Method for detecting active metal elements in hard zinc
A detection method, a technology of active metals, applied in the field of detection of active metals in hard zinc, can solve problems such as difficult detection of active metals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
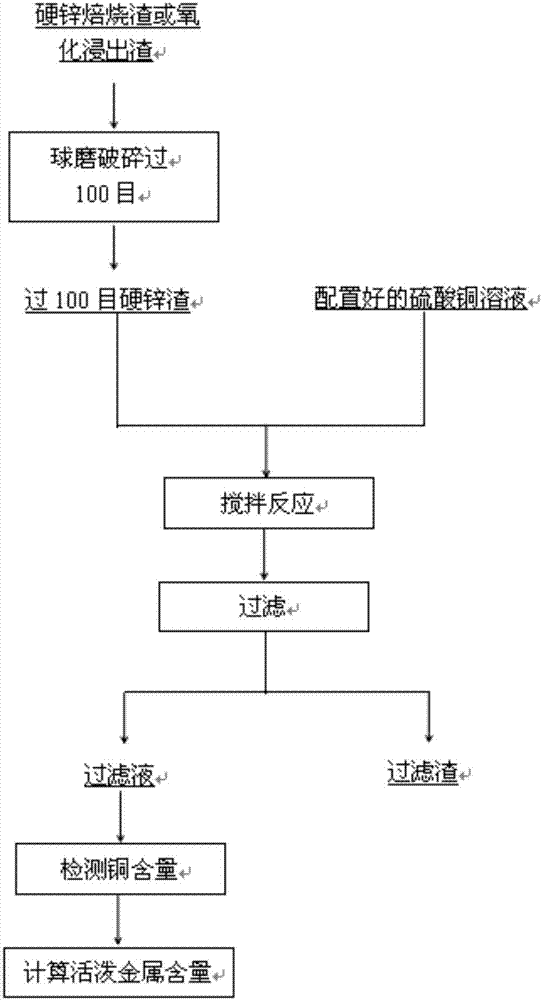
[0041] Take 150g of hard zinc roasting slag, pass it through a 100-mesh sieve after ball milling, and take 100g of the sieved slag for use; configure 1L of copper sulfate solution with a copper content of about 200ppm for use, and submit it for inspection with a copper content of 203ppm; The slag after sieving was added to 400mL copper sulfate solution, stirred and reacted at 60°C for 1 hour, and the filtered filtrate solution was sent for inspection, and the copper content was 132ppm. Assuming that the active metal was iron, the elemental iron in 100g of slag was calculated to be 24.47mg, the content is 0.02447%.
[0042] The reaction equation is: Fe+Cu 2+ → Fe 2+ +Cu.
Embodiment 2
[0044] Take 150g of hard zinc roasting slag, pass it through a 100-mesh sieve after ball milling, and take 100g of the sieved slag for use; configure 1L of copper sulfate solution with a copper content of about 2000ppm for use, and submit it for inspection with a copper content of 2052ppm; The slag after sieving was added to 400mL copper sulfate solution, stirred and reacted at 80°C for 3 hours, and the filtered filtrate solution was sent for inspection, and the copper content was 1058ppm. Assuming that the active metal was iron, the elemental iron in 100g of slag was calculated to be 397.6mg, the content is 0.3976%.
[0045] The reaction equation is: Fe+Cu 2+ → Fe 2+ +Cu.
Embodiment 3
[0047]Take 150g of hard zinc roasting slag, pass it through a 100-mesh sieve after ball milling, and take 100g of the sieved slag for use; configure 1L of copper sulfate solution with a copper content of about 5000ppm for use, and submit it for inspection. The copper content is 4987ppm; The slag after sieving was added to 600mL copper sulfate solution, stirred and reacted at 60°C for 1 hour, and the filtered filtrate solution was submitted for inspection to obtain a copper content of 2028ppm. Assuming that the active metal was iron, the elemental iron in 100g of slag was calculated to be 1775mg, and the content was 1.775%.
[0048] The reaction equation is: Fe+Cu 2+ → Fe 2+ +Cu.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com