Three-dimensional cell gradient mechanics loading experiment platform based on tissue specific shape
A technology of three-dimensional cells and specific shapes, which is applied in the field of mechanical stimulation of cells and tissues, can solve the problems that mechanical gradients and mechanical stimulation cannot be simulated, and achieve the effects of adjustable mechanical gradient, controllable size and convenient use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0040] The preparation of the three-dimensional tissue module 3 encapsulating cells is firstly to mix the biological material and the cells, and then inject the formed mixture into a mold with a specific geometric configuration prepared from organic or inorganic materials, and the specific geometric configuration The type of die is a geometric configuration with a mechanical gradient.
[0041] The geometric configuration of the mechanical gradient is a conical structure or a terraced structure.
[0042] The shape of the three-dimensional tissue module 3 encapsulating the cells is a geometric configuration with a mechanical gradient, preferably a frustoconical structure or a terraced structure.
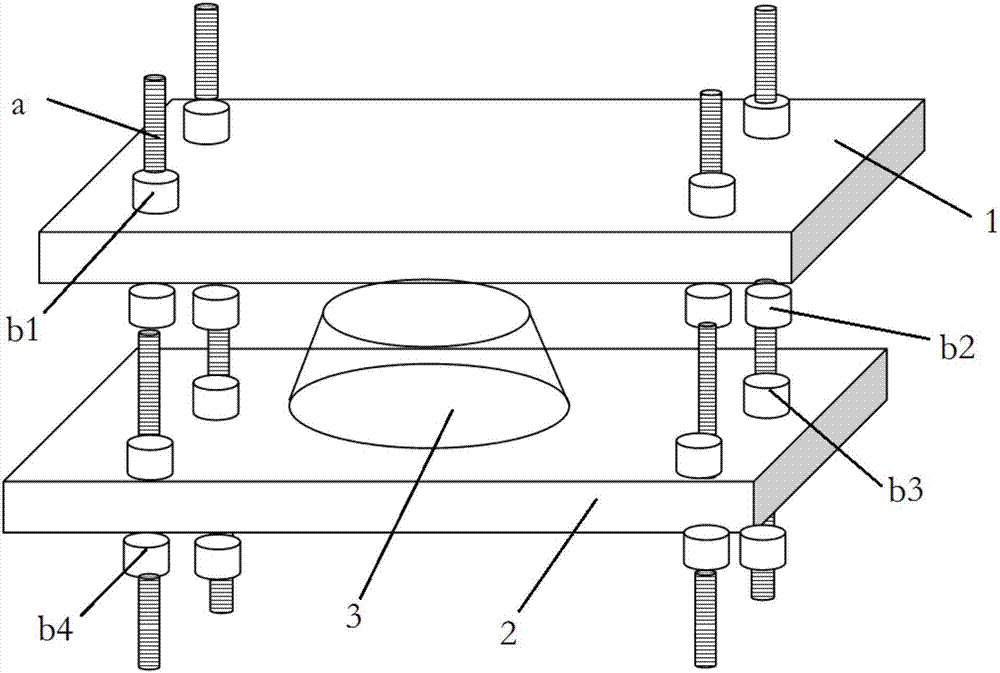
[0043] The three-dimensional tissue module 3 encapsulating the cells is respectively connected to the first splint 1 and the second splint 2 through 502 glue.
[0044] The two splints are respectively provided with four passage holes corresponding to each other. The first splint 1 and...
Embodiment 1
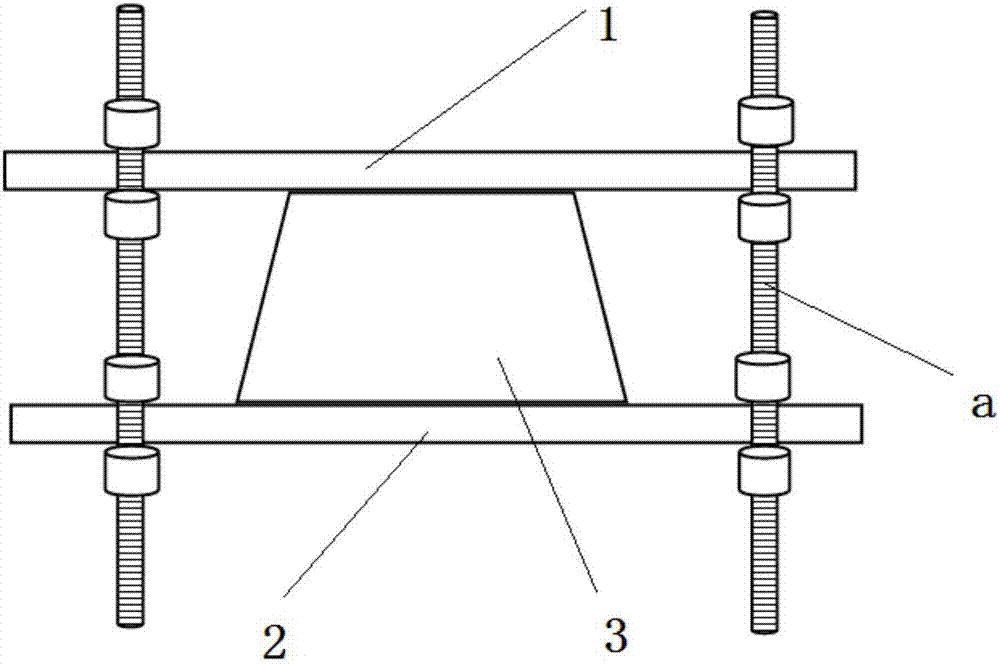
[0052] refer to Figure 1a and Figure 1b , use computer to design two rectangles (the length of the rectangle is 25mm, the width is 15mm, and the thickness is 5mm) as the upper and lower splints of the three-dimensional cell gradient mechanical loading mold. The mechanical loading device is obtained by cutting the organic material PMMA. Four through holes with the same diameter as the threaded column b are drilled at both ends of the two PMMA splints, and the diameter of the threaded column b is 1.5 mm.
