Additive for magnetorheological fluids
A technology of magnetorheological fluids and additives, applied in the direction of additives, magnetic objects, magnetic liquids, etc., can solve problems such as sedimentation, particle wear, and limited material usable temperature range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Example 1 - Effect of oleic acid amine salt in MR fluid
[0060] fluid preparation :
[0061] In these examples, a polyalphaolefin / dioctyl sebacate (PAO / DOS) carrier fluid, Duomeen TDO friction reducer, and organic molybdenum and sulfur The phosphorous additive was mixed for about 10 to 15 minutes to prepare the MR fluid.
[0062] When the additive is sufficiently incorporated into the carrier fluid, the organoclay is added and the mixture is mixed using the disperser blade for about 15 minutes. The carbonyl iron is then added to the system a little at a time until it is wetted and incorporated. The whole mixture was then milled for an additional 15 minutes. The final MR fluid contained a solids concentration of about 26% by volume and about 0.58% by weight Duomeen TDO.
[0063] Viscosity test :
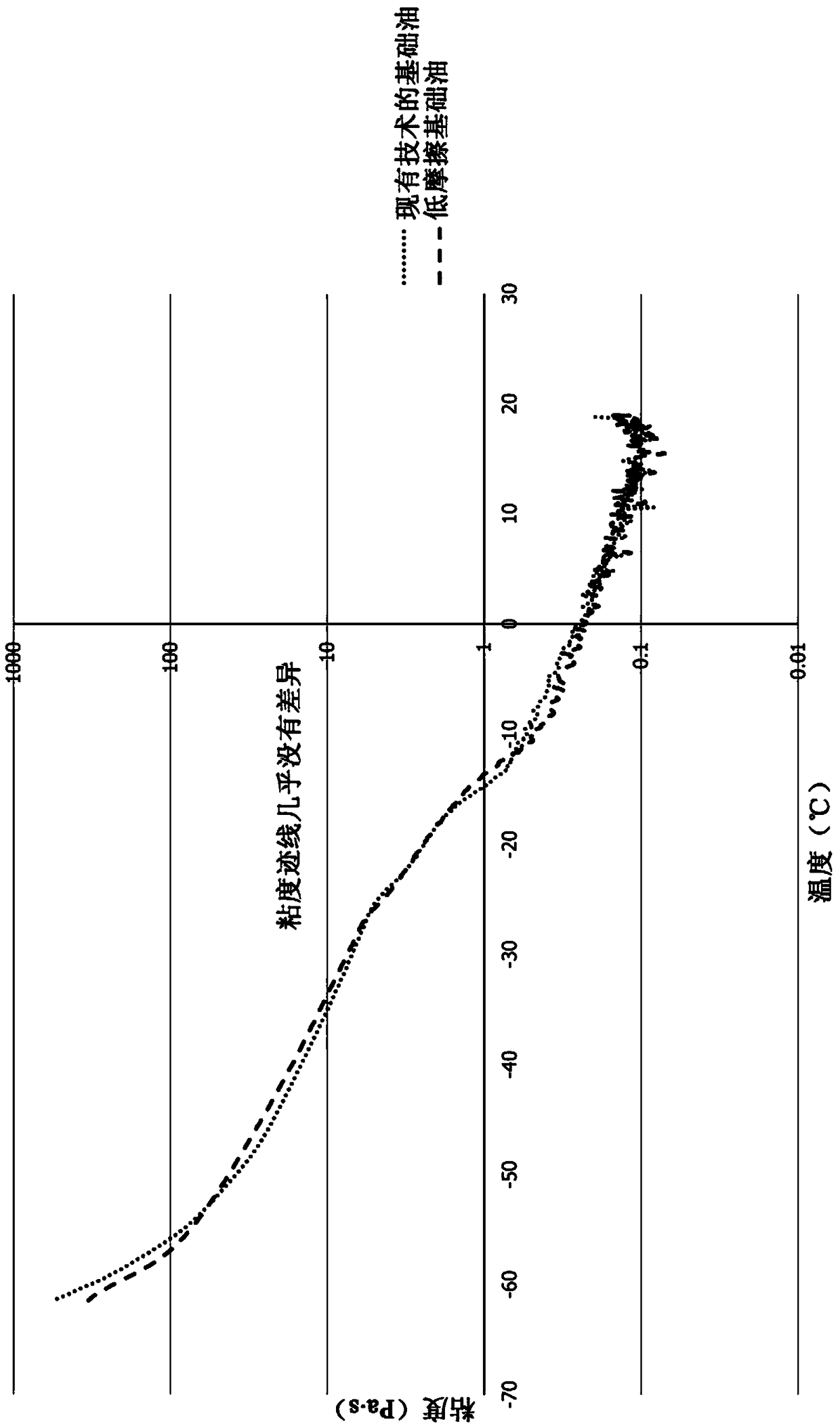
