A high temperature strength prediction method for martensitic steel based on microstructure degradation
A microstructure and high-temperature strength technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve problems such as the development of high-temperature strength prediction methods that have not been considered, and achieve the effect of ensuring safe service
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] A method for predicting high temperature strength of martensitic steel based on microstructure degradation, comprising the following steps:
[0039] Step 1, select the new martensitic heat-resistant steel G115, and prepare a creep sample with a gauge length of 40mm and a diameter of 5mm as the research object;
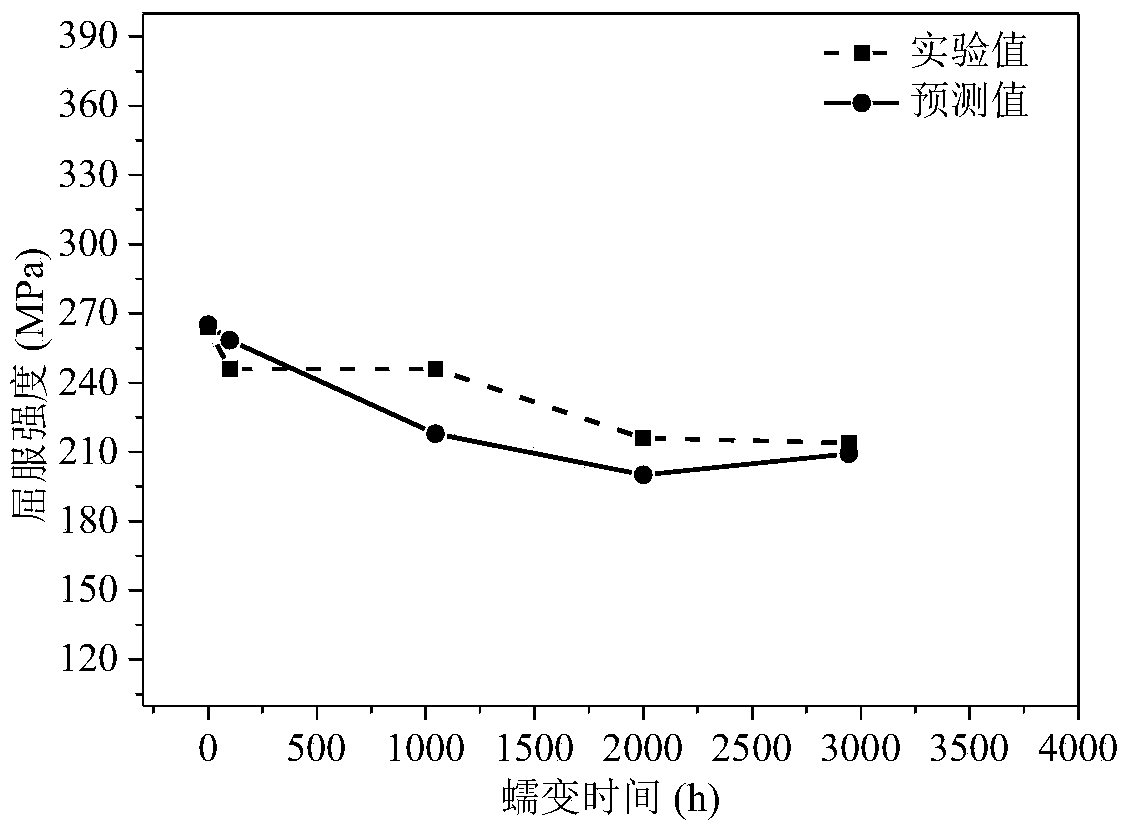
[0040] Step 2, applying a stress of 140 MPa to the creep sample at 650° C. to obtain creep tests of the sample under different aging creep damage states;
[0041] Step 3, performing microscopic test technical characterization of the creep samples in different creep damage states obtained in step 2, and obtaining the microstructure parameters of the creep samples in different creep damage states, the microstructure parameters Including: the local misorientation between θ grains, the unit is rad; λ m The average width of the martensitic lath structure, in nm; N i The number density of the i-th precipitated phase, in μm -2The microscopic testing technology chara...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com