Microgravity vacuum environment oriented lunar surface in-situ resource 3D printing device
A 3D printing, vacuum environment technology, applied in the directions of manufacturing auxiliary devices, 3D object support structures, accessories for processing main materials, etc., can solve the problems of long construction period, waste of transportation resources, and difficulty in meeting, to expand production scale, reduce Manufacturing cost and effect of improving production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention. In addition, the technical features involved in the various embodiments of the present invention described below can be combined with each other as long as they do not constitute a conflict with each other.
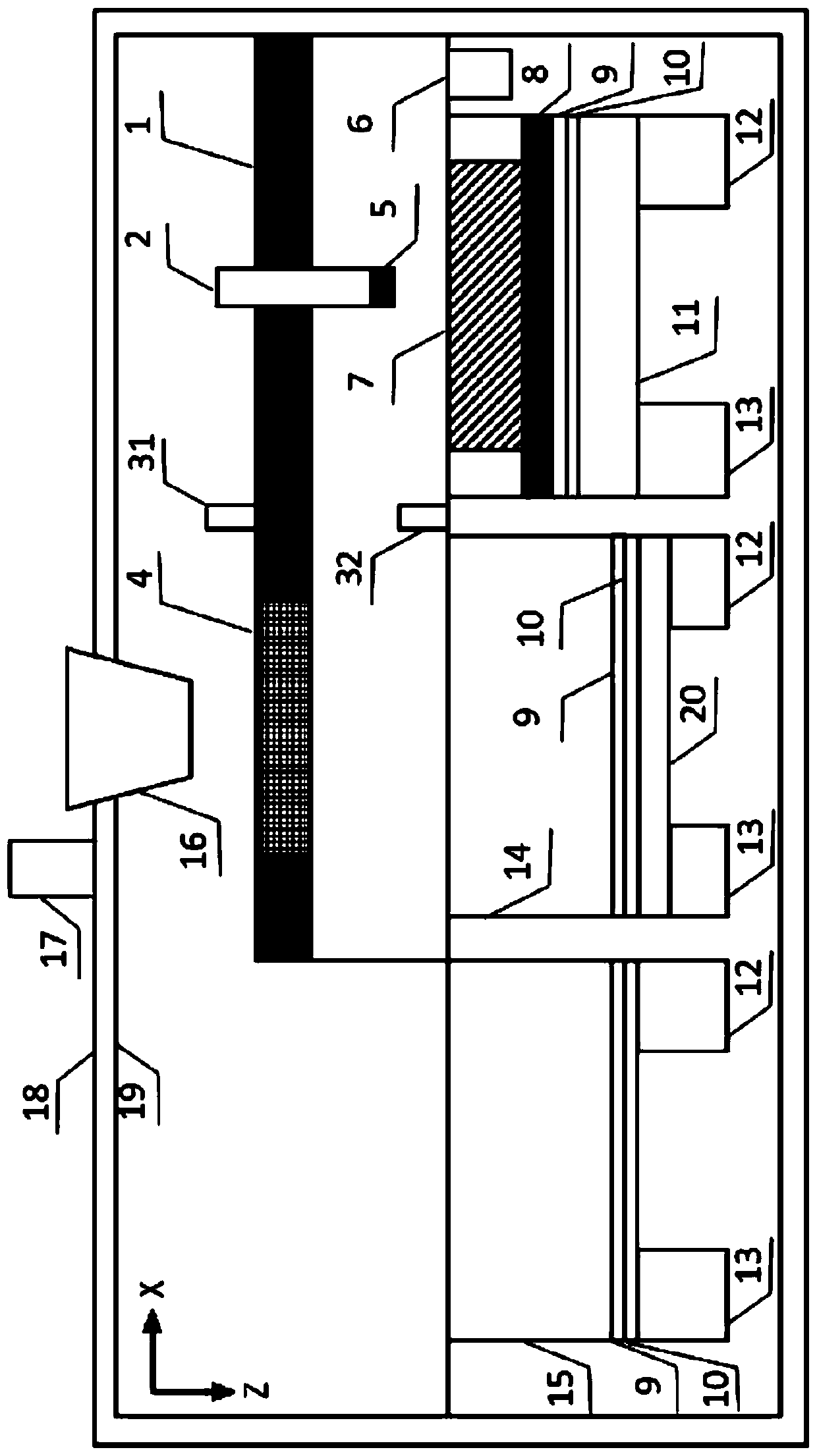
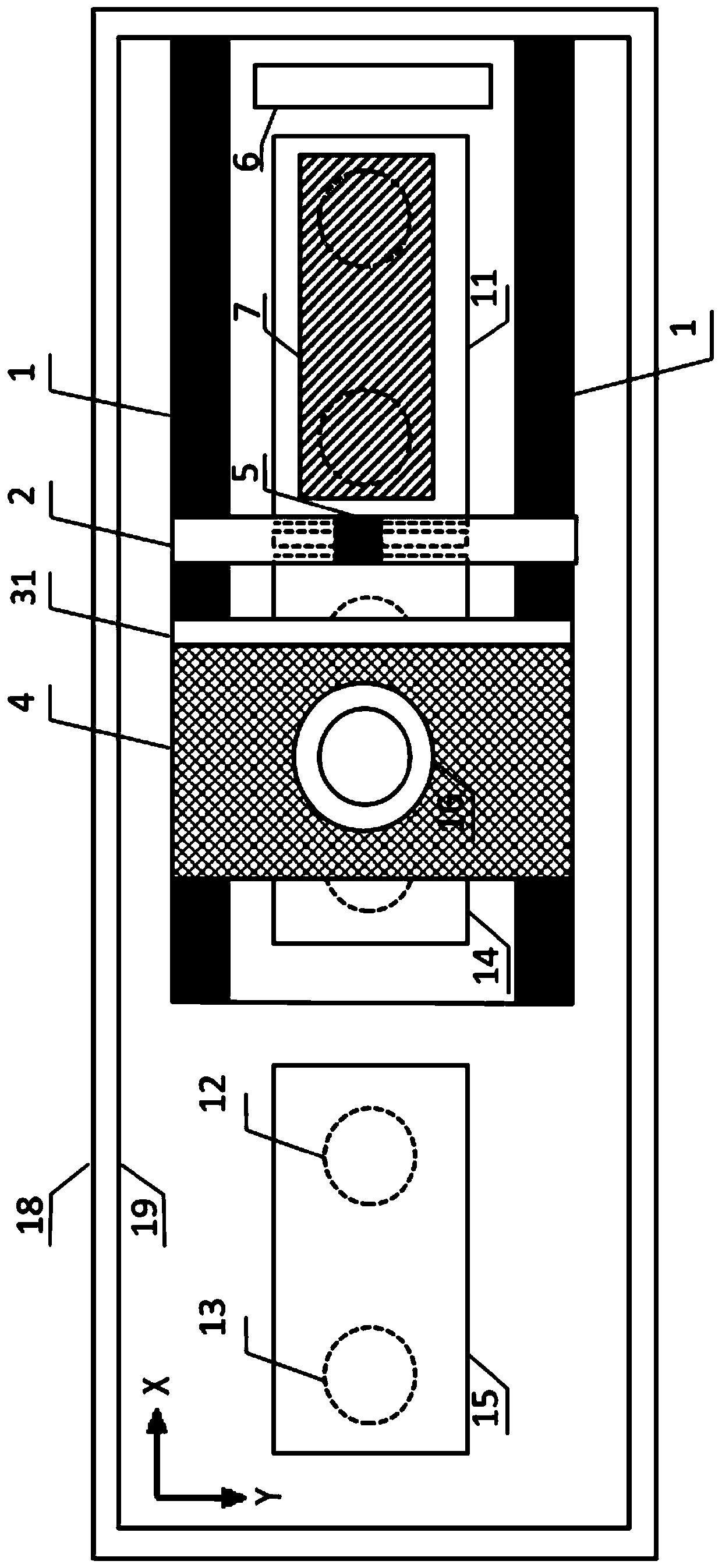
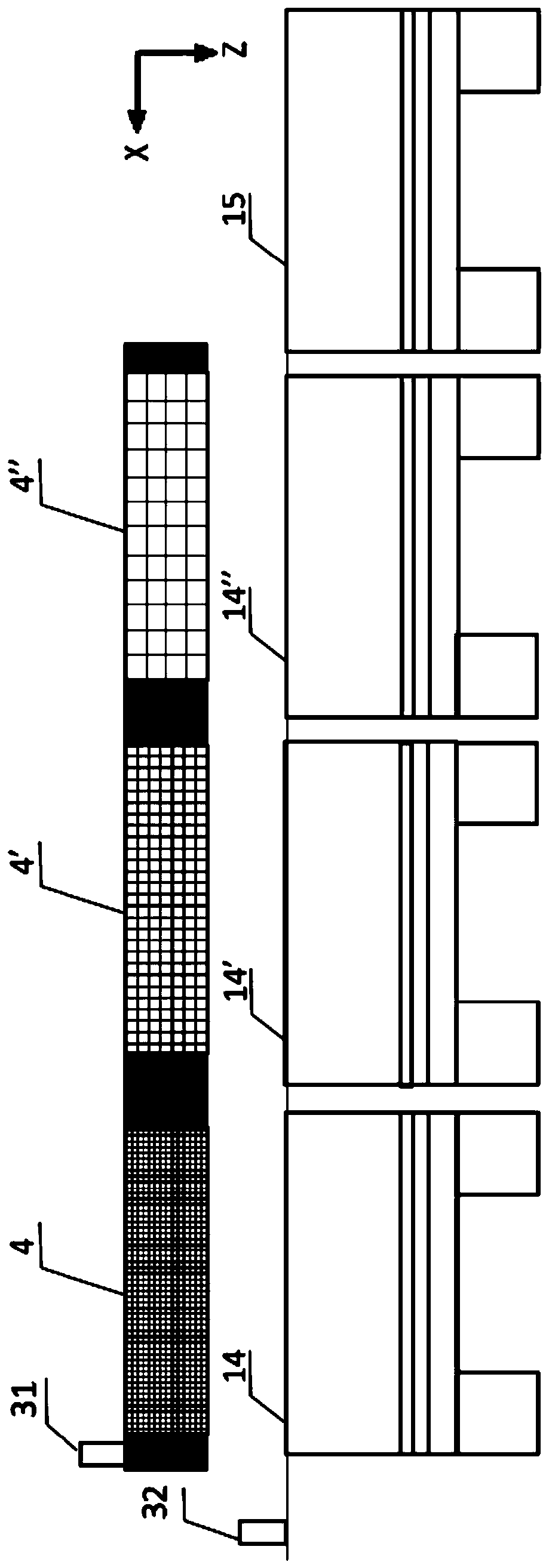
[0033]The present invention provides a 3D printing device for in-situ resources on the lunar surface facing a microgravity vacuum environment, mainly including a grasping and screening unit for in-situ resources on the lunar surface, and an inkjet 3D printing forming unit. The existing 3D printing devices in outer space all carry materials to outer space for 3D printing. Carrying materials waste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com