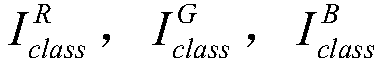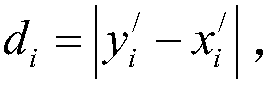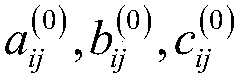A relative radiation correction method based on pseudo-invariant feature point classification and layering
A technology of relative radiation correction and radiation correction, which is applied in image analysis, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of low correction accuracy and achieve the effect of small mean difference, small root mean square error, and reduced mean difference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0022] A relative radiation correction method based on classification and layering of pseudo-invariant feature points. The relative radiation correction method includes the following steps:
[0023] Step 1: Obtain sub-images of ground features based on remote sensing image classification;
[0024] Step 2: Based on the nonlinear regression analysis of the spectrum, determine the initial relative radiation correction model and initial PIFs of the ground object sub-images; where PIFs refer to pseudo-invariant pixels;
[0025] Step 3: Based on the gradient-based fine nonlinear regression analysis, determine the refined nonlinear relative radiation correction model and refined PIFs of the ground object sub-images;
[0026] Step 4: Use refined PIFs and refined nonlinear relative radiation correction model to perform relative radiation correction on the sub-image of the ground object to be corrected;
[0027] Step 5: Synthesize the corrected image into a complete image, and evaluate its accura...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] The difference from the first embodiment is that the relative radiation correction method of this embodiment is based on the classification and stratification of pseudo-invariant feature points. In the first step, the specific process of obtaining sub-images of ground objects based on remote sensing image classification is :
[0029] Step 1: Reference image production and analysis, select the original remote sensing image with clear cloud content less than or equal to 2%, use the calibration information of the original data to calibrate the image, and then use the atmospheric condition data acquired at the same time to correct The remote sensing image is subjected to atmospheric correction to obtain the reference image required for relative radiometric correction; among them, the original remote sensing image with clear cloud content less than or equal to 2% is in the multiple original remote sensing images with clear cloud content information provided by the image data sel...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0039] The difference from the second embodiment is that the relative radiation correction method of this embodiment is based on the classification and stratification of pseudo-invariant feature points. In the second step, the non-linear regression analysis of the spectrum is used to determine the The specific process of the initial relative radiation correction model and initial PIFs is:
[0040] (1) The process of determining the initial relative radiation correction model of the ground object sub-image based on the nonlinear regression analysis of the spectrum is as follows:
[0041] Based on the theoretically non-linear relationship between the invariant pixel radiation relationship between the reference image and the corresponding ground object sub-image of the image to be corrected, a second-order polynomial is used to describe the radiation relationship of the corresponding pixels of the two sub-images, as shown in the following equation:
[0042]
[0043] Where x ij Represen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com