Glycoprotein surface imprinted polymer based on team boron affinity as well as preparation method and application of glycoprotein surface imprinted polymer
A technology of surface imprinting and polymers, applied in chemical instruments and methods, and other chemical processes, can solve the problems of low selectivity, easy loss of biological activity, poor adsorption and separation effect, etc., to maintain biological activity and avoid secondary pollution , good biological activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
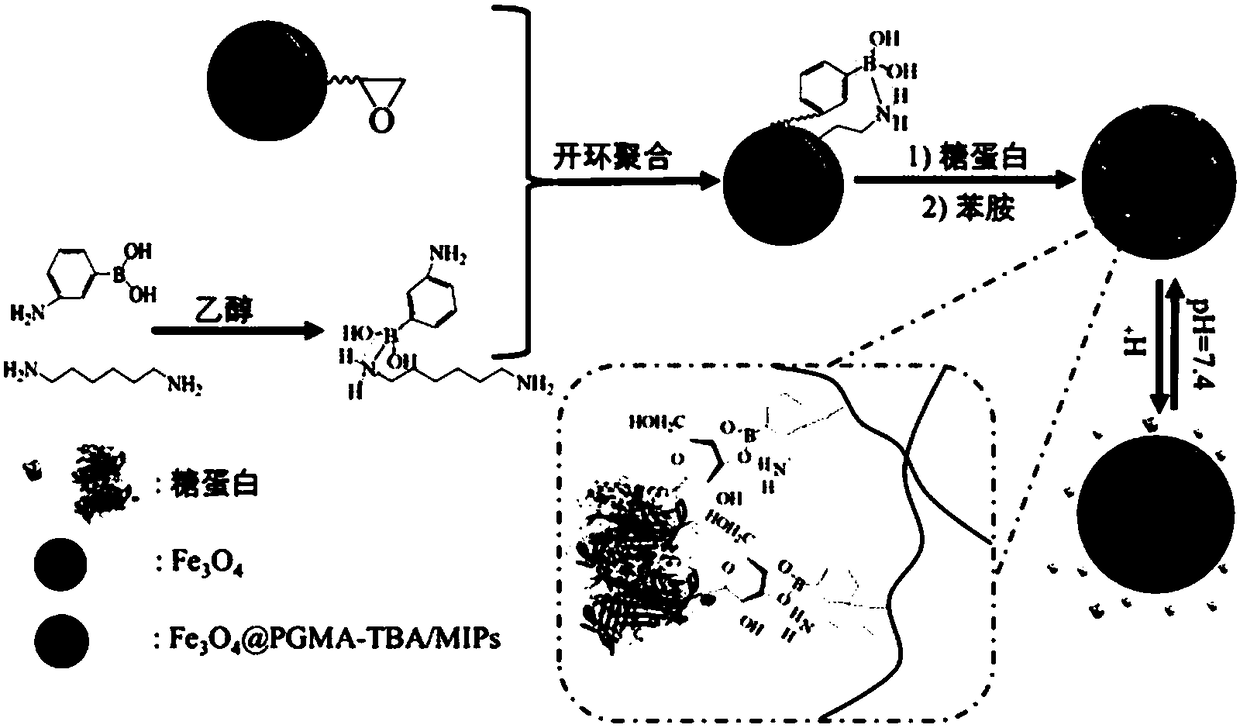
[0039] (1) Preparation of TBA-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles:
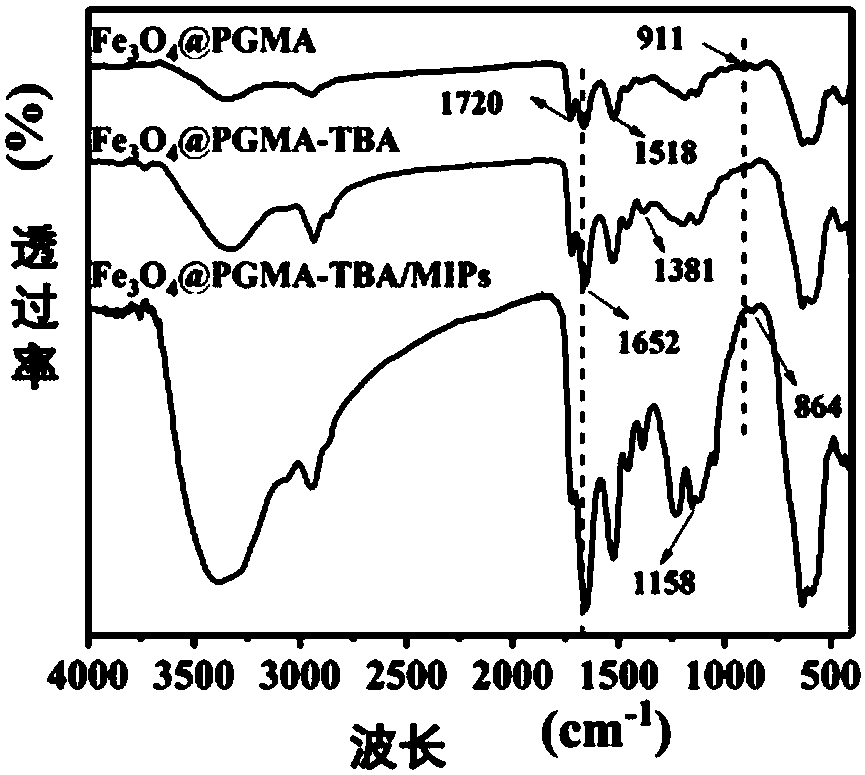
[0040] First, for Fe 3 o 4 @PGMA nanoparticles for surface modification. First, 0.1 g of 3-aminophenylboronic acid and 0.1 g of 1,6-hexanediamine were dispersed in 20 mL of ethanol, followed by stirring at 30 °C for 30 min to form B-N coordinated team boron affinity molecules. Then add 0.025 g core-shell Fe 3 o 4 @PGMA nanoparticles and reflux at 60°C for 12h, and then dry to constant weight in a vacuum oven at 40°C to obtain TBA-modified ferric oxide nanoparticles (Fe 3 o 4 @PGMA-TBA).
[0041] (2) Preparation of imprinted polymers on the surface of glycoproteins:
[0042] First, 0.005 g template protein egg albumin and 0.025 g Fe obtained in step (1) 3 o 4 @PGMA-TBA was added to 20 mL of phosphate buffer solution with pH=7.4, ultrasonically dispersed for 5 min, and then left to stand in the dark for 0.5 h to allow egg albumin and Fe 3 o 4 The TBA molecules on the @PGMA-TBA surface are bound together by ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] (1) Preparation of TBA-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles:
