Patents
Literature
156 results about "Reaction rate constant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemical kinetics a reaction rate constant or reaction rate coefficient, k, quantifies the rate of a chemical reaction. For a reaction between reactants A and B to form product C a A + b B → c C the reaction rate is often found to have the form: r=k(T)[A]ᵐ[B]ⁿ Here k(T) is the reaction rate constant that depends on temperature, and [A] and [B] are the molar concentrations of substances A and B in moles per unit volume of solution, assuming the reaction is taking place throughout the volume of the solution.
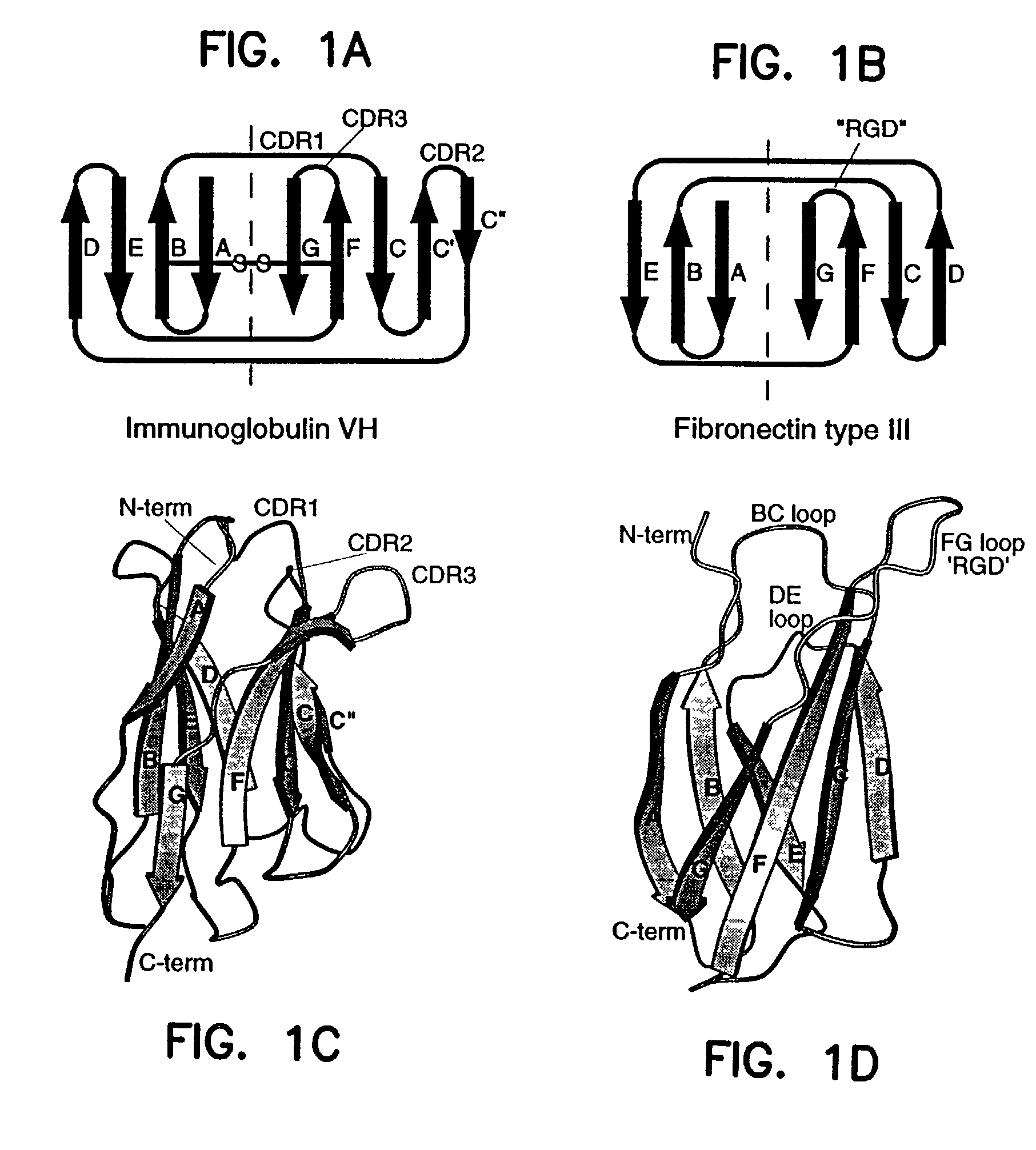
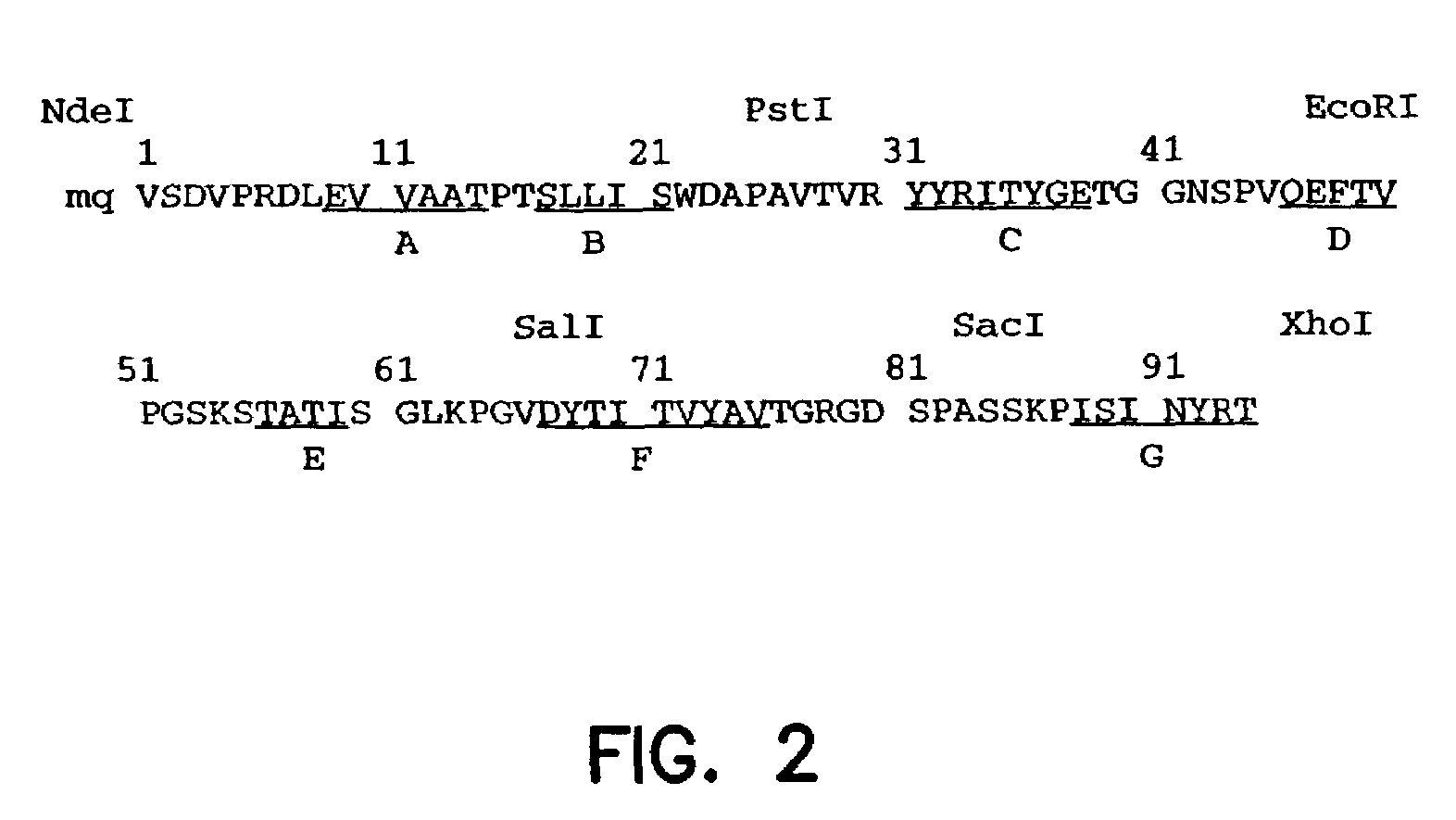
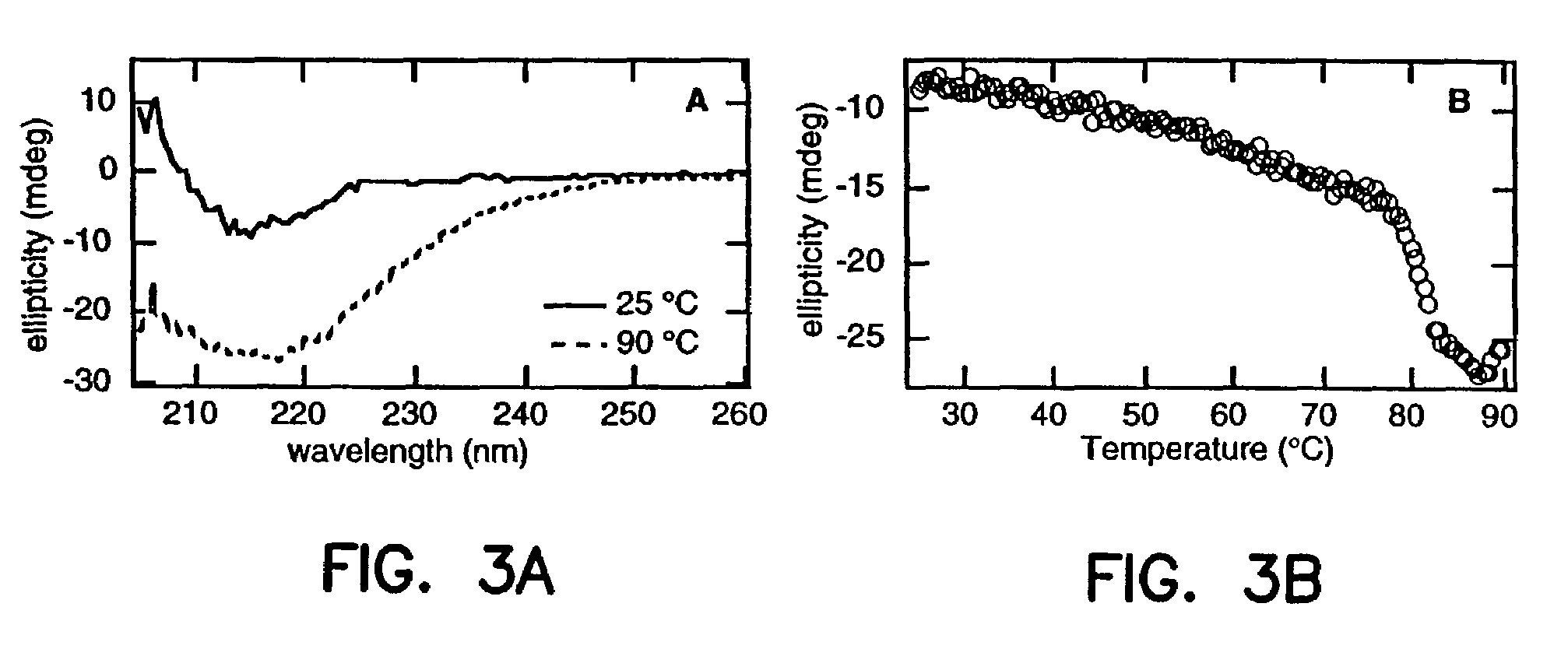
Artificial antibody polypeptides
A fibronectin type III (Fn3) polypeptide monobody, a nucleic acid molecule encoding a monobody, and a variegated nucleic acid library encoding a monobody, are provided by the invention. Also provided are methods of preparing an Fn3 polypeptide monobody, and kits to perform such methods. Further provided is a method of identifying the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide molecule capable of binding to a specific binding partner (SBP) so as to form a polypeptide:SSP complex, and a method of identifying the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide molecule capable of catalyzing a chemical reaction with a catalyzed rate constant, kcat, and an uncatalyzed rate constant, kuncat, such that the ratio of kcat / kuncat is greater than 10.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Ink set, ink cartridge, ink jet printer and recording method
ActiveUS20040050291A1Excellent in handleabilityExcellent in odorMonoazo dyesMeasurement apparatus componentsComputer printingImage recording
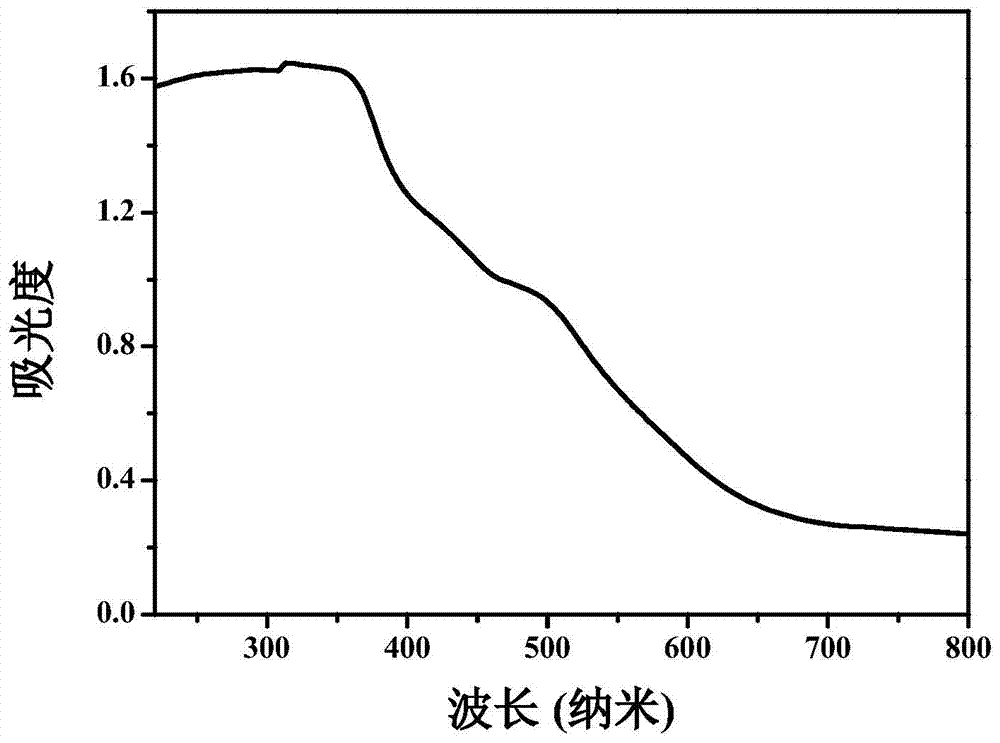
The ink set of the present invention provides a high ejection stability, gives an image having an excellent hue, light-resistance and waterproofness and improves the image preservability under severe conditions in ink jet recording, in which the ink set comprising a plurality of inks different in hues, wherein the plurality of inks includes a yellow ink containing a coloring agent that is a dye having: a lambdamax of from 390 nm to 470 nm; an I(lambdamax+70 nm) / I(lambdamax) ratio of not greater than 0.4, in which I(lambdamax) is the absorbance at lambdamax and I(lambdamax+70 nm) is the absorbance at (lambdamax+70 nm); and a forced fading rate constant of not greater than 5.0x10<-2 >[hour<-1>], an ink cartridge having the ink set received therein, an ink jet printer comprising the ink cartridge mounted therein and an image recording method.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
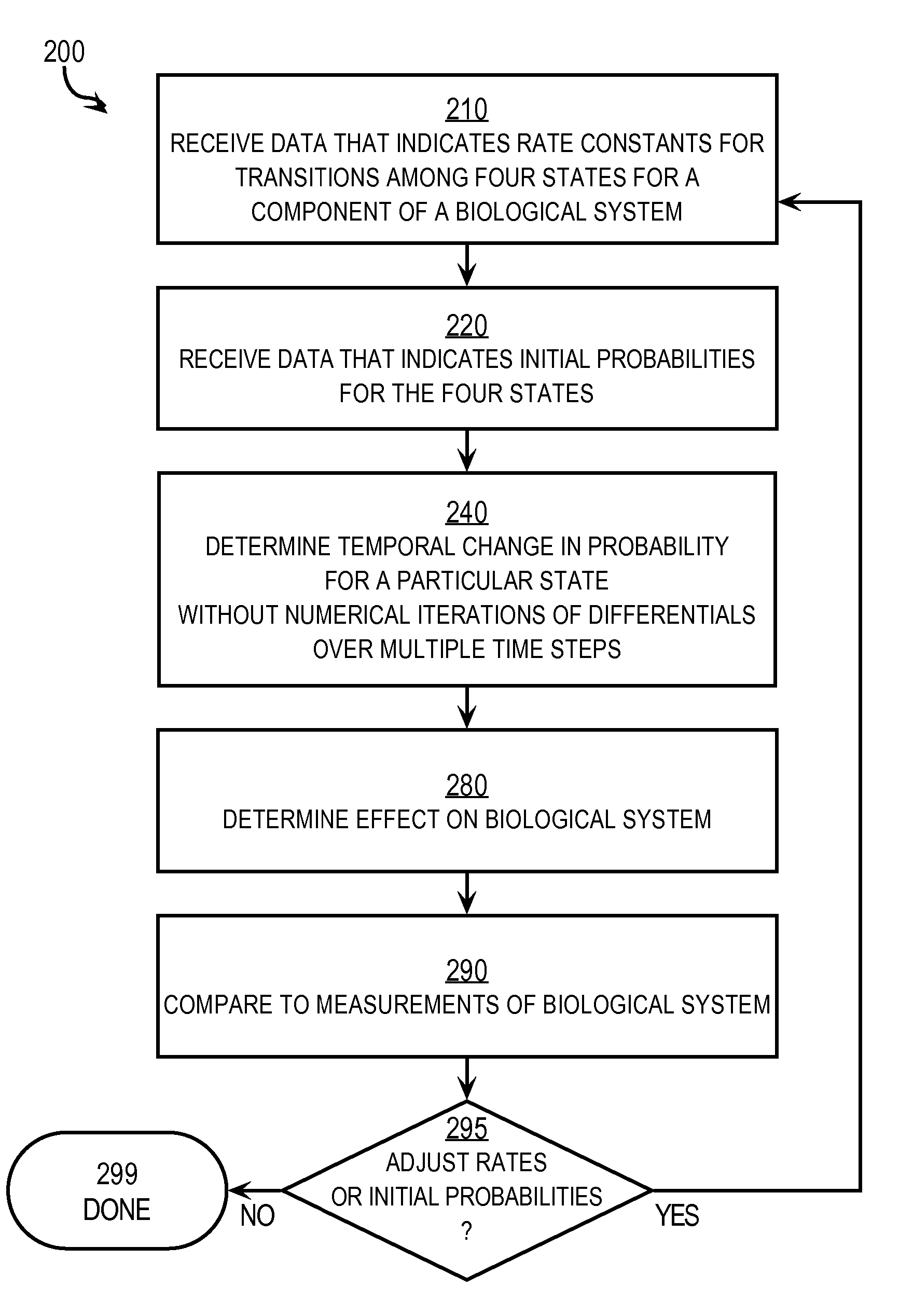
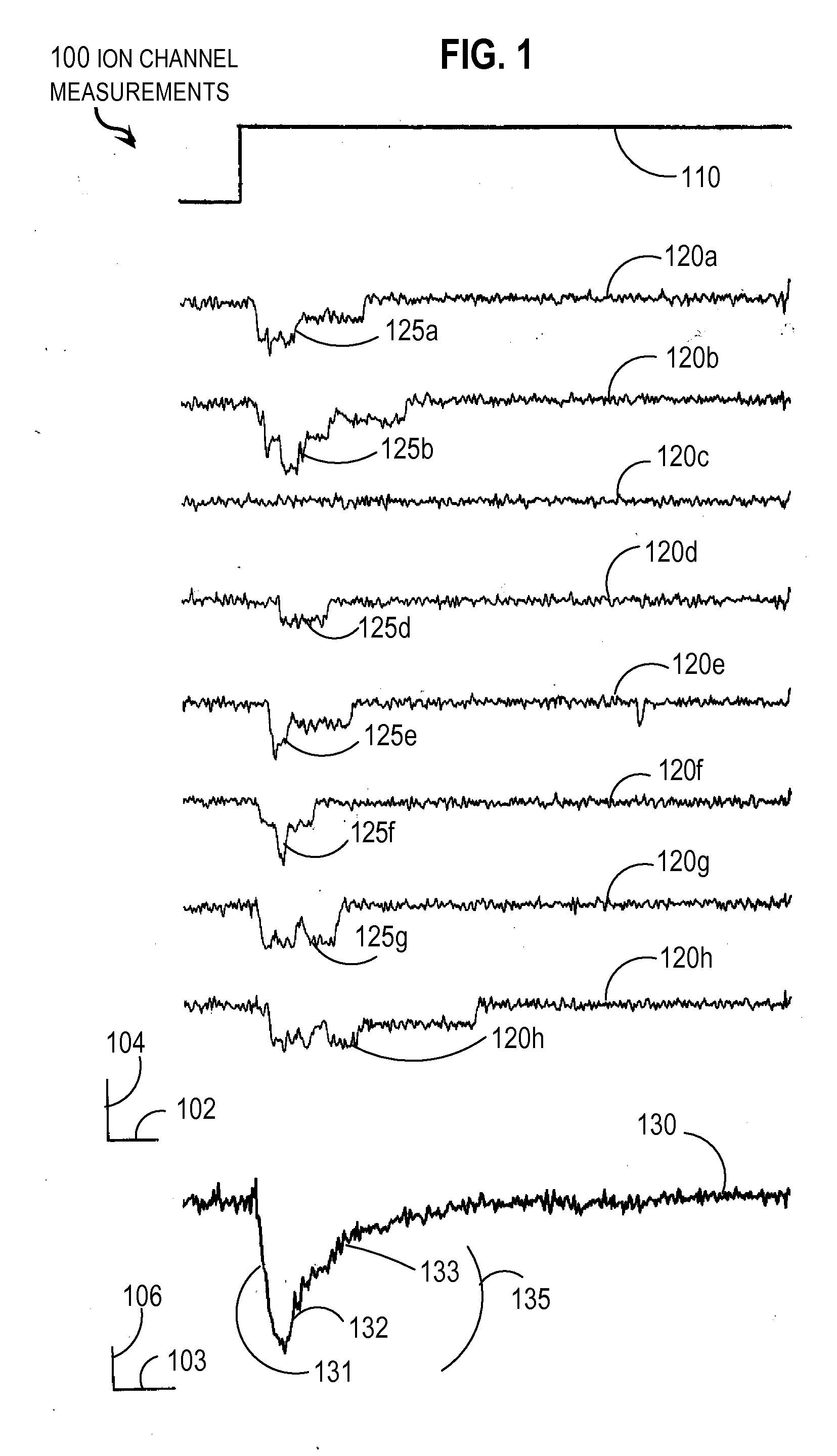
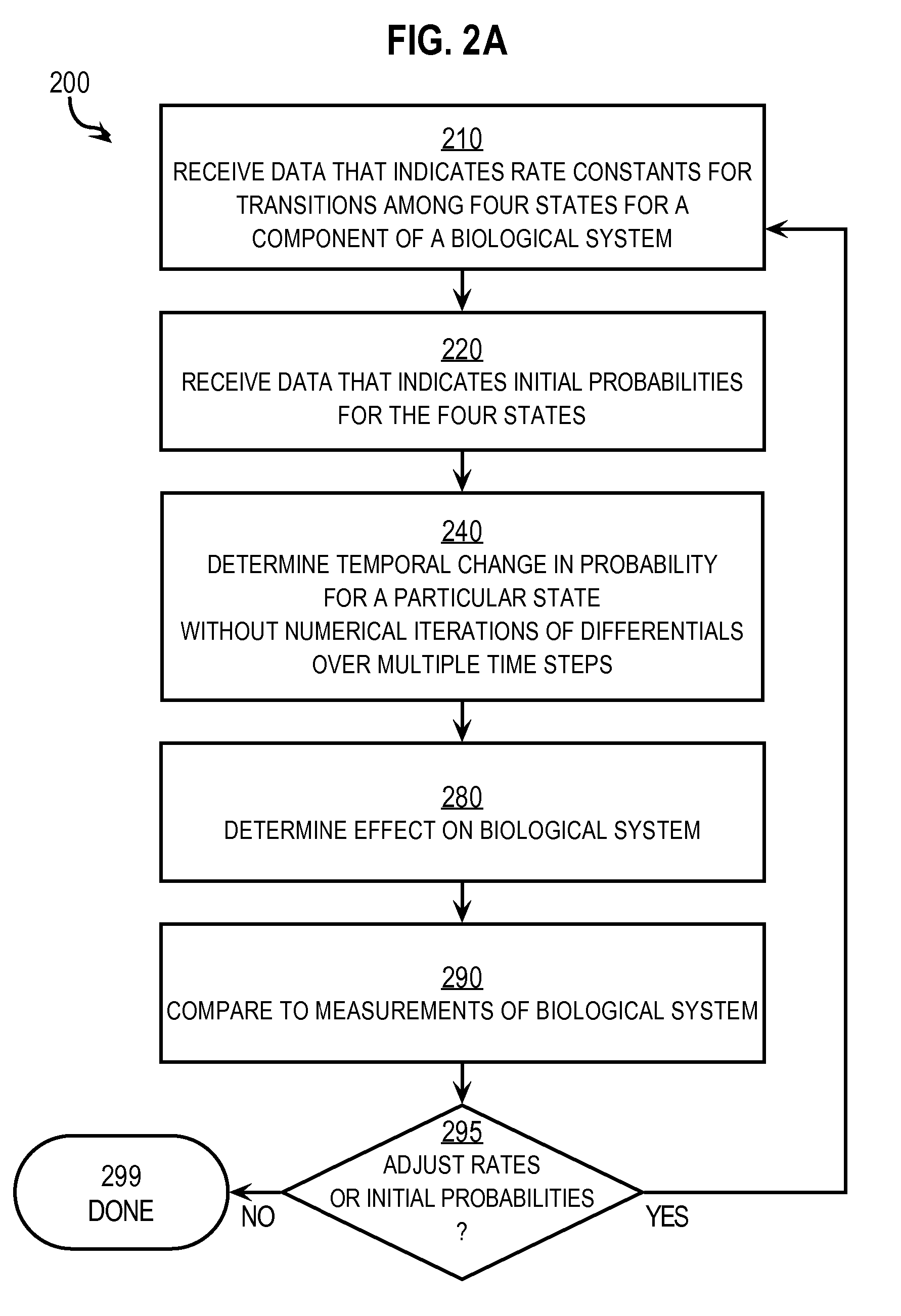
Techniques for Determining the Effects on a System of a Component that has Four States
InactiveUS20070288215A1Prediction is simpleConstant rateAnalogue computers for chemical processesSystems biologyTemporal changeReaction rate constant
Techniques for determining effects on a biological system include determining rate constants for a particular time interval starting at an initial time. Each rate constant indicates a rate of transition from one of four states to a different one of the four states for a component of a biological system in presence of an external factor. A temporal change in a probability that the component is in a particular state after the initial time is determined without numerical iteration over multiple time steps. This includes determining three relaxation time constants that describe exponential changes based on the rate constants. The effect of the external factor on the biological system is determined based on the temporal change in the probability that the component is in the particular state. The probability at an arbitrary time is determined based on the rate constants and initial probabilities.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Rubber-storage-life predicting model based on test equipment for room-temperature and high-pressure compression stress relaxation of rubber
InactiveCN102589976AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed repeatabilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringLinear regression
