Method for manufacturing liquid crystal electro-optical components
A liquid crystal, electro-optical technology, applied in optics, nonlinear optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult liquid crystal molecules, alignment processing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
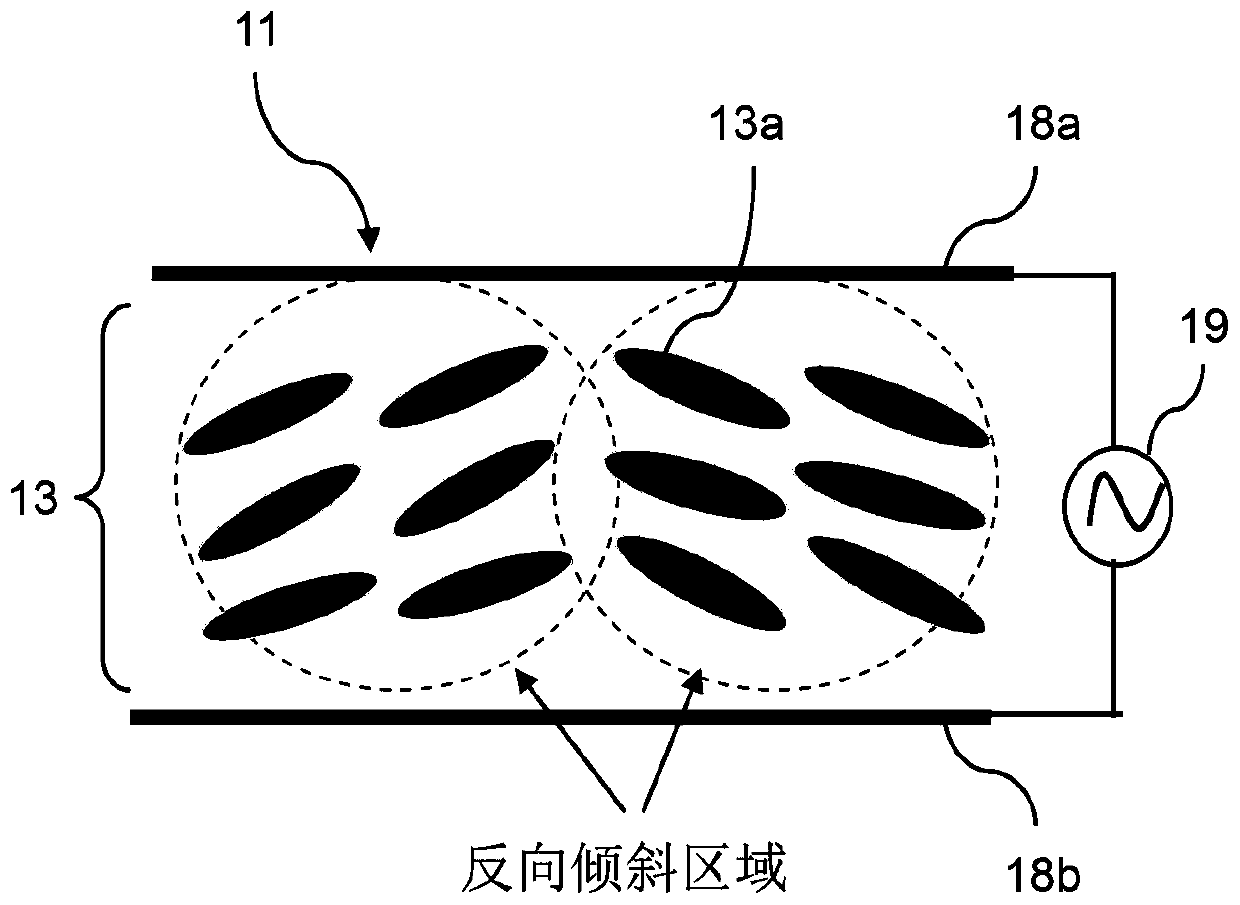
[0055] [First embodiment: Gradient electric field experiment]
[0056] Step 1: In order to generate a gradient electric field in the experiment, the ITO film of the ITO (indium tin oxide, indium tin oxide) glass substrate is directly used as the electrode plate for supplying the external voltage.
