In-situ layered utilization of building solid wastes and application to reduction of salt and alkali in soil
A technology for solid waste and plant waste, which is applied to the in-situ stratified utilization of building solid waste and the application field of reducing soil salinity, can solve the problems of unfavorable site ecological utilization, poor site soil nutrients, etc. Achieve the effect of being beneficial to ecological utilization, accelerating the reduction of salinity and increasing infiltration rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
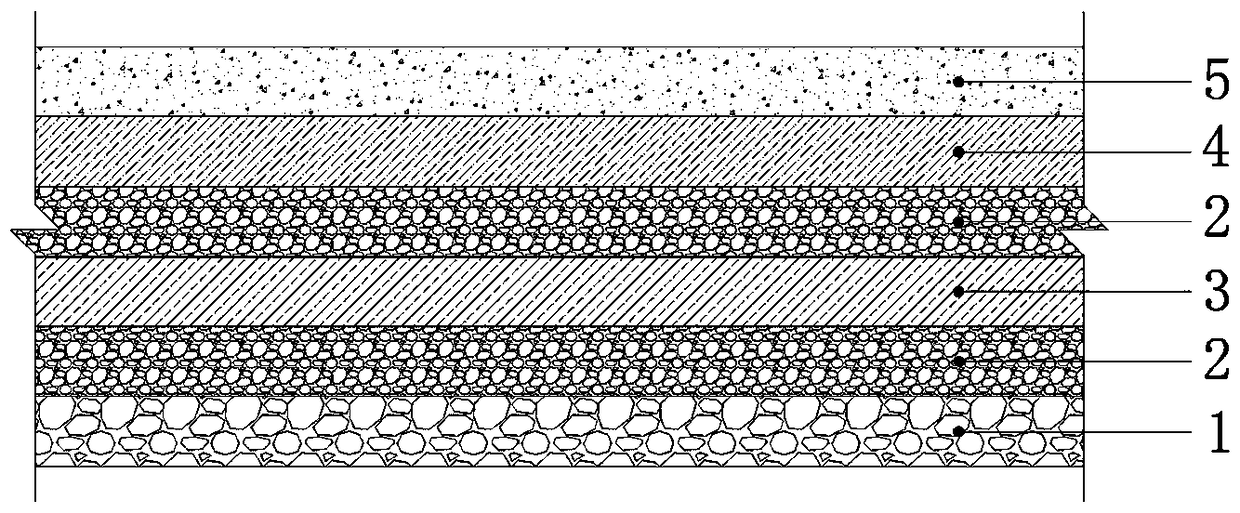
[0035] (1) Crushing and screening of solid waste from buildings on the site:
[0036] Crush and screen the solid waste of the site and buildings according to two types of coarse solid waste and fine solid waste; sort out materials that will rot for a long time and cause volume variables to cause foundation deformation (such as residual branches, foam, etc.);
[0037] The coarse solid waste: refers to the solid waste that is formed after the demolition of buildings and floors is sorted and crushed, with a particle size of 20-30 cm;
[0038] The fine solid waste refers to the solid waste that is formed after the demolition of buildings and floors is sorted and crushed, with a particle size of 10-16 cm.
[0039] (2) Preparation of greening plant waste:
[0040] Crush the plant residues, weeds, fallen leaves and branches according to two types of coarse green plant waste and fine green plant waste;
[0041] The crude greening plant waste refers to the shrub trimmings, thinnings, lawn trimmin...
Embodiment 2
[0053] (1) Crushing and screening of solid waste from buildings on the site:
[0054] Crush and screen the solid waste of the site and buildings according to two types of coarse solid waste and fine solid waste; sort out materials that will rot for a long time and cause volume variables to cause foundation deformation (such as residual branches, foam, etc.);
[0055] The said coarse solid waste: refers to the solid waste that is formed after the demolition of buildings and floors is sorted and crushed, with a particle size of 16cm-20cm;
[0056] The fine solid waste refers to the solid waste formed after the demolition of buildings and floors is sorted and crushed, with a particle size of 10cm-16cm.
[0057] (2) Preparation of greening plant waste:
[0058] Crush the plant residues, weeds, fallen leaves and branches according to two types of coarse green plant waste and fine green plant waste;
[0059] The crude greening plant waste refers to the shrub trimmings, thinnings, lawn trimming...
Embodiment 3
[0072] (1) Crushing and screening of solid waste from buildings on the site:
[0073] Crush and screen the solid waste of the site and buildings according to two types of coarse solid waste and fine solid waste; sort out materials that will rot for a long time and cause volume variables to cause foundation deformation (such as residual branches, foam, etc.);
[0074] The said coarse solid waste: refers to solid waste with a particle size of 25-30 cm after sorting and crushing the solid waste formed after the demolition of buildings and floors;
[0075] The fine solid wastes refer to solid wastes with a particle size of 8-12 cm after sorting and crushing the solid wastes formed after the demolition of buildings and floors.
[0076] (2) Preparation of greening plant waste:
[0077] Crush the plant residues, weeds, fallen leaves and branches according to two types of coarse green plant waste and fine green plant waste;
[0078] The crude greening plant waste refers to the shrub trimmings, t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com