[0064] All experiments were performed using an ARES-G2 rheometer with parallel plate geometry. The environmental chamber was filled with liquid nitrogen, and the sam...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2 - Effect of Ultrafine Molybdenum Disulfide
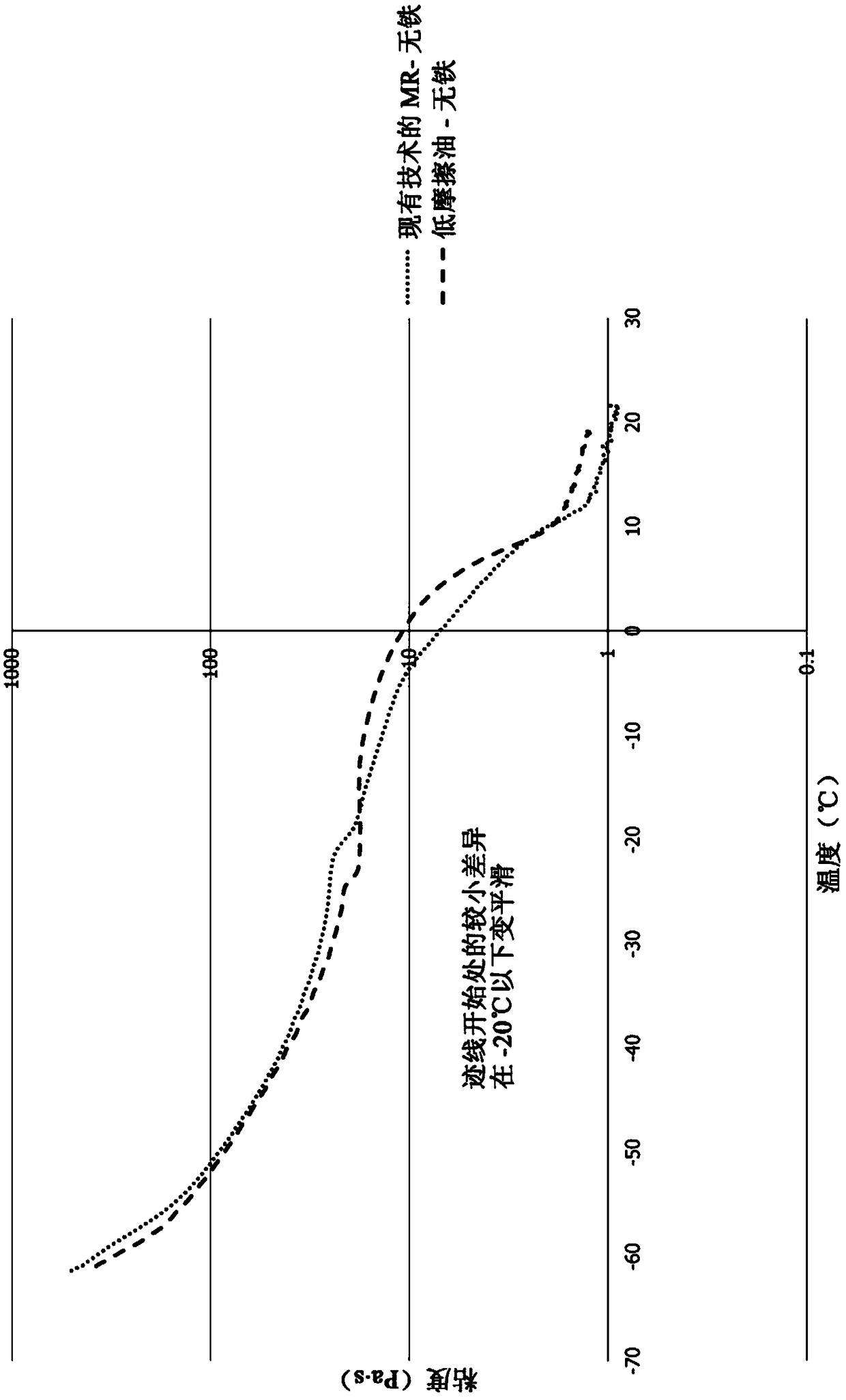
[0077] Additives for magnetorheological (MR) fluids that provide improved friction properties typically cause an increase in the transparent layer of the fluid over time. This is due to the reduced friction between the fluids allowing solids to settle to the bottom of the fluid chamber when the fluid is not in use. A transparent top layer becomes visible as the particles settle into a dense bottom layer. Therefore, measurement of the clear layer is one method for determining the effectiveness of anti-settling agents in MR fluids. Another indicator is to measure the viscosity at certain points throughout the MR fluid column.
[0078] fluid preparation :
[0079] In these examples, a polyalphaolefin / dioctyl sebacate (PAO / DOS) carrier fluid, about 0.6 wt. % Duomeen TDO and about 3.6 wt. % molybdenum disulfide (when used) and other additives were mixed for about 10 to 15 minutes to prepare the MR fluid.
[0080] ...
