Deep sea broadband target depth estimation method based on stripe interference structure
A technology of target depth and interference structure, which is applied in the field of deep-sea broadband target depth estimation based on fringe interference structure, and can solve the problems of less application of waveguide invariants and other problems.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0055] Now in conjunction with embodiment, accompanying drawing, the present invention will be further described:
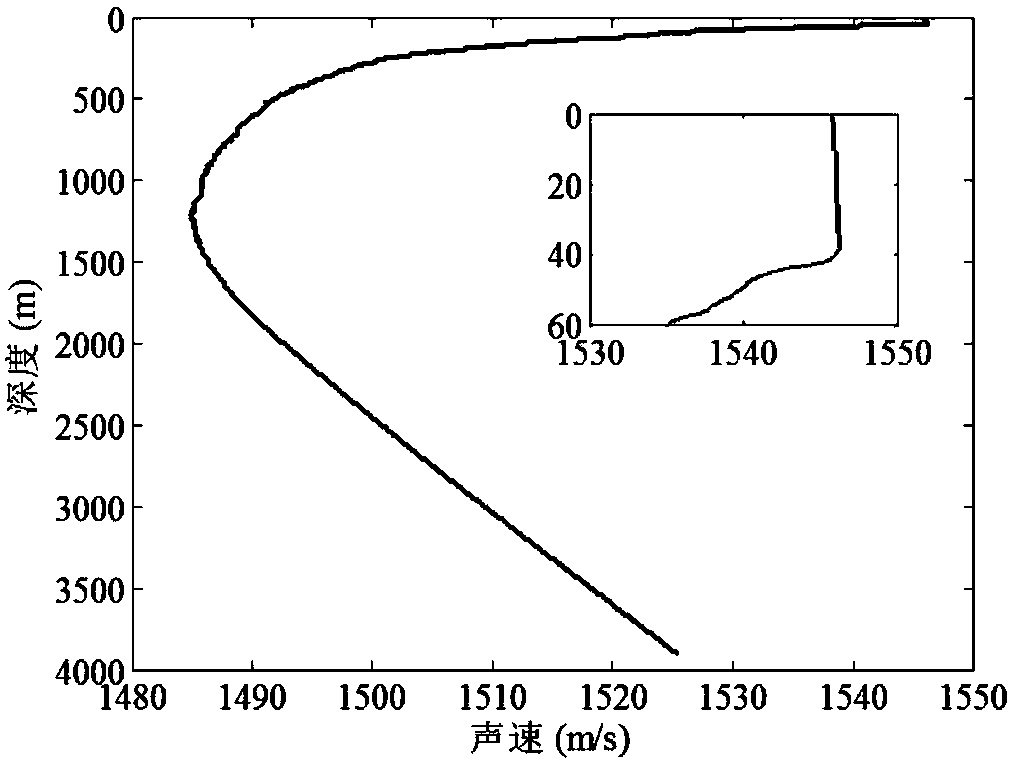
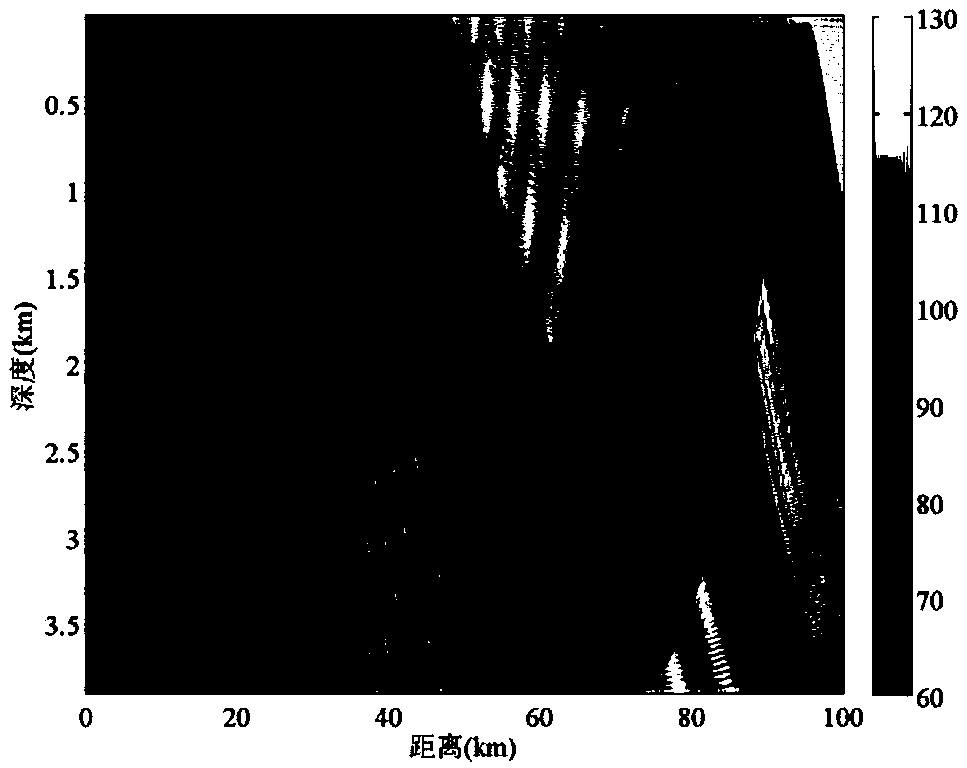
[0056] This example figure 1 The sound velocity profile of the experimental sea area is given, the water depth is 3904m, and the depth of the mixed layer is 40m. The bottom of the sea is basically flat. The receiving array is a 16-element vertical line array, located on the seabed, the array element spacing is 4m, and the depth of the array element center is 3700m. The seabed sound velocity, density and attenuation coefficient are 1560m / s and 1.6g / cm respectively 3 and 0.2dB / λ. figure 2 It is the propagation loss map in this environment. It can be seen that the typical deep sea acoustic propagation path has lower propagation loss near the seabed of 20 kilometers and 70 kilometers, and the received underwater acoustic signal has a higher signal-to-noise ratio. Object depth estimation is accomplished through the following four steps:
[0057] Step 1 assumes ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com