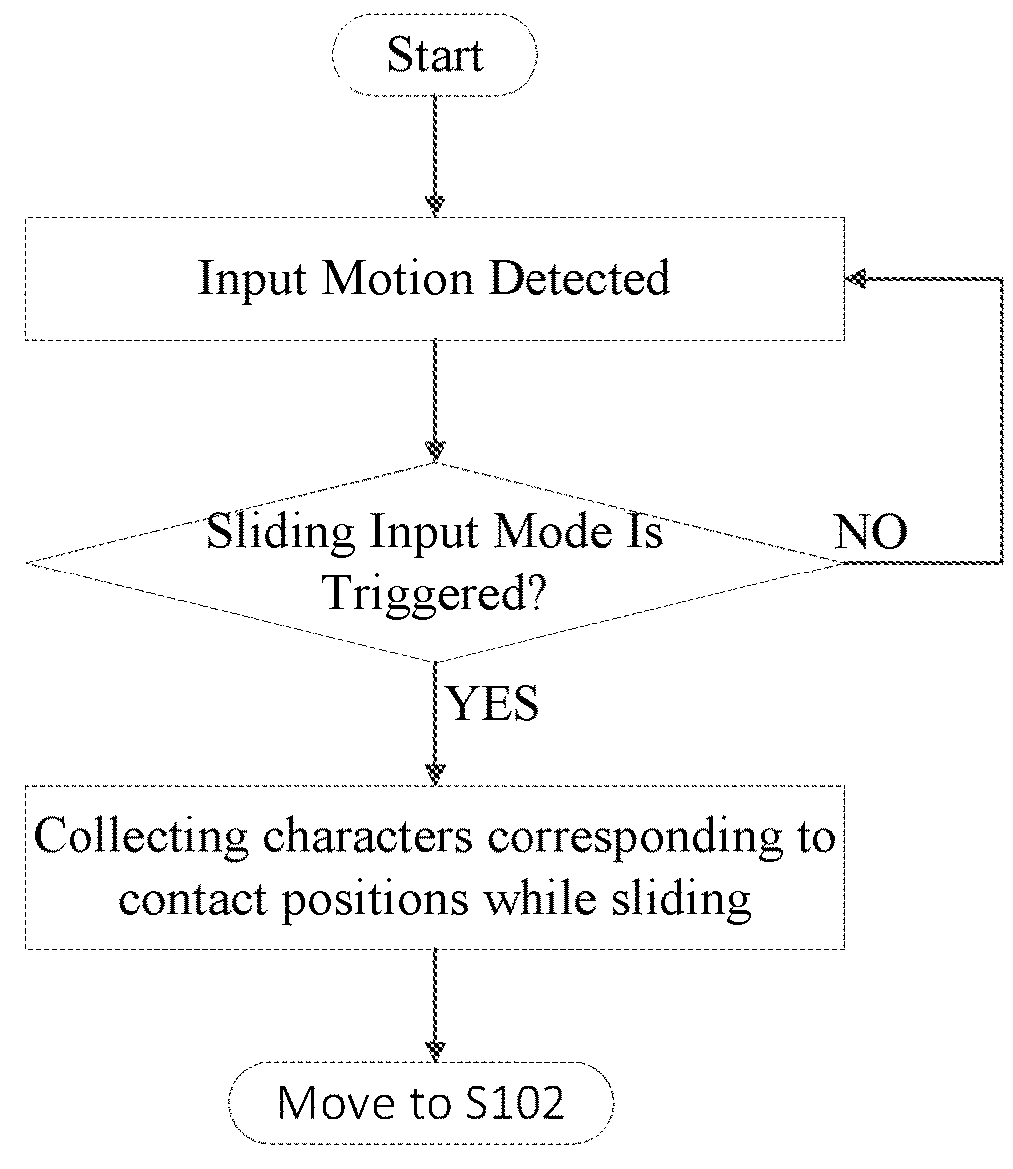
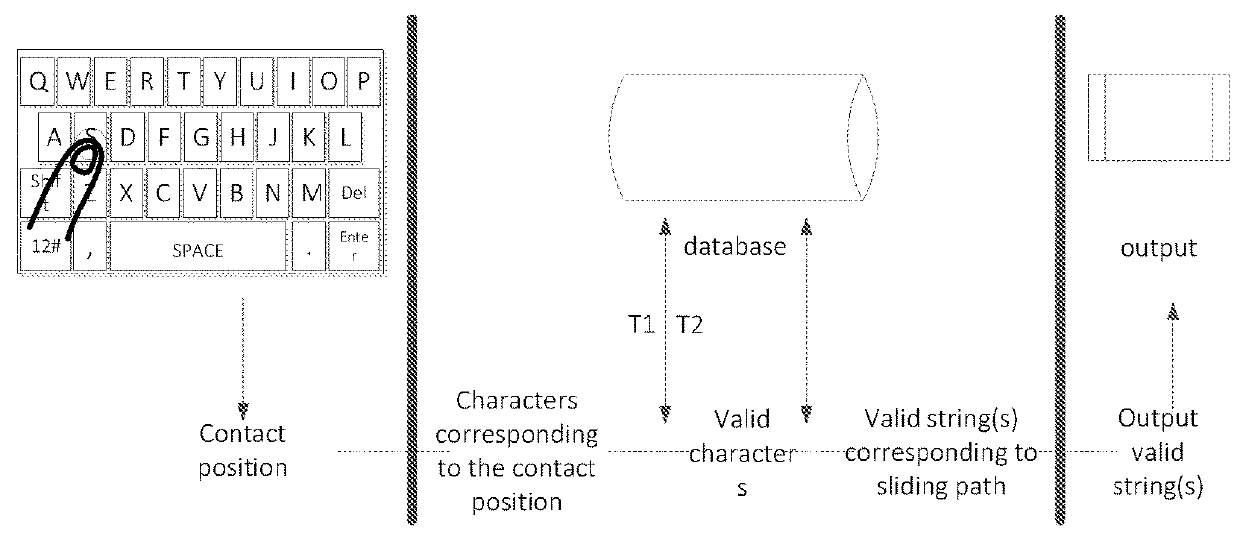
Sliding input method and device
InactiveUS20180165001A1Quick and accurate selectionReduce the amount of calculationInput/output processes for data processingAlgorithmEngineering
A sliding input method and device are disclosed. The method comprises: upon detection of a sliding input motion, obtaining a character corresponding to a contact position; performing a filtering process on a database based on the character corresponding to the contact position to obtain valid character and obtaining valid string(s) corresponding to a sliding path based on the valid character. During the filtering process, it includes selecting character combination(s) in the database, each containing the character corresponding to the contact position at its predefined character position. When the sliding path satisfies a predefined feedback condition, a valid string is output. According to the present invention, considerable reductions in the required calculation amount and improvements in input efficiency can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHULE (COOTEK) INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
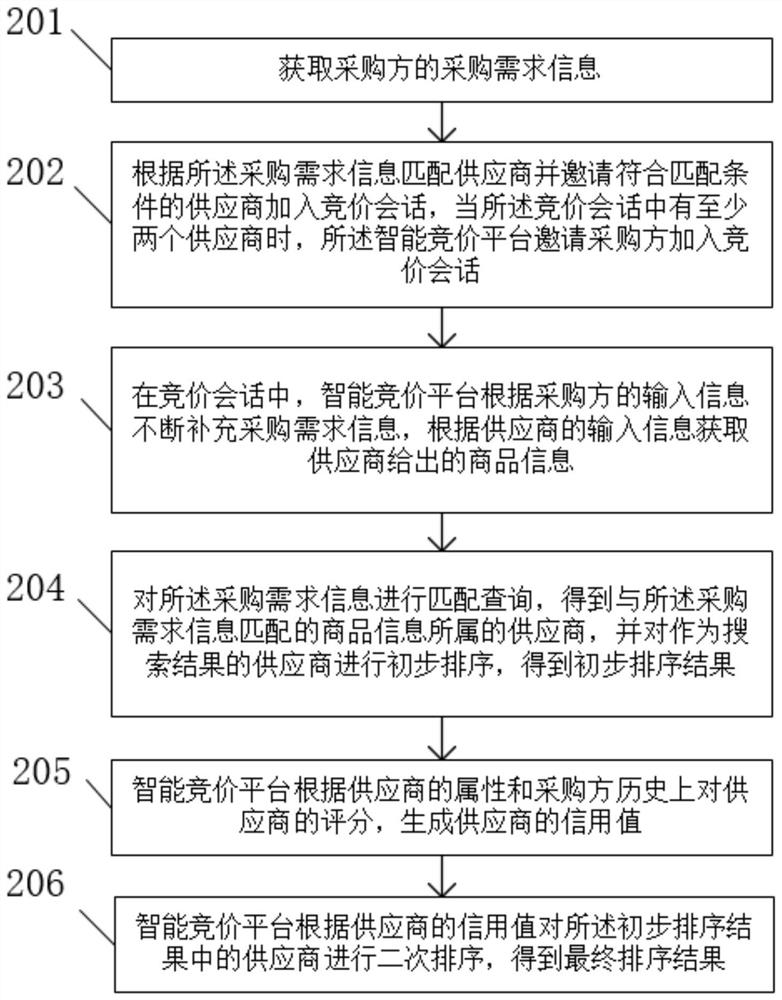
Supplier sorting method based on intelligent bidding platform
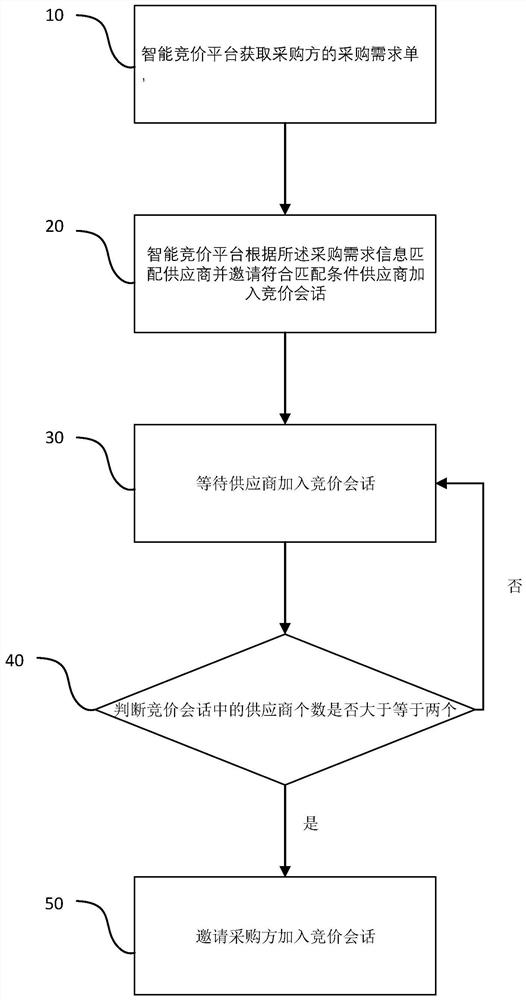
PendingCN112819568AImprove consumer experienceQuick and accurate selectionBuying/selling/leasing transactionsE-commerceData mining
Owner:万象春天实业集团(武汉)有限公司
Optional control processing method and device, processor and electronic device
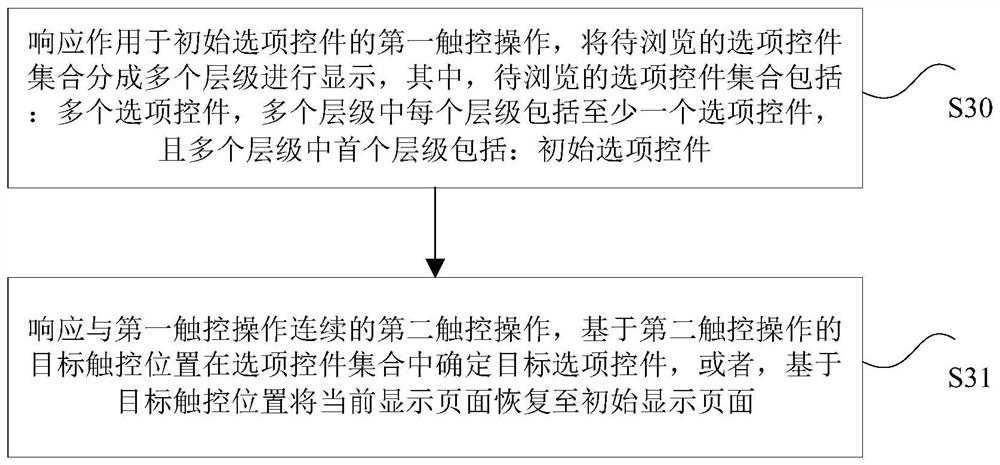
PendingCN113262472AQuick and accurate selectionReduce operational complexityVideo gamesComputer hardwareControl set
The invention discloses an option control processing method and device, a processor and an electronic device. The method comprises the steps: in response to a first touch operation acting on an initial option control, dividing a to-be-browsed option control set into multiple levels to be displayed, wherein the to-be-browsed option control set comprises multiple option controls, each level in the multiple levels comprises at least one option control, and the first level in the multiple levels comprises the initial option control; and in response to a second touch operation continuous