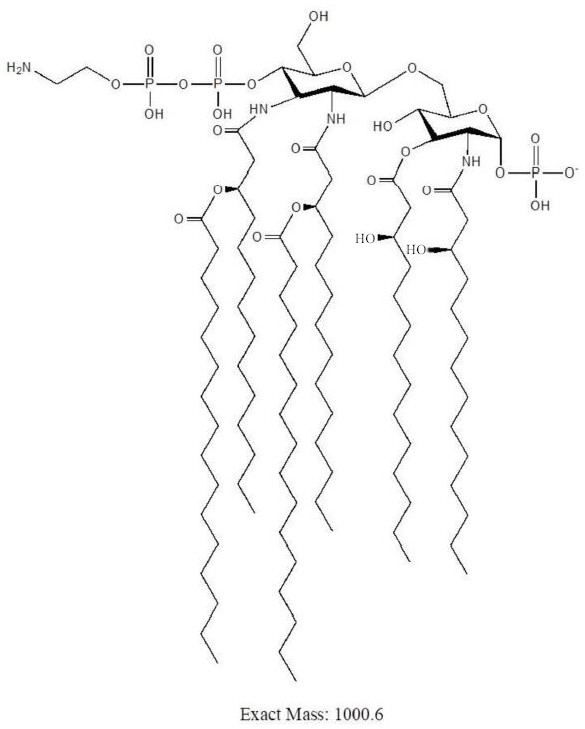
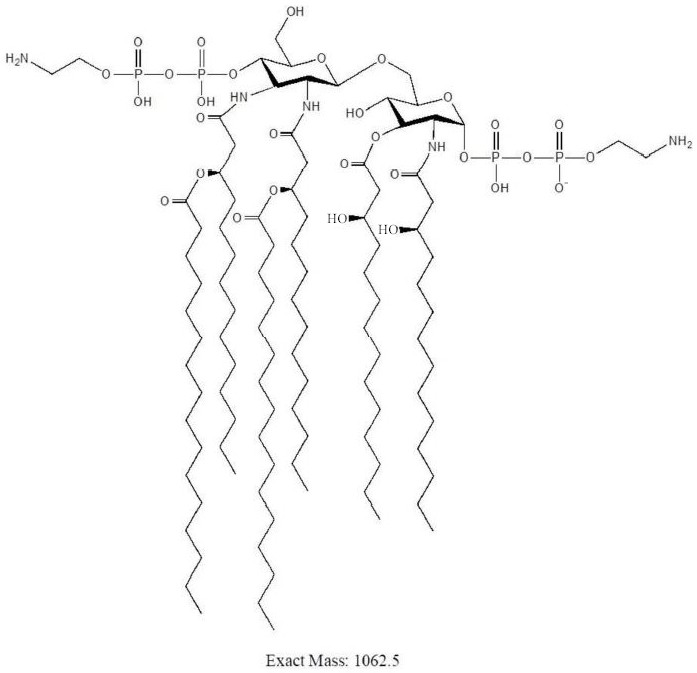
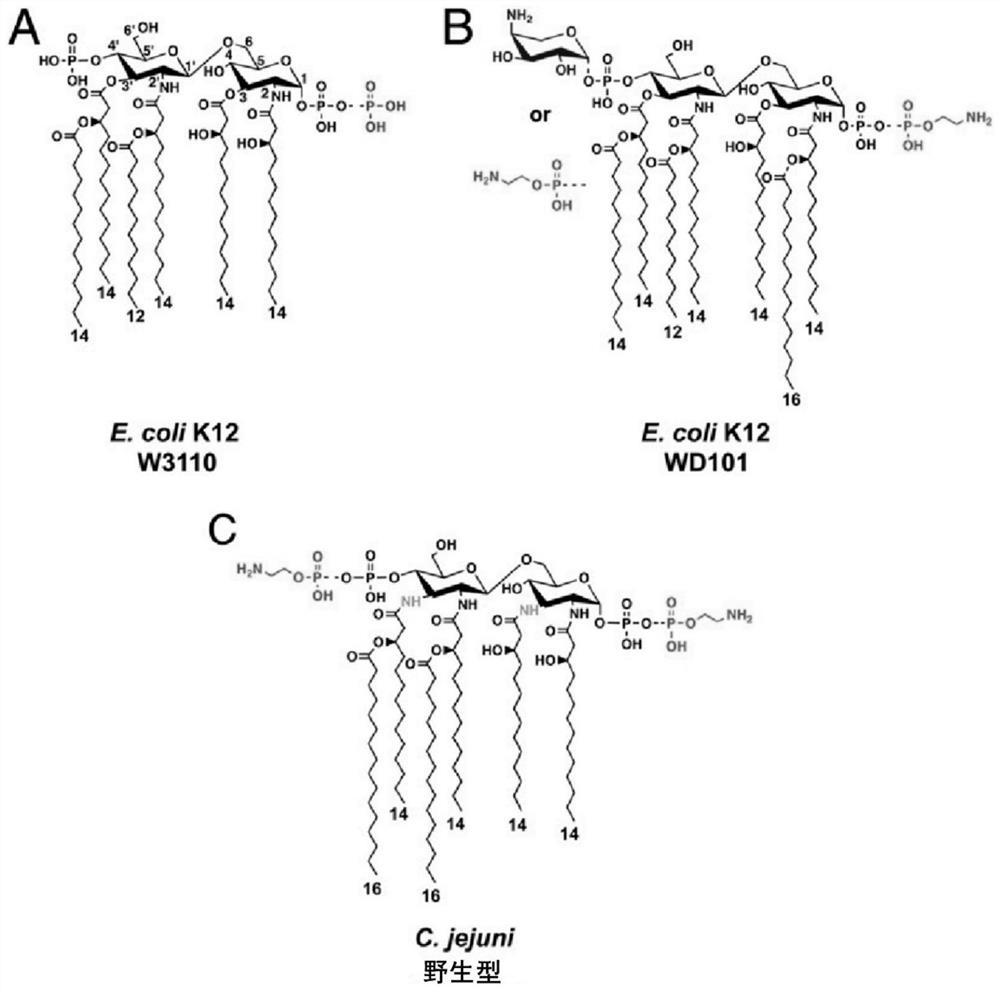
A method for analyzing endotoxin lipid a by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
A liquid mass spectrometry and endotoxin technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry mass spectrometry identification, can solve the problems of different degrees of phosphorylation, achieve complete hydrolysis, improve the detection limit, and improve the effect of extraction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] Preparation of ammonium salt of EDTA: 700 mg of EDTA was dissolved in 1 ml of 30% ammonia water, freeze-dried and stored, and all reagents were of analytical grade.
[0033] It is found through research that the present invention is suitable for analyzing the cell membrane lipid A of Gram-negative bacteria or a small amount of cells. Specifically, the analysis strain in the embodiment is Campylobacter jejuni C. jejuni strains are examples and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
Embodiment 1
[0035] A method for analyzing lipooligosaccharide lipid A by liquid chromatography-mass chromatography (HPLC-MS), comprising the steps of:
[0036] S1. Strain treatment (Campylobacter jejuni C. jejuni Strains 81176 and 11168): Suspend the dried bacterial cells evenly in the aqueous solution, control the cell concentration to 1 mg / mL, freeze at -40°C or -44°C or at -40°C or -44°C or -46°C or -48°C or -50°C) freeze-dried storage;