The utility model provides a life predicting model based on test equipment for room-temperature and high-pressure compression stress relaxation of rubber. The life predicting model comprises the following steps of: firstly, drawing stress relaxation change data acquired by the device into a diagram to obtain the relation between the stress relaxation condition and the ageing time and the relation between the speed constant and the ageing temperature; secondly, obtaining all coefficients in the equation by utilizing an approximation method, a linear regression method and MATLAB programming software, and judging the linear regression effect according to the related method; and finally, determining a rubber life predicting value after giving critical values of temperature and stress relaxation. The life predicting model has the advantages that the device for testing the compression stress relaxation of high-temperature rubber can be utilized for monitoring the change of the compression stress, so as to establish the life predicting model, and the accuracy, the repeatability and the reproducibility of a life predicting result are guaranteed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Titanium dioxide photo-catalyzed film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102864481ALarge specific surface areaGood light transmissionSurface reaction electrolytic coatingVacuum evaporation coatingPhotocatalytic reactionHeat treated
The invention discloses a titanium dioxide photo-catalyzed film and a preparation method thereof. The titanium dioxide photo-catalyzed film has a spongy porous structure; the length of holes along the growth direction is 200nm-800nm; and the maximal width of the holes along the direction vertical to the growth direction is 10nm-300nm. The preparation method for the titanium dioxide photo-catalyzed film comprises the following steps: depositing a columnar structural titanium film on a substrate by adopting a magnetron sputtering method, wherein the depositing pressure is 0.1-1Pa; preparing the titanium dioxide having a porous structure by anodizing the titanium film; sputtering the deposited titanium film as an anode and taking graphite as a cathode; taking a mixed solution of ammonium fluoride, water and organic saturate alcohol as an electrolyte; keeping a constant voltage at 25-50V; and thermally treating, thereby obtaining the titanium dioxide photo-catalyzed film. The titanium dioxide photo-catalyzed film provided by the invention has the characteristics of high light transmission and high photo-catalytic reaction rate constant and meets the requirements of photo-catalyzed materials, such as self-cleaning glass, air and waste water purifier, and the like.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A method for improving temperature applicability and accuracy modeling of electrochemical-thermal coupling model
ActiveCN109344429AHigh precisionImprove temperature adaptabilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsReaction rateThermal coefficient
The invention discloses a method for improving the temperature applicability and accuracy modeling of an electrochemical-thermal coupling model, comprising the steps of testing and measuring an entropy thermal coefficient, wherein the entropy thermal coefficient of a battery is closely related to the heat production of the battery; establishing a lithium ion battery electrochemical model accordingto the measured entropy thermal coefficient and the electrochemical modeling control equation; establishing the electrochemical-thermal coupling model of a lithium ion battery by combining the lithium ion battery electrochemical model with the thermal characteristic equation of the lithium ion battery; establishing the correction functions S (T) and H (T) of the solid diffusion coefficient and reference reaction rate with temperature; introducing the correction functions into the electrochemical-thermal coupling model of the lithium ion battery; adding the tested and measured entropy thermalcoefficient in the electrochemical-thermal coupling model to the accuracy of the electrochemical-thermal coupling model along with the temperature change of the battery. By carrying out the temperature correction factor adjustment on the two parameters of the solid diffusion coefficient and the reference reaction rate constant, the electrochemical-thermal coupling model can be used for battery electrochemistry-thermal characteristic research at different temperatures and operating conditions, thereby improving the temperature adaptability of the model.
