AADL (architecture analysis and design language) model extension based software system security verification and assessment method
A software system and security technology, applied in platform integrity maintenance, electrical digital data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of direct processing of difficult system models, computational redundancy, huge computational cost, etc., to improve the accuracy of evaluation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
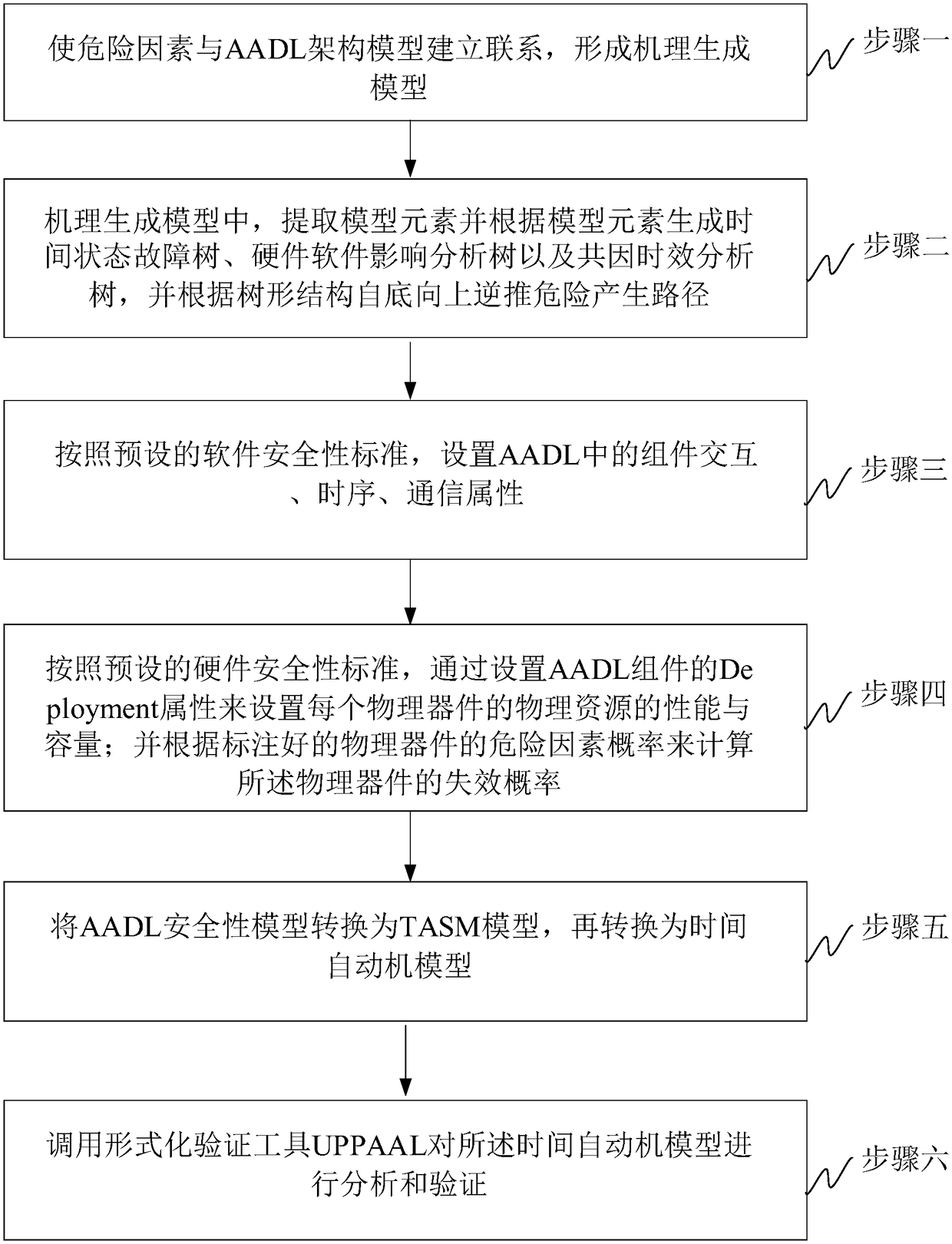
[0018] Specific implementation mode one: the software system security verification and evaluation method based on the AADL model extension of this implementation mode, such as figure 1 shown, including:
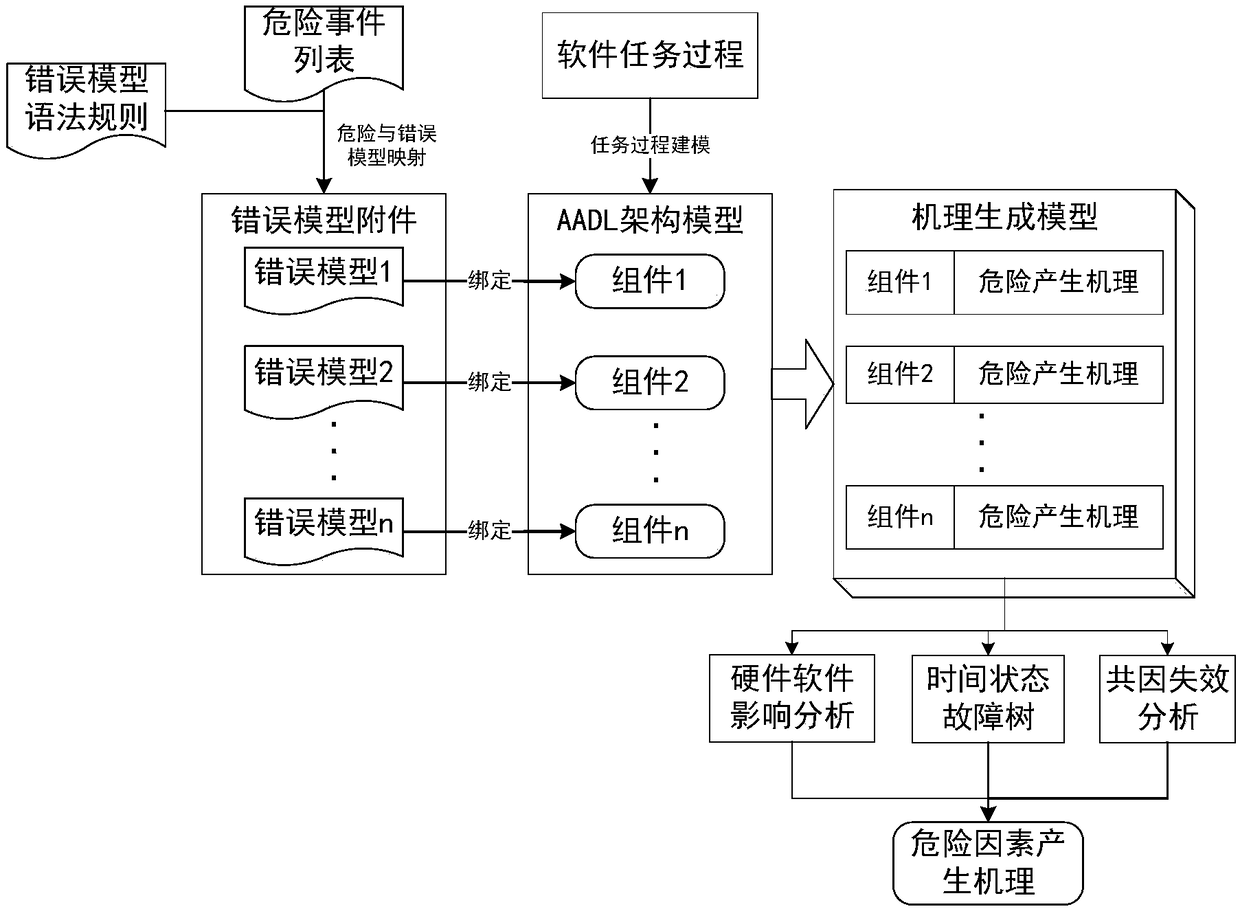
[0019] Step 1. Determine the risk factor list of the system to be evaluated, and establish a mapping relationship between each risk factor in the risk factor list and the AADL error model attachment according to the preset grammatical rules; then establish a mapping relationship between the AADL error model attachment and the AADL architecture model, In order to establish the relationship between the risk factors and the AADL framework model; and the set of all established relationships is called the mechanism generation model. For example, the list of risk factors determined for a certain flight control software may include abnormal bus voltage, abnormal power supply of a single aircraft, failed self-test of a single aircraft, inaccurate navigation calculation, incorrect tim...
