Super-resolution imaging method and device based on sparse matrix reconstruction and electronic equipment
A super-resolution imaging and sparse matrix technology, applied in the field of two-dimensional imaging, can solve problems such as difficult to obtain high-resolution imaging, and achieve the effect of reducing imaging time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
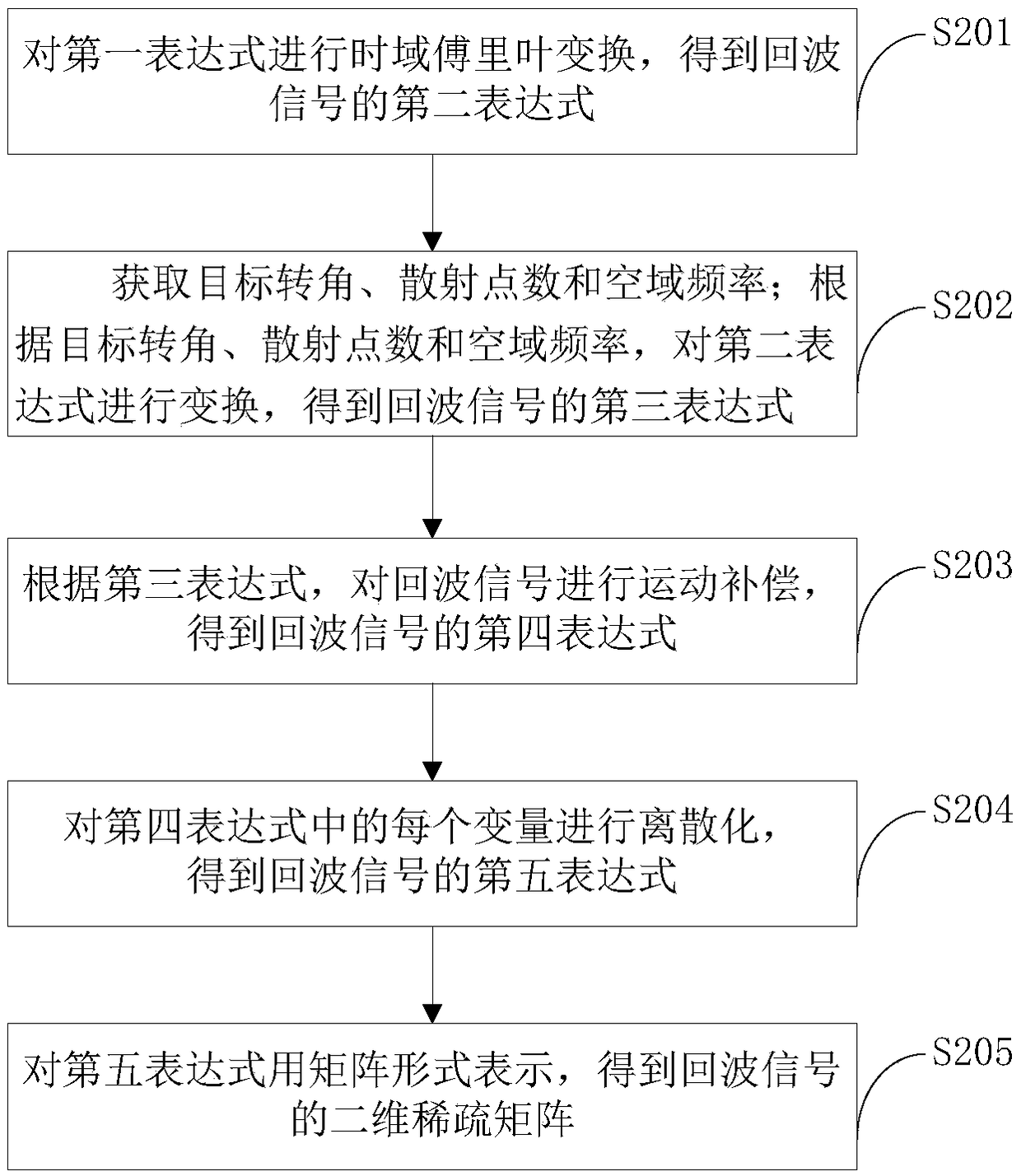
[0055] figure 1 It is a flow chart of a super-resolution imaging method based on sparse matrix reconstruction provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0056] refer to figure 1 , the method includes the following steps:
[0057] Step S101, acquiring an echo signal of a target object, and obtaining a first expression according to the echo signal.