Owner:安徽巡鹰新能源集团有限公司
Automatic analyze
ActiveCN101520461APrevents situations where erroneous data output is ignoredAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionColor/spectral properties measurementsChemical reactionReaction speed
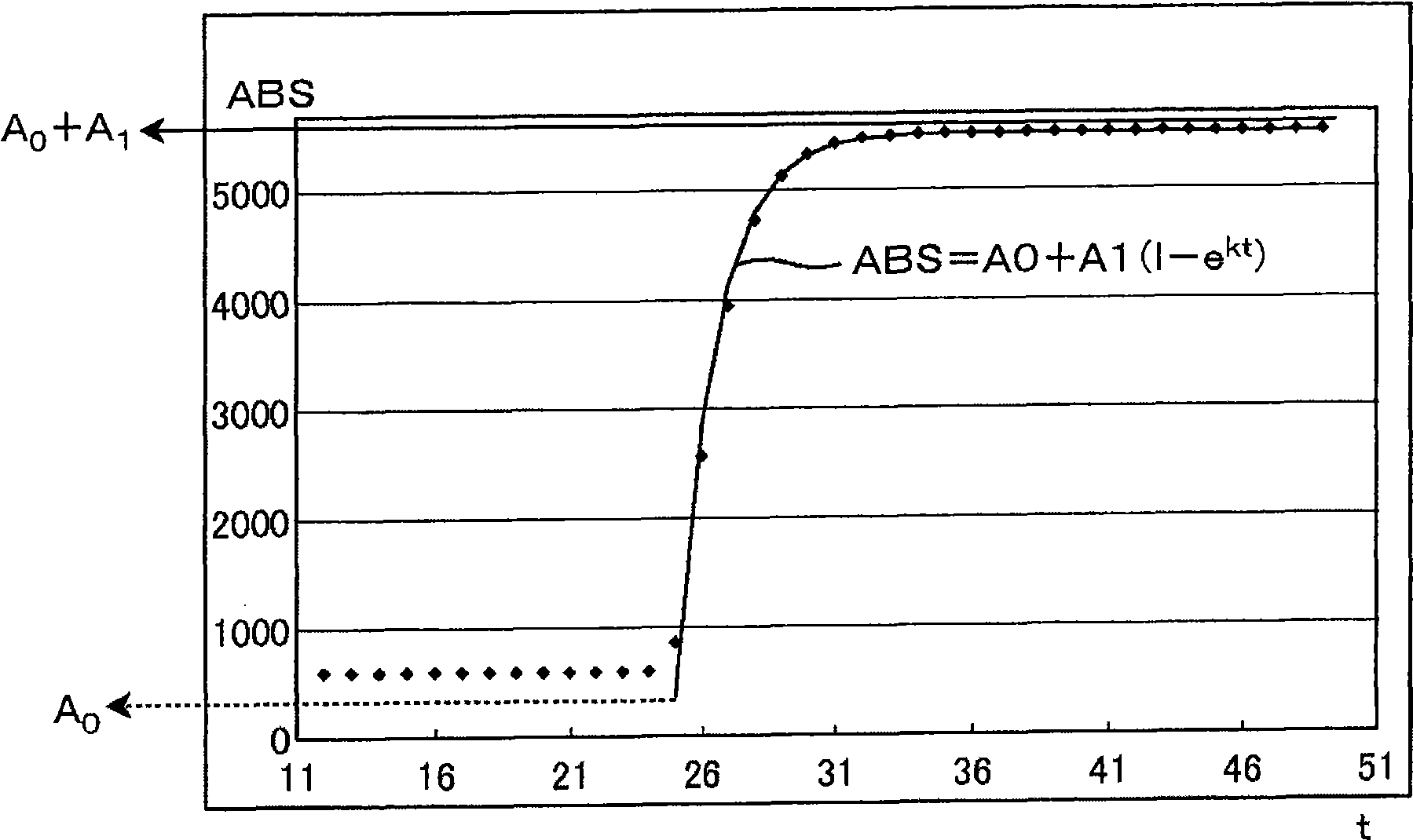
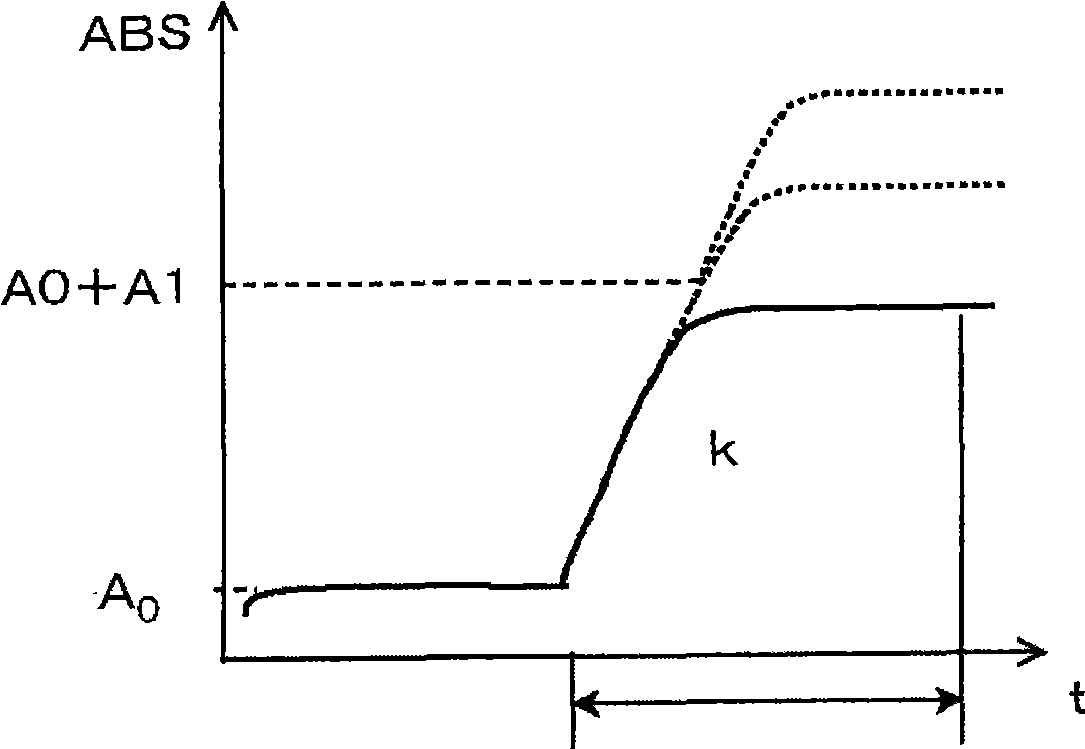
The present invention provides an index that uses, in an automatic analyzer, an approximate expression based on a theoretical chemical reaction formula derived from reaction process data, and automatically check for apparatus abnormalities, reagent deteriorations, and improper accuracy control during each continuous or individual inspection. Reaction process data, which is measured when the automatic analyzer determines the relationship between reaction absorbance and time, is approximated to ABS = A 0 + A 1 (1-e -kt) by the least-squares method. The resulting reaction start point absorbance A 0, final reaction absorbance A 1, reaction rate constant k, and residual error, which is the aggregate sum of differences between approximate values and measured values, are then used as the index of reaction status.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Magnetic nano catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101703936ASimple processReduce pollutionOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationNano catalystSolvent
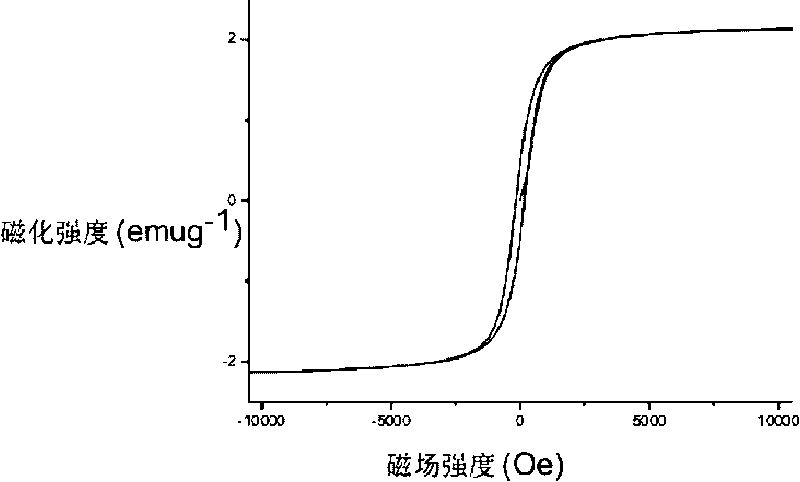
The invention relate to a magnetic nano catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: sequentially adding a pure metal precursor, a long-chain organic polymer, a ferrite precursor and metal acetate to reducing ethanol and stirring to form a uniform suspension; transferring the uniform suspension into a reaction kettle for heating and then naturally cooling to room temperature to prepare a mixed catalysis body; settling and separating the mixed catalysis body under the action of an outer magnetic field, then scattering obtained solid substances into a mixed solvent for carrying out settlement, separation and a cleaning cycle respectively for 2-3 times; and finally, drying in vacuum at room temperature to obtain the magnetic nano catalyst. The preparation method is simple; the prepared catalyst has a reaction constant of 17.21-1.65 mmol-1s-1 in a p-nitrophenol hydrogenation reduction process; and the catalytic reaction rate constant has no obvious reduction during recycling the catalyst for many times.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
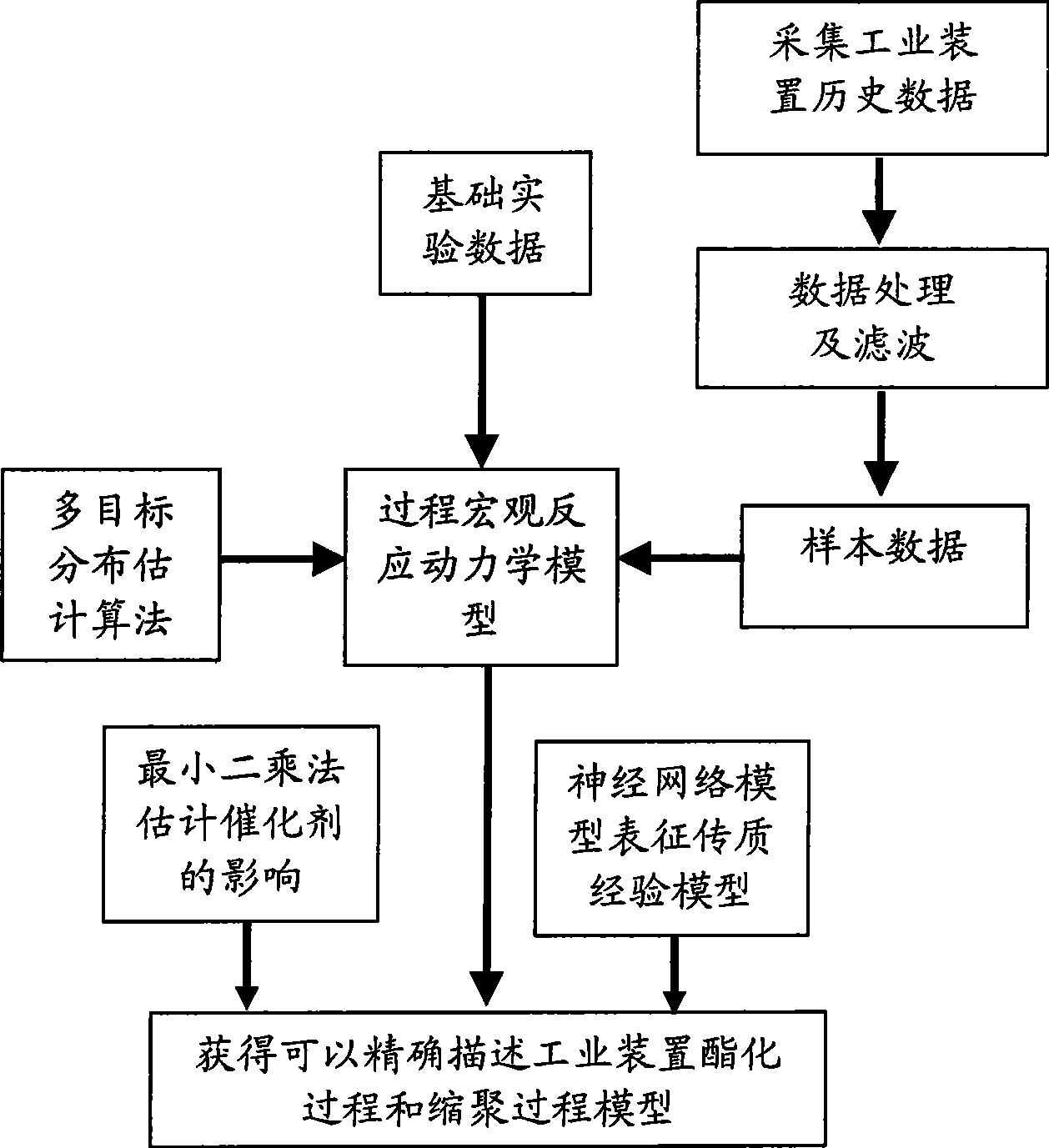
Intelligent modeling method in industrial polyester production process
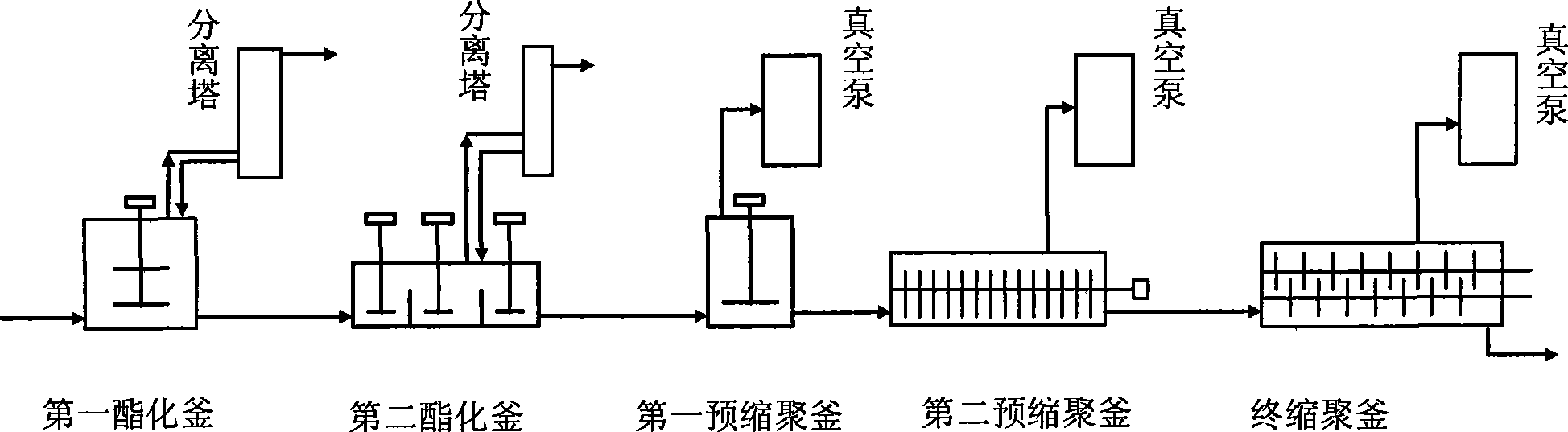
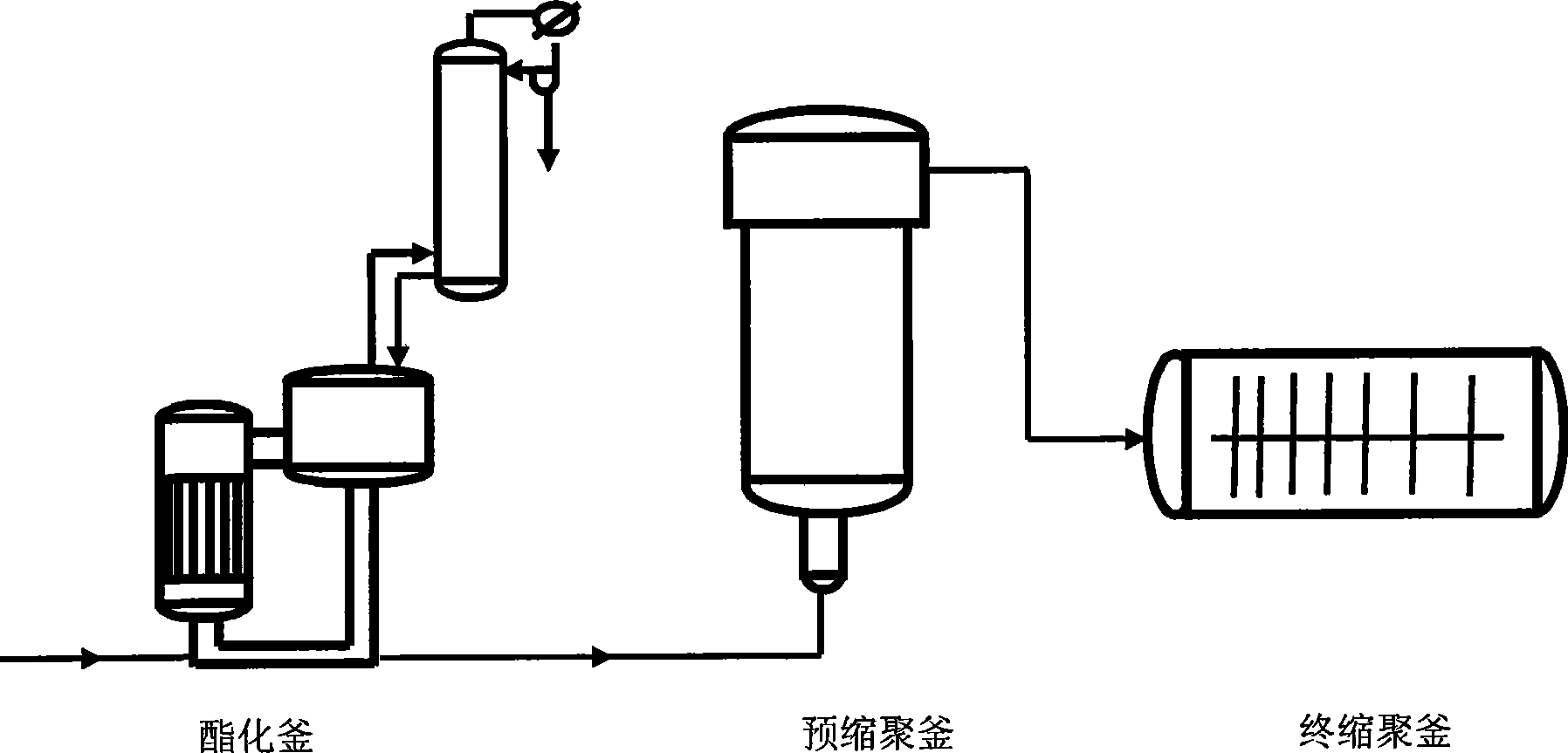
The invention relates to an intelligent modeling method during the industrial polyester production process. Firstly, a mechanism model of the polyester production process based on reaction kinetics is established according to the mechanism of polyester reaction process; and then, parameters in the technical mechanism model are optimized by a multiple-target distribution estimation algorithm, so as to describe the actual operation characteristic of the industrial polyester production process exactly. At the same time, considering the influence on the reaction during the pre-polycondensation stage caused by catalyst, influence factor of the catalyst is added in reaction speed constant of the mechanism model, and a model between the catalyst and the reaction speed constant is established by a least square method; in a final polycondensation reactor, the mass transfer rate is reduced, and the influence on the process speed is increased, so that an artificial neural network is used for establishing an empirical model while the influence of mass transfer is considered, and the process speed is expressed in a form of resistance equation while combining with the reaction speed to ensure that the model is exacter. The modeling method can be applied to the modeling during three-reaction and five-reaction technical process during the industrial polyester production process at present.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bioanalytical assay
InactiveUS20040076948A1Small sizeHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividual molecule manipulationEnergy transferExcited state
The present invention relates to a nanoparticle comprising a specific binding reactant, said nanoparticle being useful for determining an analyte to which analyte or complex comprising said analyte said binding reactant is specific. Characteristic for the nanoparticle is that the diameter of said nanoparticle is less than 200 nm, said nanoparticle is coated with multiple said specific binding reactants to the extent that the affinity constant of said nanoparticle towards said analyte essentially exceeds that of free said binding reactant towards said analyte and / or the association rate constant between said nanoparticle and said analyte essentially exceeds the association rate constant between free said binding reactant and said analyte; and said nanoparticle comprises a detectable feature. The invention also relates to biochemical assays using said nanoparticle. The assay further relates to a proximity based homogenous assay comprising a first group labeled with an energy donating compound (donor) and a second group labeled with an energy accepting compound (acceptor), wherein the donor is luminescent and has a long excited state lifetime and the acceptor is luminescent having a short or long excited state lifetime or the acceptor is non-luminescent, and the increase or decrease, respectively, in the energy transfer from the donor to the acceptor resulting from shortening or lengthening, respectively, of the distance between said groups, is measured. Characteristic for the assay is that the donor is a nanoparticle.
