Method for predicting residual fatigue life of composite material containing initial delamination damage
A composite material, fatigue life technology, applied in instrumentation, calculation, electrical and digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of decreased fatigue life, high cost, layer-to-layer debonding, etc. Guaranteed accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
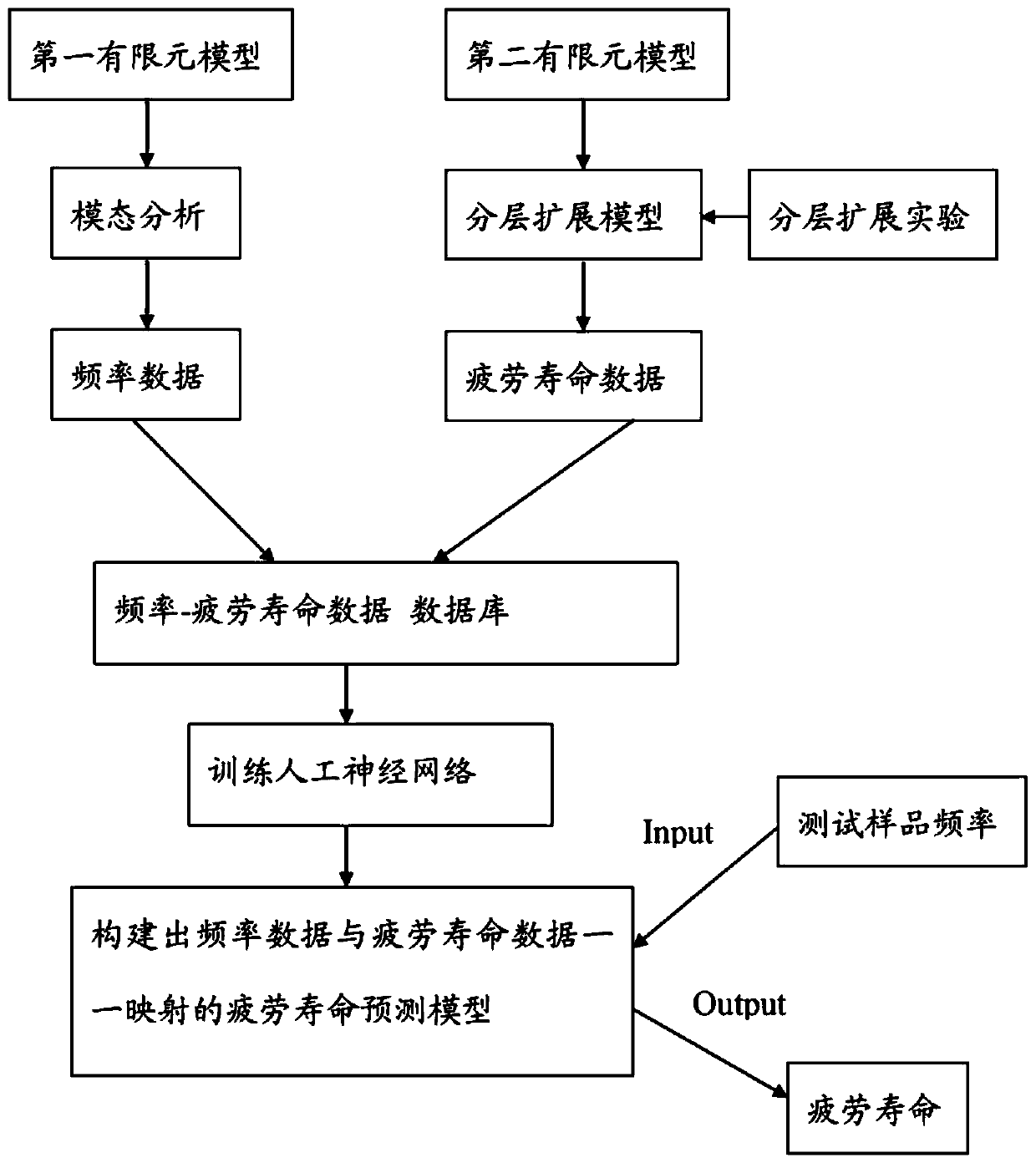
[0038] A method of predicting the remaining fatigue life of a fatigue life composite containing initial delamination damage, the method comprising the steps of:
[0039] (1) Establish a first finite element model of a composite material with initial delamination damage, perform modal analysis, and obtain modal frequency data under initial delamination damage parameters;
[0040] (2) Establish a second finite element model of a composite material containing initial delamination damage, use the empirical parameters of the composite material to construct a delamination expansion model, and then perform stress analysis, and under the stress, use the delamination expansion model for fatigue Delamination extension analysis under load to the failure of the composite material to obtain fatigue life data, the composite material containing initial delamination damage in step (1) is the same as the composite material containing initial delamination damage in step (2);
[0041] (3) Input ...
