Resistive random access memory and preparation method thereof
A resistive variable memory and electrode layer technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, can solve the problems of unfavorable large-scale integration, low current density, small energy band gap, etc., to achieve three-dimensional integration, improve read efficiency, and reduce device size. area effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
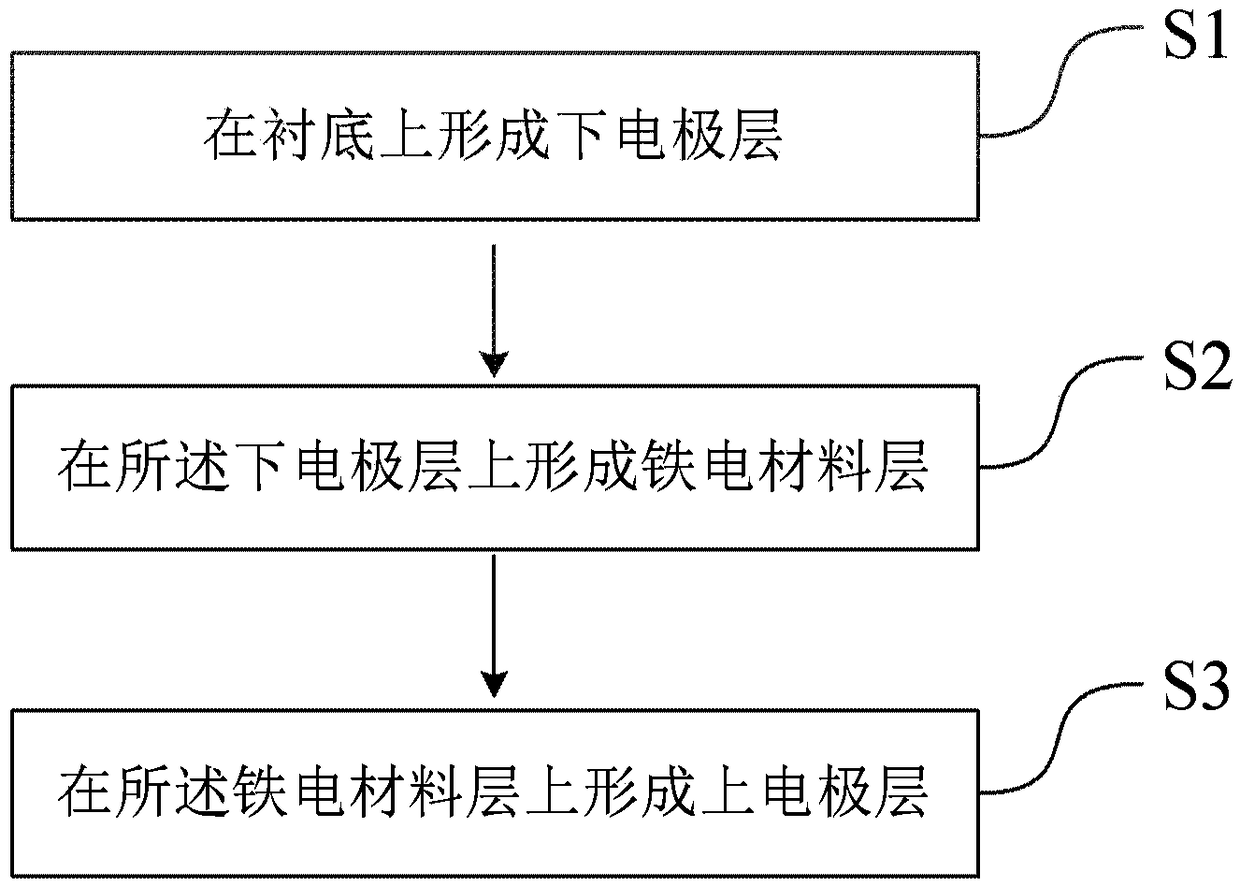
[0025] figure 2 shows the preparation figure 1 Flowchart of the method for the resistive variable memory. Such as figure 2 As shown, the preparation method of the resistive variable memory may include the following steps:
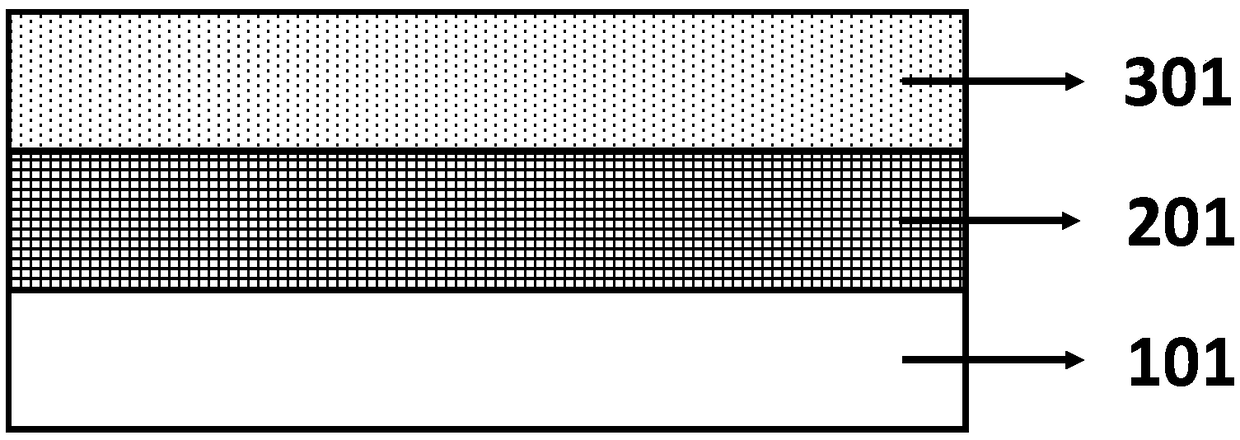
[0026] S1, forming a lower electrode layer 101 on the substrate;
[0027] S2, forming a ferroelectric material layer 201 on the lower electrode layer 101, the ferroelectric material layer 201 may include doped HfO 2 The ferroelectric thin film, specifically, the ferroelectric material layer 201 may include HfO doped with at least one element among Zr, Al, Si, La 2 Ferroelectric thin film;
[0028] S3, forming an upper electrode layer 301 on the ferroelectric material layer 201 .