Owner:INNOTRAC DIAGNOSTISC
Preparation method of silicon dioxide
The invention discloses a preparation method of silicon dioxide, which sequentially comprises the following steps of: 1, preparing a sodium silicate solution A; 2, sectionally adding a sodium silicate solution B with sodium silicate mass concentration of 22-26 percent in a reaction kettle containing the sodium silicate solution A at a variable speed, controlling and regulating the addition speed of concentrated sulfuric acid at each section so as to keep pH of a reaction medium constant; 3, stopping adding the sodium silicate solution B, continuously adding the concentrated sulfuric acid, regulating the pH of the material obtained from the steps 2 to be 3.0-4.0, and preparing a sediment silicon dioxide suspension; 4, adding an organic surfactant in the suspension obtained in the step 3, ageing; and 5, filtering, washing, drying, post-treating and crushing to prepare the silicon dioxide product. According to the invention, the defect of poor dispersity of silicon dioxide in high-temperature vulcanized silicon rubber is overcome, yellowing performance of the silicon dioxide is improved, filtering and washing efficiencies are increased, washing time is shortened and washing water is saved.
Owner:FUJIAN YUANXIANG CHEM
Preparation method of TiO2 photocatalyst for loading on ceramic surface
The invention relates to the process for preparing TiO2 photo-catalyst carrier on ceramic surface, wherein the compact ceramic carrier material is supported with TiO2 colloidal sol through sol-gal process, the TiO2 colloidal sol is prepared through dissolving butyl titanate or propyl titanate into acids, alcohols and water, washing and drying the finished ceramic carrier into TiO2 colloidal sol for 2-40 minutes, seasoning, sintering the carrying agent with carried colloidal sol in the furnace, elevating the temperature from room temperature to 80-250 deg. C, heat preserving for 10-80 minutes, elevating temperature again to 250-400 deg. C, heat preserving for 20-80 minutes, elevating the temperature to 450-550 deg. C, heat preserving for 40-90 minutes, furnace cooling to room temperature. A stabilized catalytic activity can be achieved by the invention.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
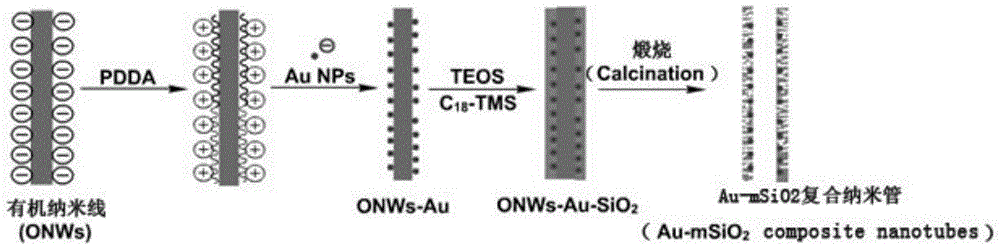
Nano gold-mesoporous silica composite nanotube, preparation and applications thereof
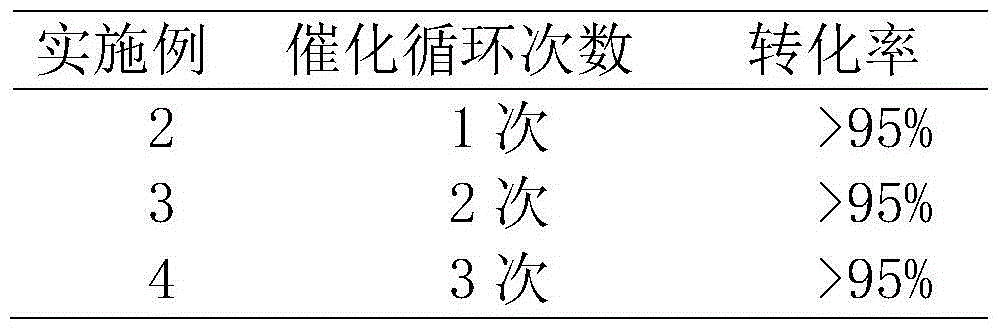
InactiveCN105312051AOriginalSimple methodWater contaminantsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNanowireMesoporous silica
For the first time, a nano gold-mesoporous silica composite nanotube is prepared by taking aniline oligomer organic nano wires as the template. The nanotube has a large specific area (the BET specific surface area can reach 469 m2 / g) and mesoporous channels (3.7 nm). The size (5 to 20 nm) and load capacity (1 to 5 wt%) of nano gold catalyst can be simply and effectively controlled, and the shortages such as shedding of catalyst, growth of crystal grains, and the like are overcome. The nanotube can be used as a catalyst for the degradation of nitrophenol dyes and the catalytic activity is high. When the concentration of nitrophenol in water is 1 mM, 1 mg of Au-mSiO2 composite nanotube is taken as the catalyst, more than 95% of degradation is completed within one hour, and the degradation rate constant (k) can reach 0.045 min<-1>. The nanotube can be repeatedly used for three times, while the catalytic performance is not degraded. Moreover, the preparation method is simple and feasible, the reactions can be carried out in a water phase environment at a room temperature, and thus the preparation method is environment-friendly and energy-saving.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
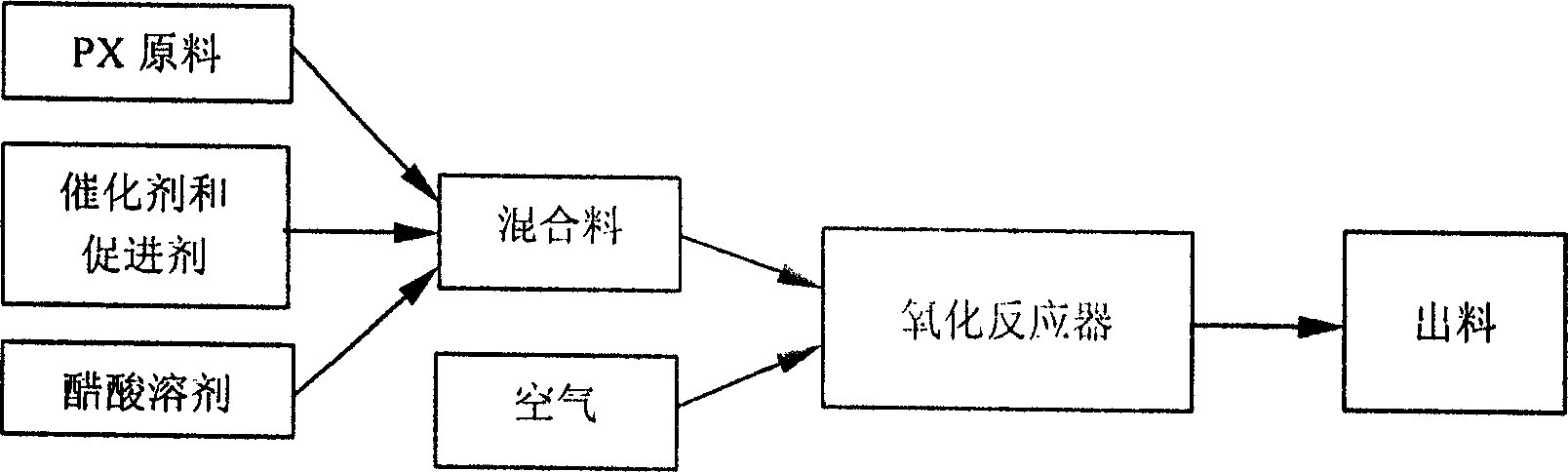
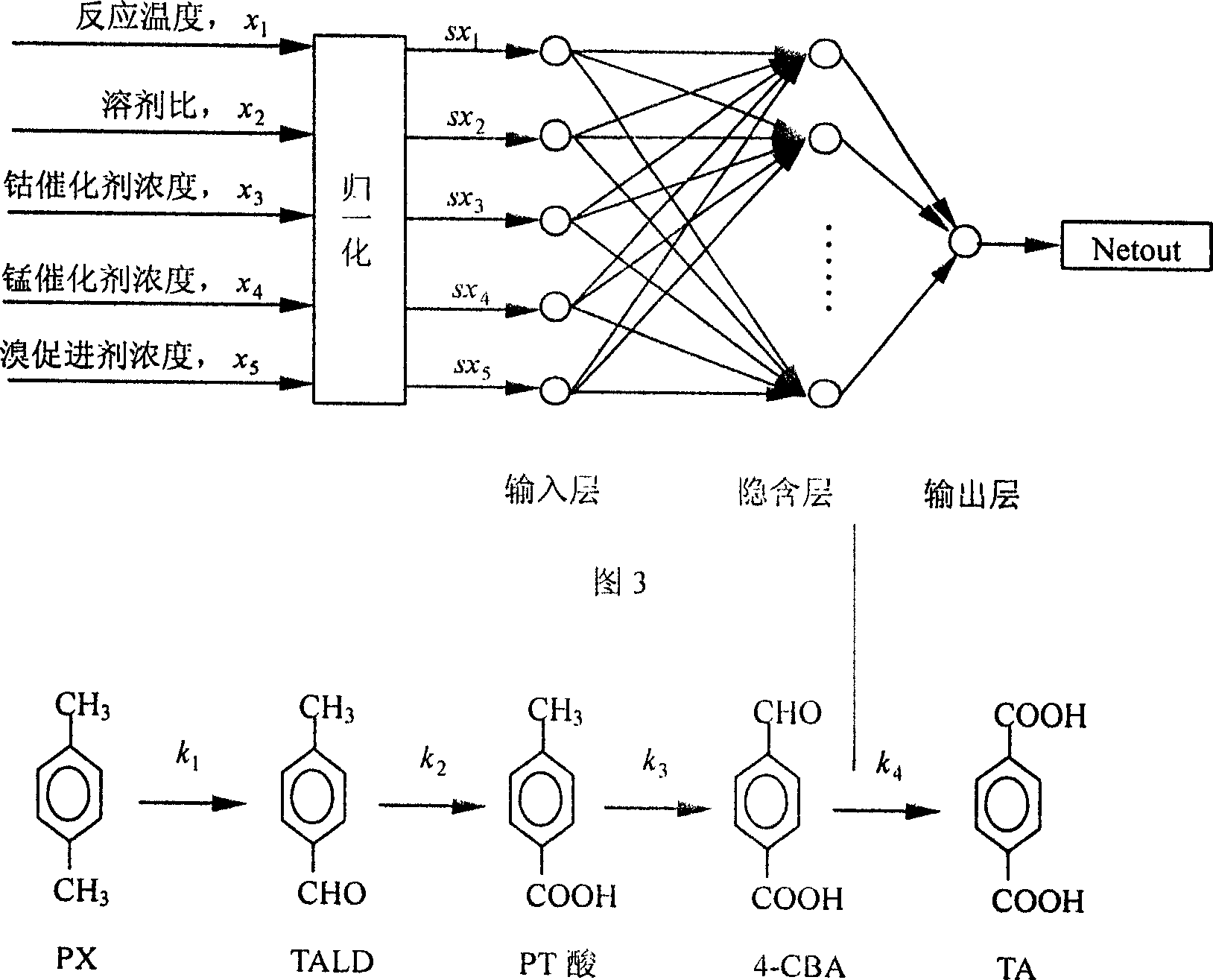
Establishing method of dynamic model of liquid phase catalytic paraxylene oxidizing reaction
InactiveCN1417192AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationIndustrial reactorDynamic models
The establishing method of dynamic model of liquid phase catalytic paraxylene oxidizing reaction comprises utilizing the reaction temperature x1 and mixed material composition including solvent ratiox2, Co catalyst concentration x3, Mr catalyst concentration x4, and Br promoter concentration x5 and the rate constant nerve net model to find out the rate constants ki, where i=1,2,3 and 4, of the steps in reaction network of industrial liquid phase catalytic paraxylene oxidizing reaction, and to find out the contents of PX, TALD, PT acid, 4-CBA, TA and other intermediate products and estimate products. The rate constant model can describe the effects of different factors on the reaction in the industrial reactor.