[0053] A cell-wrapped three-dimensional tissue module 3 is sandwiched between the two splints, and the contact parts between the cell-wrapped three-dimensional tissue module 3 and the two splints are bonded with 502 glue. The two splints are arranged in parallel, and the two ends of the two splints are provided with through holes with a diameter of 1.5 mm. The two through holes corresponding to the positions of the two splints pass through a threaded column a, and the outer ...
Embodiment 2
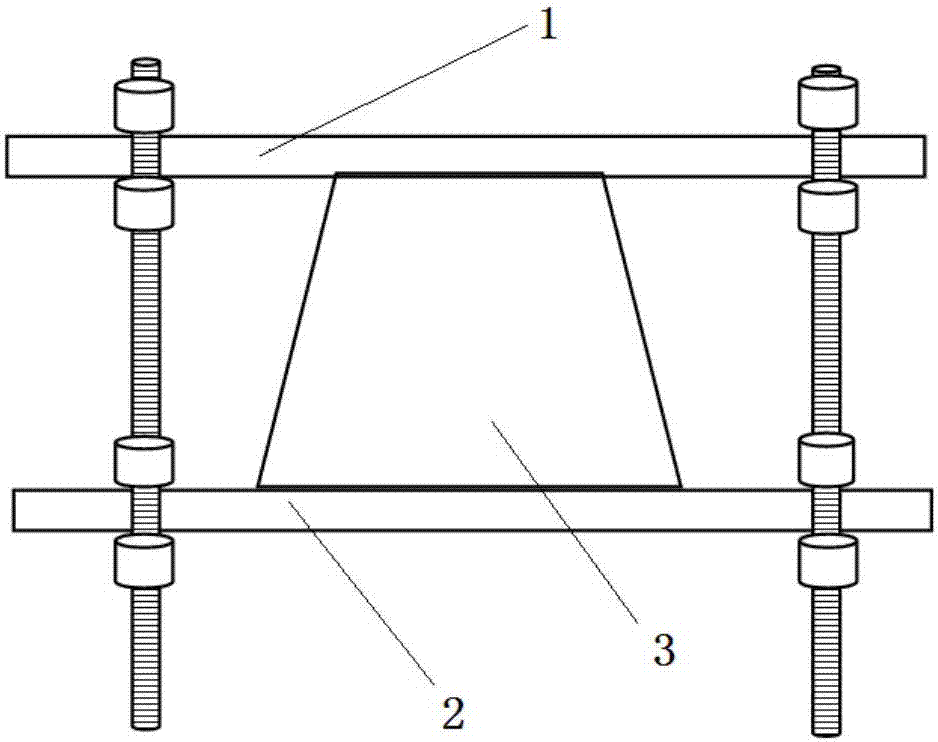
[0057] refer to Figure 4 , a truncated circular three-dimensional cell mechanical gradient dynamic loading platform, comprising a mold composed of two splints 1, 2, a cell-encapsulated three-dimensional tissue module 3 is sandwiched between the two splints 1, 2, a cell-encapsulated three-dimensional tissue module The contact parts between the module 3 and the splints 1 and 2 are connected with 502 glue, and the two ends of the two splints 1 and 2 are respectively connected to the control clips 6 on the one-dimensional mobile platforms 4 and 5, and the four control clips 6 are respectively connected to the first A motor 8, a second motor 9, a third motor 10 and a fourth motor 11 are connected. The computer can control the four motors to move on the one-dimensional mobile platform, and the displacement is transmitted to the two splints 1 and 2 through the four control clips 6 to generate strain gradients.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com