Novel aspartokinase mutant and method for production of l-amino acid using same
A technology of aspartate kinase, aspartate, applied in the field of aspartate kinase variants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Example 1: Preparation of bacterial strains introducing lysC variants
[0070] A variant whose activity can be enhanced compared with the wild type was selected by structural modeling of aspartokinase, and a strain into which the variant was introduced was prepared as described below.
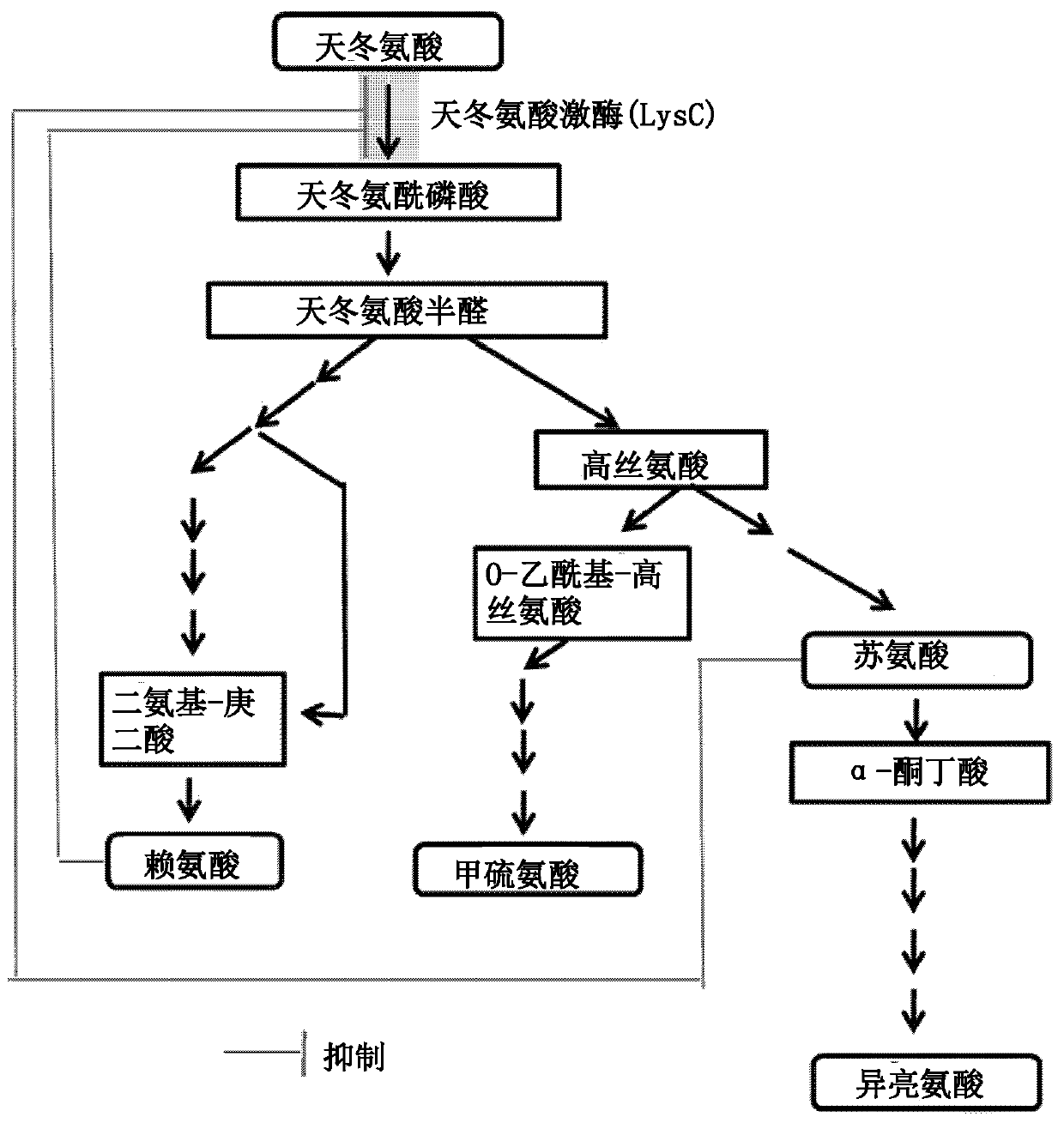
[0071] In the gene lysC (SEQ ID NO: 2) encoding the aspartokinase (SEQ ID NO: 1) derived from Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032 (hereinafter referred to as WT), the amino acid at position 377 was selected as the mutation site , and selected the basic amino acid L-lysine and the nonpolar amino acid L-methionine as representative examples of other amino acids for substitution.
