Air-cooled reinforced steel for hot-air expansion forming and preparation method of air-cooled reinforced steel
A technology for strengthening steel and air cooling, applied in the field of alloy steel hot forming, can solve the problems of affecting production efficiency, long cooling time, high mold cost, and achieve the effect of fast production cycle, improved casting performance, and simplified production process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0027] The invention provides an air-cooled strengthened steel for thermal expansion forming and a preparation method thereof.
[0028] The chemical composition mass percentage of the strengthened steel is: C: 0.08% ~ 0.25%, Mn: 1.5% ~ 2.5%, Si: 0.2% ~ 0.5%, Cr: 0.5% ~ 1.5%, Mo: 0.2% ~ 0.5%, Al : 0.05%~0.1%, Nb: 0.05~0.15%, V: 0.05~0.15%, Ti: 0.05~0.15%, B: 0.003~0.01%, P<0.03%, S<0.03%, the balance is Fe and Unavoidable impurities.
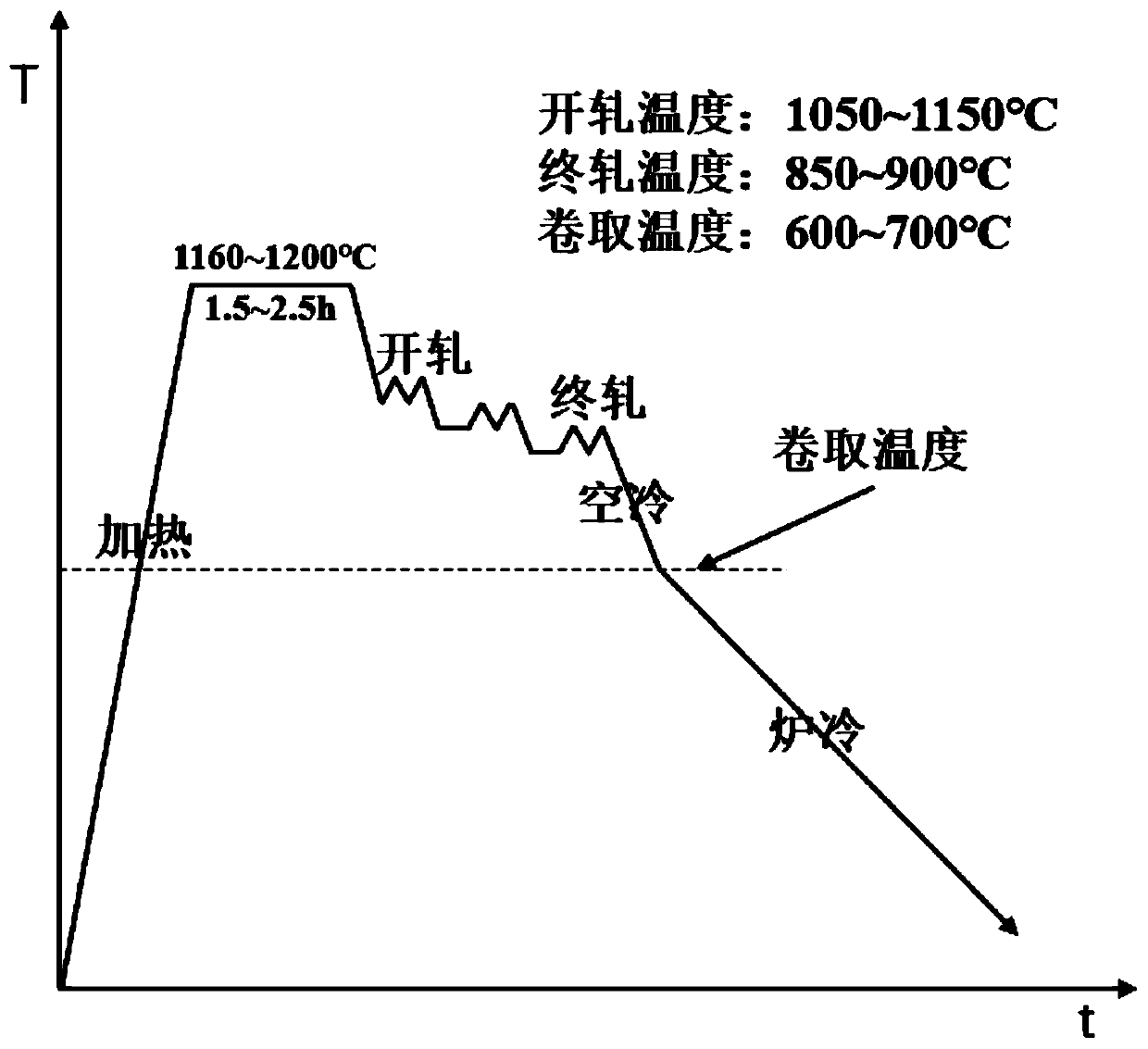
[0029] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the preparation method of the air-cooled reinforced steel for hot air expansion forming comprises the steps as follows:
[0030] (1) Smelting, casting and forging into slabs;
[0031] (2) Hot rolling: heat the slab obtained in step (1), perform multi-pass hot rolling deformation after homogenization treatment, air cool to coiling temperature after rolling, and furnace cool to room temperature after coiling to obtain strengthened steel.
Embodiment 1
[0034] The air-cooled strengthened steel for hot air expansion forming produced in this example has the following chemical composition mass percentages: C: 0.088%, Mn: 1.85%, Si: 0.25%, Cr: 0.75%, Mo: 0.25%, Al: 0.05% , Nb: 0.05%, V: 0.06%, Ti: 0.05%, B: 0.005%, P<0.03%, S<0.03%, and the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurities.
[0035] The preparation method of the air-cooled strengthened steel for thermal expansion forming in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0036] (1) Forging into slabs after smelting and casting: melt the prepared raw materials in a vacuum induction melting furnace at a melting temperature of 1660°C, and pour them into ingots, forge and deform the ingots, and finally forge them into slabs. The accumulated deformation is 80%. After forging, it is air-cooled to room temperature. The heating temperature of the ingot is 1160°C, the holding time is 2h, the starting forging temperature is 1130°C, and the final forging temperature is ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The difference from Example 1 is that the coiling temperature of the hot-rolled plate is 600°C, and the mechanical properties of the high-strength structural parts obtained by air-cooling the hot-rolled plate after high-temperature thermal expansion are tested according to the national standard, and the yield strength is 677MPa. The tensile strength is 1023MPa and the elongation is 18.6%, meeting the performance requirements of the new generation of high-strength steel for automobiles.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com