Distributed Cooperative Navigation Filtering Method for Multi-satellite Formation System Facing Satellite Failure
A technology for satellite failure and collaborative navigation, applied in the field of satellite navigation, can solve the problem of not taking into account the impact of multi-satellite formation systems, and achieve the effect of improving fault tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0094] Example 1: The situation where some nodes are not observable.
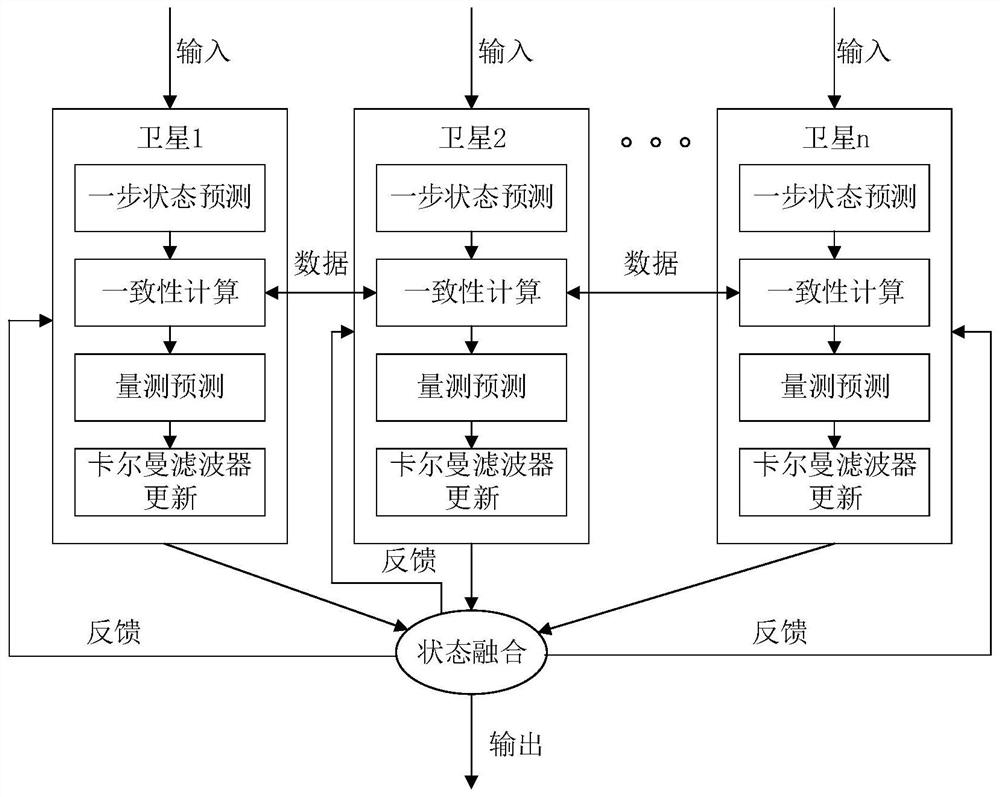
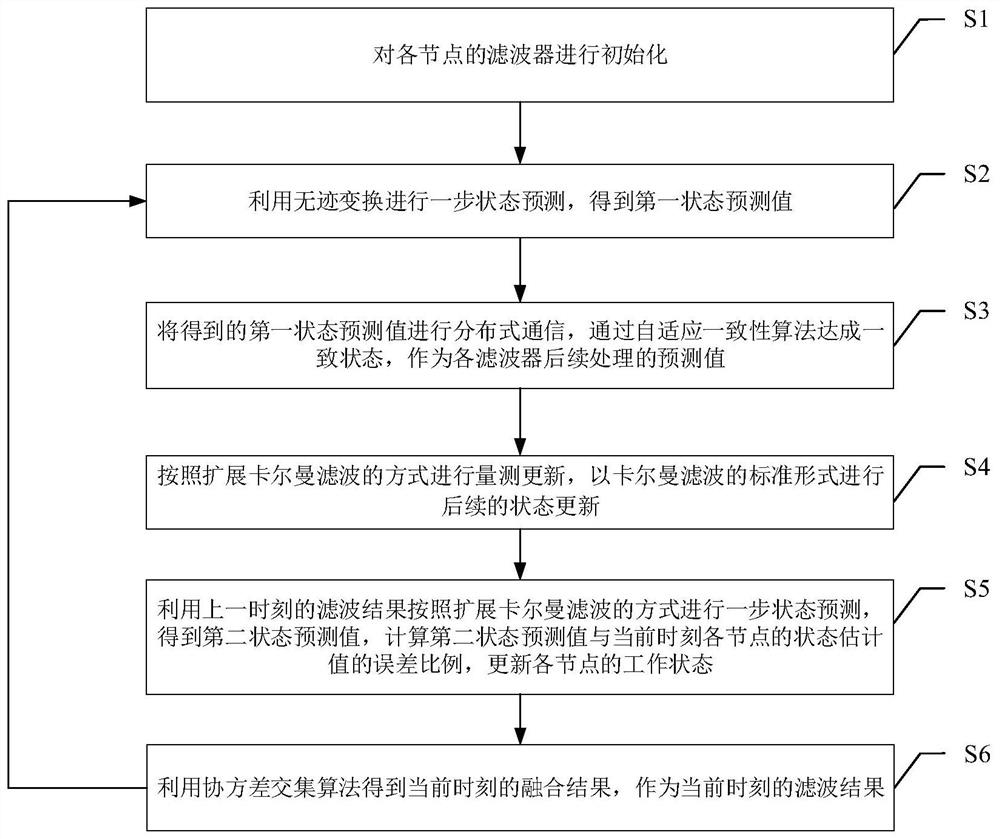
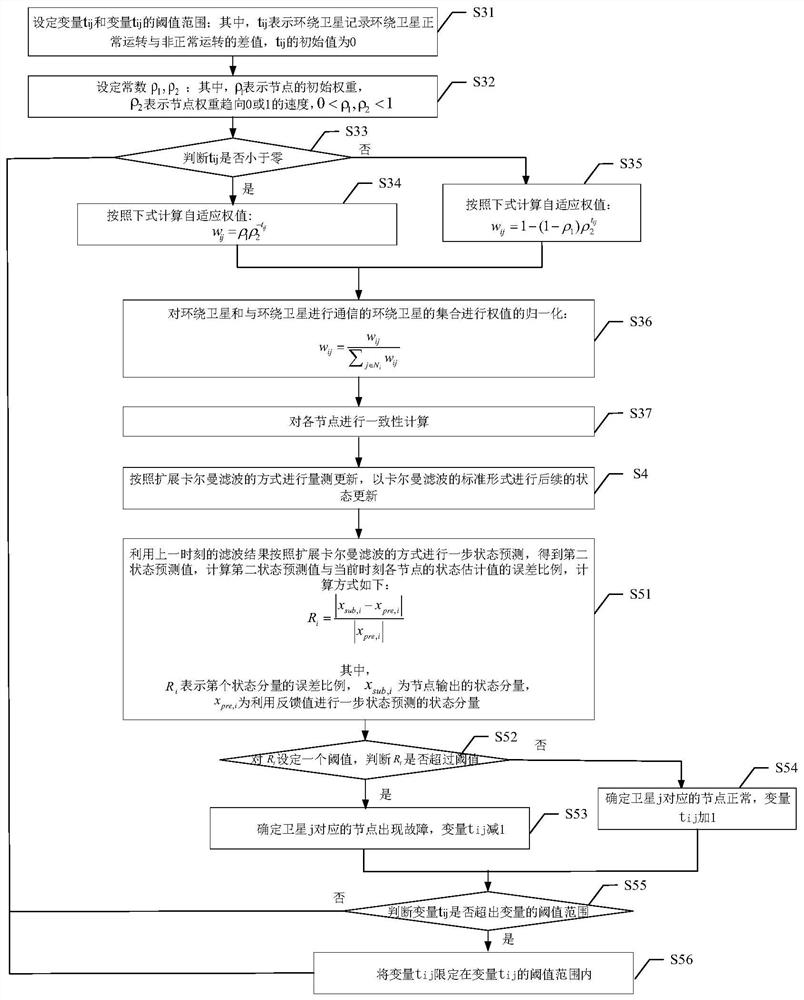
[0095] The distributed cooperative navigation filtering method of the multi-satellite formation system is a method to collaboratively obtain the state of the target satellite when the state (spatial position and velocity) of each surrounding satellite is known. Surrounding the satellite can measure the target satellite and obtain some or all of the state measurement values. Each orbiting satellite forms a communication link according to a certain topology, performs data interaction, and forms multiple computing nodes. A node is a basic unit that can perform algorithm calculations, and is a collection of surrounding satellites with inter-satellite links. This set contains an orbiting satellite that has information channels with other orbiting satellites in the node to obtain measurements from other orbiting satellites and perform calculations on that satellite. A node is a virtual whole. The same group of ...
example 2