Owner:SINOPEC YANGZI PETROCHEM +1
Inkjet black ink
InactiveUS7211133B2Durability of image is goodMaintain image qualityInksPhthalocyanine dyeImaging quality
The invention provides an inkjet black ink ensuring excellent image durability capable of satisfactorily maintaining the image quality such as non-loosening of black and gradation even when the image is stored for a long period of time, which is a inkjet black ink having a discoloration rate constant (kvis) of 5.0×10−2 [hour−1] or less, which is measured by using an ozone gas, the ink comprising an aqueous medium having dissolved or dispersed therein at least one dye selected from (1) an azo dye having a specific structure where a heterocyclic group is bonded to both of two N atoms, (2) a phthalocyanine dye having a specific structure, (3) an azo dye having a specific structure where a 5-membered heterocyclic group is bonded to one of two N atoms and a 6-membered 2-amino heterocyclic group is bonded to the other, and (4) a bisazo dye constituted by a specific aromatic or heterocyclic group and an azo group.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
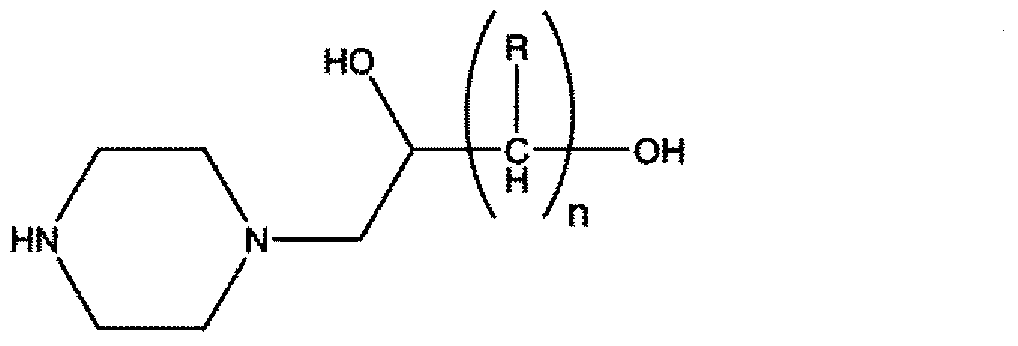
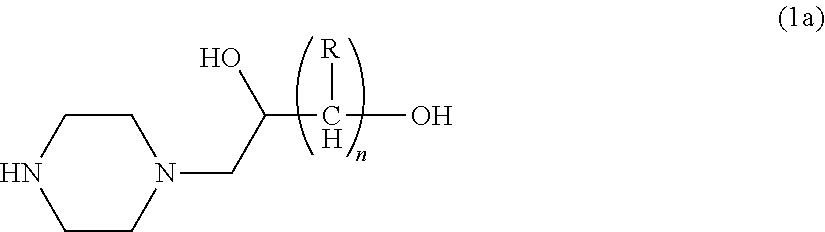
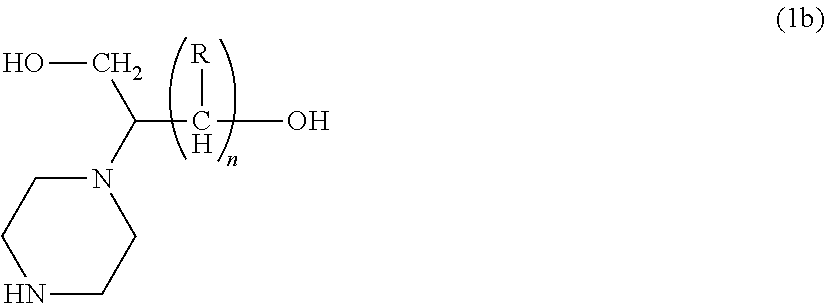
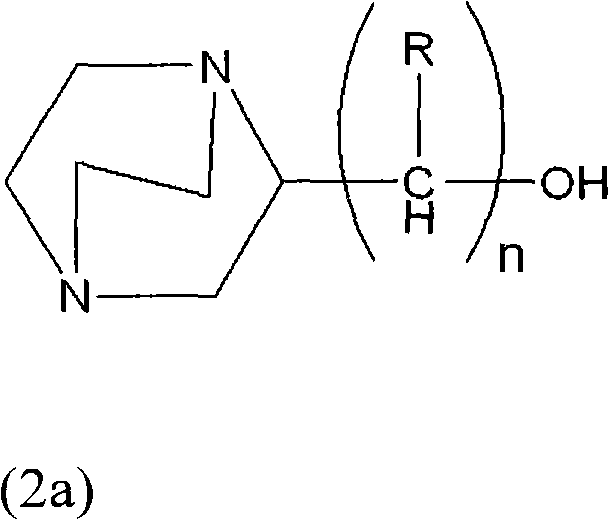
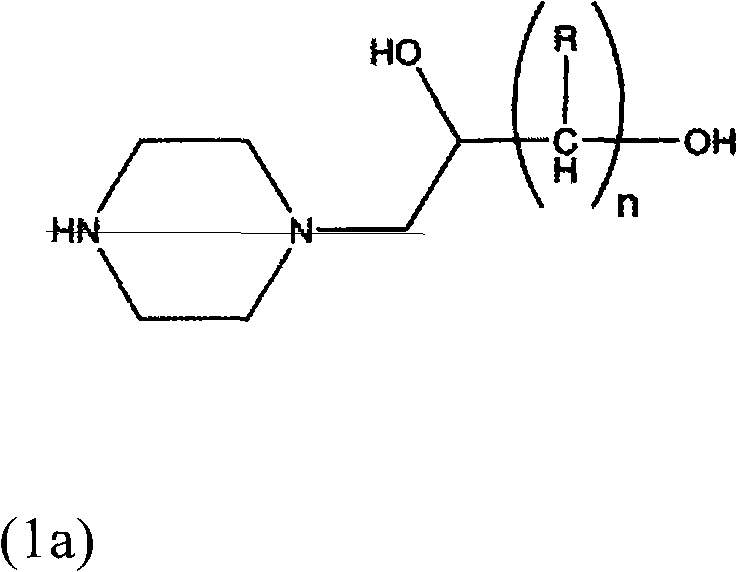
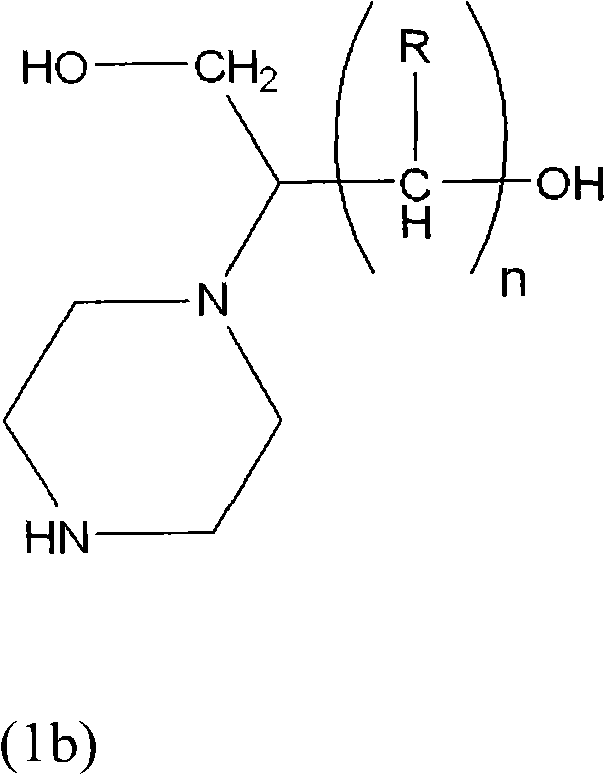
Process for producing hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine compound, and catalyst composition for the production of polyurethane resin using the hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine compound
ActiveCN103265677AWon't happenReduce the number of processesOrganic chemistryProduction rateReaction speed
To provide a process for producing a hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine or hydroxytriethylenediamine simply and in a small number of steps without requiring multistage reaction steps; a novel catalyst composition whereby a polyurethane product can be obtained with good productivity and good moldability without bringing about odor problems or environmental problems; and a process for producing a polyurethane resin using the catalyst composition. For example, a hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine or hydroxytriethylenediamine is produced by subjecting a mono-substituted dihydroxyalkylpiperazine and / or a di-substituted hydroxyalkylpiperazine to an intramolecular dehydration condensation reaction in the presence of an acid catalyst. Further, for example, a polyurethane resin is produced by using a catalyst composition which comprises a hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine or hydroxytriethylenediamine (A), and an amine compound (B) having, in its molecule, one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of a hydroxy group, a primary amino group and a secondary amino group, or a tertiary amine compound (C) having a value of [blowing reaction rate constant / gelling reaction rate constant] of at least 0.5.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
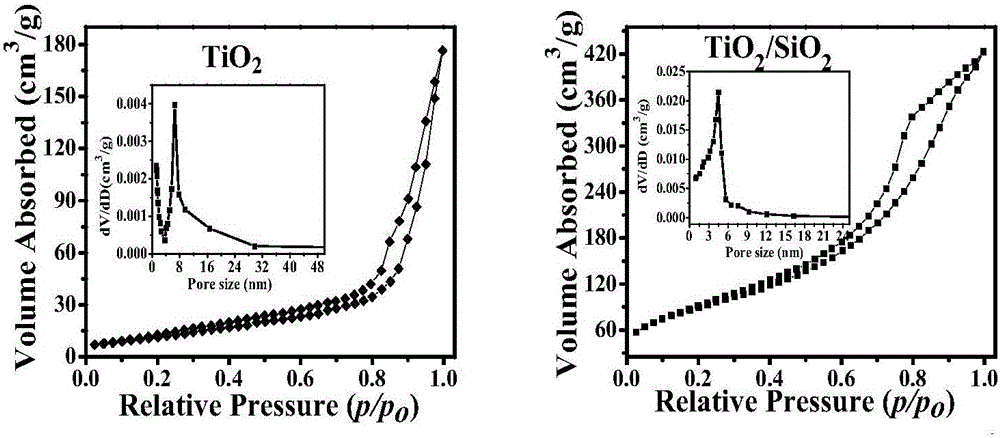
Preparation and photocatalytic degradation method of TiO2/SiO2 composite oxide
InactiveCN105126799AInhibitory complexPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationFluorescenceX-ray
The invention discloses preparation and a photocatalytic degradation method of a TiO2 / SiO2 composite oxide; a structure and optical properties of the catalyst are characterized by using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, specific surface area, ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflection, thermal gravimetric-differential thermal and fluorescence and other techniques. Terephthalic acid is used as a probe molecule, and the chemical fluorescence technique is combined for researching generation of hydroxyl free radicals of the TiO2 / SiO2 composite photocatalyst surface. Photocatalytic degradation of a rhodamine B solution shows that the TiO2 / SiO2 composite oxide has the degradation rate of 98.6% under visible light illumination for 40 min, while the degradation rate of pure TiO2 is only 11.9%. When the titanium-silicon molar ratio is 1 to 1, the TiO2 / SiO2 apparent first-order rate constant is more than 33 times that of pure TiO2 and is more than six times that of P25, the reason of photocatalytic activity enhancement is attributed to effective inhibition of hole-electron pair combination. After the TiO2 / SiO2 photocatalyst is reused for five times, the rhodamine B degradation rate can reach 89.2%. The degradation of the photocatalyst on rhodamine B has specificity.
Owner:HUBEI NORMAL UNIV
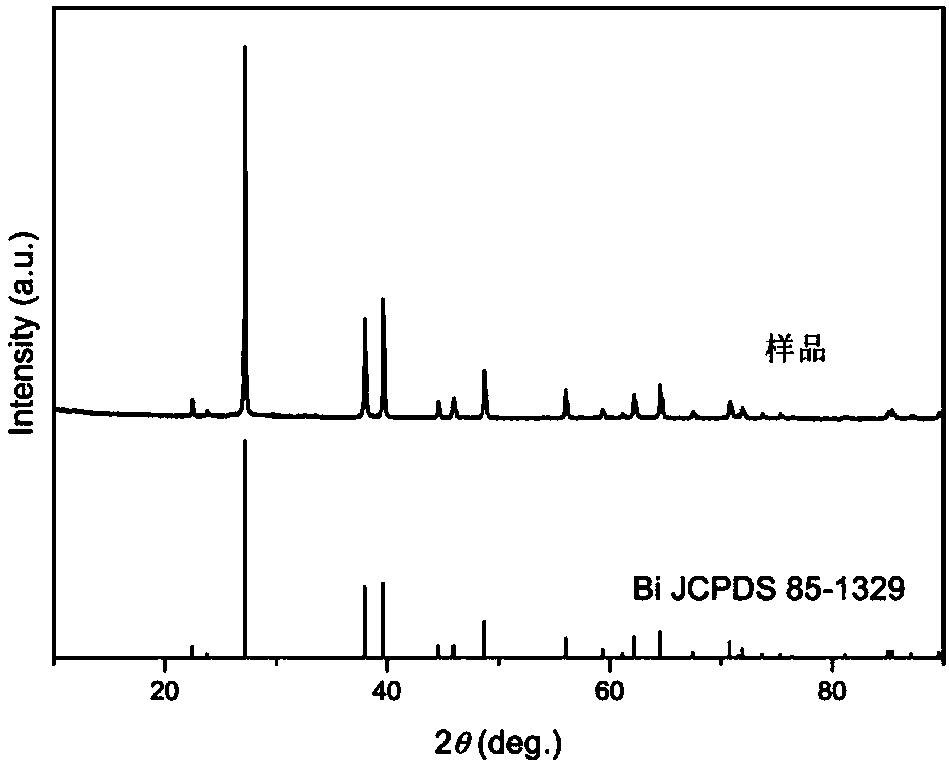
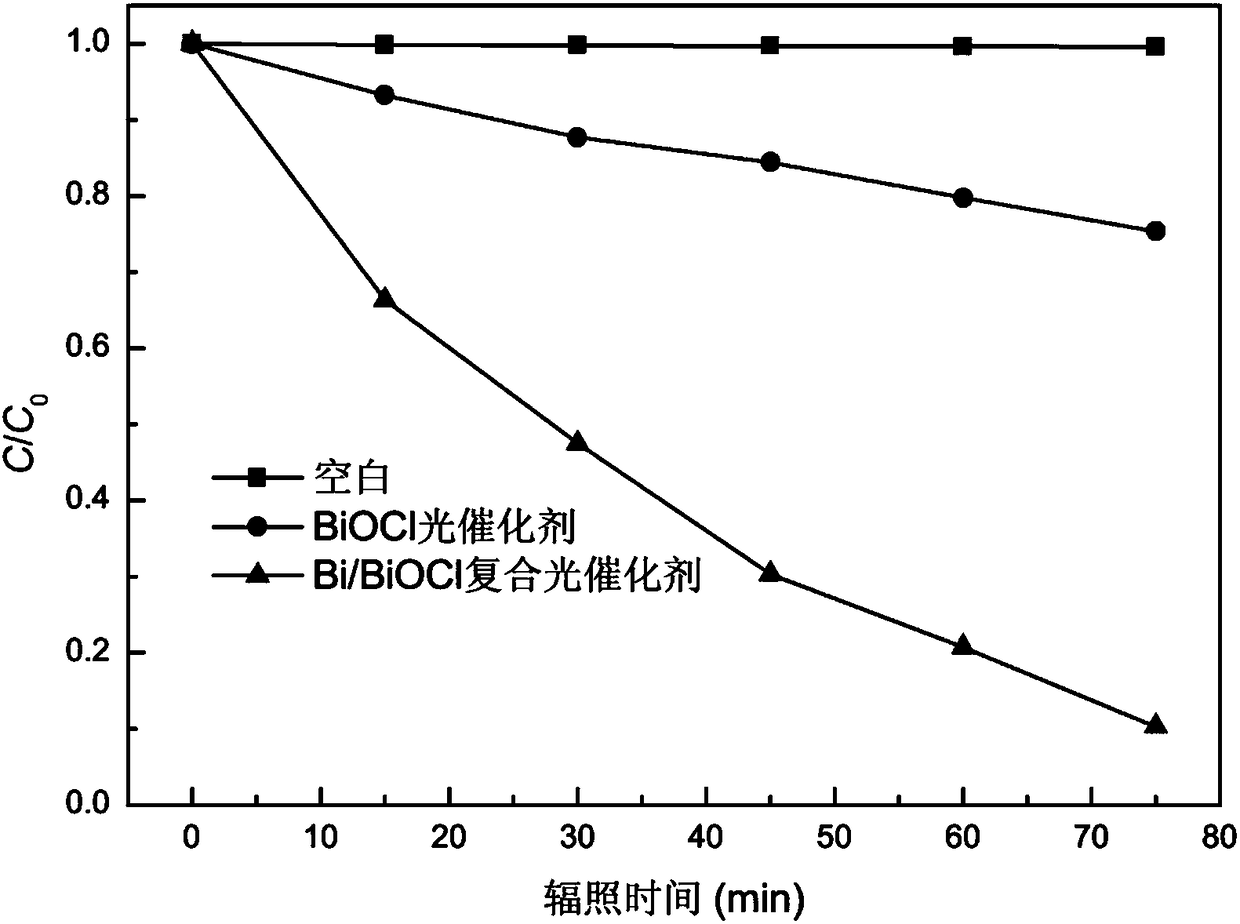
Bismuth nanosheets, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108480657AUniform sizeUniform size distributionTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusPhotocatalytic reactionPotassium
The invention provides bismuth nanosheets, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps that bismuth nitrate pentahydrate, ascorbic acid and ethylene glycol are mixed, and thus a mixed solution A is obtained; sodium citrate, potassium chloride and water are mixed, and thus a mixed solution B is obtained; and the solution A and the solutionB are mixed, after the pH value is adjusted, reacting is conducted under the ultrasonic condition, and the bismuth nanosheets are obtained. According to the preparation method, the bismuth nanosheetscan be obtained, and size distribution of the prepared bismuth nanosheets are uniform. The preparation method is simple, the cost of adopted raw materials is low, the raw materials are nonhazardous tothe environment, batch and mass production is easy, and the prepared bismuth nanosheets are few in impurity and high in purity; bismuth powder is in a sheet shape, the size is uniform, and obvious agglomerated large particles do not occur; and the average width of the bismuth nanosheets is 0.5-1 [mu]m, and the average thickness of the bismuth nanosheets is 80-100 nm; and a bismuth / BiOCl compositecatalytic material degrades 90% of methyl orange, and the rate constant of a photo-catalytic reaction is 0.0283 min<-1>.