[0057] Step 2: first attach the fiber or photonic crystal fiber filled with liquid crystal / photosensitive monomer mixture on the ITO glass substrate (lower electrode 48b), and then cover another ITO glass substrate (upper electrode 48a) on the upper end, as Figure 4 as shown in part (a).
[0058] Step 3: In order to generate a gradient electric field between the electrode plates, slightly tilt the upper electrode 48a so that it forms a small angle with the lower electrode 48b, as Figure 4 as shown in part (b).
[0059] Step 4: After applying a voltage, a gradient electric field can be formed between the upper electrode 48a and the lower electrode 48b. Subsequently, use a polari...
no. 2 example
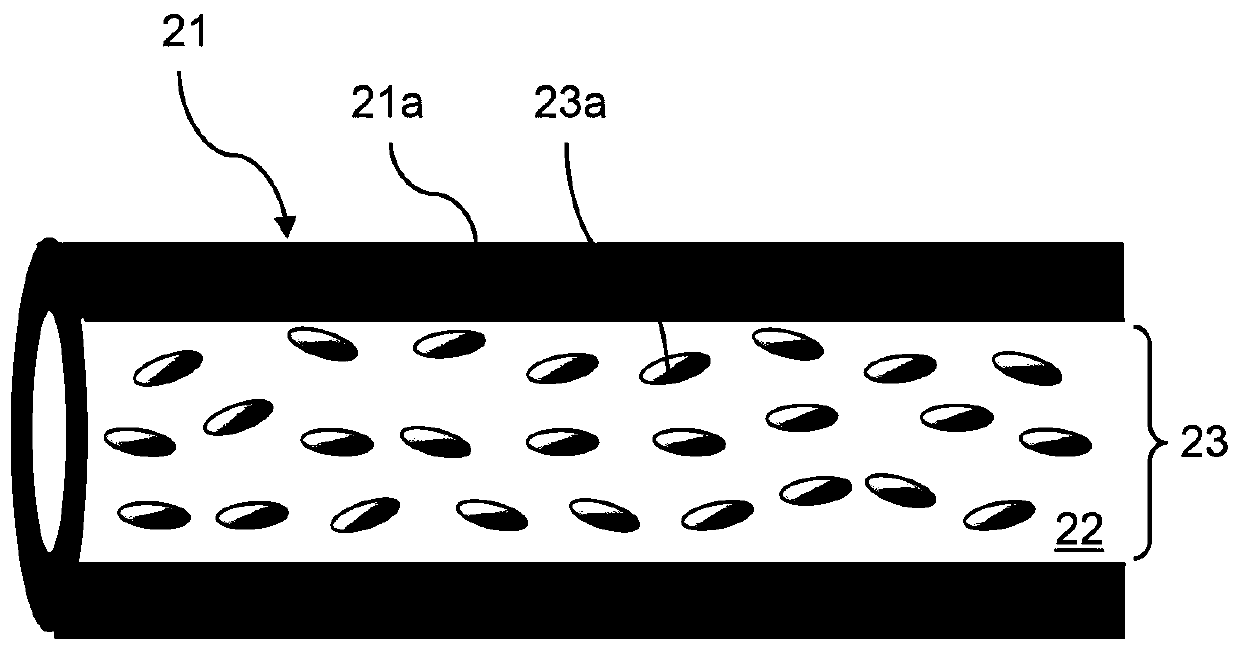
[0068] [Second embodiment: Gradient temperature field experiment]
[0069] Step 1: Fix the liquid crystal optical fiber 51 between two electrode plates (not shown in the figure), and place it on the heating table 52, such as Figure 9 shown.
[0070] Step 2: In order to generate the gradient temperature field, the method is as follows:
[0071] (1) The right side of the optical fiber 51A is raised (~2mm) by means of a heat-insulating spacer 57, so that the substrate is inclined and the farther to the right side it is from the heating surface of the heating table 52, the optical fiber 51A will be heated unevenly And the temperature distribution characteristics with a temperature gradient, such as Figure 9 shown. Or, (2) the right side of the optical fiber 51B is emptied and only the left side is in contact with the heating stage 52 (~70°C), so that the heated part on the left side of the optical fiber 51B exhibits the highest temperature, and the temperature increases with ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com