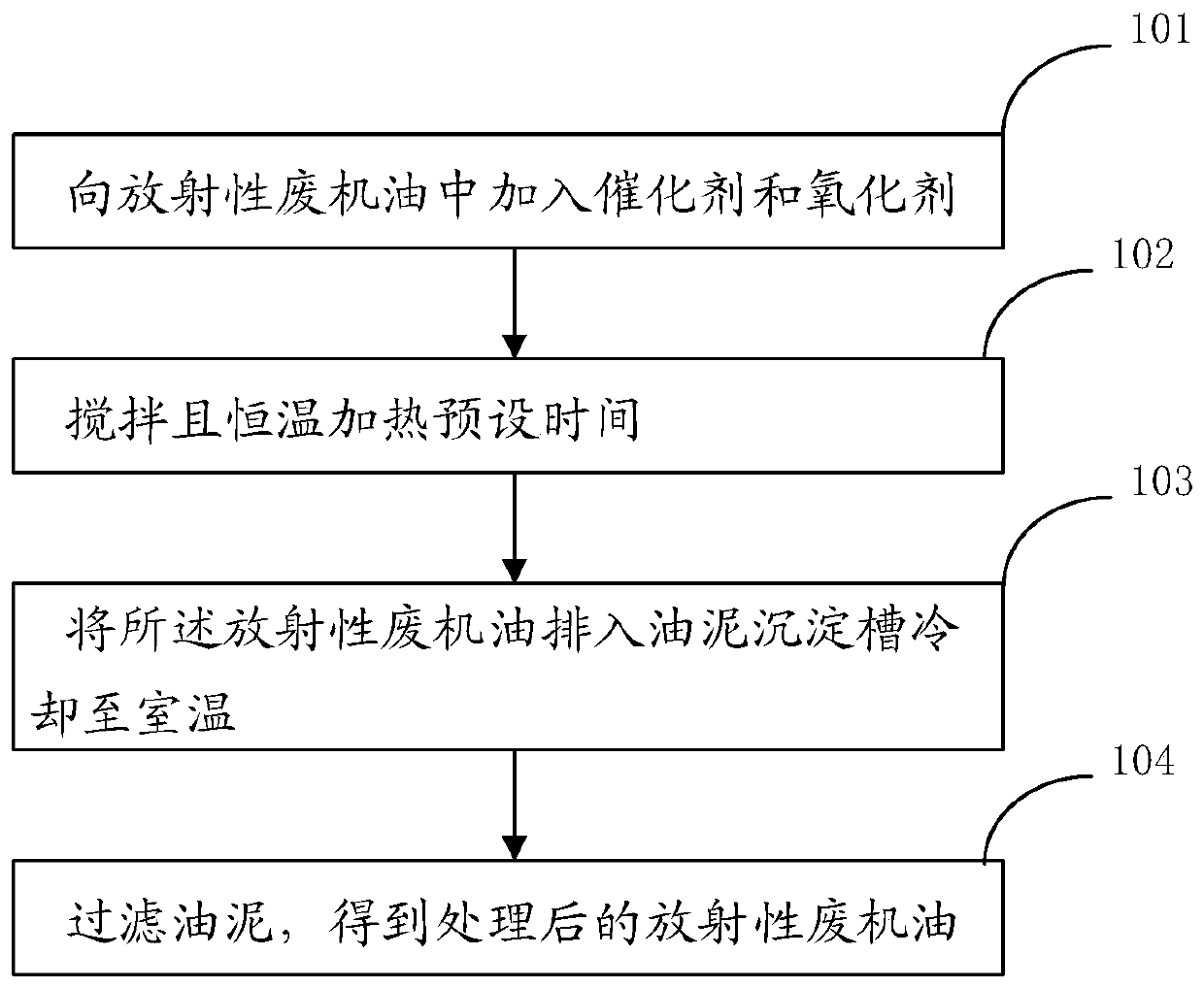
Method for separating nuclides from radioactive waste engine oil
A radioactive waste and separation method technology, applied in radioactive purification, nuclear engineering, etc., can solve the problems that radioactive waste engine oil cannot be formally treated, the incineration tail gas treatment is difficult, and the emulsification-solidification method has a large volume increase, etc., to achieve radioactive waste The effects of management minimization, reduction of fire hazards, reduction of possibility of radioactive leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] The radioactive waste engine oil was taken from the No. 2 waste engine oil storage tank of Daya Bay Nuclear Power Plant. The heating temperature was 160°C and the heating reaction time was 7 days. During the reaction process, the surface of the catalytic copper was covered with black engine oil sludge, and the color of the waste engine oil turned dark black.
[0041] After the reaction, the radioactive waste engine oil is filtered with a filtration accuracy of 2μ. The quality of the final separated filter residue is about 1 / 10 of the quality of the waste engine oil. The radioactivity of the waste engine oil is measured by a gamma spectrometer. The radioactivity level is reduced by about 120 times. The final radioactivity The activity concentration is less than the relevant exemption limit specified in the "Activity Concentration of Radionuclide in Materials Exempt from Radiation Supervision" (GB27742-2011).
example 2
[0043] The radioactive waste engine oil was taken from the No. 2 waste engine oil storage tank of the Daya Bay Nuclear Power Plant. The heating reaction time was 12 days, and the heating temperature was 140°C and 160°C. After the reaction is filtered, the filtering accuracy is 2μ. The radioactivity of the filtered waste engine oil is measured by a gamma spectrometer. The radioactivity level is reduced by about 10 times and 180 times, respectively. The effect of temperature on the removal of radionuclides can be seen: 160℃>>140℃ .
example 3
[0045] The radioactive waste engine oil was taken from the No. 2 waste engine oil storage tank of Daya Bay Nuclear Power Plant. The heating temperature was 160℃, and the heating reaction time was 12 days. After the reaction, the waste engine oil was filtered with a precision of 80μ, 50μ, 30μ, 5μ and 2μ, and then passed through the gamma spectrum. The instrument measures radioactivity, and the radioactivity levels are reduced by about 1.5, 3.6, 11.4, 72.3 and 79.4 times respectively.
[0046] Different from the features of the prior art, the present invention provides a method for separating radionuclides in radioactive waste engine oil, which utilizes the characteristics of the catalytic oxidation of waste engine oil to produce engine oil sludge that carries radionuclides and realizes the concentration of radionuclides in radioactive waste engine oil. With separation treatment, the waste engine oil is released and controlled, and the danger of radioactive waste is reduced to a nea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com