Embodiment 2
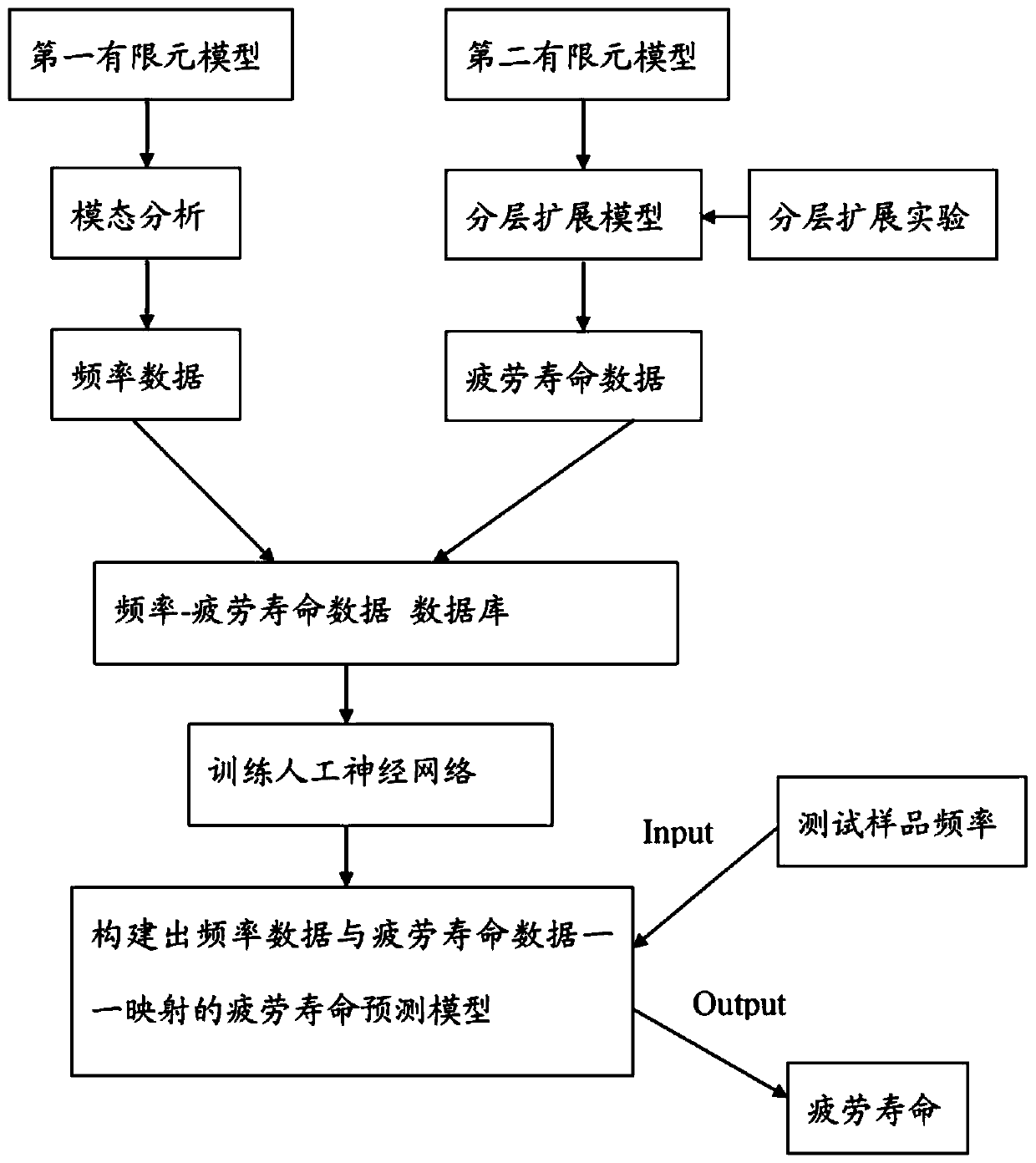
[0048] As an embodiment of the present invention, a system for predicting the remaining fatigue life of a fatigue life composite material containing initial delamination damage composite material, the system includes:
[0049] The first modeling module is used to establish a first finite element model of a composite material containing initial delamination damage, and the first finite element model is used for modal analysis of the structure;
[0050] The first analysis module is used to perform modal analysis through the first finite element model to obtain modal frequency data under initial delamination damage parameters;
[0051] The second modeling module is used to establish a second finite element model of a composite material containing initial delamination damage, the second finite element model is used for delamination expansion analysis, and the second modeling module is the same as the first modeling module Composite materials with initial delamination damage in the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com