[0037] S2. Extract endotoxin lipid A: hydrolyze the freeze-dried cells, centrifuge the mixture after cooling at 0 or 5 or 8 or 12 or 15 or 21 or 25°C, add a volume ratio to the washed precipitate A 4:4:1 mixed solution of chloroform, methanol, and ammonium acetate was centrifuged, the supernatant was collected, and dried with nitrogen;
[0038] S3. HPLC-MS analysis:
[0039] Chromatographic conditions: amide column inner diameter 0.3mm, length 10cm; mobile phase A: 10 mM ammonium acetate in water; mobile phase B: 96% tetrahydrofuran solution conta...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Hydrolysis condition optimization
[0049] After step S1 was completed, 50 μg of freeze-dried cells were divided into 3 groups, suspended in 150 μL of 1% acetic acid, 150 μL of 50 mM pH4.0 ammonium citrate (NH 4 Cit) and 150 μL of 50 mM pH5.5 ammonium citrate, the suspension was heated to 100 °C, and the hydrolysis reaction continued for 1 hour under the same conditions. After the hydrolyzate was cooled, centrifuged, and washed, chloroform-methanol-water with a volume ratio of 4:4:1 was added to extract lipid A and the MALDI-TOF spectrum was obtained according to the MALDI-TOF / TOF analysis method described, as shown in figure 2 shown.
[0050] The target structure ions m / z 1921.4, m / z 1798.4 and m / z 1879.4 can be detected in the three hydrolysis methods, compared with figure 2 In (A) there are fewer impurity ions, and the proportion of target ions is relatively high, so 1% acetic acid can hydrolyze lipooligosaccharide LOS more thoroughly, which is the preferred hydr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com