with the first touch operation, determining a target option control in the option control set based on a target touch position of the second touch operation or restoring the current display page to the initial display page based on the target touch position. According to the invention, the technical problems that the operation complexity is easily increased and misoperation is easily induced in the touch control mode of the multiple options with the preposition relation provided in the related technology are solved.
Owner:NETEASE (HANGZHOU) NETWORK CO LTD
System and method for XML based data driven generation of a composite source user interface
InactiveUS20080040679A1Efficient and easy generationQuick and accurate selectionExecution for user interfacesMemory systemsGraphicsDisplay device
The subject application is directed to a system and method for generating a dynamic composite source user interface. Text data is received into a data document stored in associated memory. Data representing each of a plurality of graphical elements that correspond to the received text data is then received. A visual indicator, corresponding to each of the graphical elements, is generated on an associated display. Selection data representing a selection of one of the graphical elements on the associated display is then received. Pointer data is then associated with the selected graphical element. The pointer data is further associated with the text data. Next, the selected graphical element is then displayed on the associated display in conjunction with the text data, as referenced by the pointer data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
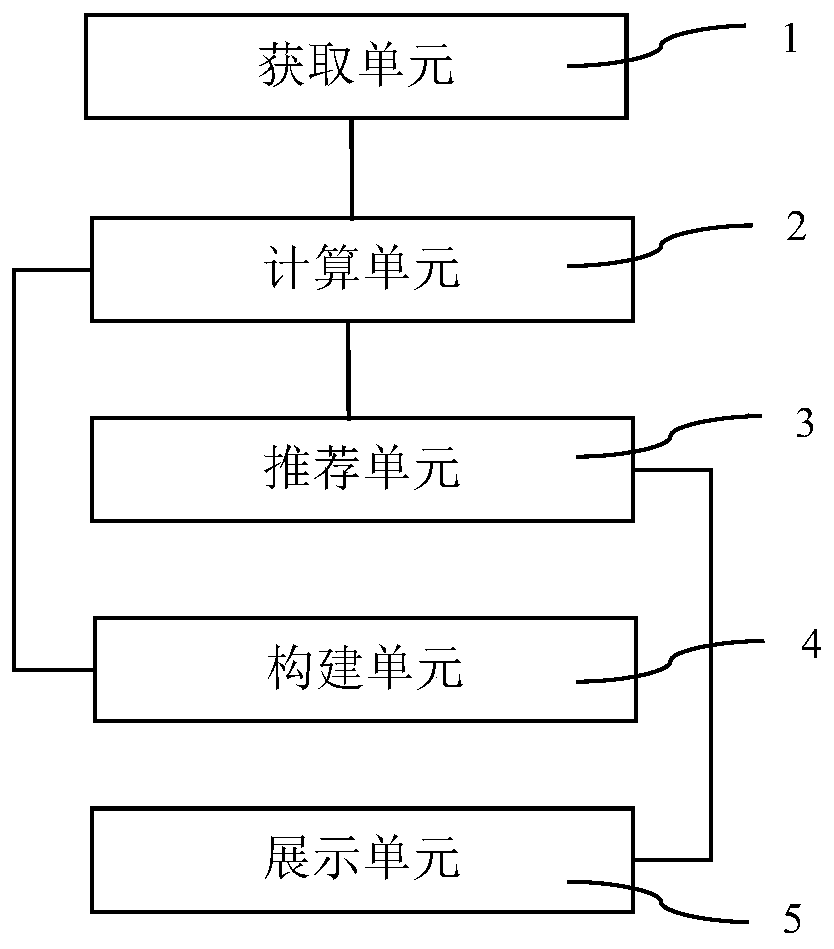
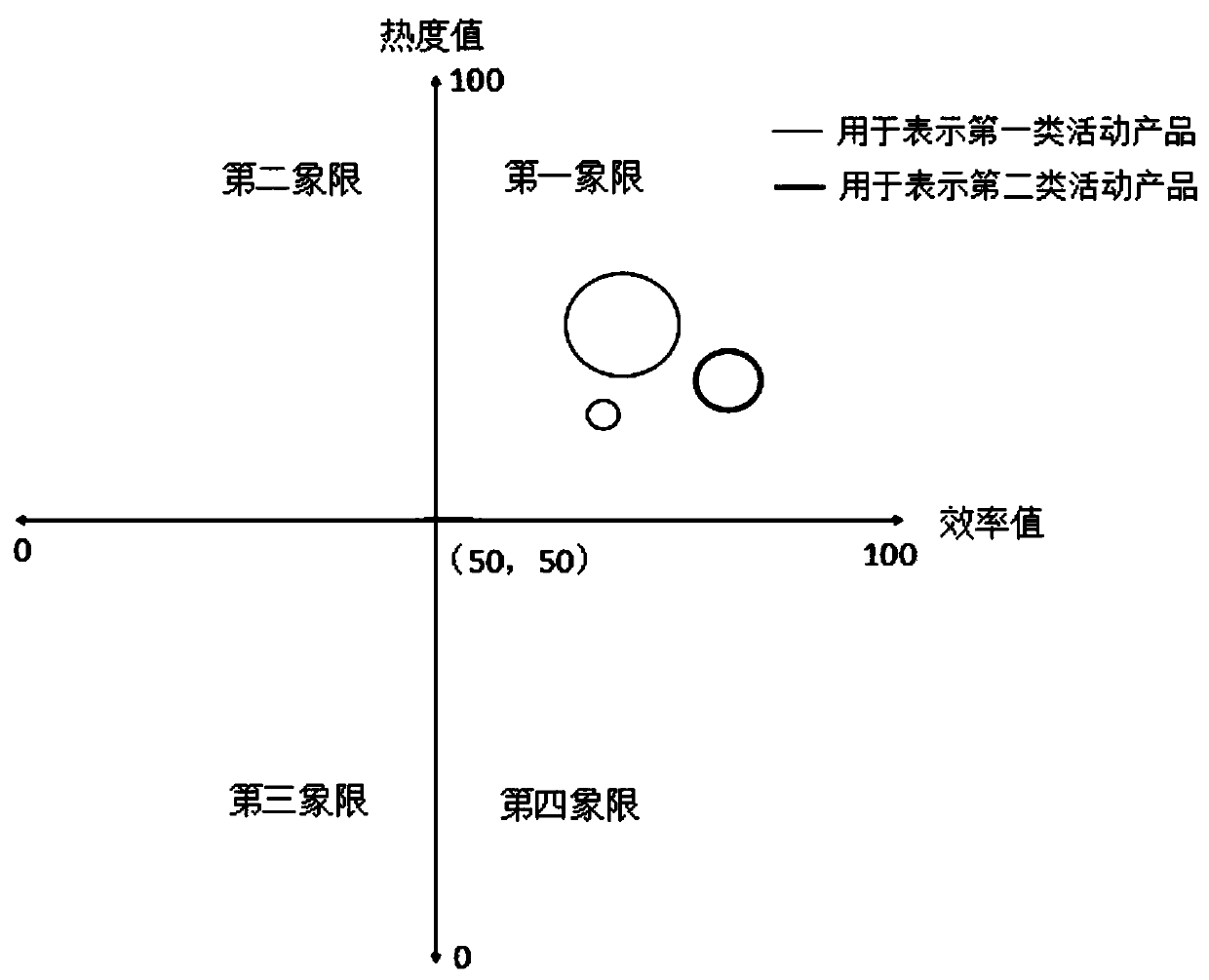
Selected product recommendation system in e-commerce activity process
PendingCN110866220AReal-time adjustmentQuick and accurate selectionDigital data information retrievalBuying/selling/leasing transactionsProduct selectionData mining
