Observation method of early developmental morphology of fishes of the genus Sniper, bream, and genus Siniperca, which lay drifting eggs
A technology for morphological observation, genus bream, applied in the field of fish morphological observation, can solve the problems that it is difficult to freeze-frame images to capture developmental details, it is difficult to obtain complete embryo images, live larvae are prone to hyperactivity, etc., to achieve complete details and vivid shooting effects Vitality, less decolorization effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Observation methods for the early developmental morphology of fish of the genus Bream and the genus Siniperca that lay drifting eggs, taking the eggs of the genus Gizzard at the blastopore closure stage as an example, the observation methods are as follows:
[0043] (1) Use a straw or a small spoon to take a fish egg from the blastopore-closed catfish roe, and put it in the central area of a clean and dry petri dish;
[0044] (2) Use a dry small strip-shaped sponge to absorb the moisture between the fish eggs and the petri dish, so that the fish eggs can be firmly placed on the petri dish;
[0045] (3) Put the above-mentioned Petri dish with fish eggs under the objective lens of the dissecting mirror, and use a dry small strip sponge to move the fish eggs to the desired viewing or shooting angle;
[0046] (4) Adjust the dissecting mirror, obtain the observation or photographing images, and complete the observation or photographing within 5 minutes;
[0047] The port ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Observation methods for the early developmental morphology of fishes of the genus Bream and Siniperca genus that lay drifting eggs, taking the eggs of the genus Gizzard during the beating period as an example, the observation method is as follows:
[0050] (1) Use a straw or a small spoon to take a fish roe from the beating period of the heart, and put it in the central area of a clean and dry petri dish;
[0051] (2) Use a dry small strip-shaped sponge to absorb the water between the fish eggs and the petri dish, so that the fish eggs can be firmly placed on the petri dish; the port area of the small strip-shaped sponge does not exceed 0.1cm 2 .
[0052](3) Place the above-mentioned petri dish with fish eggs under the objective lens of the dissecting mirror, adjust the microscopic magnification of the dissecting mirror, and use a thread needle to pierce the fish egg membrane from the left and right sides of the fish eggs, and the vertical height of the puncture poi...
Embodiment 3
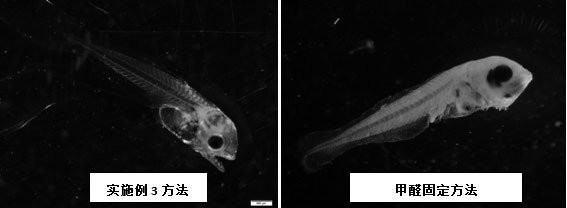
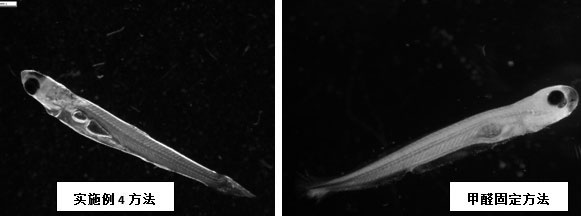
[0059] The observation method of the early developmental morphology of fishes of the genus Snipper, the genus Bream, and the genus Siniperca that lay drifting eggs, taking the mandarin fish as an example, the observation method is as follows:
[0060] (1) Take a mandarin fish with a straw or a small spoon, and put it in the central area of a clean and dry petri dish;
[0061] (2) Add or absorb with a 10ml syringe, and control the water in the contact part of the larvae and the petri dish to 0.5ml;
[0062] (3) Use a 10ml syringe to drop 0.08ml of 90% ethanol around the larvae, let it stand for 2 minutes, then use a 10ml syringe to drop 0.08ml of 50% ethanol around the larvae, and let it stand for 3 minutes;
[0063] (4) Control 0.35ml liquid to cover the larvae; the control method is: 10ml syringe absorbs excess liquid;
[0064] (5) Move the petri dish until the larvae are within the observation field of the dissecting mirror, adjust the multiple of the dissecting mirror, o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com