[0029] Further, after the ferroelectric material layer 201 is formed on the lower electrode layer 101, an annealing treatment is performed, the annealing temperature is 400-1000°C, and the annealing time is 30-300s.
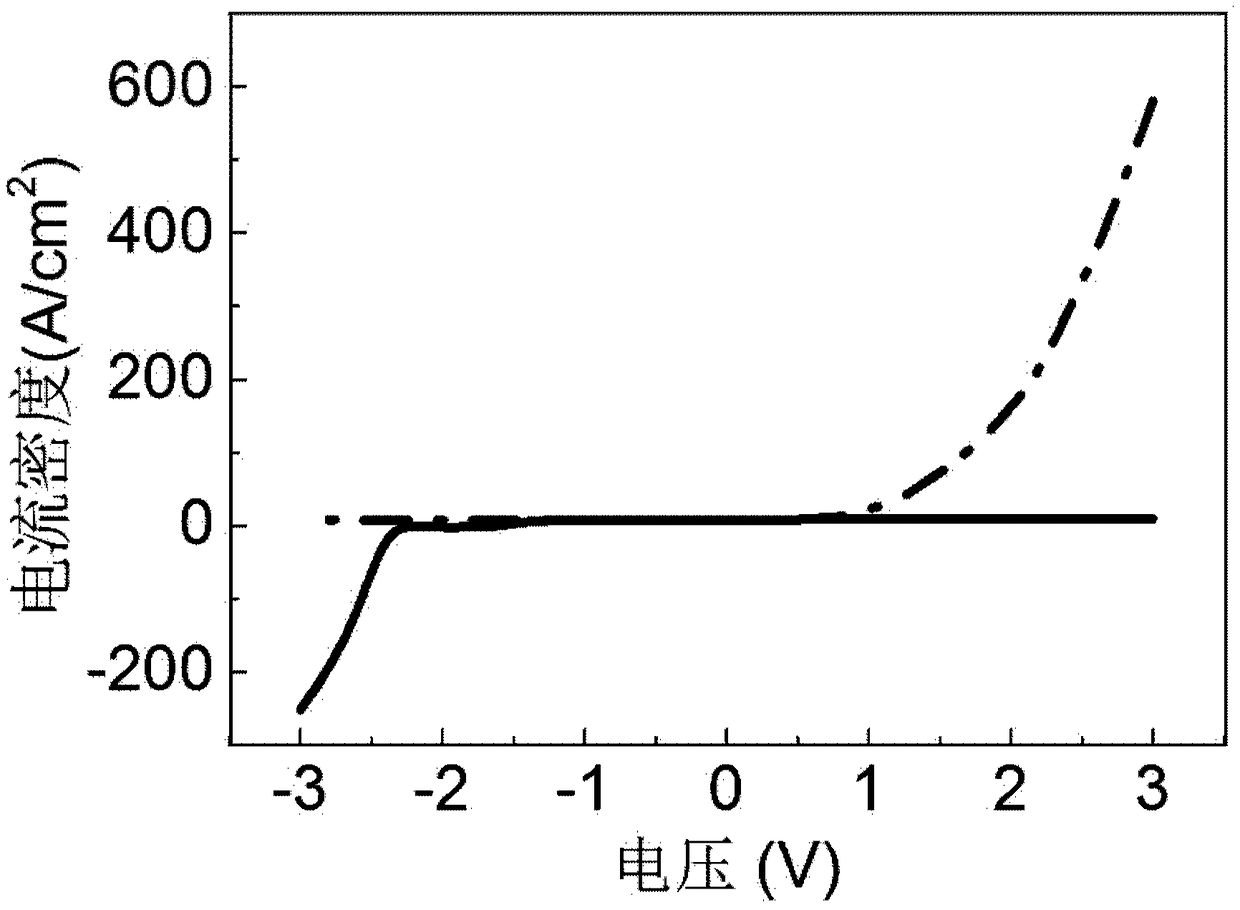
[0030] image 3 show figure 1 The current-voltage ch...
Embodiment 1
[0033] Preparation based on Hf 0.5 Zr 0.5 o 2 The resistive sensor with ferroelectric layer, the preparation process is as follows:
[0034] Step 1, adopting the sputtering method to form the TiN lower electrode layer, the process conditions are: power 25W~500W; pressure 0.1Pa~100Pa; Ar gas flow 0.5sccm~100sccm; the thickness of the obtained TiN lower electrode layer is 10nm~500nm;
[0035] Step 2: Cyclic growth of HfO on the TiN bottom electrode layer by ALD 2 and ZrO 2 to get Hf 0.5 Zr 0.5 o 2 For the ferroelectric layer, the process conditions are: power 25W~500W; pressure 0.1Pa~100Pa; gas flow 60sccm; temperature 250℃~300℃; rate about 0.07nm / cycle; growth cycle (cycle) HfO 2 followed by growing a cycle of ZrO 2 , reciprocating in this way, the two materials are mixed and deposited at a molar ratio of 1:1;
[0036] Step 3, performing annealing treatment, the annealing temperature is 400°C, and the annealing time is 30s;
[0037] Step 4, using the method of sputter...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com