Owner:XUCHANG UNIV
Ink set for inkjet recording and inkjet recording method
InactiveUS6874882B2Quality improvementMaintain image qualityMeasurement apparatus componentsInksImaging qualityPhotographic printing
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Flight control test simulator system and method
ActiveUS9454911B2Cosmonautic condition simulationsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSimulator couplingAerodynamic load
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Heterocyclic compound and use thereof
InactiveCN109867646ALong drive lifeImprove luminous efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesDisplay deviceLight-emitting diode
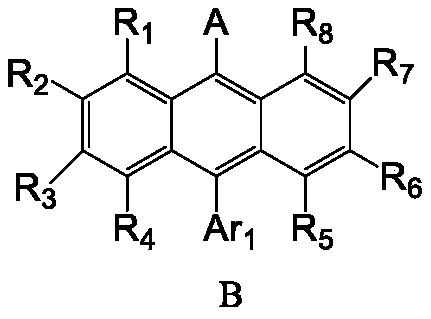
The invention belongs to the field of organic electroluminescent materials, and discloses a heterocyclic compound and use thereof. The heterocyclic compound provided by the invention has a structure of a formula (B) and has the advantages of serving as a blue-light or dark-blue-light luminescent material for an organic electroluminescent device and overcoming the defects of an existing blue-lightluminescent material; and the compound, as a luminescent material, has a closely matched hole-electron transmission rate, which is conducive to improving the luminescence efficiency of the material and device stability. In addition, the compound has extremely high bond dissociation energy, which is conducive to prolonging the driving life of a display device. Moreover, the compound has an extremely high radiative transition rate constant, which is conducive to prolonging the driving life of an organic light-emitting diode device.
Owner:AAC TECH NANJING
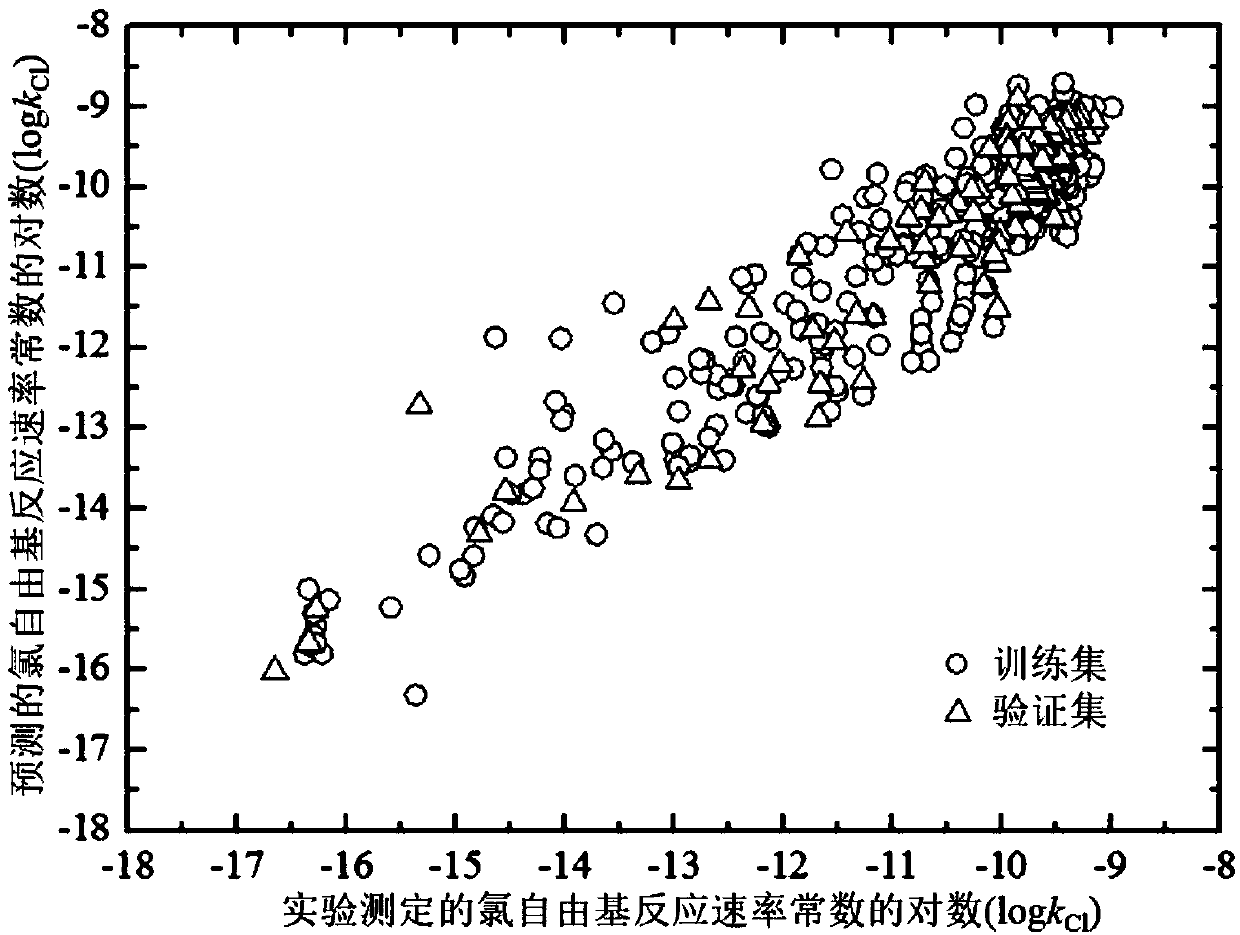
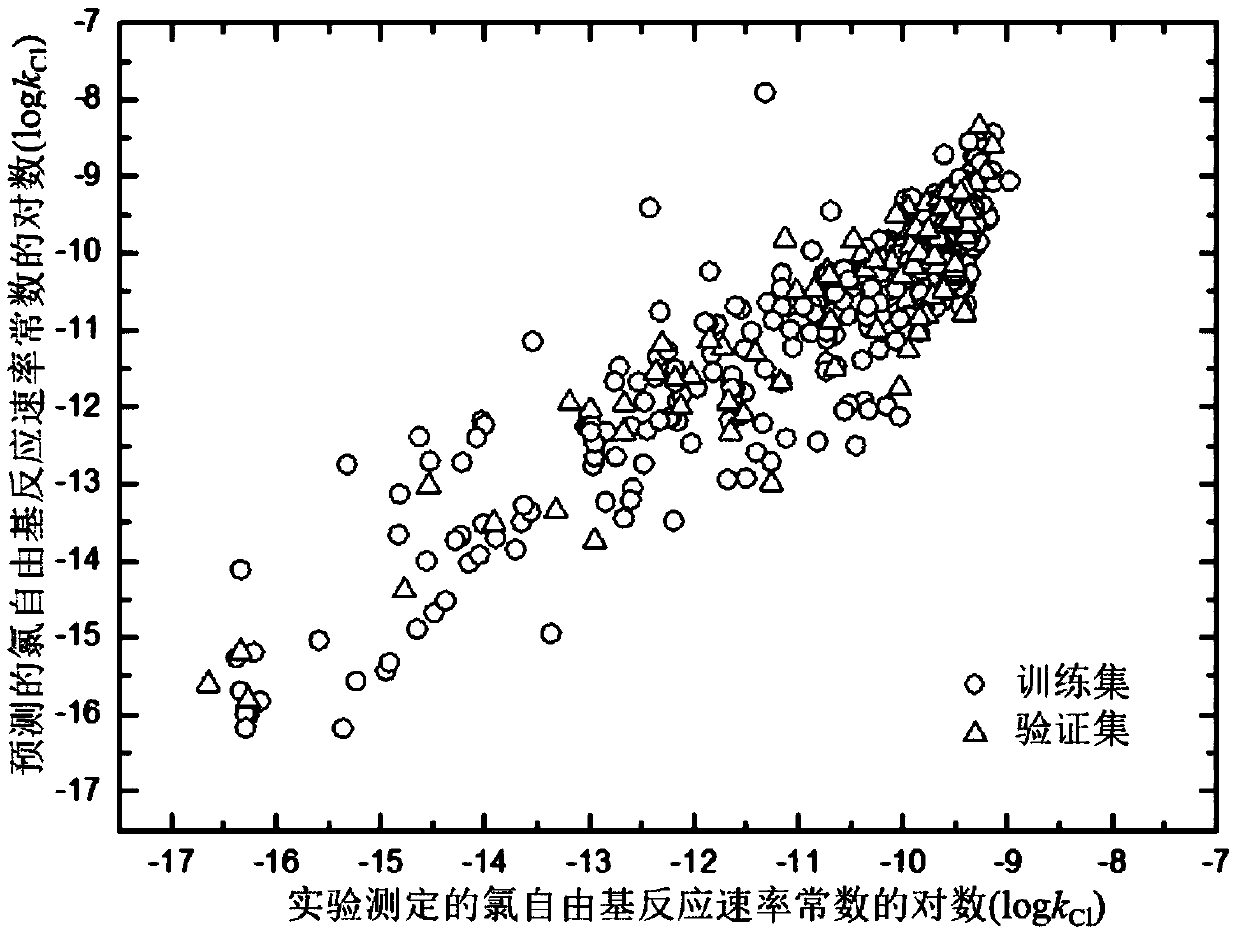
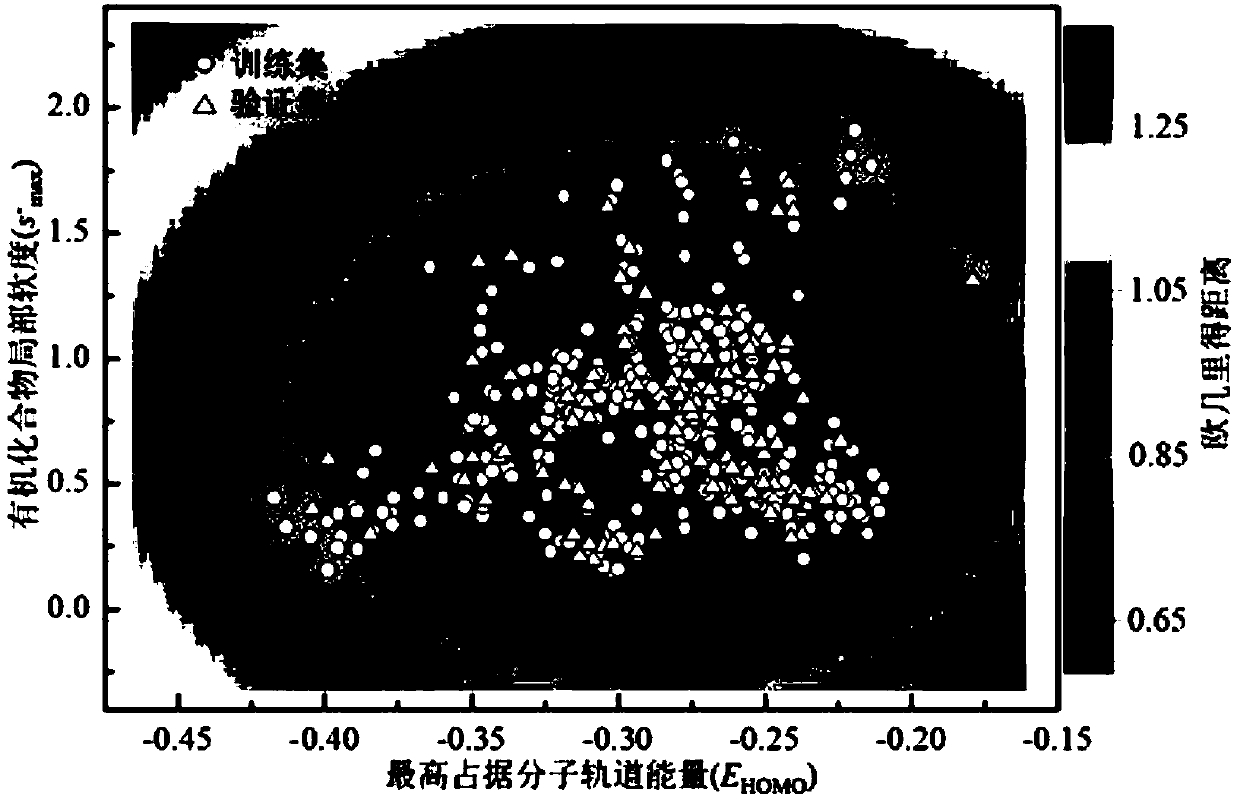
Method for adopting quantitative structure-activity relation model to predict reaction rate constant of chlorine free radical of organic chemicals
ActiveCN107563133AMechanism explanatoryLow costSpecial data processing applicationsRelational modelComputational chemistry
The invention discloses a method for adopting a quantitative structure-activity relation model to predict a reaction rate constant of chlorine free radical of organic chemicals. According to the method, a quantum chemistry descriptor with structural characters is figured out only by means of basic molecular structure information of the organic chemicals, and by adopting a constructed QSAR prediction model, a kCl value of the organic chemicals can be predicted quickly and efficiently. The method follows a guide rule issued for the construction and verification of a QSAR model by the Organization For Economic Co-Operation And Development (OECD). According to the method, by adopting a genetic algorithm-multiple linear stepwise regression analysis combination use method (GA-MLR) and a supportvector machine-multiple linear stepwise regression analysis combination use method (SVM-MLR), the transparency degree is high and more convenience is provided for application; since quantum chemistrydescriptors are adopted in all GA-MLR models, the physical meaning of the descriptors is clear; the method has a specific application domain, and is applicable to abundant organic varieties, excellentin goodness of fit, robustness and prediction capability, easy to program and capable of supplying important data support to environmental risk evaluation and management of the organic chemicals.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
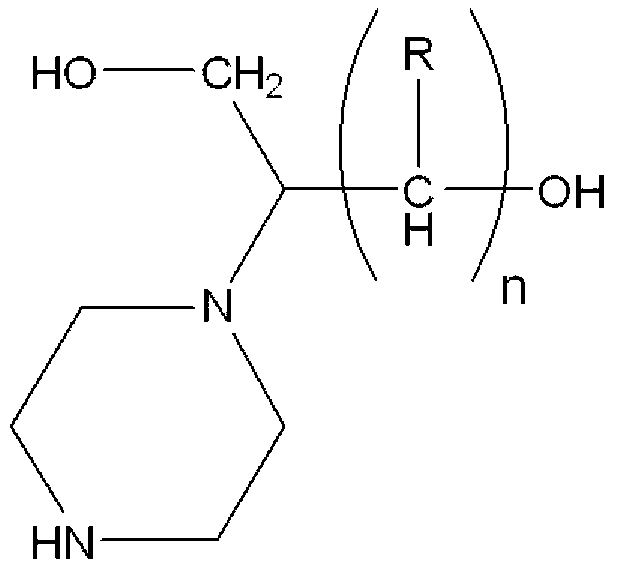
Process for producing hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine, and catalyst composition for the production of polyurethane resin using it
InactiveUS20110077376A1Easy accessEfficiently obtainedOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsProduction rateReaction rate constant
To provide a process for producing a hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine or hydroxytriethylenediamine simply and in a small number of steps without requiring multi-stage reaction steps; a novel catalyst composition whereby a polyurethane product can be obtained with good productivity and good moldability without bringing about odor problems or environmental problems; and a process for producing a polyurethane resin using the catalyst composition.For example, a hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine or hydroxytriethylenediamine is produced by subjecting a mono-substituted dihydroxyalkylpiperazine and / or a di-substituted hydroxyalkylpiperazine to an intramolecular dehydration condensation reaction in the presence of an acid catalyst.Further, for example, a polyurethane resin is produced by using a catalyst composition which comprises a hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine or hydroxytriethylenediamine (A), and an amine compound (B) having, in its molecule, one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of a hydroxy group, a primary amino group and a secondary amino group, or a tertiary amine compound (C) having a value of [blowing reaction rate constant / gelling reaction rate constant] of at least 0.5.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
