Mixture Raman spectrum qualitative analysis method based on sparse non-negative least square
A Raman spectroscopy and least squares technology, applied in the field of Raman spectroscopy, can solve the problems of reduced detection accuracy and reduced spectral similarity of mixtures, and achieves the effect of simple operation and high accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
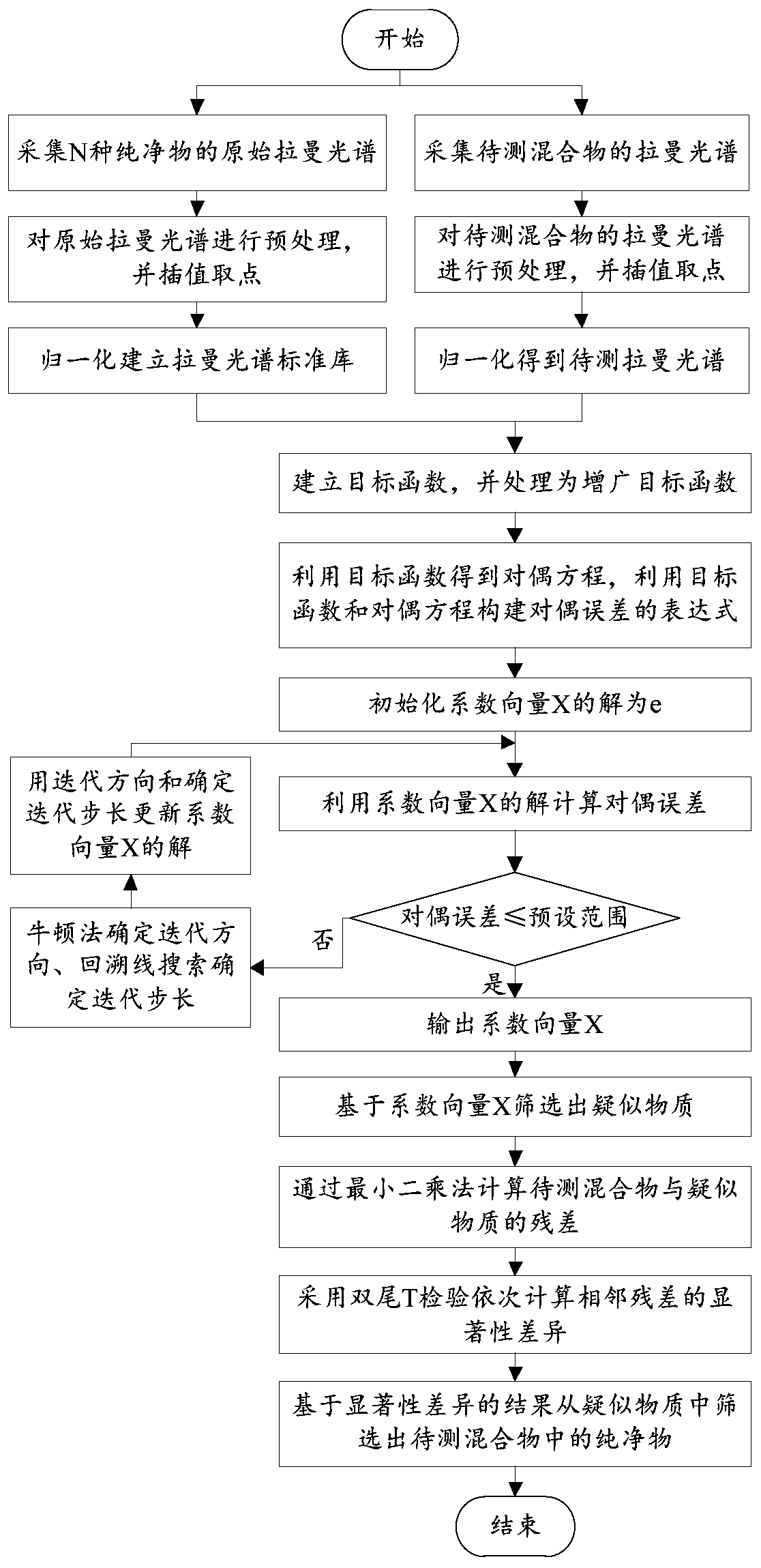
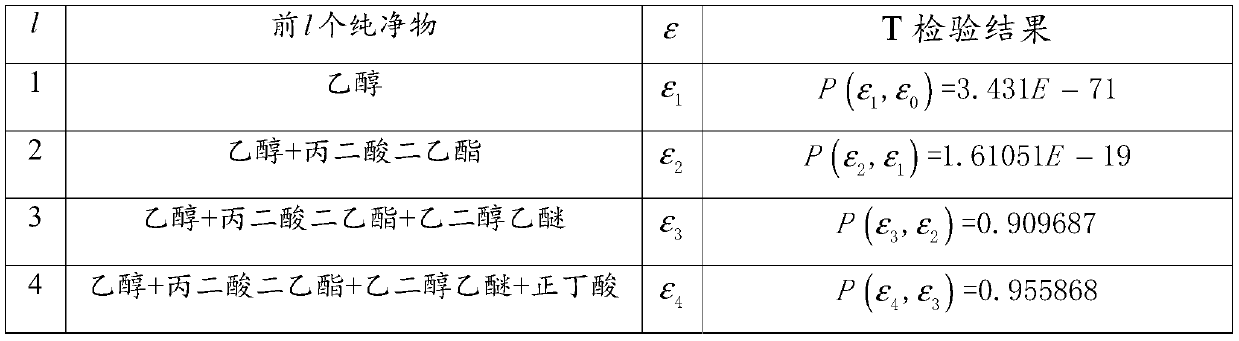
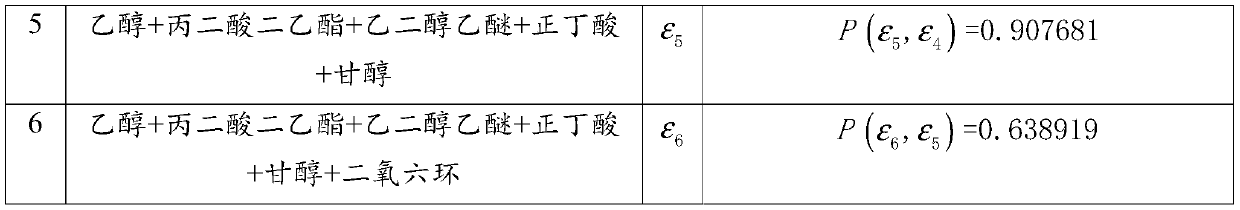
[0040] This application discloses a method for qualitative detection of mixture Raman spectroscopy based on sparse non-negative least squares, the method includes the following steps, please refer to figure 1 The flow chart:
[0041] Step S01, establish Raman spectrum standard library A of pure substances, Raman spectrum standard library A includes Raman spectra of N kinds of pure substances, N is a positive integer and the value of N should be as large as possible to enrich Raman spectrum standards Library A to improve detection coverage. The Raman spectrum of each pure substance is a column vector with M dimensions, M is also a positive integer and the value of M is determined according to the actual situation. The established Raman spectrum standard library A is in the form of a matrix of M rows and N columns, the Raman spectrum of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com