The invention relates to the technical field of product recommendation, in particular to a selected product recommendation system in an e-commerce activity process, which comprises an acquisition unitfor acquiring sales data of each type of sales products sold by a user; a calculation unit, connected with the acquisition unit and used for calculating to obtain a reference value associated with each type of sales products according to the sales data and representing the sales state of each type of sales products by adopting the reference value; and a recommendation unit connected with the calculation unit and used for processing the reference value of each type of sales products according to preset activity information to obtain appropriate activity products and outputting the appropriateactivity products to serve as a product selection recommendation result of the current e-commerce activity process. The system has the beneficial effects that the activity product in the e-commerce activity process can be accurately and quickly selected from the sold commodities, and the selected commodity recommendation scheme can be adjusted in real time in the e-commerce activity process, so that the recommendation efficiency is improved, and the sales target is achieved.
Owner:上海新蕴力电子商务有限公司
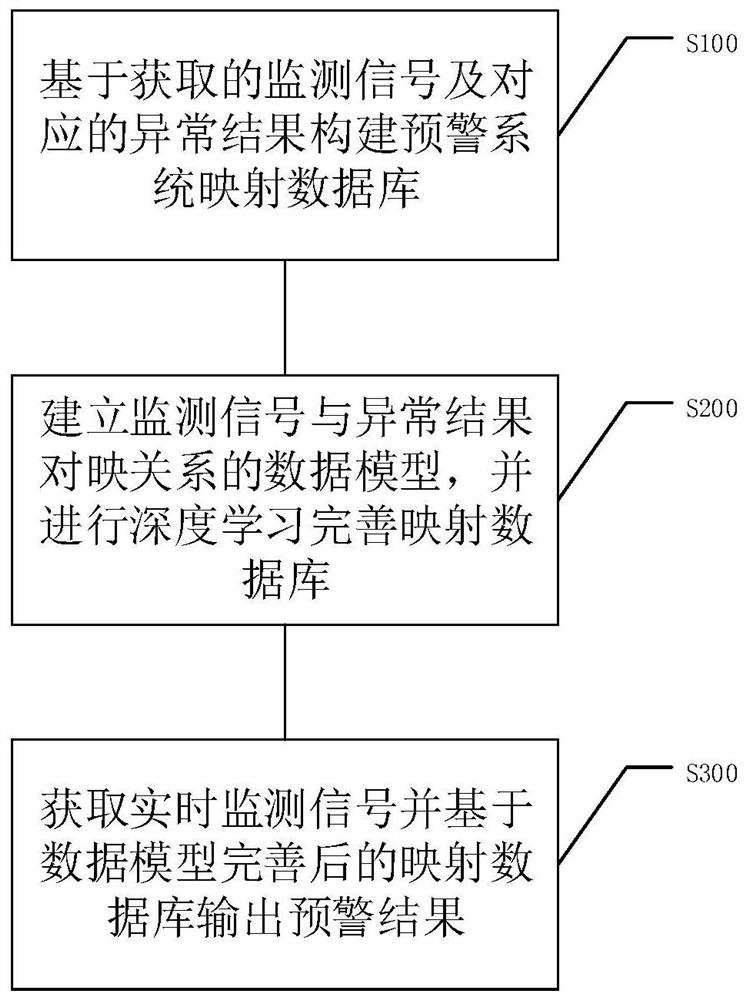
Data model construction method applied to industrial early warning system
InactiveCN113177353AEarly warning is accurateEfficient outputDesign optimisation/simulationMachine learningEarly warning systemAccident risk
The invention discloses a data model construction method applied to an industrial early warning system. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an early warning system mapping database based on an obtained monitoring signal and a corresponding abnormal result; establishing a data model of the enantiomers of the monitoring signals and the abnormal results, and performing deep learning to perfect a mapping database; and acquiring a real-time monitoring signal and outputting an early warning result based on the mapping database after the data model is perfected. By constructing the data model and optimizing the data model through deep learning, accurate early warning can be carried out for specific equipment, efficient output of the blast furnace equipment is achieved, the service life of the blast furnace equipment is prolonged, and the accident risk is reduced; two data models with different dimensions are constructed, the first dimension ensures that the applicability of the data models is good, and the second dimension ensures that the data models are selected quickly and accurately.
