Small celestial body high-speed impact terminal guidance method based on speed increment corridor
A speed increment and small celestial body technology, applied in the field of deep space exploration, can solve the problems of large mass of kinetic energy impactor, insufficient terminal guidance precision, and short control window time, so as to improve the terminal guidance precision, reduce adverse effects, and have universal adaptive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
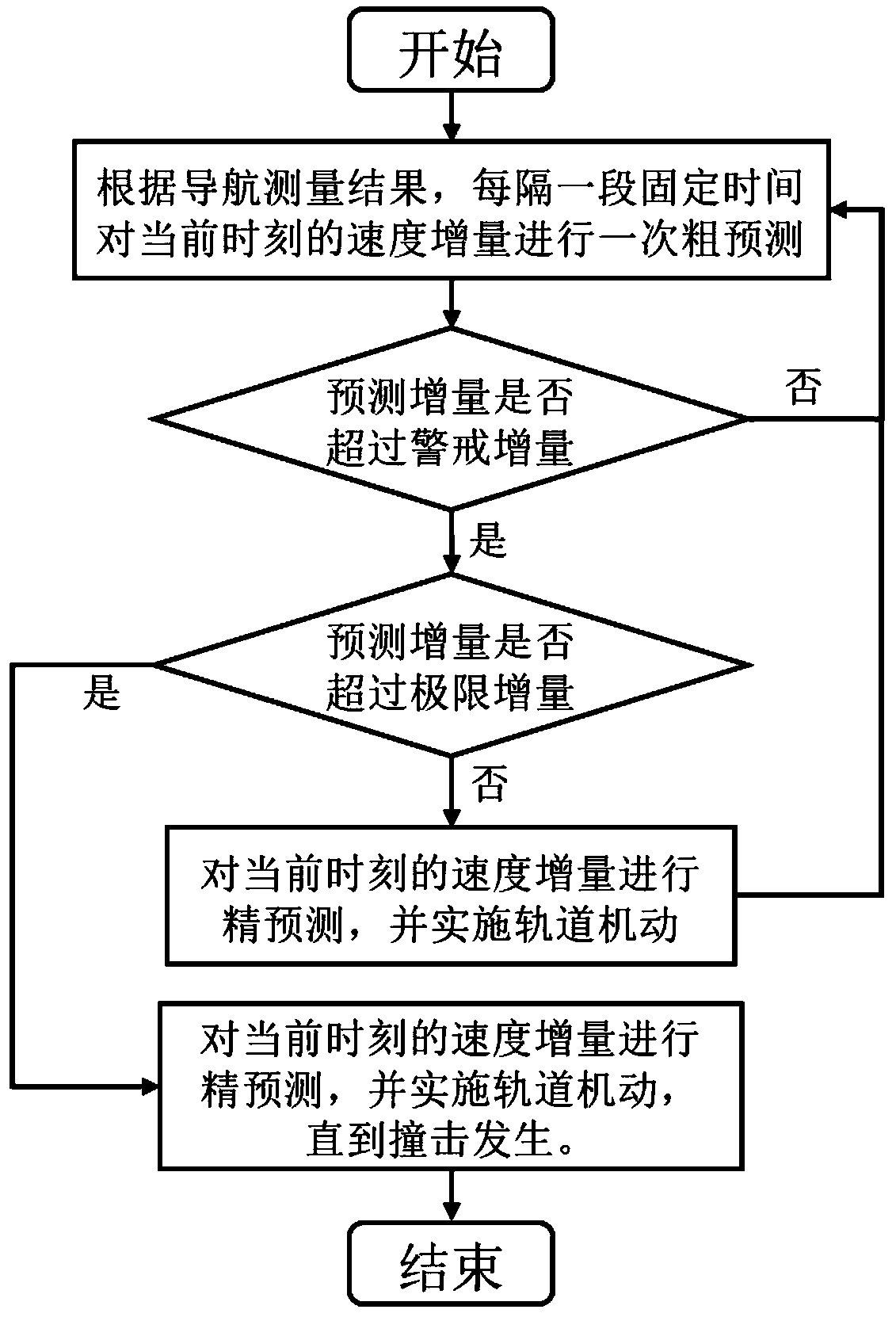
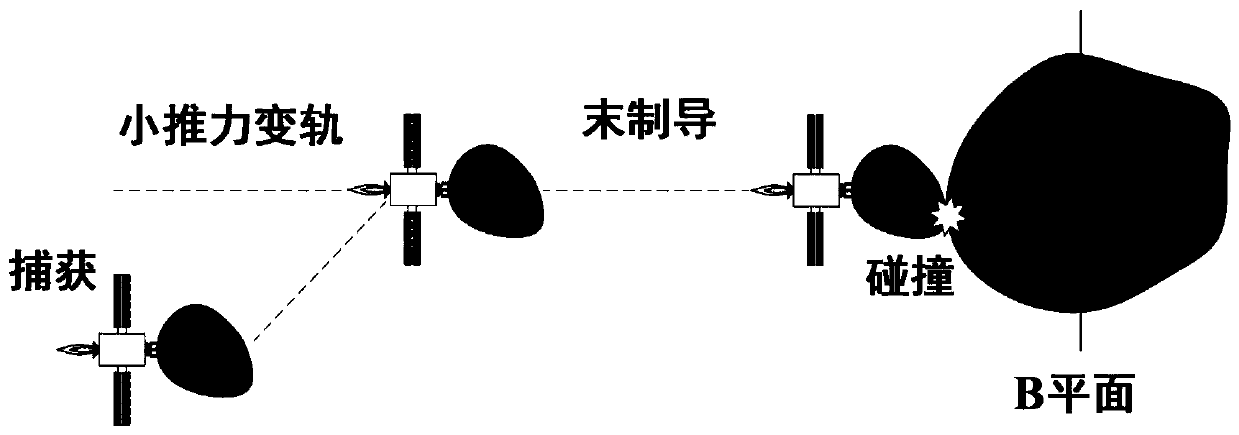
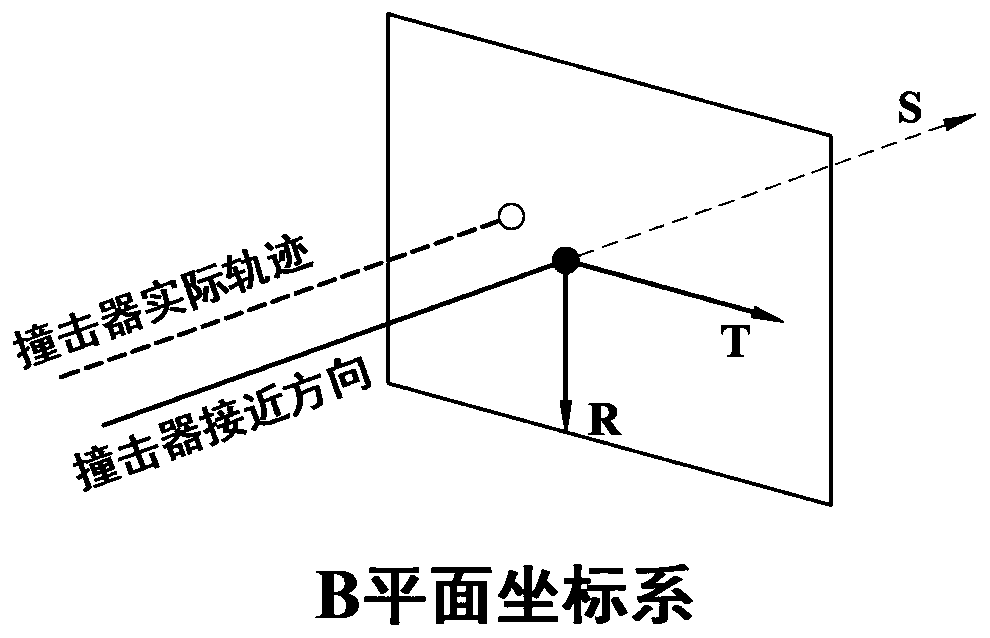
[0055] In order to verify the feasibility of the method, take the high-speed guided impact mission for a small near-Earth object as an example, the schematic diagram of the mission process is as follows figure 2 As shown, the B-plane coordinate system is defined as image 3 shown. Note that the small celestial body carried by the impactor is an α star, and the target small celestial body is a β star. The sphere radii of the two small celestial bodies are r α and r β , the expected impact point is the centroid of star β, when the impact deviation Δr f α + r β , it is considered a hit. According to the density ρ α =2g / cm 3 Estimate the mass of the alpha star. In addition, set the average orbit radius of β star to 1AU, the initial position of the impactor on the B plane is [73440 0 0] (unit: km), the initial velocity is [-10.2 0 0] (unit: km / s), and the three-axis position error standard The difference is 100km, 10km, 10km, and the standard deviation of the three-axis s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com