A method for controlling rice sheath blight and rice leaf roller by intercropping pikegrass with rice
A technology for rice sheath blight and rice leaf roller, applied in the field of rice pest control, can solve the problems of loss of agricultural biodiversity, increased resistance to diseases, insect pests and weeds, and farmland environmental pollution, achieving good control effect and easy operation , The effect of facilitating the promotion and application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
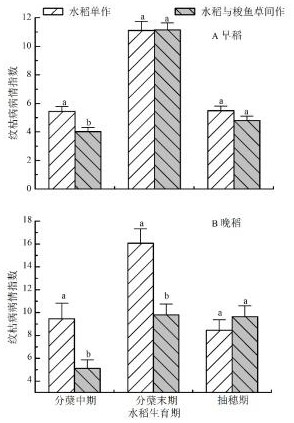
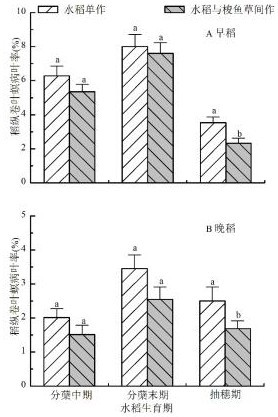
[0022] The rice variety selected in this example is Huanghuazhan (Xiangshendao 2007018). The barracuda variety was purchased from the rural aquatic plant farm in Gaoming District, Foshan City, and planted during the early rice season. This study was divided into three experimental treatments, of which A treatment was rice monoculture treatment, B treatment was Pikegrass monoculture treatment, and C treatment was intercropping rice and pikegrass. In addition to the application of basal fertilizer and consistent daily water management, the three experimental treatments did not apply other chemical fertilizers and pesticides during the normal rice growth cycle. Each treatment was repeated three times and arranged in random blocks.
[0023] The specific production management operation process of experimental treatments A, B, and C is as follows:
[0024] 1. Planting of rice and pike grass:
[0025] Soil preparation for planting rice and pikegrass: rice seedling raising, leveling ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The rice variety selected in this example is Huanghuazhan (Xiangshendao 2007018). The barracuda variety was purchased from the rural aquatic plant farm in Gaoming District, Foshan City, and planted during the late rice season.
[0038] 1. Planting of rice and pike grass:
[0039] Soil preparation for planting rice and pikegrass: rice seedling raising, leveling paddy field. Apply basal fertilizer about 20 days before rice transplanting, and the standard of basal fertilizer application is every 667m 2 Apply 211.75 kg of decomposed chicken manure, and then transplant pike grass seedlings with a plant height of 20 cm 7 days before rice transplanting; rice seedlings and pike grass are intercropped at 4:2, that is, 2 rows of pike are planted for every 4 rows of rice intercropping Grass; the distance between the rice planting belt and the barracuda planting belt is 40cm; the row spacing of transplanted rice seedlings is 25cm×20cm, and the row spacing of transplanted barracuda...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The rice variety selected in this example is Huanghuazhan (Xiangshendao 2007018). The barracuda variety was purchased from the rural aquatic plant farm in Gaoming District, Foshan City, and was planted in two seasons during the early rice and late rice seasons.
[0052] 1. Planting of rice and pike grass:
[0053] Soil preparation for planting rice and pikegrass: rice seedling raising, leveling paddy field. Apply basal fertilizer about 20 days before rice transplanting, and the standard of basal fertilizer application is every 667m 2 Apply 250 kg of decomposed chicken manure, and then transplant the pike grass seedlings with a plant height of 25 cm 7 days before rice transplanting; the rice seedlings and pike grass are intercropped at a ratio of 5:2, that is, 2 rows of pike grass are planted for every 5 rows of rice intercropping The distance between the rice planting belt and the barracuda planting belt is 40cm; the row spacing of transplanted rice seedlings is 25cm×2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com