Owner:贾选选
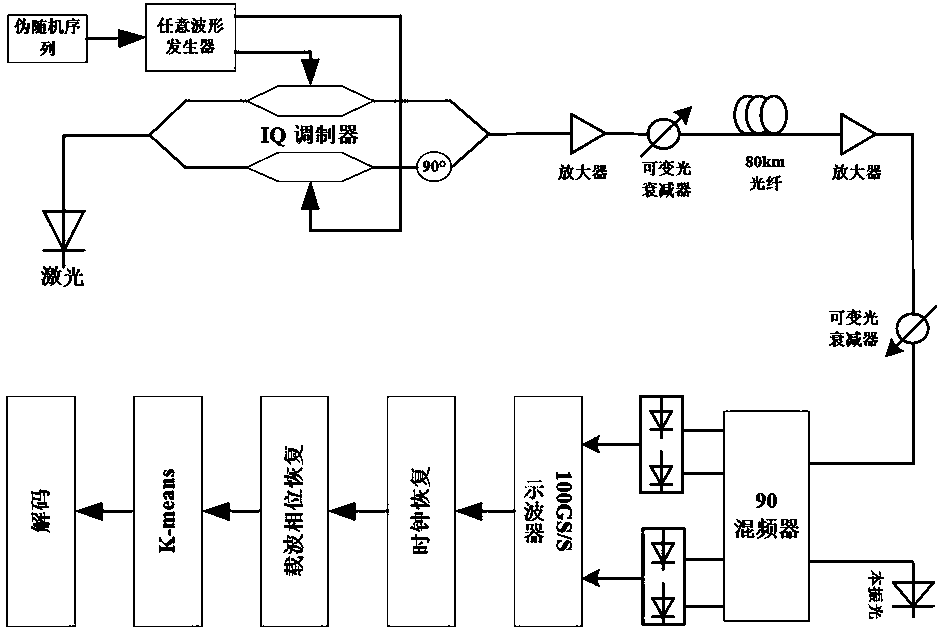
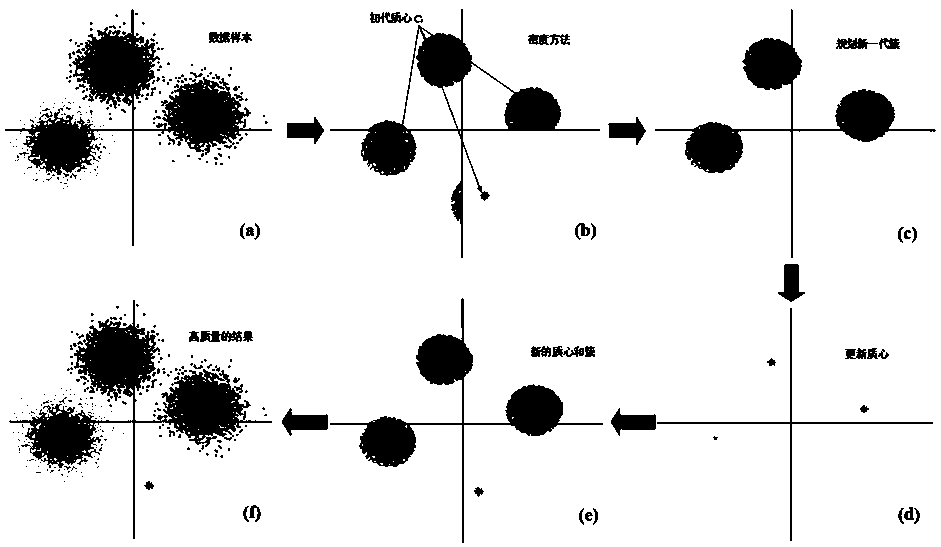
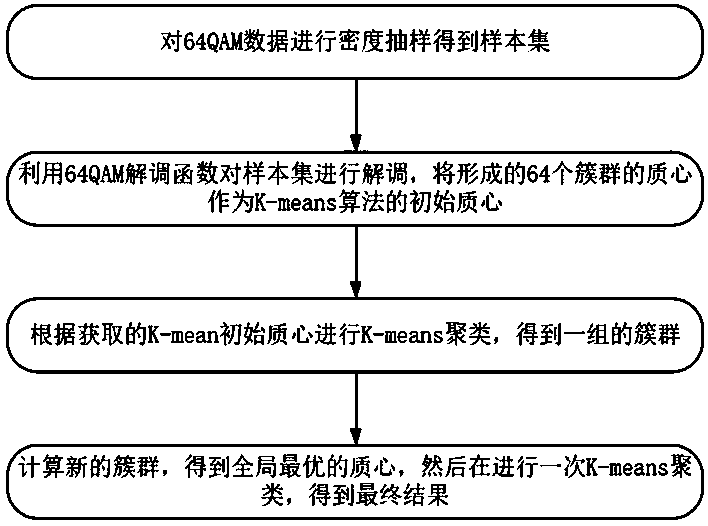
Fiber nonlinear equalization method for 64-qam coherent optical communication system
ActiveCN107707494BReduce the effect of Kerr nonlinearityImprove bit error rate performanceTransmitter/receiver shaping networksElectromagnetic receiversData setEngineering
Disclosed in the present invention is an optical fiber nonlinearity equalization method used in a 64-QAM coherent light communications system, processing received 64-QAM data, and comprising: configuring a received data set to be a first-level data set, calculating a density parameter of each data point, setting a threshold, and selecting data having a density parameter exceeding the designated threshold as a second-level data set; demodulating the second-level data set, dividing into 64 clusters, and acquiring 64 centroids; according to the acquired centroids, categorizing data in the second-level data set into corresponding clusters according to a nearest Euclidean distance, and updating using centroids of 64 acquired new clusters; allocating data in the first-level data set into corresponding clusters according to a nearest Euclidean distance, acquiring 64 clusters after categorization, and calculating an optimum centroid of an acquired cluster. The present invention can rapidly and precisely select a globally optimal K-means cluster centroid without requiring iteration, greatly decreasing the effects of Kerr nonlinearity in optical fiber, and enabling an obtained bit error rate performance to be half an order of magnitude higher than previous un-processed performance.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
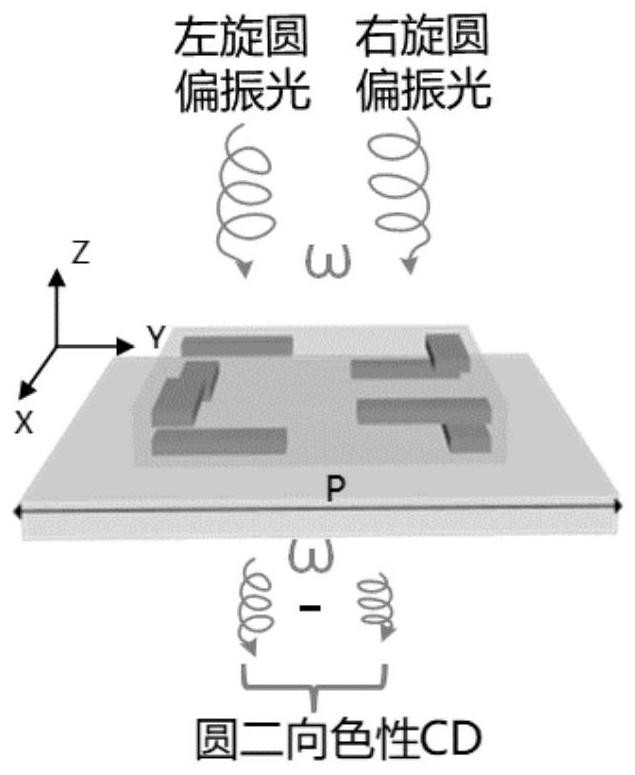
Structure parameter optimization method of chiral super-structure surface and micro-nano device
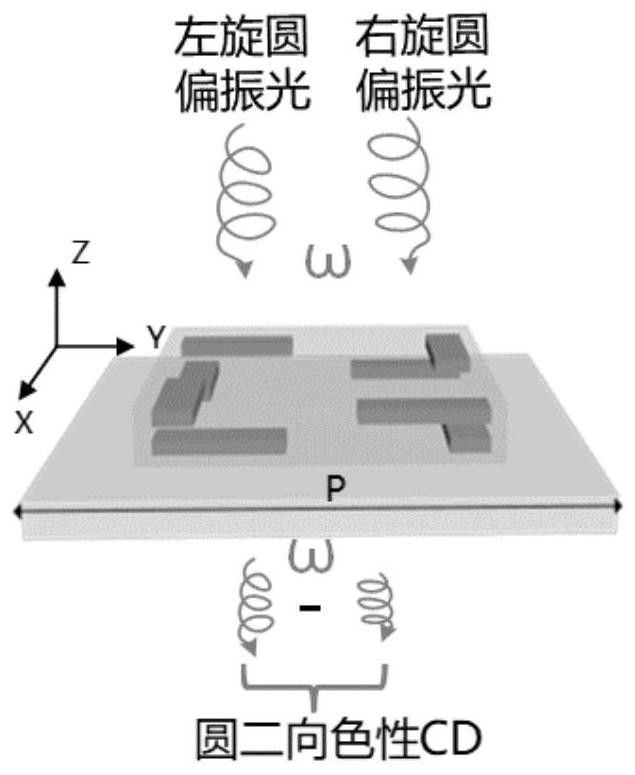
ActiveCN113268911AOptimizing Spectral ResponseImprove speed and optimize resultsDesign optimisation/simulationProbabilistic CADTransmittanceMolecular physics
The invention provides a structure parameter optimization method for a chiral super-structure surface and a micro-nano device, and the method comprises the steps: determining a parameter space of structure parameters based on the optimization range of the structure parameters, and determining an initial population according to the parameter space of the structure parameters; obtaining the transmissivity of the left-handed circularly polarized light and the right-handed circularly polarized light of the chiral metasurface corresponding to each individual in the population under the target wavelength by using a finite difference time domain algorithm, and solving the difference value; determining the fitness of each individual based on the obtained transmissivity difference value corresponding to each individual; selecting, crossing and mutating the individuals in the initial population based on the fitness of each individual, and generating an optimized population; and selecting an individual corresponding to the minimum transmissivity difference value of the left-handed circularly polarized light and the right-handed circularly polarized light under the target wavelength from the optimized population as an optimal structure parameter of the chiral super-structure surface, wherein the individual corresponds to the minimum transmissivity difference value of the left-handed circularly polarized light and the right-handed circularly polarized light under the target wavelength. By adopting the method, the optimal structure parameters of the chiral super-structure surface can be quickly and accurately obtained in a huge parameter space.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
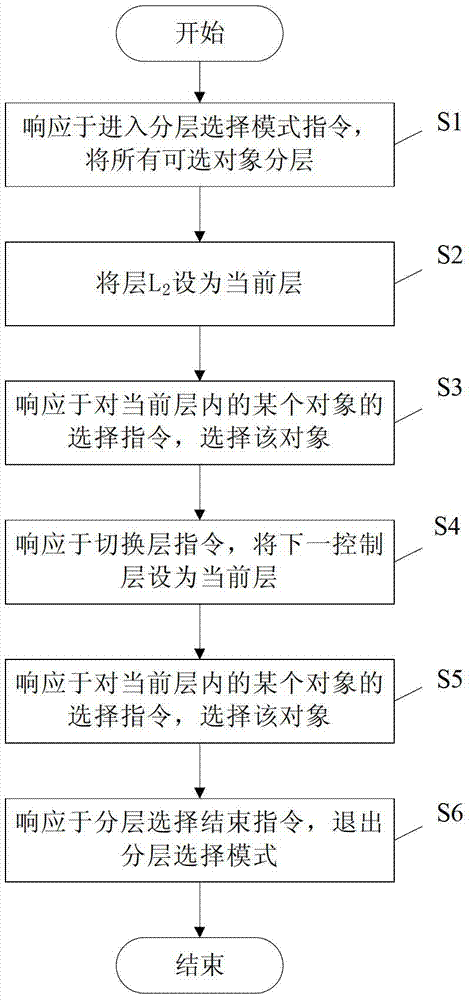
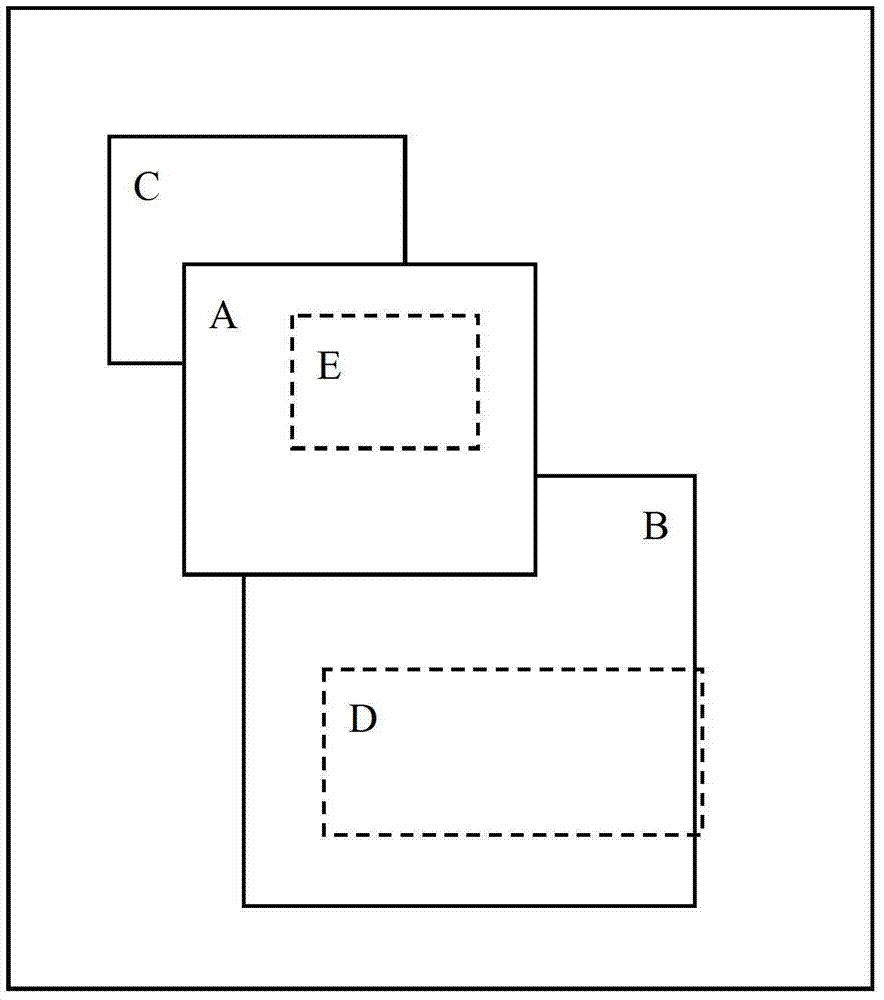
Layered object processing device and method
InactiveCN104182113BQuick and accurate selectionEasy to follow upInput/output processes for data processingComputer architectureObject processing