Method for treating ship ballast water by injecting oxygen active particles in transmission pipe
InactiveCN102173485AIncrease concentrationIncrease productionWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processBallast water treatmentOxygen
The invention provides a method for treating ship ballast water by injecting oxygen active particles in a transmission pipe and belongs to the technical fields of plasma physics and marine environmental protection application. The method is characterized in that oxygen is ionized and dissociated in a strong ionization electric field to form oxygen active particles (O2+, O(1D), O(3P) and O3), and the concentration of the oxygen active particles reaches 100 mg / L to 400 mg / L; the oxygen active particles react with the ballast water to generate a HO2- initiator with a reaction rate constant of 2.2*106 L / mol.s, and the concentration of the HO2- initiator reaches 40 mg / L to 300 mg / L; the oxygen active particles react with the ballast water under the action of the HO2- initiator to generate hydroxyl radicals (.OH), and the concentration of the hydroxyl radicals reaches 0.4 mg / L to 160 mg / L; and the efficiency of killing aquatic organisms and pathogens in the ballast water reaches 96% to 100%. The invention has the benefit and advantage of solving the problems of ballast water treatment and providing the simple and high-efficiency ballast water treatment method which does not need catalysts, absorbents or reducers and does not cause any adverse effect on the environment.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
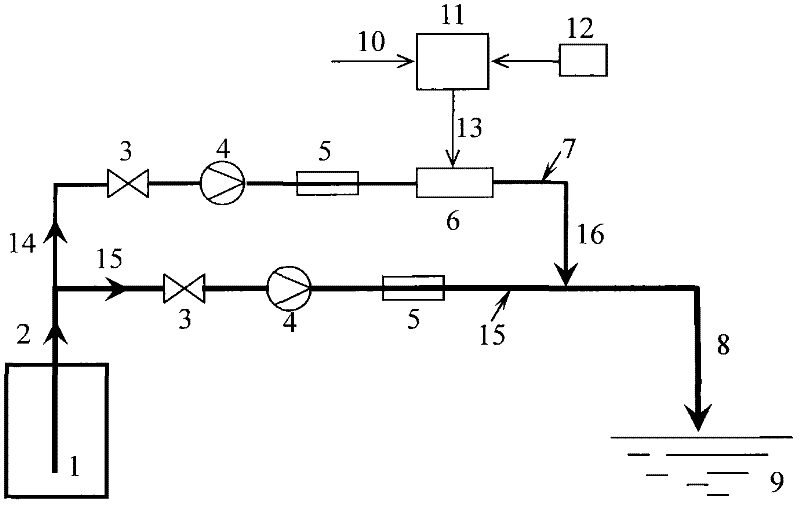
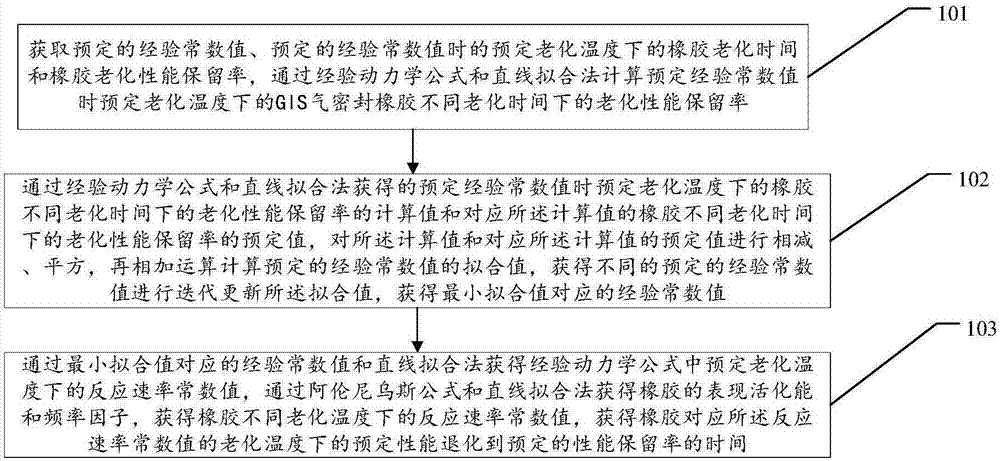
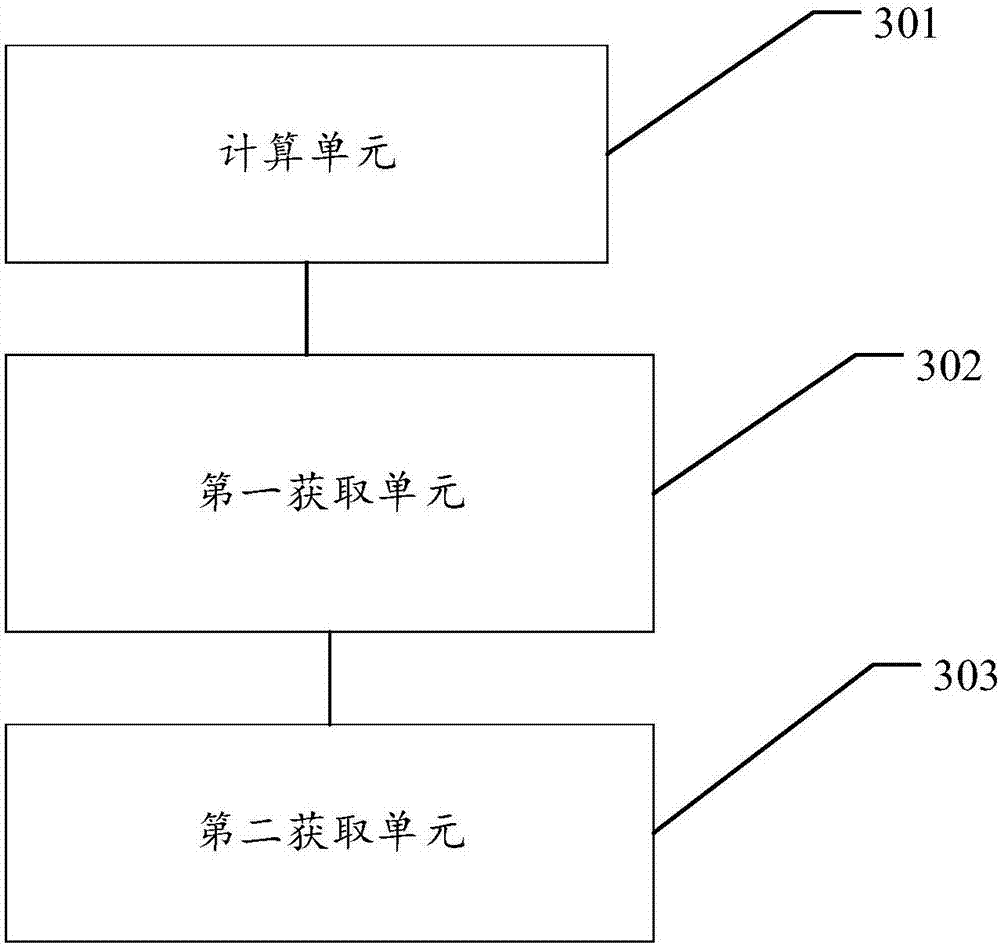
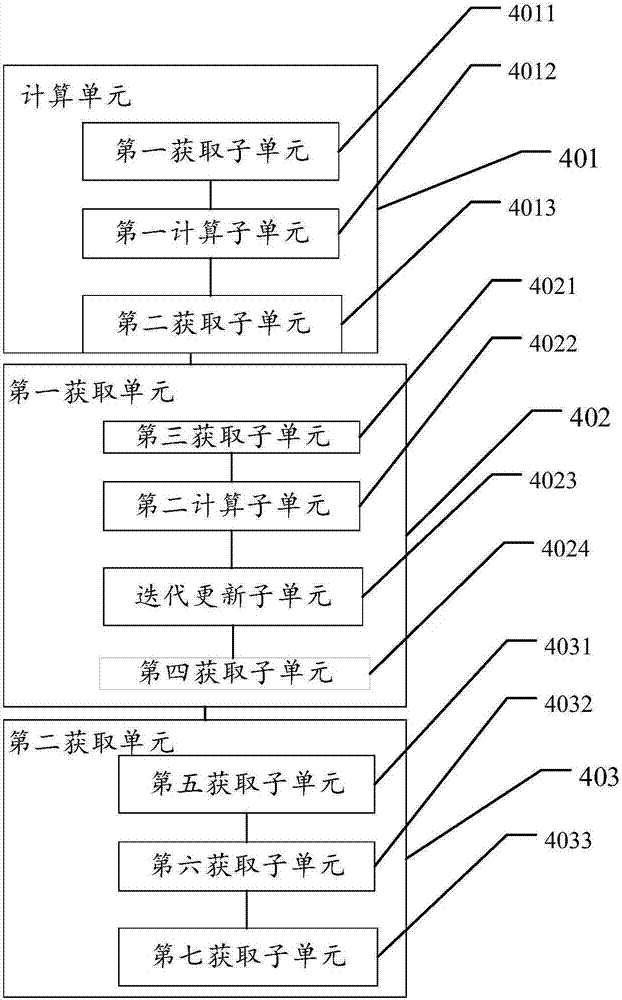
Calculation method and device for service life prediction of GIS (Geographic Information System) air-tight seal rubber
InactiveCN107122563AThe calculation result is accurateDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsLife timeLine fitting
The embodiment of the invention discloses a calculation method for the service life prediction of GIS (Geographic Information System) air-tight seal rubber. The method comprises the following steps that: S1: obtaining a preset empirical constant value as well as rubber aging time and a rubber aging performance retention rate under preset aging temperature during the preset empirical constant value, and calculating the aging performance retention rate under different aging time of the GIS air-tight seal rubber at the preset aging time during the preset empirical constant value; S2: through the calculation value of the aging performance retention rate and a preset value of the aging performance retention rate corresponding to the calculation value, calculating the fitted value of the preset empirical constant value, and carrying out iterative update on the fitted value to obtain the empirical constant value corresponding to a minimum fitted value; and S3: through the empirical constant value corresponding to the minimum fitted value and a linear fitting method, obtaining a reaction rate constant value at the preset aging temperature, obtaining the apparent activation energy and the frequency factor of rubber, obtaining the reaction rate constant value of the rubber at different aging temperature, and obtaining the rubber prediction service life.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Method for analyzing kinetic parameters of ozone oxidation reaction through dynamics curve of chemiluminescence
InactiveCN1916605AAccurate analysisAccurately determineChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSpecial data processing applicationsChemical physicsLight signal
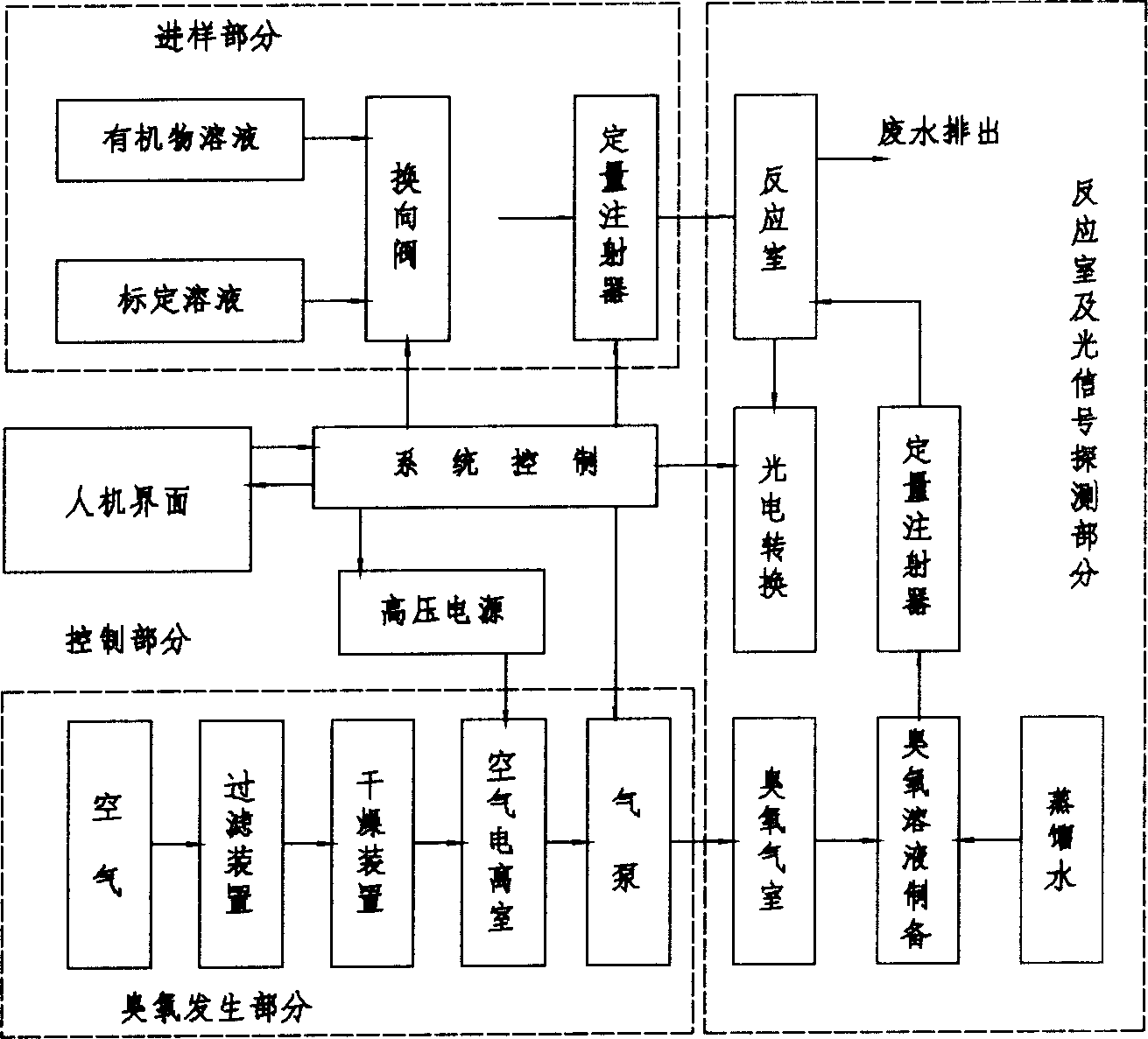
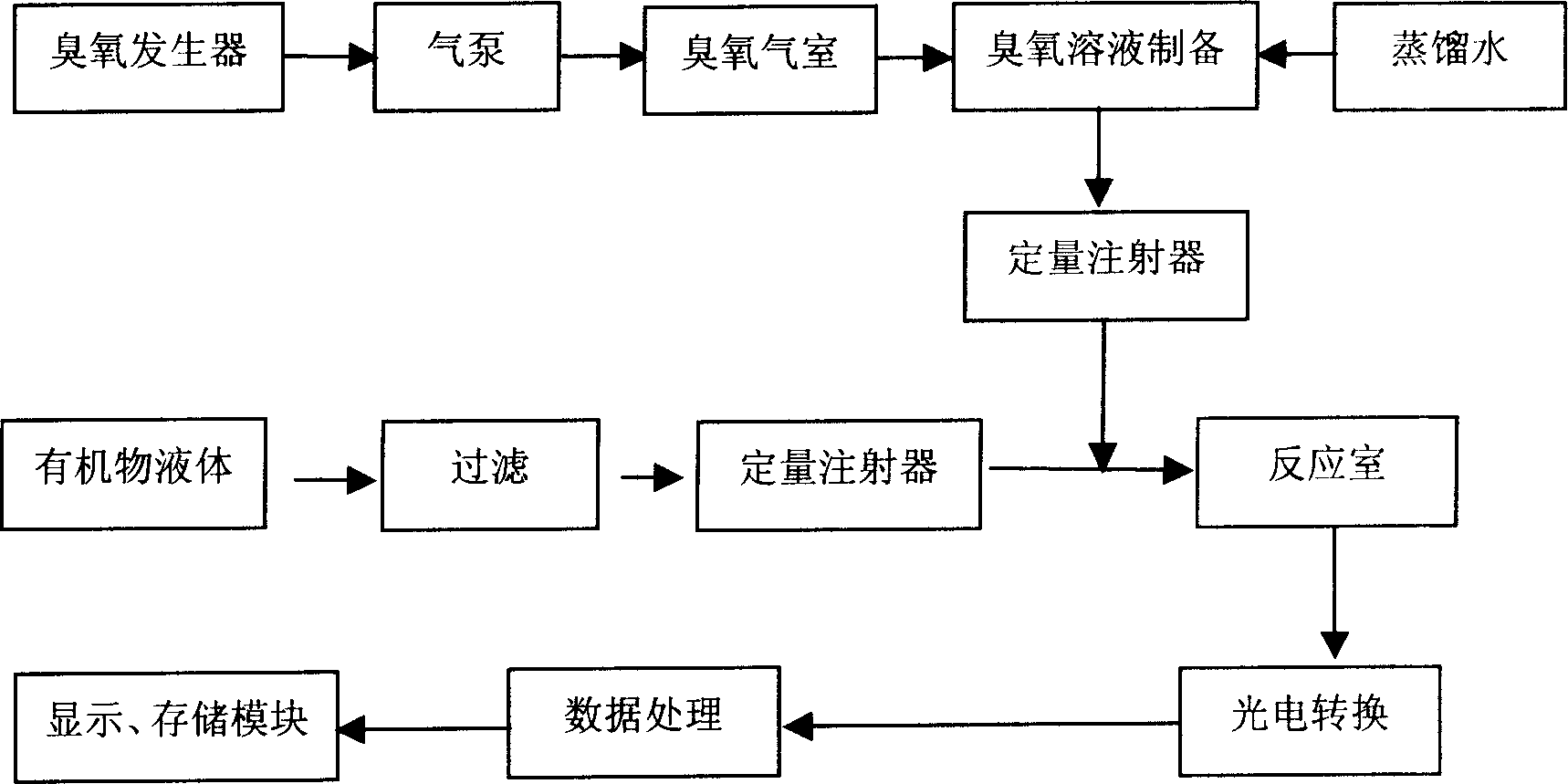
A method of utilizing chemiluminescence dynamic curve to analyze dynamic parameter of ozone oxidizing reaction uses relation of light signal intensity I to time T to confirm reaction grade and reaction rate constant.
