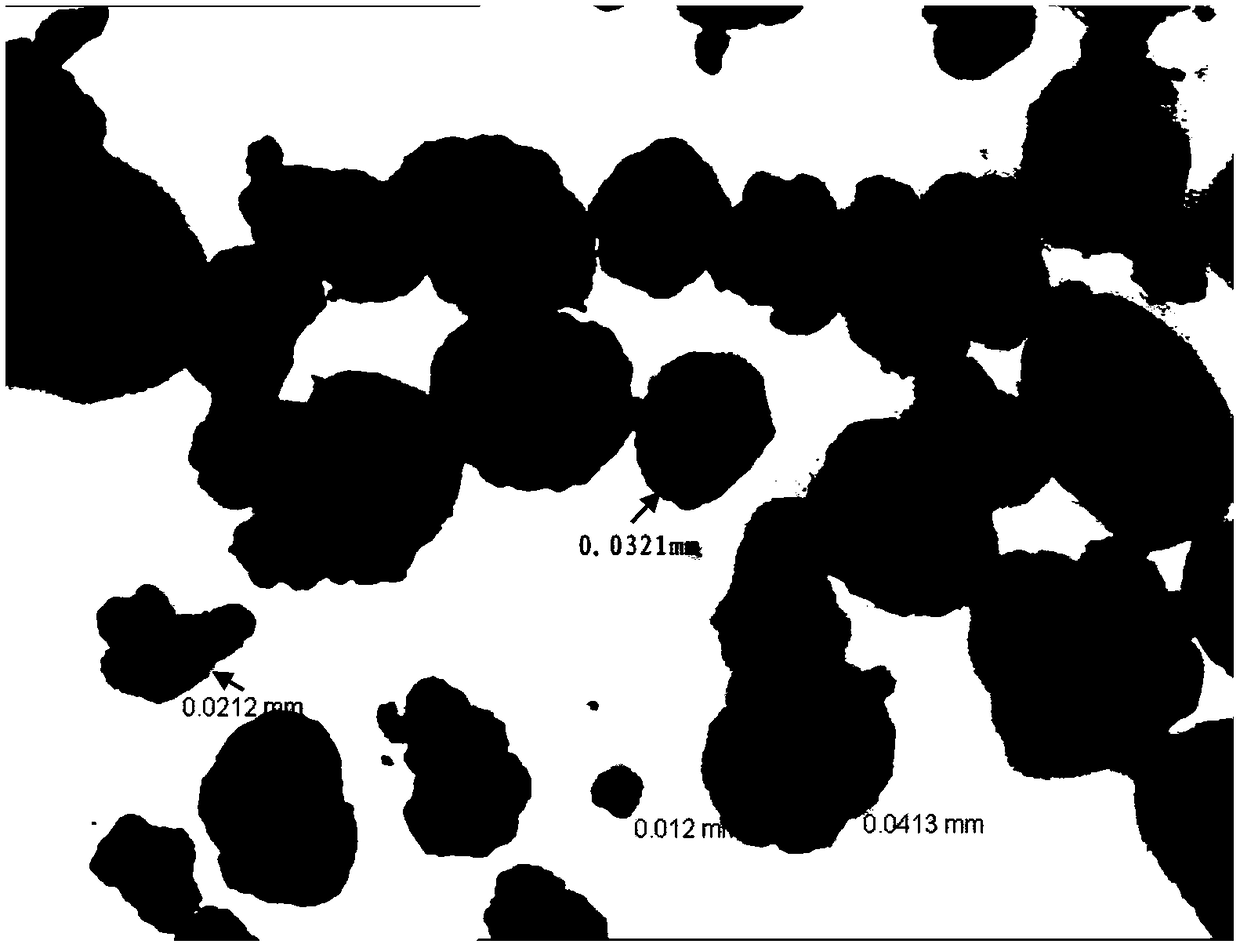
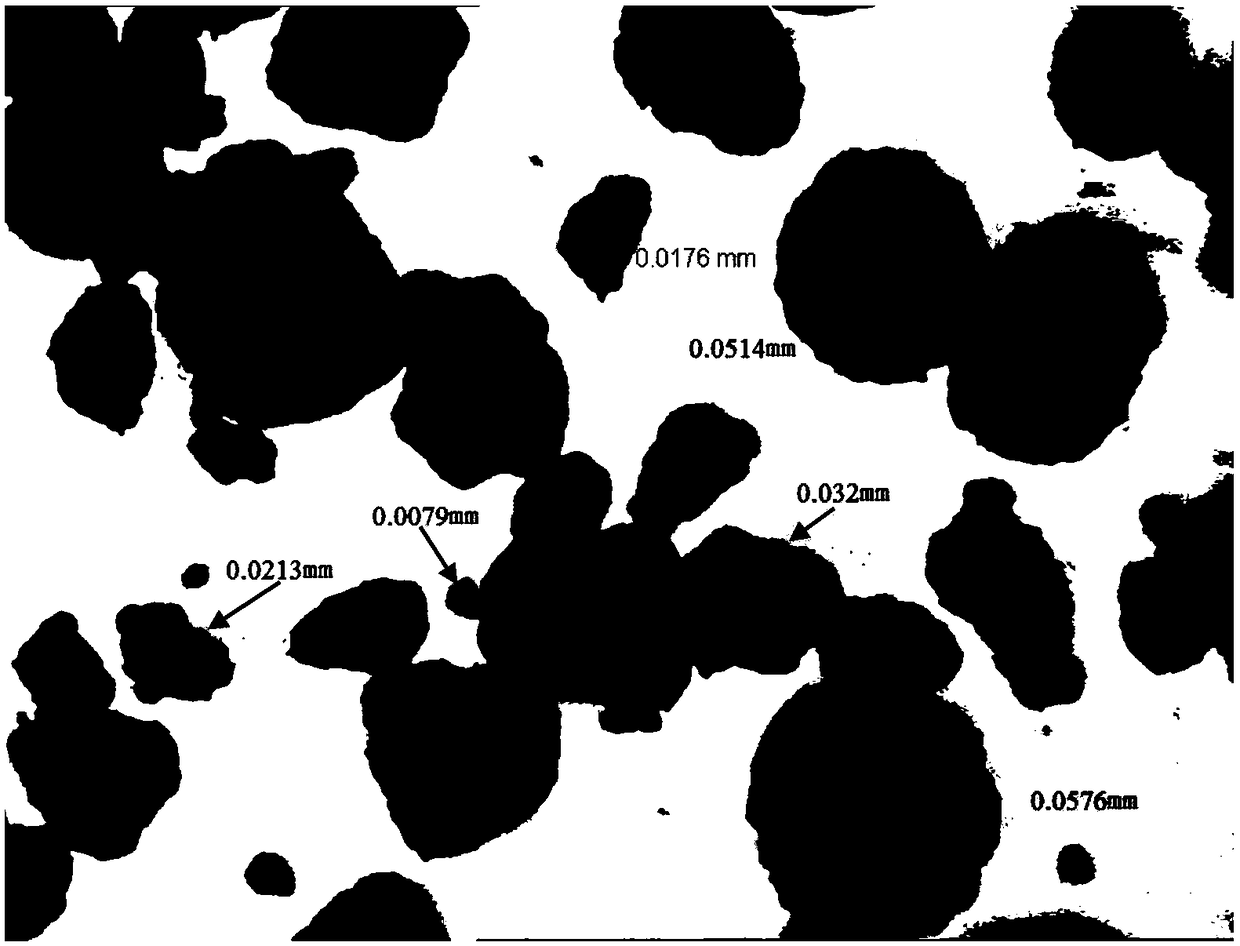
Production method for basic copper chloride
A production method and technology of cupric chloride, applied in the direction of cupric chloride, cupric halide, etc., can solve the problems of unstable particle size and color of basic cupric chloride, and unsteady control of product quality.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
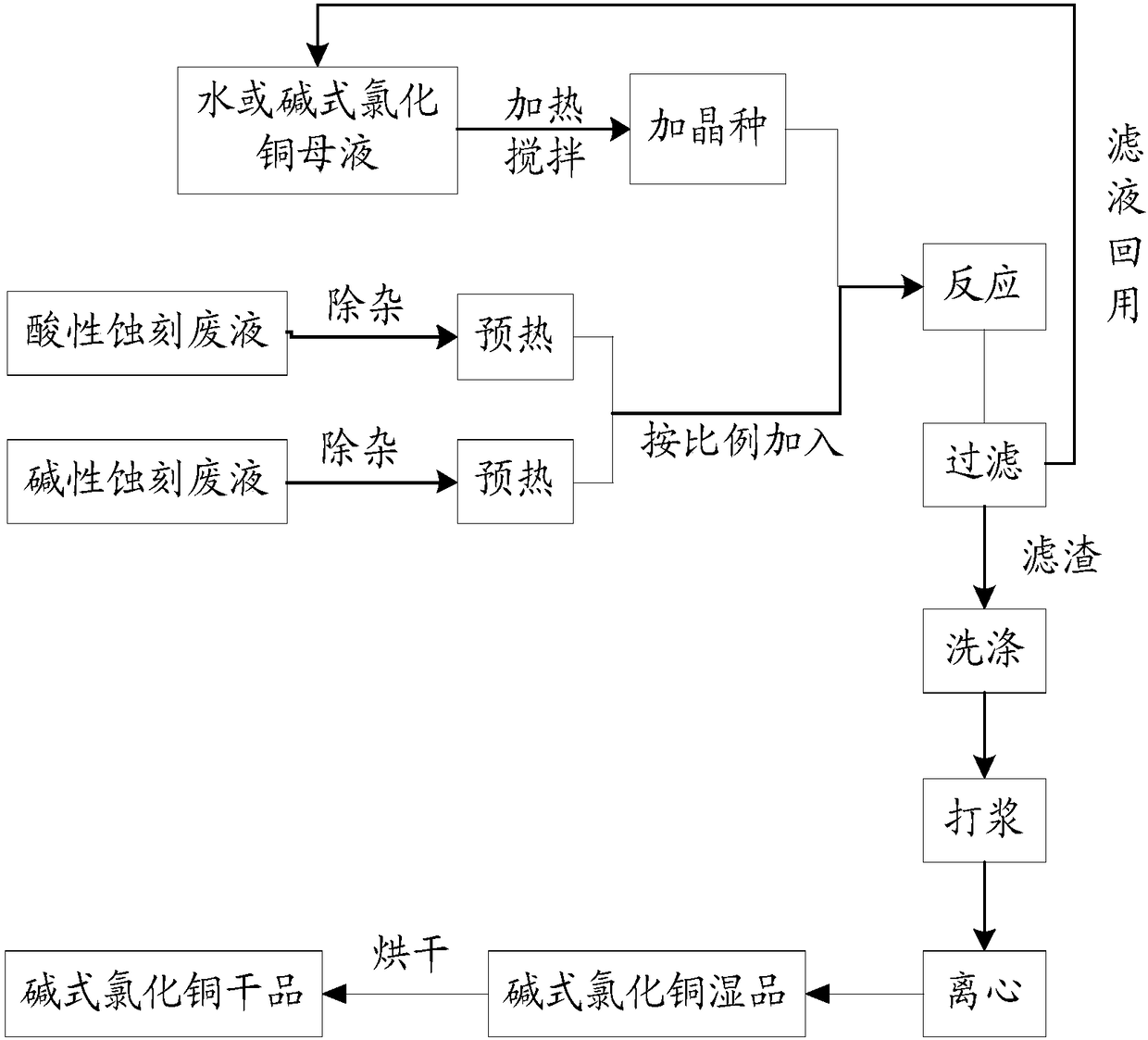
[0054] 1. Removal of impurities in acidic etching waste liquid:
[0055] Start the acid etching waste liquid lifting pump, start the press filtration, the filtrate produced overflows to the acid etching waste hydraulic pressure filter tank, and lifts the filtrate to the acid etching waste liquid purification tank through the filter pressure tank lifting pump for purification treatment.
[0056] Turn on the mixer, add sodium chlorate solution to the acid etching waste liquid purification tank to remove the Cu in the acid etching waste liquid + , Fe 2+ Oxidized to Cu 2+ , Fe 3+ , according to the color of the acidic etching waste liquid to judge the oxidation end point, when the acidic etching