[0049] First, for Fe 3 o 4 @PGMA nanoparticles for surface modification. First, 0.167 g of 3-aminophenylboronic acid and 0.138 g of 1,6-hexanediamine were dispersed in 40 mL of ethanol, followed by stirring at 40 °C for 60 min to form B-N coordinated team boron affinity molecules. Then add 0.050 g core-shell Fe 3 o 4 @PGMA nanoparticles and reflux at 60-100°C for 12h, and then dry to constant weight in a vacuum oven at 40-60°C to obtain TBA-modified ferric oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4@PGMA-TBA).
[0050] (2) Preparation of imprinted polymers on the surface of glycoproteins:
[0051] First, 0.010 g template protein egg albumin and 0.050 g Fe obtained in step (1) 3 o 4 @PGMA-TBA was added to 30 mL of phosphate buffer solution with pH=7.4, ultrasonically dispersed for 10 min, and then left to stand in the dark for 1 h to allow egg albumin to bind to the TBA molecules on the surface of Fe3O4@PGMA-TBA through boron ...
Embodiment 3
[0053] (1) Preparation of TBA-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles:
[0054] First, for Fe 3 o 4 @PGMA nanoparticles for surface modification. First, 0.2 g of 3-aminophenylboronic acid and 0.15 g of 1,6-hexanediamine were dispersed in 60 mL of ethanol, followed by stirring at 60 °C for 390 min to form B-N coordinated team boron affinity molecules. Then add 0.075 g core-shell Fe 3 o 4 @PGMA nanoparticles were refluxed at 100°C for 12 h, and then dried to constant weight in a vacuum oven at 60°C to obtain TBA-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles (Fe3O4@PGMA-TBA).
[0055] (2) Preparation of imprinted polymers on the surface of glycoproteins:
[0056] First, 0.015 g template protein egg albumin and 0.075 g Fe obtained in step (1) 3 o 4 @PGMA-TBA was added to 40 mL of pH=7.4 phosphate buffer solution, ultrasonically dispersed for 15 min, and then left to stand in the dark for 1.5 h to allow egg albumin and Fe 3 o 4 The TBA molecules on the @PGMA-TBA surface are bound together by boron af...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com