The present invention provides a layered object processing device, comprising: an instruction input unit that receives an instruction for layering a plurality of operation objects; a processing unit that responds to the layering instruction and assigns a plurality of operation objects to In multiple layers, each operand is assigned to a layer, and each operand has an area that is not covered by other operands in the layer. Accordingly, a method for processing stacked objects is provided. Through the present invention, a plurality of stacked operation objects are processed in layers, so that the overlapping degree of all operation objects in each layer is most conducive to subsequent processing, even if the object is completely covered by other objects, the object can be selected quickly and accurately to process.
Owner:NEW FOUNDER HLDG DEV LLC +1
Mascara applicator
ActiveCN109770524AConvenience guaranteedMeet makeup needsPackaging toiletriesPackaging cosmeticsMascaraEngineering
The invention discloses a mascara applicator and relates to the field of cosmetic tools. The mascara applicator comprises a bottle, an end cover, two mascara brush rods and a brush body, wherein the end cover covers an opening of the bottle, the two mascara brush rods are fixed to the end cover, and the brush body is fixed to the mascara brush rods; the end cover comprises an inner cover body, andthe two ends of the inner cover body are both provided with a rotary connecting part; the mascara brush rods are fixed to the inner cover body and positioned in the middles of the inner sides of thetwo rotary connecting parts respectively; the brush body comprises a thick brush and a sparse brush, wherein the thick brush and the sparse brush are fixed to the ends, away from the inner cover body,of the two mascara brush rods respectively. The end cover also comprises an outer cover body, and the outer cover body is detachably fixed to the outer side wall of the inner cover body. The providedmascara applicator is convenient to use, stable in structure and high in portability and can meet diversified make-up demands of users and greatly improve the make-up experience of the users.
Owner:上海洋明塑料科技有限公司
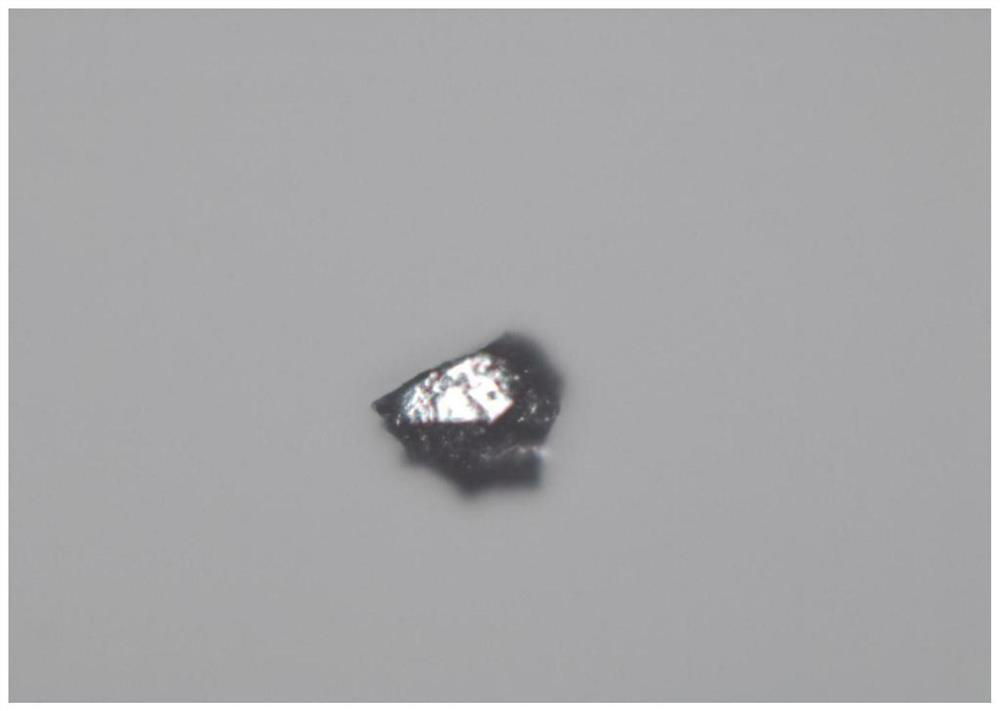
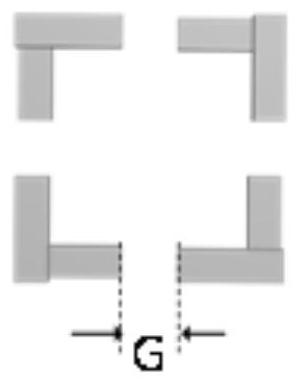
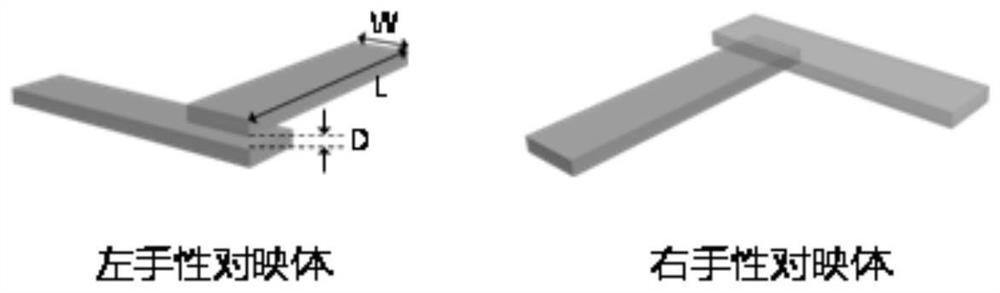
A method for preparing al-pd-fe two-dimensional quasicrystal particles
A method for preparing Al-Pd-Fe two-dimensional quasi-crystal particles, the atomic ratio of the chemical composition of the Al-Pd-Fe quasi-crystal is: Al 70-75%, Pd 10-25%, Fe 5-15 %, fully and uniformly mix high-purity Al powder, Pd powder and Fe powder with a mortar, evenly distribute the mixed metal powder in the cavity of the graphite abrasive tool, pre-press on the mold tablet press, and keep 60 at 1-2MPa ‑100s, wrap a layer of carbon felt outside the graphite crucible, and then follow the steps of carbon paper, large graphite pad, carbon paper, small graphite pad, prepared graphite crucible, small graphite pad, carbon paper, large graphite pad, The carbon papers are sequentially placed in the pressure cavity of the SPS and pressed tightly, the sintering pressure is 50MPa, the temperature is raised to 1000-1100°C and kept for 10-20min, and then cooled to room temperature with the furnace. The invention has the advantages of simple process, strong operability, conventional equipment, less time consumption, and can directly use mixed raw materials to synthesize the two-dimensional quasi-crystal phase while reducing the treatment of raw materials.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Brain wave analysis method based on Hilbert-Huang transform and support vector machine optimization
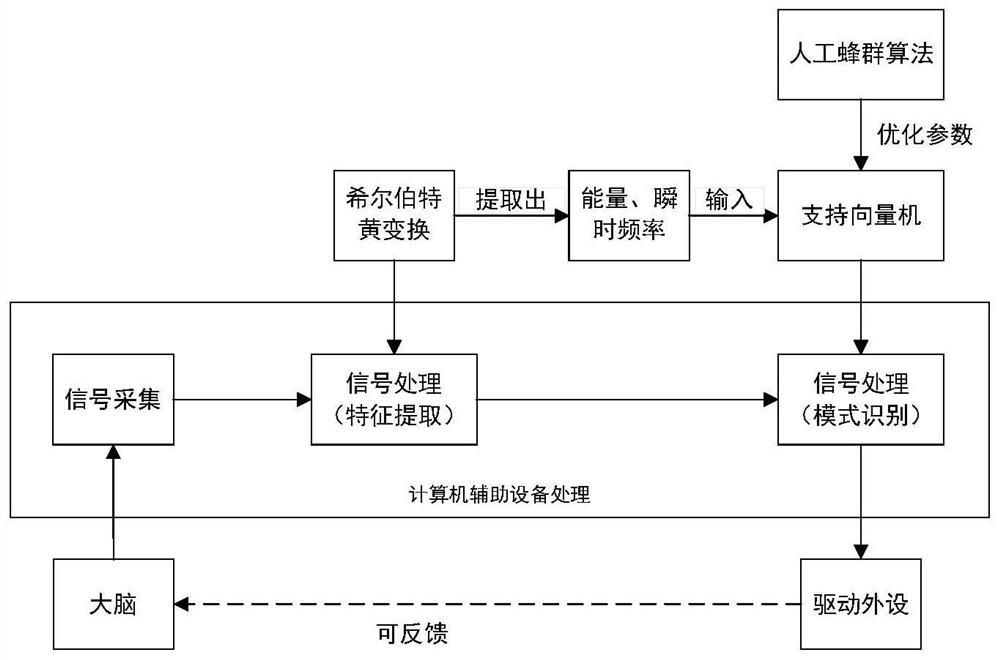
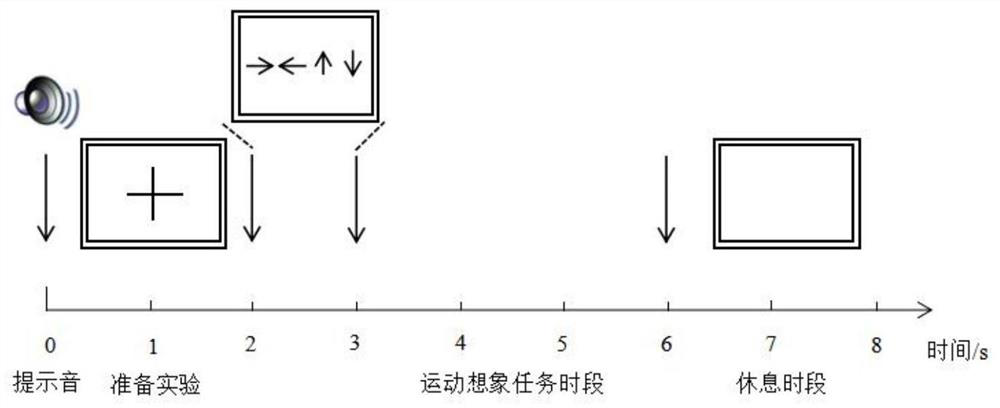
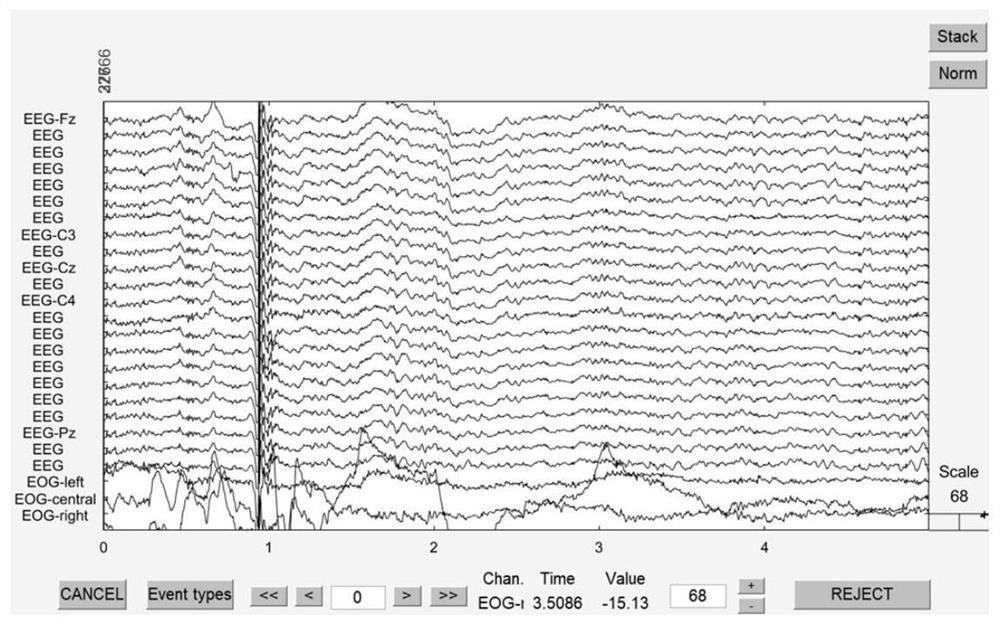
PendingCN112668402AFast and accurate selectionReduce generalization errorBiological modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionHilbert huang transformationSupport vector machine classification
The invention relates to the field of computer signal processing, in particular to a brain wave signal analysis method. The invention discloses a brain wave analysis method based on Hilbert-Huang transform and optimization of an artificial bee colony algorithm and optimization of a support vector machine. The method comprises the following steps: collecting brain wave signal data; wherein the brain wave data are brain wave signals corresponding to imagination of different motion states; decomposing the original brain wave signal by adopting an empirical mode decomposition method to obtain a series of intrinsic mode functions; extracting brain wave features from the intrinsic mode function; and taking the extracted brain wave features as input vectors, and classifying the input vectors by using a classifier so as to distinguish motion states corresponding to the brain wave signals. According to the method, Hilbert-Huang transform is used to extract features, and artificial bee colony algorithm is used to optimize support vector machine classification, so that the method has stronger adaptability, better classification capability and higher calculation efficiency, and is helpful to improve the accuracy of brain wave classification.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
