Efficient and convenient and quick simple robot calibrating method
A calibration method and robot technology, applied in manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of poor practicability and convenience of zero-position calibration, low robot control accuracy, and complicated processes, so as to reduce the cost of measurement equipment, Improve usability and convenience, measure simple effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
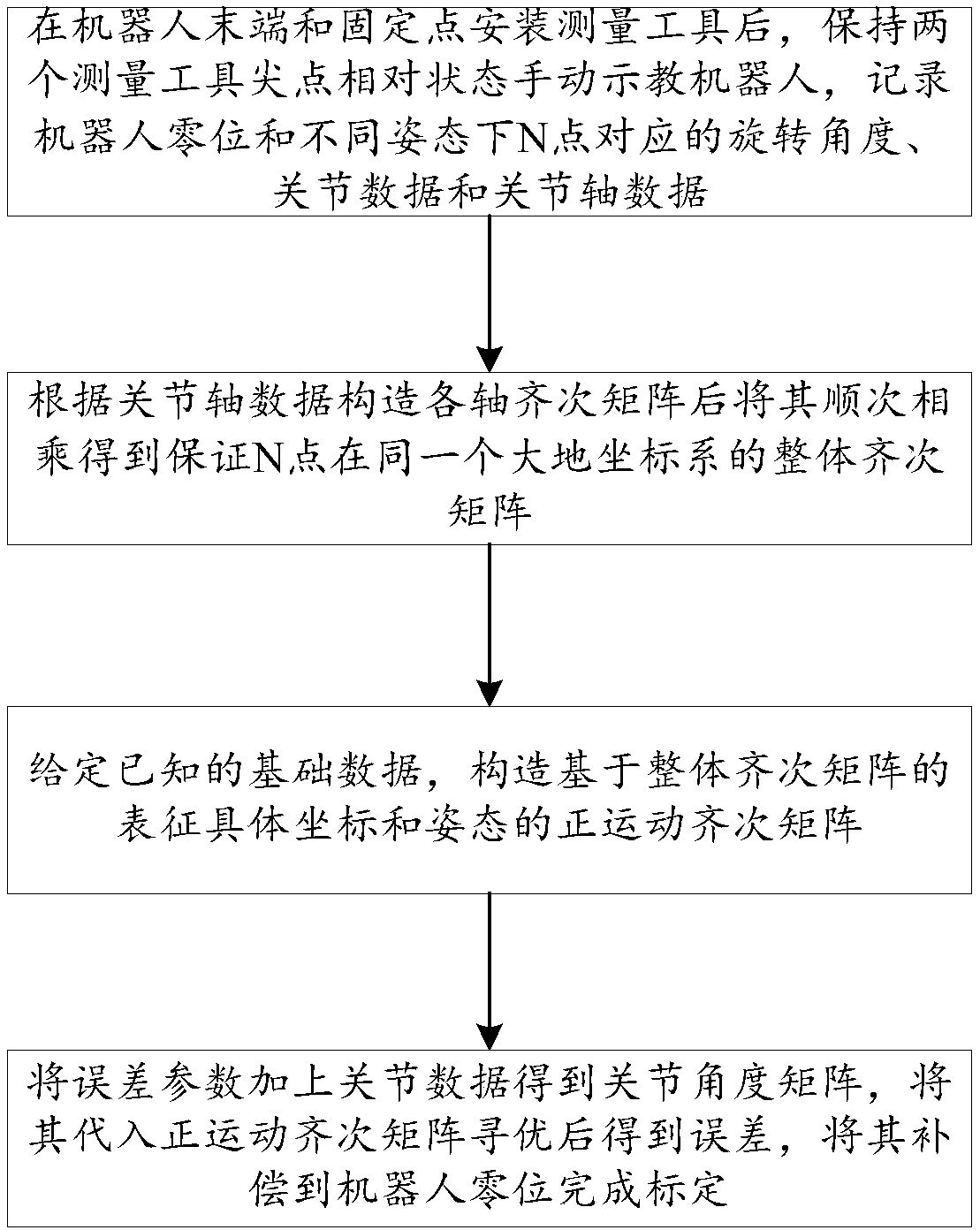
[0037] An efficient and convenient simple robot calibration method, comprising the following steps:
[0038] Step 1: After installing the measuring tool at the end of the robot and the fixed point, keep the sharp points of the two measuring tools facing each other and teach the robot manually, and record the robot zero position and the rotation angle, joint data and joint axis data corresponding to the N point in different postures;
[0039] Step 1 includes the following steps:
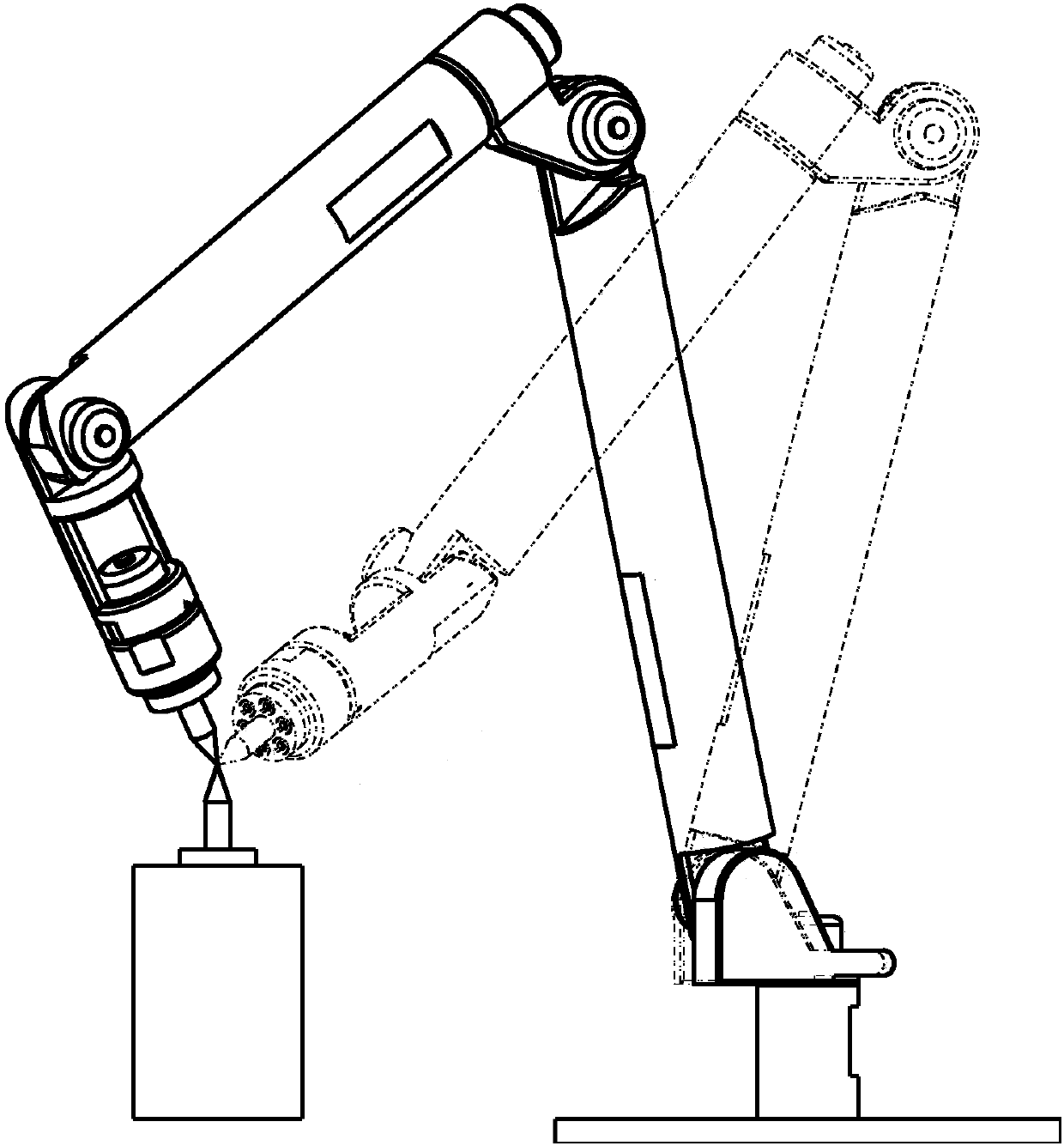
[0040] Step 1.1: Install measuring tool 1 on the end flange of the robot, and install measuring tool 2 at a fixed point within the robot’s motion range;
