Multi-wavelet-basis function expansion-based accurate identification method of spike-potential time-varying Granger causality (GC)
An identification method and basis function technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instrumentation, calculation, etc., can solve problems such as slow convergence speed, inaccurate results of time-varying Granger causal identification methods, and poor performance of time-varying parameter estimation, etc. Achieve the effect of improving calculation speed, overcoming slow convergence speed, and reducing model complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] In order to better illustrate the specific implementation of the present invention, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
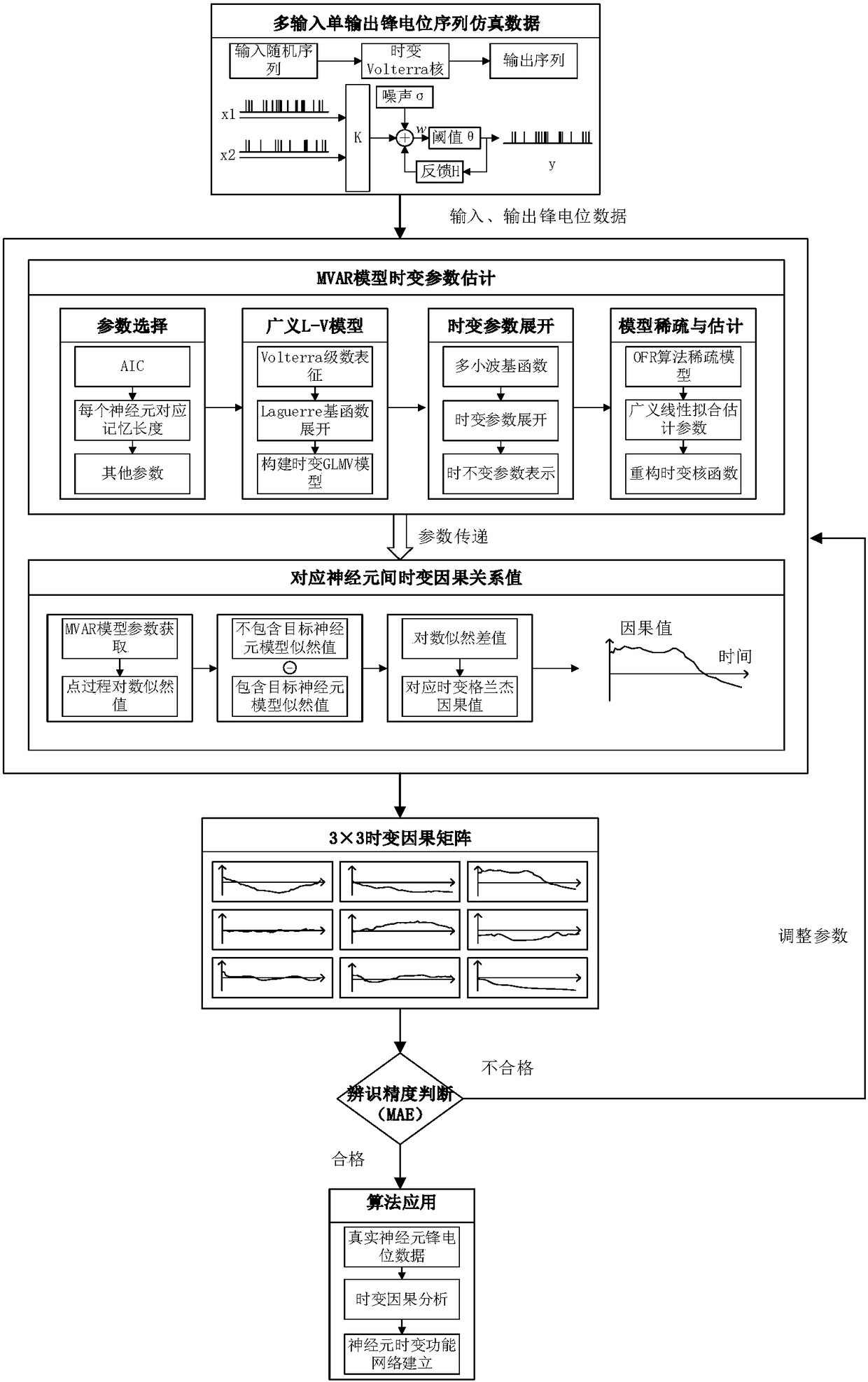
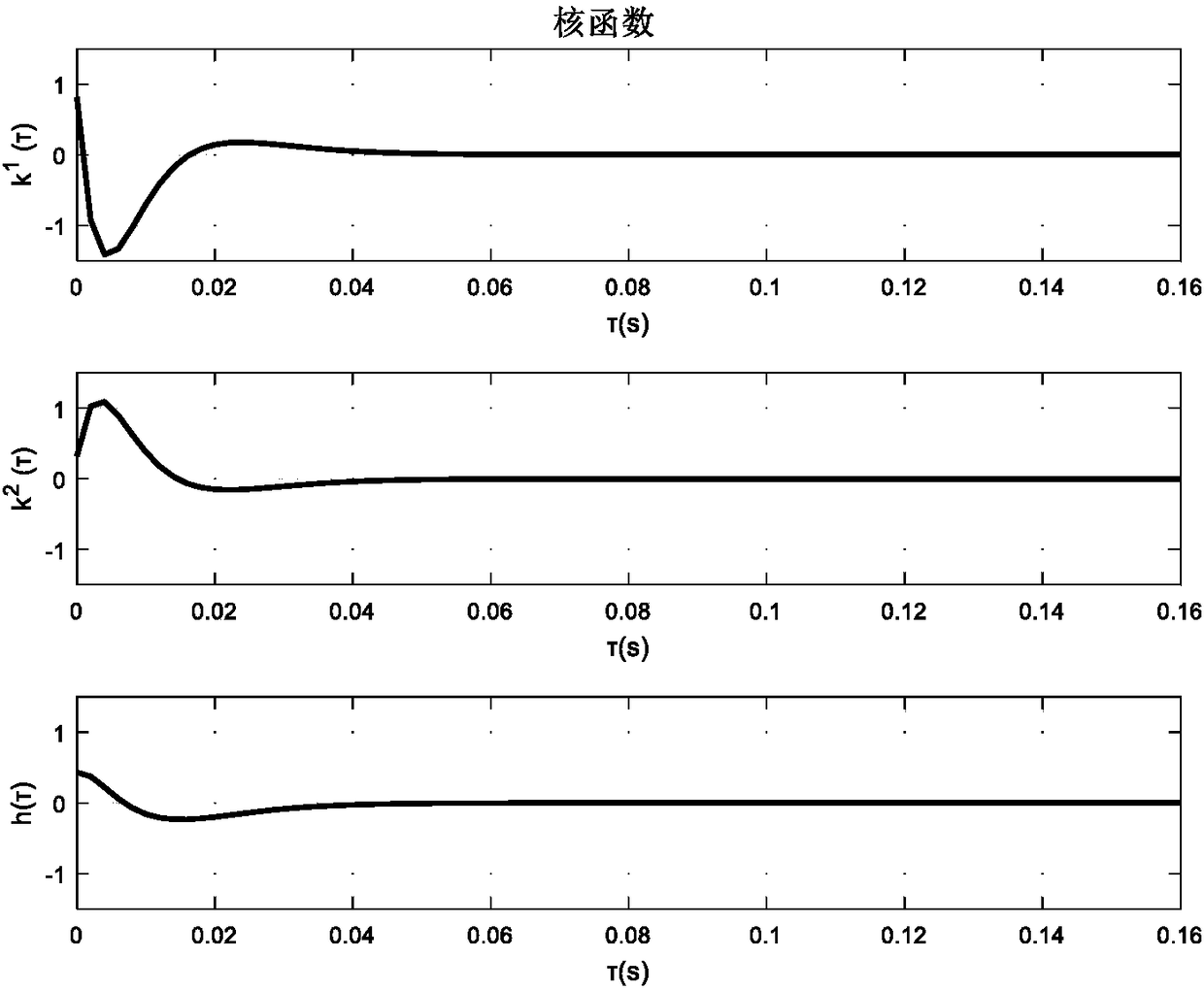
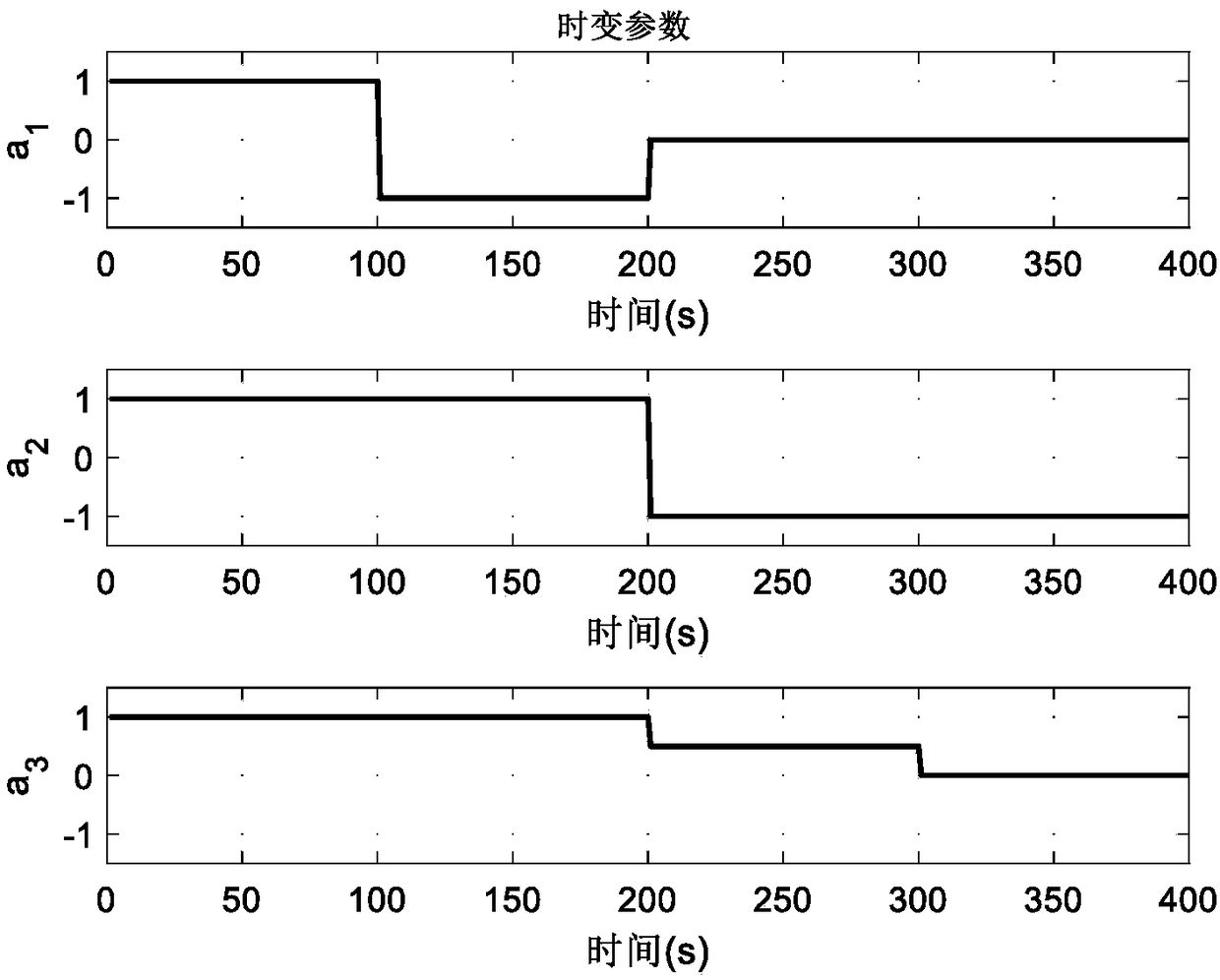
[0028] The purpose of the present invention is to provide a spike time-varying Granger causality identification method based on multi-wavelet basis function expansion, by using the multi-wavelet basis function expansion model to accurately identify time-varying MVAR model parameters, and solve the corresponding neuron Granger Causal results, to solve the problems of low time resolution and difficulty in quickly tracking the causal connection of neurons in existing sliding window-based neuron time-varying causal relationship identification methods, and can accurately and quickly track changes in neuron causal connections.
[0029] figure 1 A flow chart showing the accurate identification method of spike time-varying Granger causality proposed by the present invention, including...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com