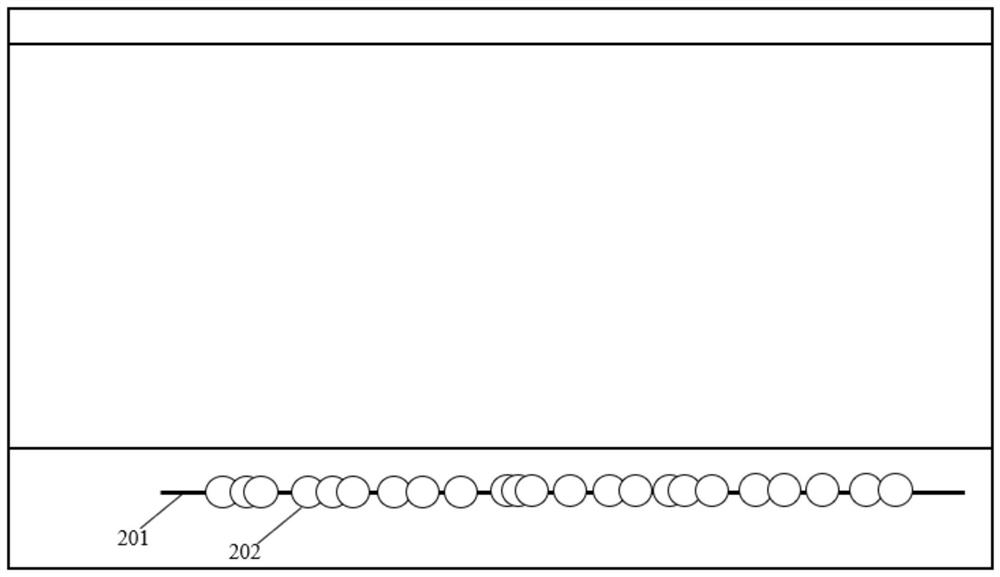
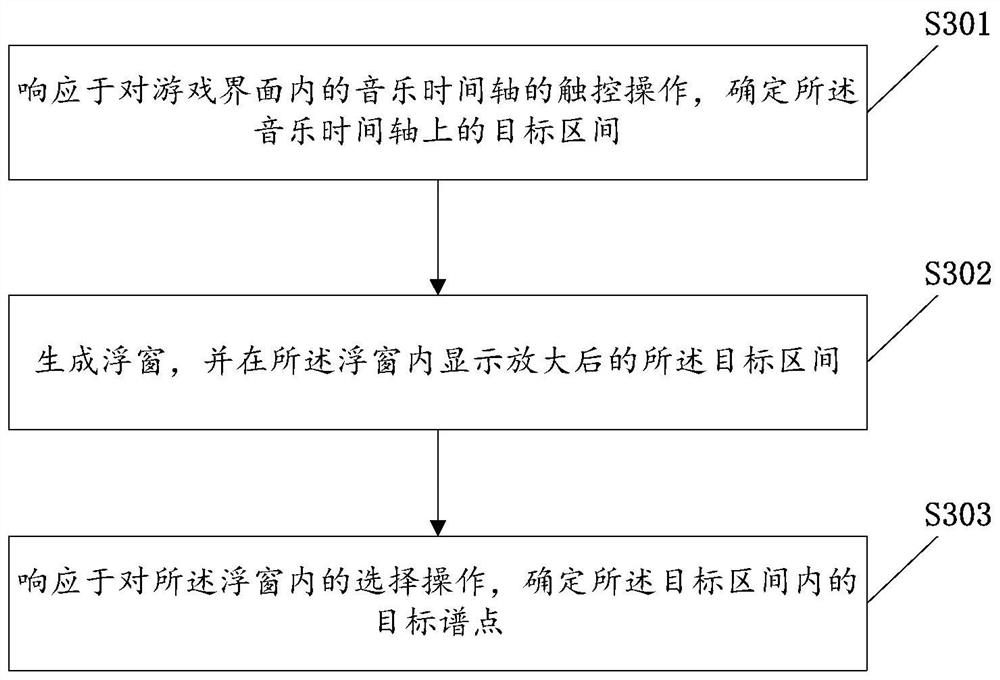
Operation processing method and device in music game, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN113908526AEasy selectionQuick and accurate selectionVideo gamesInput/output processes for data processingComputer hardwareGame interface
The invention provides an operation processing method and device in a music game, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: in response to a touch operation on a music time axis in a game interface, determining a target interval on the music time axis; generating a floating window, and displaying the amplified target interval in the floating window; and in response to a selection operation in the floating window, determining a target spectrum point in the target interval. Through the simple touch operation on the music time axis, the form of the music time axis is kept unchanged, and the amplified target interval is displayed through the floating window, so that a player can further quickly and accurately select the target music point based on the floating window, and while the accurate selection of the music point is realized, the bad problems of high complexity and low efficiency of the existing operation are effectively solved, and the user can accurately, simply and efficiently select the spectrum point when editing the spectrum point.
Owner:NETEASE (HANGZHOU) NETWORK CO LTD
Structural parameter optimization method of chiral metasurfaces and micro/nano devices
ActiveCN113268911BResponsiveQuick and accurate selectionDesign optimisation/simulationProbabilistic CADNano-deviceTransmittance
The invention provides a structural parameter optimization method of a chiral metasurface and a micro-nano device. The method includes: determining the parameter space of the structural parameter based on the optimization range of the structural parameter, and determining the initial population according to the parameter space of the structural parameter; The domain finite difference algorithm obtains the transmittance of the left-handed circularly polarized light and the right-handed circularly polarized light of the chiral metasurface corresponding to each individual in the population at the target wavelength, and calculates the difference; The corresponding transmittance difference determines the fitness of each individual; based on the fitness of each individual, select, cross, and mutate individuals in the initial population to generate an optimized population; select left-handed circular polarization at the target wavelength from the optimized population The individual corresponding to the minimum value of the transmittance difference between light and right-handed circularly polarized light is the optimal structural parameter of the chiral metasurface. Using this method, the optimal structural parameters of the chiral metasurface can be quickly and accurately obtained in a huge parameter space.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Double-end lip gloss pen
ActiveCN109527775AMultiple choiceMeet diverse makeup needsPackaging toiletriesPackaging cosmeticsEngineering