[0058] Specifically, according to the ISAR imaging theory, under the "stop-and-go" model, the translational component of the target is not beneficial to imaging, assuming that the translational component of the target has been compensated. In this case, during the process of transmitting and receiving a pulse, the target can be approximated as stationary, so the slow time can be regarded as a discrete variable, which is denoted as n here. In this embodiment, the received echo signal can be represented by formula (1)
[0059] the s R (t,nT R )=s R (t,n)=∫ V γ′(z)s T (t-τ(z,n),n)h(n)dz (1)
[0060] Among them, s T...
Embodiment 2
[0154] Figure 7 A super-resolution imaging device based on sparse matrix reconstruction provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
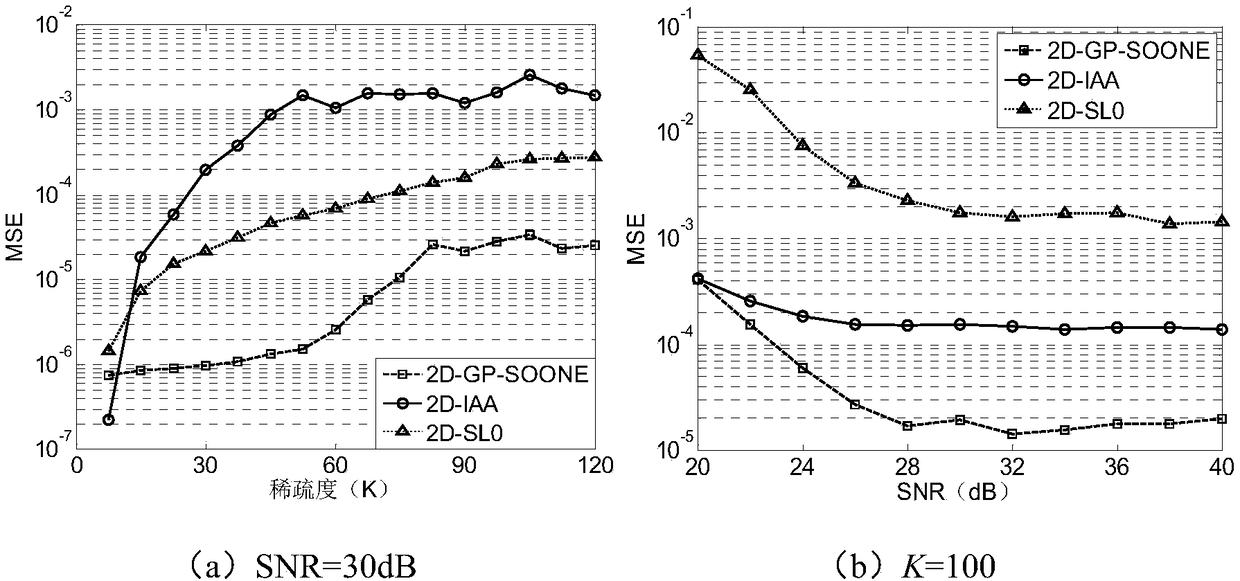
[0155] refer to Figure 7 , the device includes a first acquisition module 10 , a transformation module 20 , a second acquisition module 30 , a transformation module 40 , an optimization module 50 , and a processing module 60 . The first acquisition module 10 is used to acquire the echo signal of the target object, and obtains the first expression according to the echo signal; the transformation module 20 is used to transform the first expression to obtain the two-dimensional sparse matrix of the echo signal; Two acquisition modules 30 are used to obtain the two-dimensional expression of the SOONE function; the conversion module 40 converts the two-dimensional sparse matrix to obtain the minimum norm solution; the optimization module 50 is used to iteratively optimize the minimum norm solution to obtain the SOONE function The minimum v...
Embodiment 3
[0159] An electronic device provided by an embodiment of the present invention, such as Figure 8 As shown, the electronic device 70 includes a memory 71, a processor 72, and a computer program that can run on the processor 72 is stored in the memory 71. When the processor 72 executes the computer program, the steps of the method provided by the first embodiment above are implemented.
[0160] refer to Figure 8 , the electronic device 70 also includes: a bus 73 and a communication interface 74, the processor 72, the communication interface 74 and the memory 71 are connected through the bus 73; the processor 72 is used to execute executable modules stored in the memory 71, such as computer programs.
[0161] Wherein, the memory 71 may include a high-speed random access memory (RAM, Random Access Memory), and may also include a non-volatile memory (non-volatile memory), such as at least one disk memory. The communication connection between the system network element and at lea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com