Asymmetric half-bridge converter and control method thereof
A half-bridge converter, asymmetrical technology, applied in control/regulation system, DC power input conversion to DC power output, instruments, etc. Consumption and other problems, to achieve the effect of effective control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
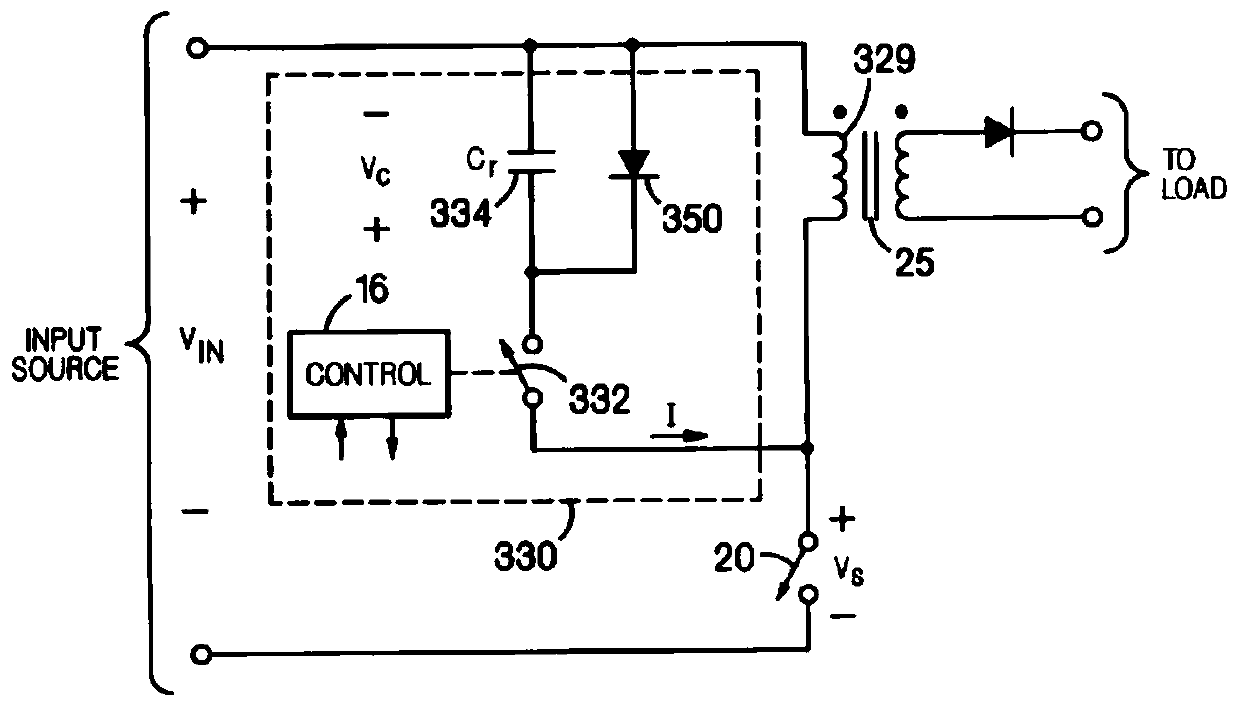
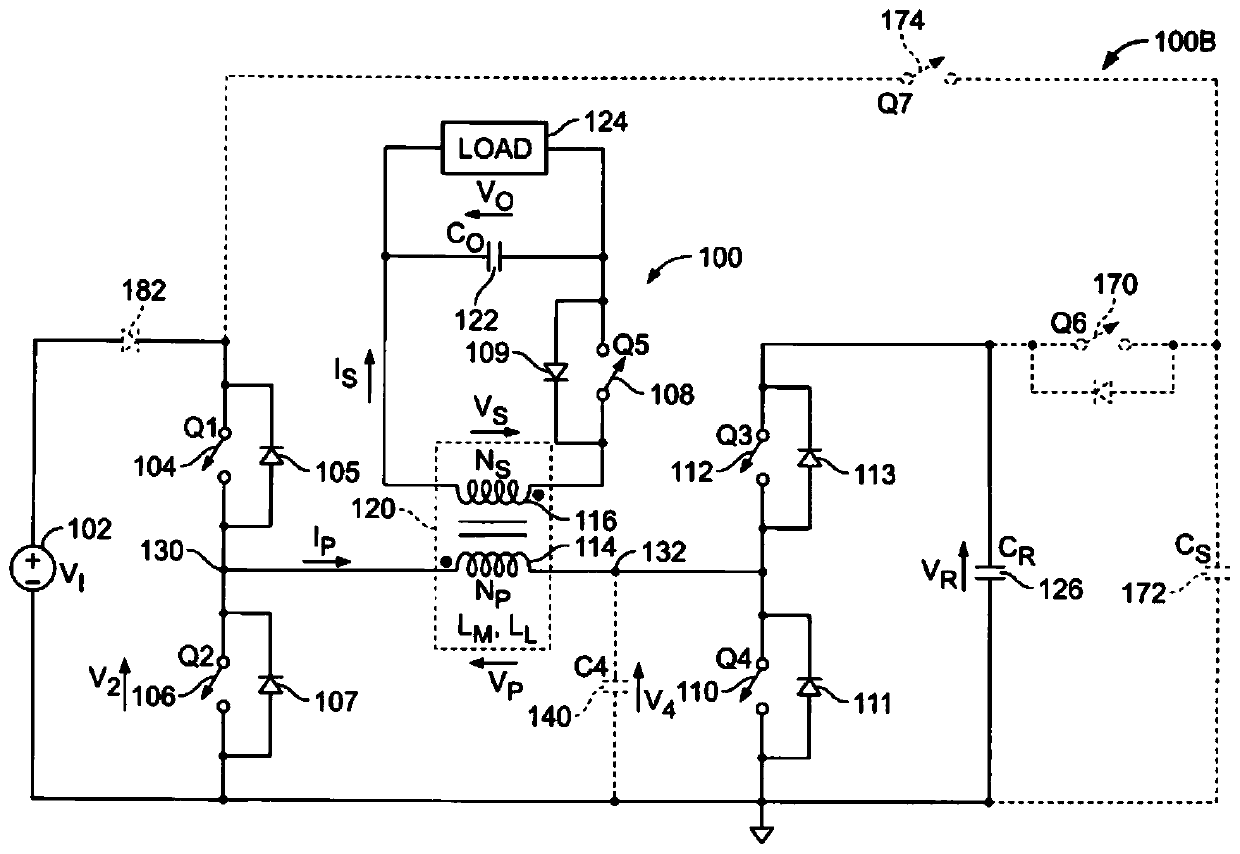
[0102] Figure 7 Shown is the circuit diagram of the first embodiment of the present invention, Figure 8 It is a schematic diagram of an equivalent circuit of an asymmetrical half-bridge flyback converter according to the first embodiment of the present invention, Figure 7 and Figure 4 , Figure 8 and Figure 5 The difference is that a unidirectional clamping network Sow is added to the primary side of the transformer, the anode of the unidirectional clamping network Sow is electrically connected to the anode of the primary winding of the transformer, and the cathode of the unidirectional clamping network Sow is connected to the primary side of the transformer Winding cathode electrical connection;
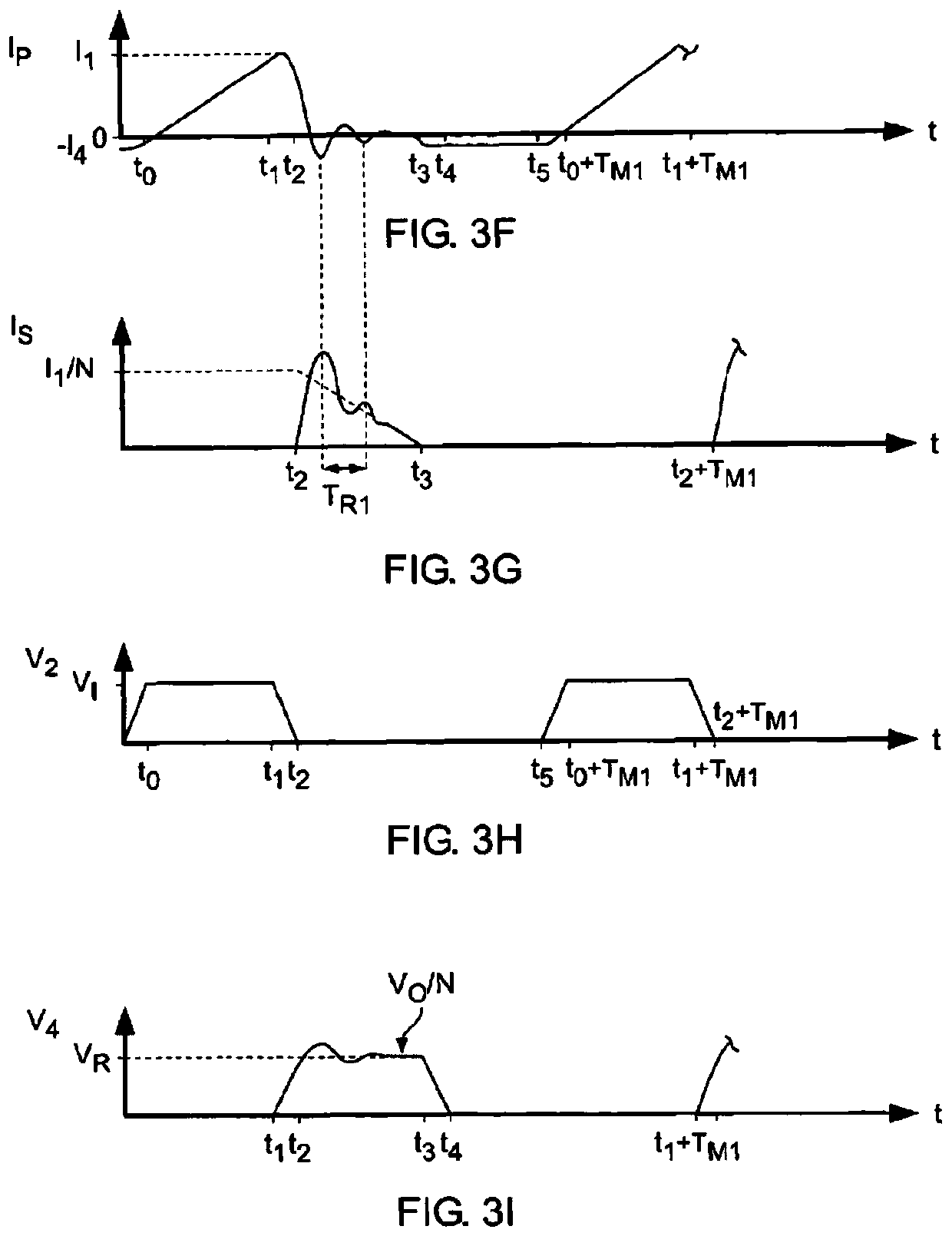