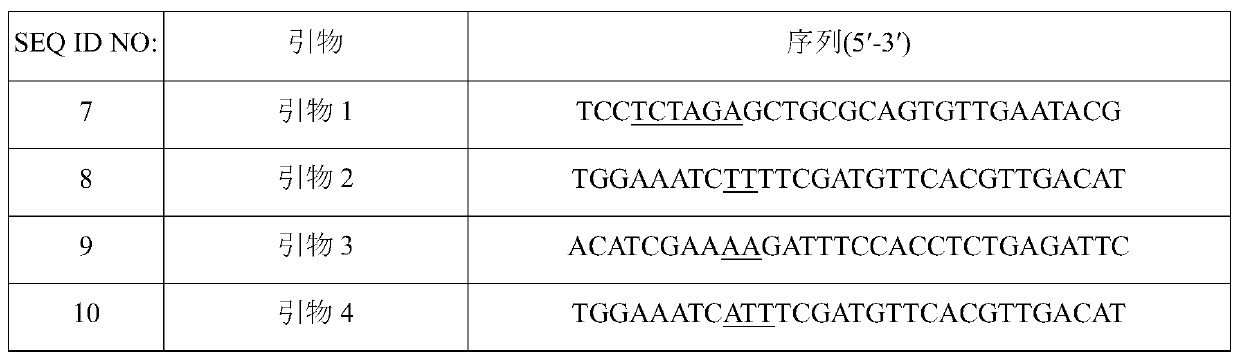
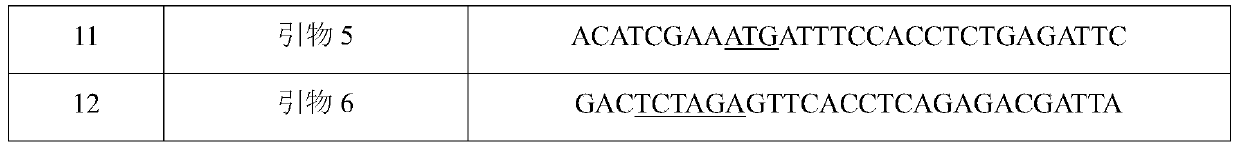
[0072] In order to prepare a vector for introducing variation, a pair of primers (SEQ ID NO: 7 and 8 or SEQ ID NO: 7 and 10) and a pair of primers for amplifying the 5' upstream region were designed with the variation site as the center. A pair of primers (SEQ ID NO: 9 and 12 or SEQ ID NO: 11 and 12) for the ...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Example 2: Confirmation of the ability of strains introducing lysC variants for the production of aspartic acid-derived amino acids
[0081] In order to compare the abilities of the strains CA01-2307 and CA01-2308 obtained from Example 1 and the strain WT for producing amino acids mainly derived from aspartic acid, the strains were cultured using the following method, and the components in the medium were analyzed.
[0082] Each strain was inoculated into a baffled flask (250 mL) containing a seed medium (25 mL), and cultured at 37° C. for 20 hours while shaking at 200 rpm. A seed culture solution (1 mL) was inoculated into a corner-baffled flask (250 mL) containing a production medium (24 mL), and then cultured at 37° C. for 24 hours while shaking at 200 rpm. The concentrations of L-lysine and L-threonine, which are representative amino acids derived from L-aspartic acid and aspartic acid, were analyzed by HPLC, and the analysis The concentrations are shown in Table...
Embodiment 3
[0093] Example 3: Preparation of L-threonine enhanced strain and confirmation of L-threonine productivity
[0094] In order to clearly confirm the change in L-threonine productivity by introducing the lysC(L377K) variant, which has the higher lysine productivity identified in Example 2, a variant was introduced into the homoserine encoding the production of homoserine Among the genes of dehydrogenases, this gene is a common intermediate in the biosynthetic pathway of L-threonine, L-isoleucine, L-methionine and homoserine derivatives. Specifically, the strain was prepared by introducing the hom(G378E) mutation known in the art (Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 45, 612-620 (1996)) into the strain CA01-2307 prepared in Example 1. In addition, a strain in which the hom(G378E) mutation was introduced into WT was also prepared as a control group. To prepare a hom(G378E)-introducing vector, PCR was performed using SEQ ID NOs: 13 and 14 and SEQ ID NOs: 15 and 16 using WT genomic DNA as...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com