specific Embodiment approach 2
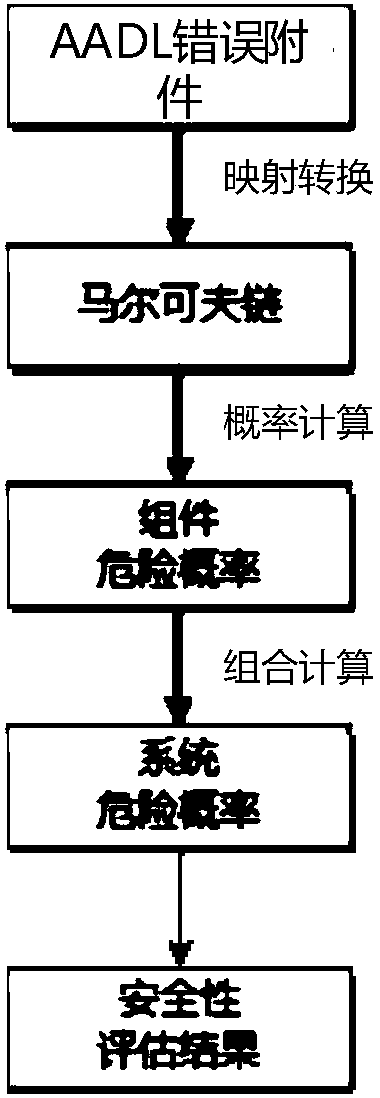
[0025] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the software system security verification and evaluation method based on AADL model expansion also includes step seven (such as image 3 shown):
[0026] The AADL error model attachment in step 1 is mapped and converted to obtain the Markov chain; the probability calculation of the Markov chain is performed to obtain the component hazard probability; the combination of component hazard probabilities is calculated to obtain the system hazard probability; sex assessment results.
[0027] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0028] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that in step one, the mapping relationship between each risk factor in the risk factor list and the AADL error model attachment is established according to the preset grammatical rules:
[0029] Map the key tasks in the main task process to the initial state in the AADL model attachment; map the error handling process in the key person to the error state in the AADL model attachment; map the elements in the risk factor list to error events; map the task's The execution sequence is mapped to the logical relationship and propagation path between components.
[0030] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com