The invention discloses a double-end lip gloss pen, and relates to the field of makeup tools. The double-end lip gloss pen comprises a main pen container and two pen point assemblies. Each pen point assembly comprises a main pen cover in threaded screwed connection to the end of the main pen container, a main pen rod fixed to the main pen cover, and a main pen point fixed to the end, away from themain pen cover, of the main pen rod. The main pen container is of a structure with openings formed in the two ends, a first sub-cavity and a second sub-cavity are formed in the main pen container atintervals, and the first sub-cavity and the second sub-cavity are close to and communicated with the openings in the two ends of the main pen container respectively. The two main pen covers are in threaded screwed connection to the openings in the two ends of the main pen container respectively, and the two main pen rods are inserted into the first sub-cavity and the second sub-cavity respectively. The double-end lip gloss pen is convenient to use, rich in makeup effect and high in interestingness, the diverse makeup requirements of users can be met, and the makeup experience of the users canbe greatly improved.
Owner:上海洋明塑料科技有限公司
Method for preparing Al-Pd-Fe two-dimensional quasicrystal particles
The invention discloses a method for preparing Al-Pd-Fe two-dimensional quasicrystal particles. The Al-Pd-Fe quasicrystal comprises 70-75% of Al, 10-25% of Pd and 5-15% of Fe. The method comprises: fully and uniformly mixing high-purity Al powder, Pd powder and Fe powder through a mortar, uniformly distributing the mixed metal powder in a graphite abrasive cavity, pre-pressing the mixed metal powder through a mold tableting machine, keeping 1-2MPa for 60-100s, coating a graphite crucible with a carbon felt, orderly placing a carbon paper, a large graphite block, a carbon paper, a small graphite cushion block, the prepared graphite crucible, a small graphite cushion block, a carbon paper, a large graphite cushion block and a carbon paper in a pressure chamber of SPS, carrying out compression, carrying out heating to 1000 to 1100 DEG C under sintering pressure of 50MPa, keeping the temperature for 10-20min and carrying out furnace cooling to the room temperature. The method has simple processes and strong operability, utilizes conventional equipment, has small time consumption, is free of raw material treatment and directly uses mixed raw materials to synthesize the two-dimensional quasicrystalline phase.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
A mascara applicator
ActiveCN109770524BConvenience guaranteedMeet diverse makeup needsPackaging toiletriesPackaging cosmeticsOphthalmologyMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a mascara applicator, which relates to the field of cosmetic tools, and comprises a bottle, an end cap covering the opening of the bottle, an eyelash brush rod fixed on the end cap, and a brush body fixed on the eyelash brush rod The end cover includes an inner cover body, and both ends of the inner cover body are formed with screw joints; the eyelash brush rod is fixed on the inner cover body, and one eyelash brush rod is respectively provided at the inner center of the two screw joint parts; the brush body includes Thickening brush and thinning brush, thickening brush and thinning brush are respectively fixed on the ends of the two mascara brush rods away from the inner cover; the end cap also includes an outer cover, which is detachably fixed on the outer wall of the inner cover. The invention provides a mascara applicator which is convenient to use, stable in structure, high in portability, can meet the diversified makeup needs of users, and can greatly improve the makeup experience of users.
Owner:上海洋明塑料科技有限公司
A double-ended lip gloss pencil
ActiveCN109527775BMeet diverse makeup needsImprove makeup experiencePackaging toiletriesPackaging cosmeticsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a double-headed lip gloss pen, which relates to the field of makeup tools, and comprises a main pen holder and a nib assembly. The main nib of the pen holder is far away from the end of the main pen cap; the main pen barrel has an open structure at both ends, and the interior of the main pen barrel is formed with a first sub-cavity and a second sub-cavity, and the first sub-cavity and the second sub-cavity are respectively close and communicated Both ends of the main pen holder are open; two sets of nib assemblies are provided, and the two main pen caps are respectively screwed to the openings at both ends of the main pen holder, and the two main pen holders are respectively inserted into the first sub-cavity and the second sub-cavity. The invention provides a double-ended lip gloss pencil which is easy to use, has rich makeup effects, and is highly interesting, helps to meet the diverse makeup needs of users, and can greatly improve the makeup experience of users.
