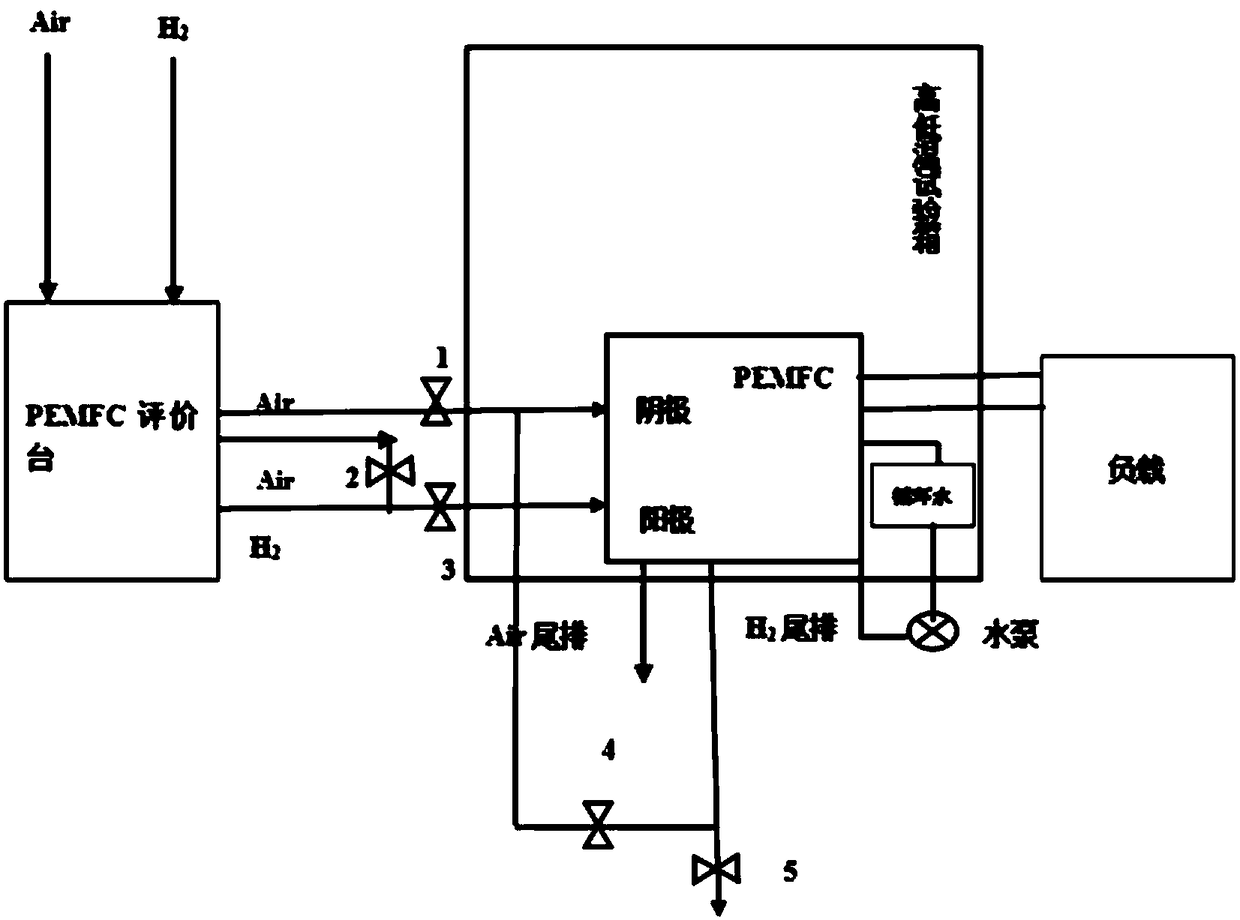
Method for starting proton exchange membrane fuel cell under low-temperature state
A proton exchange membrane and fuel cell technology, applied in fuel cells, fuel cell additives, fuel cell heat exchange, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the volume and quality of the battery system, the incomplete reaction of the mixed gas, and the impact on the structure and performance of the battery, etc. Problems, to achieve the effect of fast low-temperature start-up, reduce low-temperature start-up power consumption, and improve utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
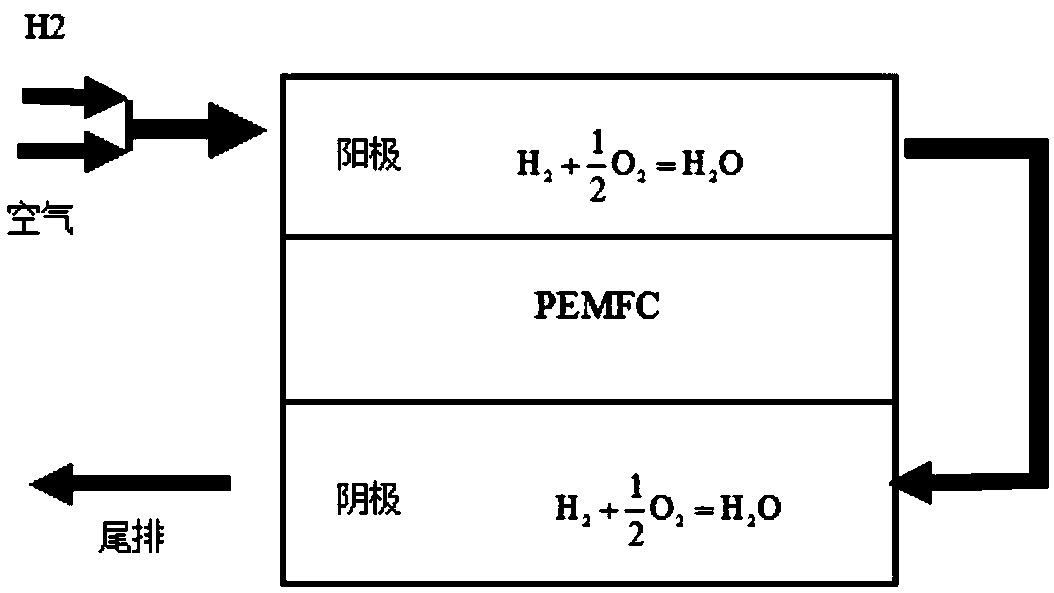
