In-situ ecological restoration method of composite polluted soil using biological and carbonized materials
A technology of ecological restoration and compound pollution, which is applied in the field of landscaping and environmental pollution restoration, can solve the problems of long-term, low efficiency of compound polluted soil, and poor effect of compound soil pollution restoration, so as to quickly restore vegetation and improve the urban ecological environment Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
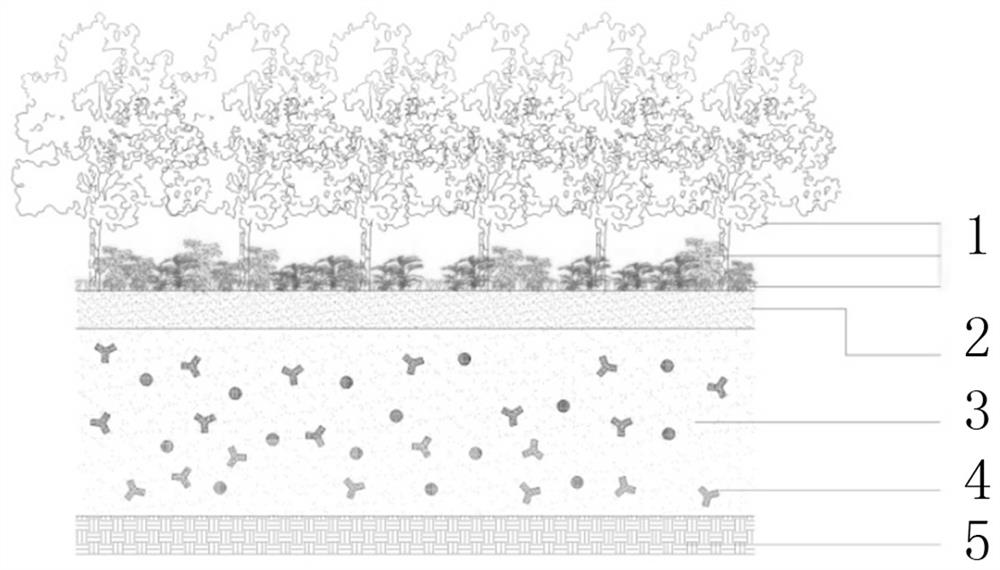
[0025] The in-situ ecological restoration method for controlling compound polluted soil comprises the following steps:
[0026] (1) Add biochar and inorganic improvement materials to the contaminated soil to be repaired, and mix and stir evenly; the biochar is a mixture of rapeseed and corn crop stalks calcined at 500 ° C to obtain particles with a particle size of less than 5 μm. The inorganic modified material described above is CoMoS 4 、Cu 2 MoS 4 With a mixture of mass ratio of 1:1, the mass ratio of biochar and inorganic improvement material is 1:0.3; the amount of biochar and inorganic improvement material is 0.5kg / square.
[0027] (2) The polluted soil layer is covered with a layer of greening planting soil, the polluted soil layer needs to be compacted and vibrated, and the layer height is 40cm; the polluted soil layer is drained by inserting water pipes every 80cm horizontally.
[0028] (3) Configure landscape plant communities according to landscape requirements, ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The in-situ ecological restoration method for controlling compound polluted soil comprises the following steps:
[0032] (1) Add biochar and inorganic improvement materials to the contaminated soil to be repaired, mix and stir evenly; the biochar is the particle size less than 3.5μm obtained after drying the sludge in the lotus root pond and calcining at 580°C , the inorganic modification material is NiMoS 4 、Cu 2 MoS 4 With a mixture of mass ratio 1:0.8, the mass ratio of biochar and inorganic improvement material is 1:0.6; the amount of biochar and inorganic improvement material is 0.35kg / square, and the mixed bacteria of Pseudomonas and Bacillus subtilis are added at the same time agent, the added amount of mixed bacteria agent is 0.15% of the total mass of biochar and inorganic improvement materials, and the concentration of Pseudomonas is 5×10 4 cfu / ml, the concentration of Bacillus subtilis is 5×10 4 cfu / ml.
[0033] (2) The polluted soil layer is covered wit...
Embodiment 3
[0037] The in-situ ecological restoration method for controlling compound polluted soil comprises the following steps:
[0038] (1) Add biochar and inorganic improvement materials to the contaminated soil to be repaired, mix and stir evenly; the biochar is the particles with a particle size of less than 3.5 μm after drying the sludge in fish ponds and calcining at 580°C , the inorganic modification material is Cu 2 MoS 4 , Zn 2 MoS 4With a mixture of mass ratio 1:0.5, the mass ratio of biochar and inorganic improvement material is 1:0.8; the amount of biochar and inorganic improvement material is 0.65kg / square, and AM mycorrhizal fungus is added at the same time, and the addition of AM mycorrhizal fungus The amount is 50g / square.
[0039] (2) The polluted soil layer is covered with a layer of greening planting soil, the polluted soil layer needs to be compacted and vibrated, and the layer height is 50cm; the polluted soil layer is drained by inserting water pipes every 70c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com