Owner:OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTR RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Process for producing hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine compound, and catalyst composition for the production of polyurethane resin using the hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine compound
InactiveCN102046629AWon't happenReduce the number of processesOrganic chemistry methodsProduction rateReaction speed
Disclosed is a process for producing a hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine compound or hydroxytriethylenediamine without multi-stage reaction steps through a small number of steps in a simple manner. Also disclosed is a novel catalyst composition that can provide a polyurethane product produced with high productivity and moldability without causing problems with odor and environment. Further disclosed is a process for producing a polyurethane resin using the catalyst composition. A hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine compound or hydroxytriethylenediamine is produced by subjecting, for example, a mono-substituted dihydroxyalkylpiperazine compound and / or a di-substituted hydroxyalkylpiperazine compound to an intramolecular dehydrocondensation in the presence of an acid catalyst. Further, a polyurethane resin is produced by using a catalyst composition comprising, for example, a hydroxyalkyltriethylenediamine compound or hydroxytriethylenediamine (A) and an amine compound (B) having one or at least two substituents, in the molecule thereof, selected from the group consisting of a hydroxy group, a primary amino group, and a secondary amino group or a tertiary amine compound (C) having a value of [foaming reaction rate constant / resinification reaction rate constant] of 0.5 or more.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
Heterojunction type ternary composite semiconductor photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104841440AProper band structureIncrease separation rateWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsHeterojunctionElectronic band structure
The invention discloses a heterojunction type ternary composite semiconductor photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof. A constant-pH coprecipitation method is adopted to prepare ternary layered double hydroxides as a precursor, and finally a ternary heterojunction composite semiconductor is obtained by high-temperature roasting. The preparation technology is simple and convenient, the obtained material is provided with a proper energy band structure, current carrier separation and migration rates can be effectively improved, visible light is efficiently used, the relative amount of metal ions is selectively regulated and controlled to prepare a series of ternary heterojunction composite semiconductors, a high-activity photocatalyst is screened out, and good dye degradation ability is shown under the visible light. A visible light catalytic degradation reaction rate constant of the ternary heterojunction composite semiconductor to methylene blue is 1.6 to 4.1 times of that of a binary composite semiconductor, and the ternary heterojunction composite semiconductor has higher catalytic activity and good universality in the aspect of dye degradation under visible light.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Inkjet color ink
InactiveUS7083664B2Excellent image preservabilityMonoazo dyesDuplicating/marking methodsYELLOW DYEAbsorbance
An inkjet color ink comprising: an aqueous medium; at least one yellow dye having a λmax of from 390 nm to 470 nm and an [I(λmax+70 nm) / I(λmax)] ratio of an absorbance I(λmax+70 nm) at λmax+70 nm to an absorbance I(λmax) at λmax of not more than 0.4; and at least one dye having a λmax of longer than 470 nm and not longer than 750 nm, the at least one yellow dye and the at least one dye being at least dissolved or dispersed in the aqueous medium, wherein both of the rate constants defined herein are not more than 5.0×10−2 hour−1.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Method for use of microdialysis
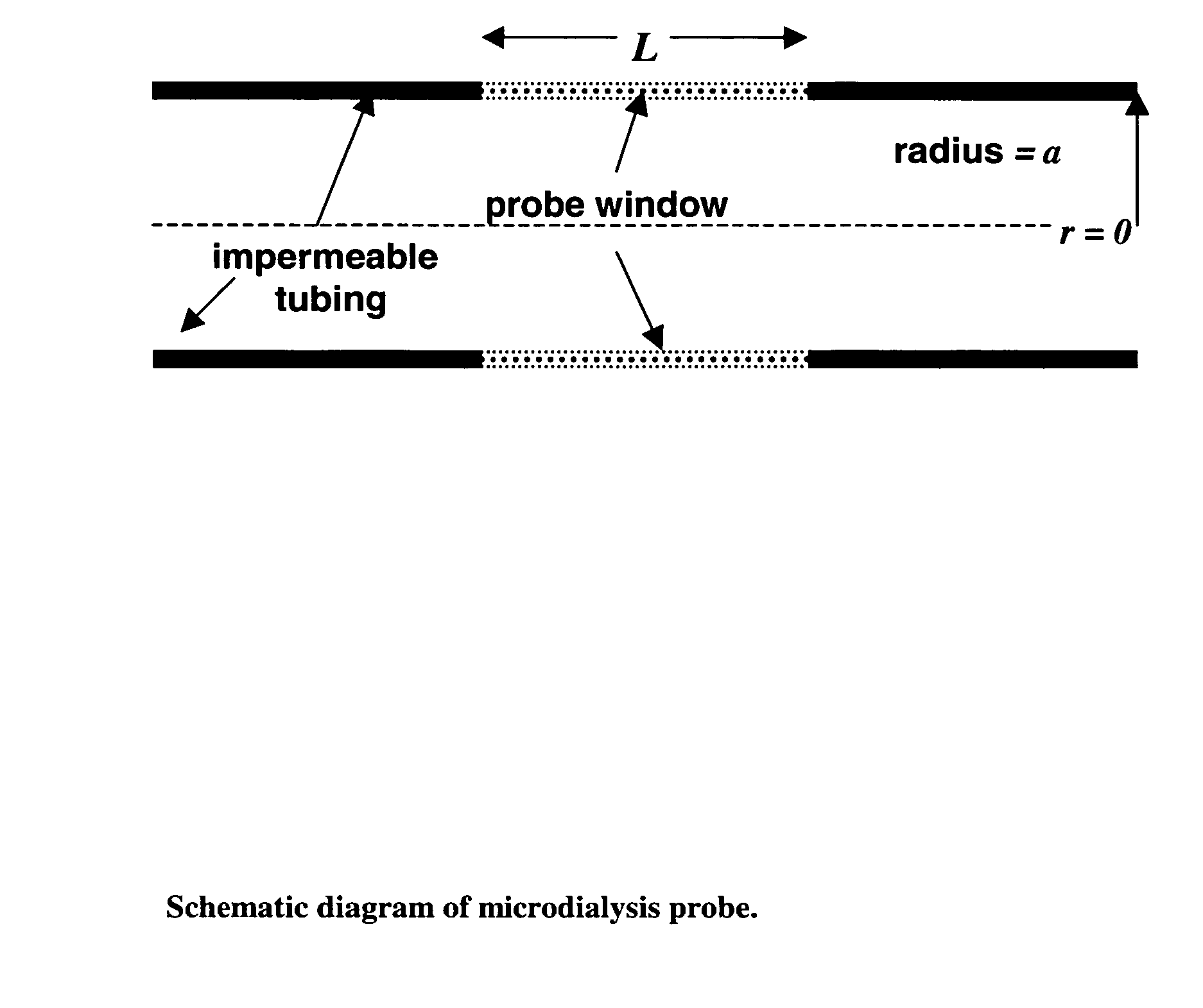
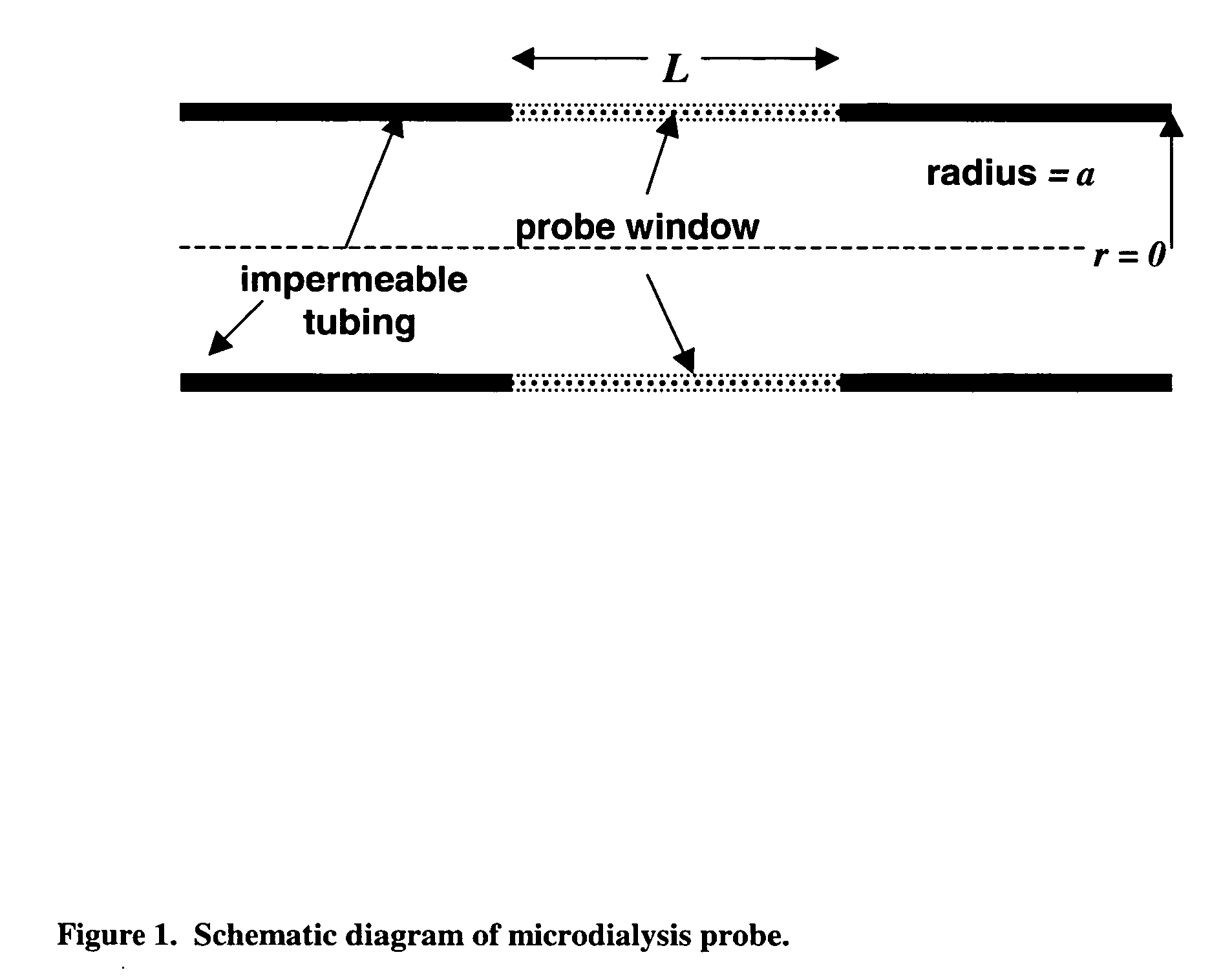
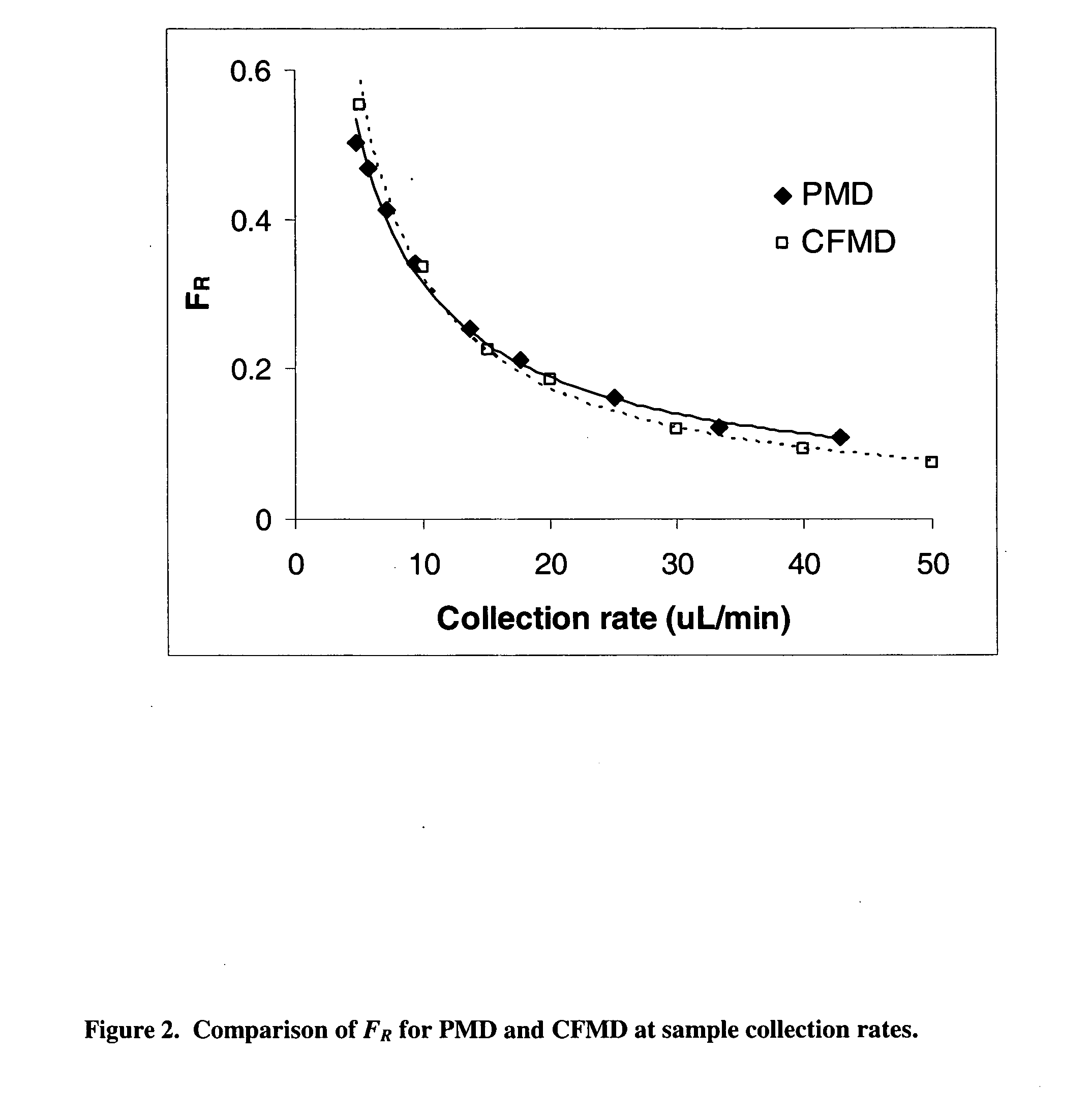
InactiveUS20070106140A1Fast resultsAccurately permeabilitySensorsBlood characterising devicesResting timeHigh rate
It has been surprisingly found that very accurate measurements of mass transfer can be made rapidly by permitting diffusion of an agent desired to be measured into a small, known volume of receiver or out of a known volume of donor, then rapidly pumping or flushing (“pulsing”) the receiver with a known volume of fluid. More specifically, a novel method of transferring small quantities of a contained material (either dissolved or suspended) between two media, based on such pulsing, hereinafter called pulsatile microdialysis (PMD), is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, one medium (the dialysate) is inside a small, permeable tube (microdialysis probe window) and the other (external medium) is outside. The transfer of material between the two media can be utilized, for example, to sample drug concentrations in the external medium, or the release of drugs from systems within the dialysate, or for other measurements as disclosed herein. In PMD, a dialysate fluid is pumped into a microdialysis probe window, allowed to occupy the probe window while at rest for some resting time, and then flushed at a high rate out as a single pulse. A model that is based on a Fick's Laws was solved, and equations were derived to calculate the effects of various experimental parameters. The models were verified against experimental data using methazolamide, warfarin and benzocaine as test drugs. The data followed the mathematical models. For cases in which the concentration of free drug in the medium outside the probe was constant or changed very slowly, the concentration calibration plots were linear. In simulated first order uptake studies, the PMD and direct donor sampling data were in nearly exact agreement with the theoretical values of k=0.09 min−1. In another experiment, the free concentration of warfarin sodium in the medium outside the probe was made to decline rapidly in a known first order manner, with rate constants as high as 0.077 sec−1. The concentration in the external medium calculated from the PMD data was in nearly exact agreement with the known concentration at various times, and the experimental rate constants were in nearly exact agreement with the theoretical rate constants. For binding of methazolamide to activated charcoal, and for the binding of sodium warfarin to bovine serum albumin, PMD was able to generate sufficient data points to accurately characterize the rapid initial binding. This invention demonstrates that PMD is an accurate method of sampling drug concentrations and measuring rates and extents of a number of processes, including protein binding, adsorption to binding agents such as activated charcoal, release from microemulsion drug delivery systems, and the determination of drug diffusion coefficients, and for various other purposes which will occur to those skilled in the art. Compared to known methods such as traditional (continuous) microdialysis, the present invention offers the ability to sample more frequently, and over much shorter time intervals, thereby accurately obtaining data not heretofore available.
Owner:BELLANTONE ROBERT ARTHUR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com