Owner:上海洋明塑料科技有限公司
A system construction method with intelligent recommendation of instruction wizard
ActiveCN112417257BQuick and accurate selectionQuick and precise constructionNatural language data processingExecution for user interfacesUser inputEngineering
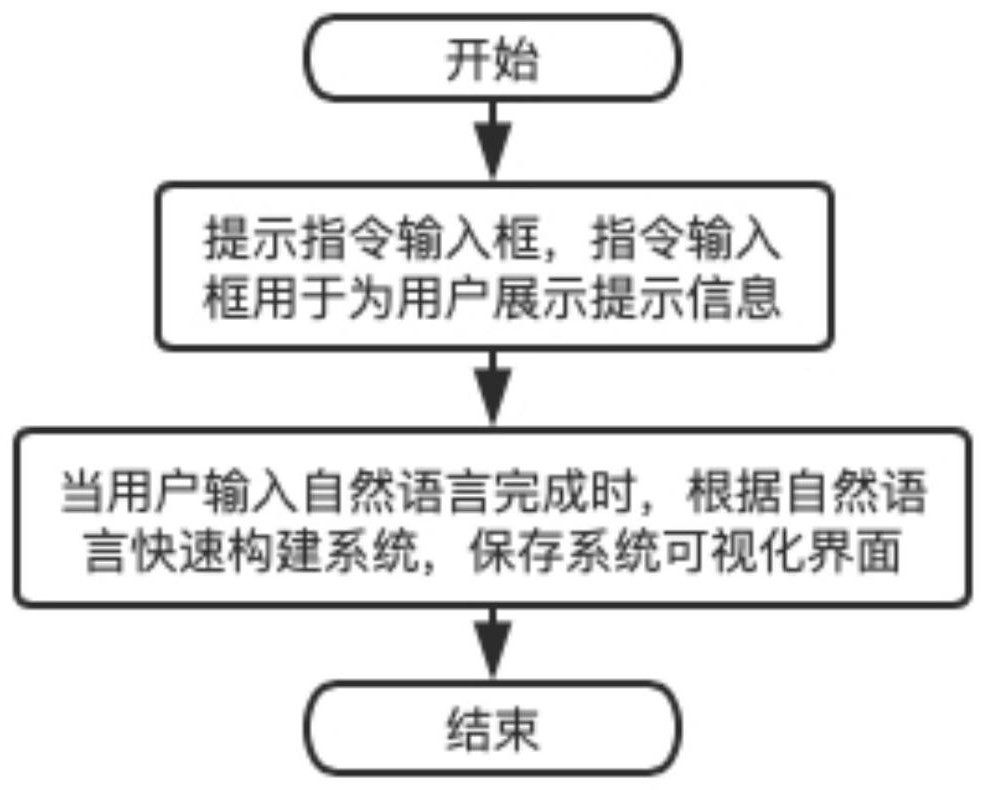
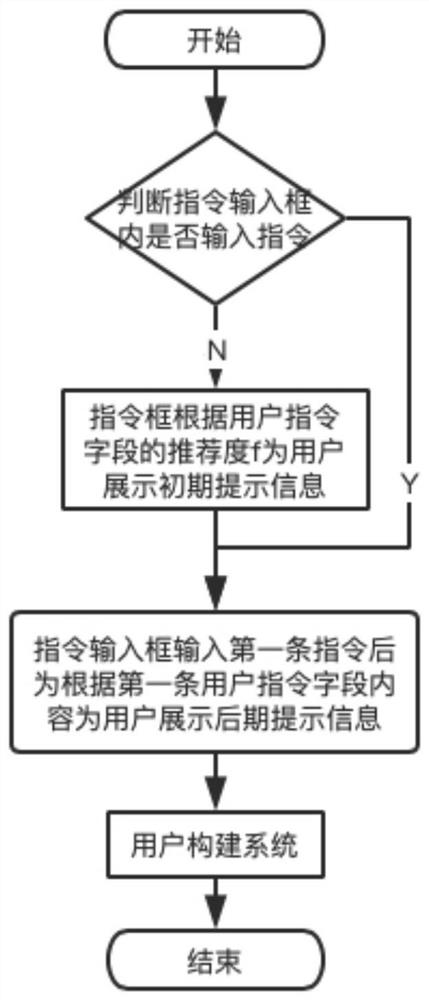
The invention discloses a system construction method with instruction guide intelligent recommendation. Overcoming the problem of complex construction process of the visual interface caused by the inability of the instruction to accurately match the field in the prior art, including providing a voice instruction input box, the present invention provides an instruction input box, and the instruction input box can provide the user with prompt information, and the prompt information includes initial prompt information and the later prompt information; the present invention displays the initial prompt information for the user when the user does not input an instruction in the instruction input box, that is, the prompt information sorted according to the recommendation degree of all characters. An instruction that provides users with different types of post-prompt information according to the different instructions entered by the user when the user enters an instruction in the instruction input box, so that the user can quickly and accurately select the desired field, save time, improve accuracy, and provide visualization The precise and rapid construction of the page provides feasibility.
Owner:杭州讯酷科技有限公司
Turbine test bed of aero-engine under high altitude and low Reynolds number, simulation method and application
ActiveCN114279714AQuick and accurate selectionImprove work efficiencyGas-turbine engine testingSustainable transportationTested timeSystems simulation
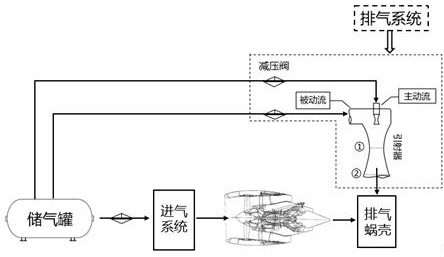
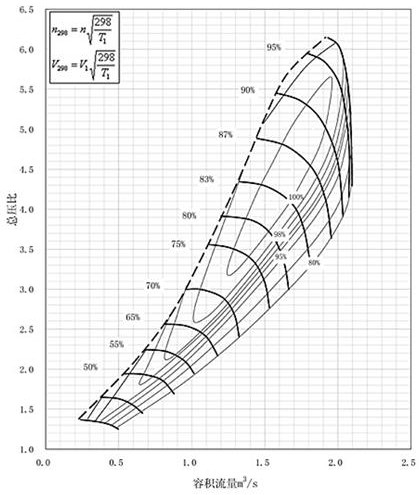
The invention provides a simulation method and application of an aero-engine turbine test system under a high-altitude low Reynolds number. The method comprises the steps that input conditions such as performance design points and limit boundaries of an aero-engine air inlet system are obtained through arrangement, and design points and limit boundaries of an exhaust system under the high-altitude low Reynolds number working environment are obtained through analysis; obtaining injection coefficients of active flow and passive flow of the ejector according to the design principle of the ejector; preliminary design parameters of the exhaust system are obtained through numerical simulation; the preliminary design parameters are repeatedly optimized according to limiting conditions, and finally the exhaust contour is determined; due to the fact that an air inlet system and the pressure and flow ranges required by active flow and passive flow of an ejector are different, a pressure reducing valve needs to be selected based on the design standard of a pressure reducing valve for compressed air JISB3372-1982, and finally the opening degree of the pressure reducing valve and the longest test time under the working condition are determined. According to the turbine test system simulation method provided by the invention, rapid design and shaping of the test system can be realized, so that the test process is simpler, more convenient and more accurate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Notification and transmission method of relay node access capability
The invention discloses a notification and transmission method of the access capability of a relay node. The notification method of the access capability of a relay node comprises the following steps: a cell broadcasts the access capability information of a relay node of the cell by system messages; and whether the relay node can access the cell is judged by the relay node according to the capability information. In the notification and transmission method disclosed by the invention, the relay node can acquire the access capability information of the relay node of the cell so as to provide a reference for the relay node in selecting the access cell, so that the problems that the access resource is wasted and the access is delayed as a relay node accesses a cell which does not support the access of the relay node are avoided.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Display style setting method of vector electronic map information
ActiveCN102789361BQuick and accurate selectionImprove visual effectsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsComputer science
The invention discloses a display style setting method of vector electronic map information and belongs to the technical field of geographical information system map arrangement. The display style setting method includes: checking whether prerequisite conditions are already; loading a map, wherein selected priority level is set according to map element types; clicking any point on a map, obtaining the coordinate of the point, and judging whether map element objects exist in a circular area formed with a point selected from all layers displayed in the map as the center and the radius as 10 pixels; judging whether a selected layer is a layer with the style to be modified by a user; and the like. According to the display style setting method, the user can use a picture base built by the user and representing the map element types as required, set the selected priority level according to objects needed to be selected, fast and accurately select the layers where the elements are located, modify the element style and enrich contents, select appropriate style display elements autonomously and modify the style of the selected layers for many times. The display style setting method improves visual effect of an electronic map.
Owner:哈尔滨哈船导航技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com