[0041] Step 1.2: Always keep the cusp of measuring tool 1 and measuring tool 2 facing each other, manually teach the robot, and record the robot zero position and the rotation angle, joint data and joint axis data corresponding to point N in different postures.
[0042] Step 2: Construct the homogeneous matrix of each axis according to the joint ax...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Take a robot with six degrees of freedom as an example:
[0059]Step 1: Install measurement tool 1 on the end flange of the robot, and install measurement tool 2 at a fixed point within the robot’s motion range; always keep the sharp point of measurement tool 1 and measurement tool 2 facing each other, and manually teach the robot to obtain different postures The rotation angle θ corresponding to the next 20 points 1 ,θ 2 ,θ 3 ,θ 4 ,θ 5 ,θ 6 , joint data and joint axis data f(θ 1 ,θ 2 ,θ 3 ,θ 4 ,θ 5 ,θ 6 ) and record the zero value;
[0060] Step 2: Construct a homogeneous matrix for each axis, such as 1 axis for Abbreviation for joint J 1 Coordinate system rotation θ 1 The homogeneous coordinate system matrix relative to the Cartesian coordinate system after degrees, where [r 11 r 12 r 13 ] represents the vector of the x-axis of the coordinate system relative to the earth coordinate system, [r 21 r 22 r 23 ] represents the vector of the y...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com