[0103] Figure 9 It is a typical working waveform diagram of the asymmetrical half-bridge flyback converter working in CCM mode according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Each cycle includes five stages: excitation stage, auxiliary switch zero-voltage turn-o...
no. 2 example
[0122] Figure 12 It is a circuit diagram of the second embodiment of the present invention, an asymmetric half-bridge flyback converter. The main difference between the second embodiment of the present invention and the first embodiment lies in the difference in the connection mode of the unidirectional clamping network Sow: the first embodiment Add a unidirectional clamping network Sow to the primary side of the transformer, the anode of the unidirectional clamping network Sow is electrically connected to the anode of the primary winding of the transformer, and the cathode of the unidirectional clamping network Sow is electrically connected to the cathode of the primary winding of the transformer In the second embodiment, a unidirectional clamping network Sow is added on the secondary side of the transformer, the anode of the unidirectional clamping network Sow is electrically connected with the same name end of the transformer secondary winding, and the cathode of the unidir...
no. 3 example
[0125] Figure 13 It is the circuit diagram of the third embodiment of the present invention, an asymmetrical half-bridge flyback converter. The difference from the first embodiment is that the transformer Tr also includes a third winding Np_ow; in the first embodiment, the primary side of the transformer is increased A unidirectional clamping network Sow, the anode of the unidirectional clamping network Sow is electrically connected with the anode of the primary winding of the transformer, and the cathode of the unidirectional clamping network Sow is electrically connected with the negative electrode of the primary winding of the transformer; in the third embodiment A unidirectional clamping network Sow is added to the third winding Np_ow of the transformer, the anode of the unidirectional clamping network Sow is electrically connected to the terminal with the same name of the third winding Np_ow, and the cathode of the unidirectional clamping network Sow is electrically conne...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com