waste liquid is green and transparent, it is the oxidation end point, and there is no need to continue to add sodium chlorate solution; otherwise, continue to add sodium chlorate solution until it is green and transparent. Add ammonia water to the purification tank until the pH value of...
Embodiment 2
[0067] 1. Seed crystal preparation
[0068] Add tap water to the crystallization tank until the specified position, that is, just soaked through the steam pipe in the crystallization tank. Start the crystallization tank agitator in the process of pumping tap water into the crystallization tank, the stirring speed is 65r / min, and open the self-circulation of the crystallization tank.
[0069] Open the steam heating valve, raise the temperature of the material in the crystallization tank to 70±2°C, and close the steam heating valve after the temperature reaches.
[0070] Add 70Kg basic copper chloride seed crystals in the crystallization tank.
[0071] 2. Raw material preheating
[0072] Referring to the method of Example 1, the waste acidic etching liquid and the waste alkaline etching liquid were respectively subjected to impurity removal treatment.
[0073] Detect the Baume degree and pH of acidic etching waste liquid and alkaline etching waste liquid. The Baume degree of...
Embodiment 3
[0102] Embodiment 3 is basically the same as Embodiment 2, the difference lies in the following aspects:
[0103] 1), seed crystal preparation steps
[0104] Embodiment 3 replaces the tap water among the embodiment 2 with basic cupric chloride mother liquor; The addition amount of kind is 85Kg.
[0105] 2), raw material preheating step
[0106] The Baume degree and pH value of raw material are different, specifically: the Baume degree of the acidic etching waste liquid of embodiment 3 is 26Be °, and the pH value is 1.5, and the Baume degree of alkaline etching waste liquid is 15Be °, and the pH value is 9.0 .
[0107] The preheating temperature is different, specifically: the preheating temperature of Example 2 is 43°C, and the preheating temperature of Example 3 is 48°C.
[0108] 3), production start-up steps
[0109] The stirring speeds during the crystallization reaction of the alkaline etching waste liquid and the acidic etching waste liquid are different, specificall...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com