High-strength magnetic-gathering permanent-magnet rotor and motor
A permanent magnet rotor, high-strength technology, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuits, electrical components, etc., to achieve the effect of high rotor strength, reducing eddy current loss, and improving magnetic concentration ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
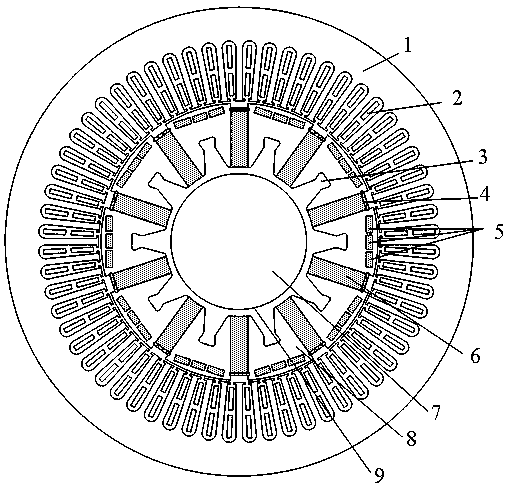
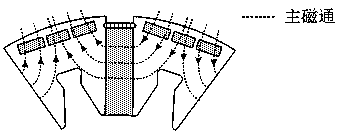
[0033] The high-strength magnetism-concentrating permanent magnet rotor of the present invention includes a rotor iron core and a permanent magnet. A number of permanent magnet slots are evenly opened on the rotor iron core along its circumferential direction, and the permanent magnet slots are arranged through the direction of the rotating shaft. There are suitable tangential permanent magnets, and there is a slot on the rotor iron core along its circumference. The slot is arranged through the direction of the rotating shaft. At least two in-line slots and two in-line permanent magnets are arranged between the two permanent magnet slots. The permanent magnet slots and the tangential permanent magnets are arranged in pairs in even groups, generally 6-12 even groups.
[0034] The cross-section of the tangential permanent magnet is a rectangle, and the tangential magnetization method is adopted. A magnetic steel baffle is installed on the end face of the tangential permanent ma...
Embodiment 2
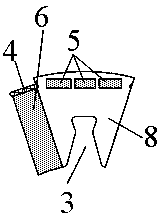
[0036] In the high-strength magnet-concentrating permanent magnet rotor of the present invention, at least N inline slots and N inline permanent magnets are arranged between two adjacent permanent magnet slots, and N satisfies the following relationship: 4≥N≥2. Assuming that the gap between adjacent inline permanent magnets 5 is A, then A satisfies the following relationship: 3mm≥A≥1mm. Assuming that the section length of each inline permanent magnet 5 is B and the width is C, then B, C and N satisfy the following relationship: 6≥(N*(A+B)-A) / C≥4. Among them, the total mechanical angle occupied by the N inline permanent magnets 5 with the center of the rotor circle and the total length of the gap is α, and the mechanical angle occupied by the rotor core part of each module is β, and α and β satisfy the following relationship: 0.9≥α / β≥0.5. The shortest distance between the inline permanent magnets 5 on both sides, that is, the inline permanent magnets 5 close to the tangential ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Optionally, in this example, an annular groove is left between the rotor core 8 and the rotating shaft 7, and the annular groove 9 protrudes toward the air gap side to provide a dovetail groove 3, and the dovetail groove 3 is evenly spaced between two adjacent permanent magnets. Between the grooves, the annular groove 9 and the dovetail groove 3 are embedded with lightweight high-strength alloy materials for enhancing the strength of the rotor. High-strength titanium alloy material is embedded in the groove, and an integral reinforced structure is adopted. The density of high-strength titanium alloy is only 60% of that of steel, and its strength is higher than that of iron core material.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com