Method for constructing dynamic metabolic network based on topological structure of elementary reactions
A technology of elementary reaction and metabolic network, applied in special data processing applications, electrical digital data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem that the rate constant of elementary reaction cannot be completely experimentally determined.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
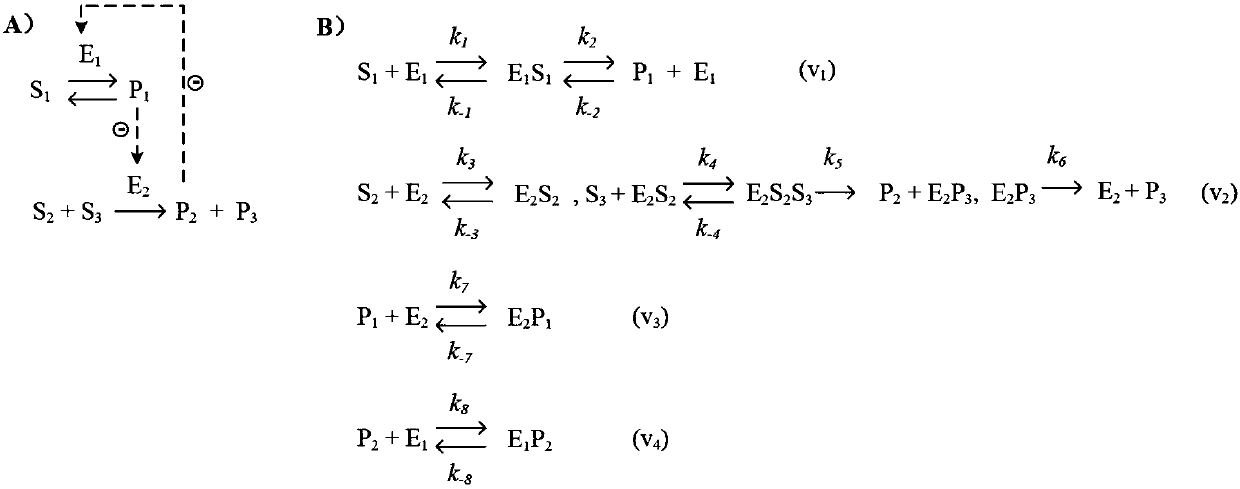
[0112]Enzyme reaction: glucose 6 phosphate → fructose 6 phosphate, the enzyme is phosphoglucose isomerase, molecular weight M=12000Da.
[0113] This reaction is an irreversible reaction with a single substrate and a single product, and the elementary reaction formula is as follows,
[0114]
[0115] Where S represents glucose 6 phosphate, E represents glucose phosphate isomerase, P represents fructose 6 phosphate, EP represents enzyme complex, k 1 、k 2 and k 3 is the elementary reaction rate constant.
[0116] Under the pseudo-steady state assumption, the elementary reaction kinetic equation is:
[0117] The classic Michaelis-Menten equation for a substrate single-product reaction is:
[0118] Among them, the Michaelis Kinetic parameters include the Michaelis constant K m and catalytic constant k cat .
[0119] k 1 、k 2 、k 3 and K m 、k cat There are the following correlations,
[0120]
[0121] And the Michaelis constant K can be obtained by experiment ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com