Embodiment 3
[0102] Example 3 - Alternative Amines
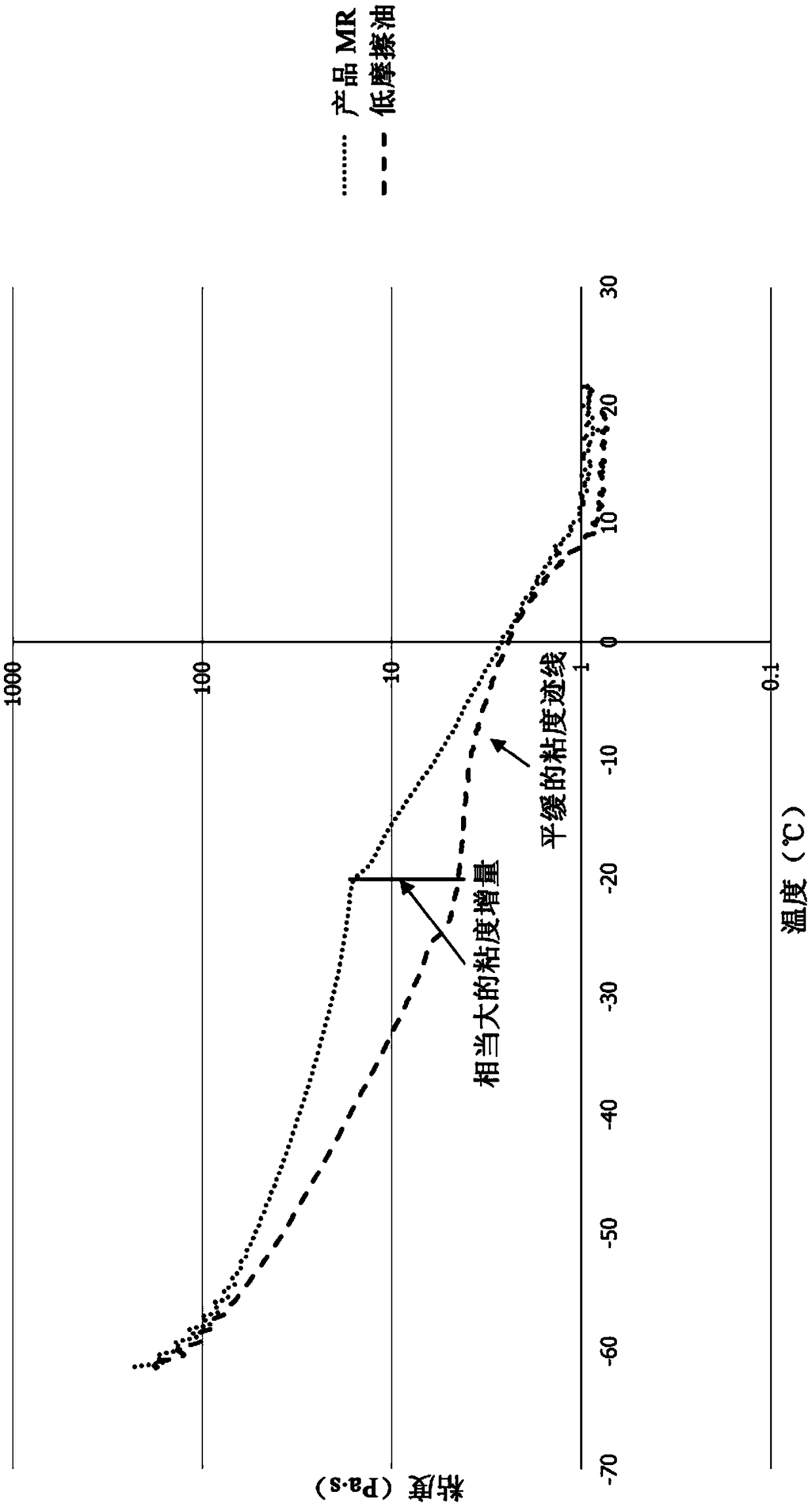
[0103] Two base fluids were prepared according to the invention, the first fluid "787 Fluid" contained PAO2.5 / DOS base fluid and Molyvan 855, while the second fluid "690 Fluid" did not contain Molyvan 855 but contained 3.6% by weight super Fine MDS powder. The content of various amine additives was about 0.6% by weight, and the friction and viscosity at a certain temperature were measured. The following additives were evaluated: Tertrameen T (linear tetraamine); Triameen T (linear triamine); Duomeen T (linear diamine); Armolube 312, Duomeen TDO and Armolube 211 (the oleic acid amine salt described herein ); and Ethomeen T15 (ethoxylated amine).
[0104] As shown in Tables 2 and 3 below, the amine oleate salts of the present invention exhibit minimal friction and viscosity, especially when the temperature is reduced. It is worth noting that while the ethoxylated amine (Ethomeen T15) exhibited reasonably good low temperature viscosity, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com