[0162] The simulation model and various values are still used, and the algorithm flow remains unchanged. Select the model 9001s ~ 11500s for simulation, and the 9001s of the model corresponds to 1s of this simulation. During this time period, the nodes are considerable. Let the orbiting satellite 1 be from 2001s to 2050s, and the distance measurement fails during these 50s, and the return value is a large value, which is set to 100000000m in the simulation. Comparing the results of this simulation with the consistent EKF algorithm and UKF combined with CI algorithm, Figure 9a and Figure 9b is the position error and speed error of this simulation under the ranging fault, Figure 10a and Figure 10b are the position error and velocity error of the consistent EKF algorithm under ranging faults, Figure 11a and Figure 11b is the position error and velocity error of UKF combined with CI algorithm under ranging fault. It can be seen from the simulation results that this ...
example 3
[0165] The simulation model and various values are still used, and the algorithm flow remains unchanged. Continue to carry out satellite communication fault simulation within the time period 9001s ~ 11500s. Taking 9000s as the start time point of the simulation, and orbiting satellite 1 within the time period of 2501s to 2550s, the settlement result is lost, and the resulting communication value is always 0. Compare the results of this simulation, the consistent EKF algorithm and the UKF combined with the CI algorithm. Figure 12a and Figure 12b is the position error and speed error of this simulation under communication failure, Figure 13a and Figure 13b is the position error and velocity error of the consistent EKF algorithm under communication failure, Figure 14a and Figure 14b It is the position error and velocity error of UKF combined with CI algorithm under communication failure. It can be seen from the simulation results that after the calculation results ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com