[0054] Such as figure 2 Shown, the present invention will H 2 and air are continuously fed into the anode of the fuel cell, and hydrogen and air are used to oxidize and release heat on the anode catalytic layer; Oxidation is exothermic.
Embodiment 2
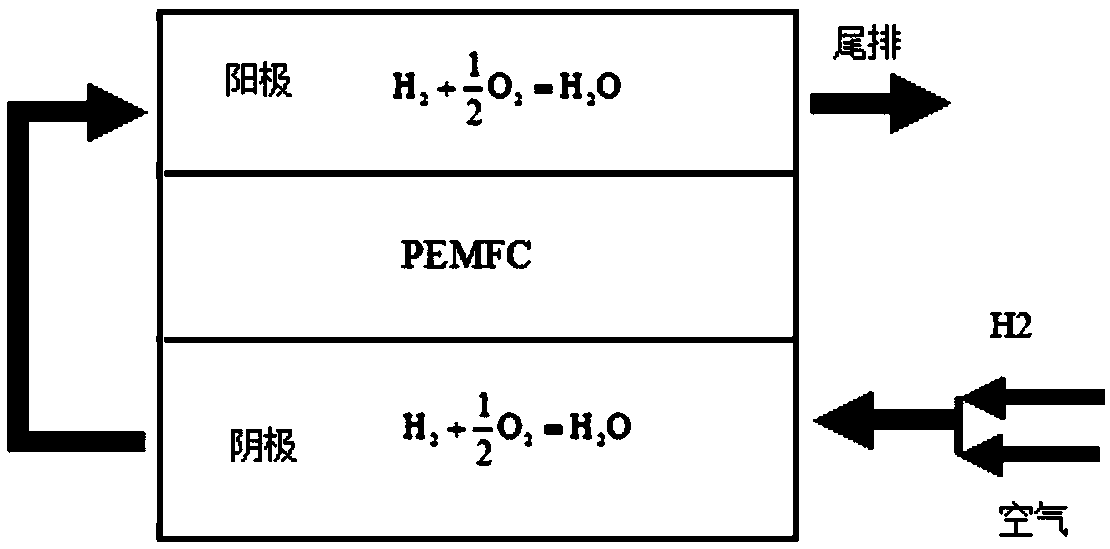
[0056] Such as image 3 Shown, the present invention will H 2 and air are continuously fed into the fuel cell cathode, and hydrogen and air are used to oxidize and release heat on the cathode catalytic layer; the tail gas of the cathode is passed to the anode, so that the unreacted hydrogen-air mixture of the anode is oxidized and released on the anode catalytic layer hot.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com